ROMAN ARCHITECTURE
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Pozzolana
Romans were the first to develop concrete from a volcanic earth known as _______
South Italy climate
tropical climate
Central Italy climate
genial and sunny
North Italy
has the climate of the temperate regions of Europe
The Etruscan Period
The Roman Period
2 Periods of Development
The Etruscans
Influenced by Greek architecture
known to be great builders and were credited with the earliest use of the true or radiating arch.
invented the new order of architecture called the TUSCAN ORDER.
ARCH
curved structural element that spans an open space and supports weight by transferring it to its endpoints, called abutments.
aqueducts, bridges, amphitheaters and stadiums
arch was used extensively in the construction of
Cloaca Maxima
“Greatest Sewer”
served as one of the earliest sewage disposal systems on a grand scale
Constructed as an open drain for the valleys between the hills of Rome
Tuscan Order
Roman adaptation of the Doric Order
has an unfluted shaft, and the column is seven diameters high.
domes, arches, and vaults.
The Romans built to impress — and one of the main ways they did this was through
vault.
arch-shaped roof
vaults used by the Romans
barrel vaults - continuous, semicylindrical ceiling or roof that resembles a tunnel
groin vaults - formed by the perpendicular intersection of two barrel vaults
Opus
Latin word which means an artistic composition or pattern, especially as used in relation to Roman stonework and walling construction.
kinds of walling:
• opus incertum
• opus reticulatum
• opus mixtum
• opus testaceum

opus incertum
first appeared in the 3rd century BCE and used small irregular chunks of stone smoothed on one side.

opus reticulatum
faced with a decorative pattern of small, diamond-shaped tuff stones, giving it a net-like appearance

opus mixtum
this was a combination of opus reticulatum with a layer (course) of horizontal brick every fourth course and at the edges of the wall.
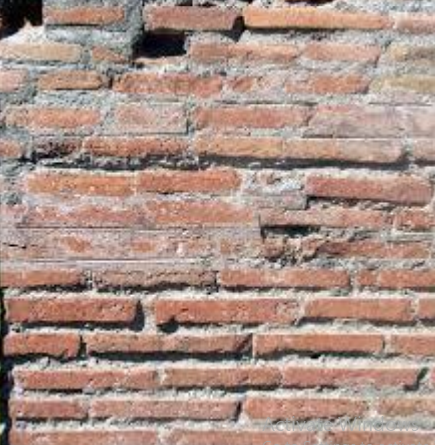

opus testaceum
common from the 1st century CE and used courses of brick only.
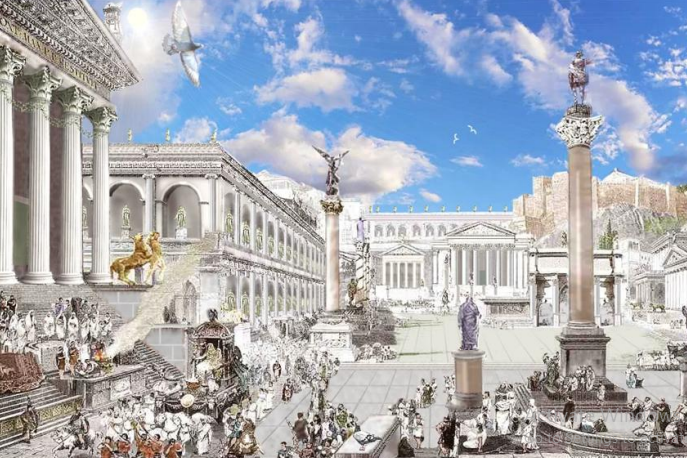

Forum
central open space used as a meeting place, market or rendezvous for political demonstration.
Forum Romanum
the oldest and greatest Forum in Rome
includes several significant structures such as the:
- Arch of Titus
- Temple of Saturn
- Temple of Vesta
- Temple of Caesar
- Curia (Senate House)
- Rostra (speaking platform)
- Central Via Sacra (Sacred Way)
Forum of Trajan
designed by the famed architect Apollodorus of Damascus.
largest forum composed of:
Massive piazza
Basilica Ulpia
Trajan’s Market
A peristyled enclosure containing the Temple of Trajan
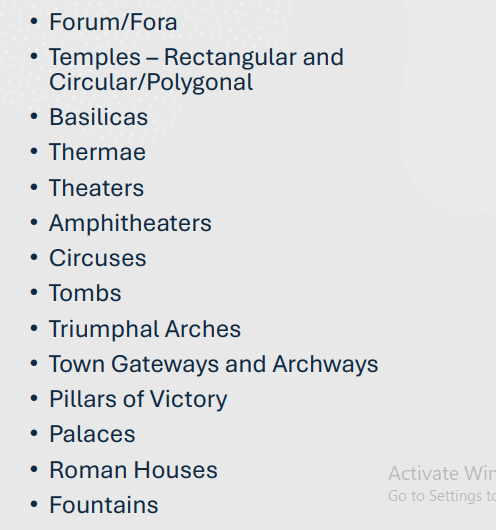
Rectangular Roman Temples parts:
Portico - A porch at the front of the temple, featuring a series of columns.
Cella - The inner sanctuary that housed the statue of the deity.
Podium - A high, elevated base that the temple rests on, with stairs leading to the front entrance.
Engaged columns - decorative columns partially embedded in the wall of the cella or other structure.
Pediment - The triangular, gable-shaped space at the front and back of the roof, often decorated with sculpture.

Temple of Mars Ultor, Rome
(Rectangular Roman Temple)
Located in the Forum of Augustus, this temple was dedicated to Mars the Avenger by Augustus in fulfillment of his vow to avenge the death of Julius Cesar.
one of the largest and finest of temples from the artistic point of view of the Romans

The Maison Carree, Nimes
(Rectangular Roman Temple)
An early and the bestpreserved Roman temple in existence.

Temple of Vesta, Rome
(Circular and Polygonal Temples)
served as the sanctuary for Vesta's sacred fire—a significant symbol representing the safety and prosperity of Rome.

The Pantheon, Rome
(Circular and Polygonal Temples)
Perfect preservation of all ancient buildings in Rome
The dome of Pantheon
World’s largest unsupported concrete dome
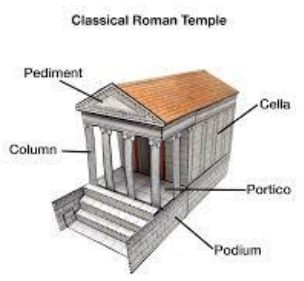
Basilica
large public building used for administrative, legal, and business purposes.
Thermae
A large, public bath complexes that served as centers for bathing, socializing, and recreation.
3 parts:
A Main building
Large open space
An outer ring of apartment
Typical Elements of Roman Baths
• apodyterium - changing rooms.
• palaestrae - exercise rooms.
• natatio - open-air swimming pool.
• laconica and sudatoria - superheated dry and wet sweating-rooms.
• calidarium - hot room, heated and with a hot-water pool and a separate basin on a stand (labrum)
• tepidarium - warm room, indirectly heated and with a tepid pool.
• frigidarium - cool room, unheated and with a cold bath, often monumental in size and domed, it was the heart of the baths complex.
• rooms for massage and other health treatments.
Thermae of Diocletian
largest bath complex ever built in the Roman period
could accommodate 3,000 bathers.
Balneum
small Roman private bath, very usual in palaces that featured rooms like the tepidarium, caldarium (hot), and frigidarium (cold).
Theaters
Shaped with a half circle or orchestra space in front of the stage.
Includes:
- cavea (seating area)
- orchestra (performance area)
- scaenae frons (elaborate stage building).
- The vomitoria (entrance and exit)
- pulpitum was the raised stage itself

The Theater in Orange, France
one of the best-preserved Roman monuments in the world.

Amphitheater
large, circular or oval, open-air venue used for public spectacles like gladiator combats, animal hunts/slaying, and public executions
The Colosseum (Flavian Amphitheater)
a freestanding structure of stone and concrete, using a complex system of barrel vaults and groin vaults
Under the main floor
location of services necessary for the shows: Cages for the animals, stores, tools, and lifts that raised the beasts to trapdoors placed on the floor of the arena.
VELARIUM
a great awning drawn over Roman theatres/ amphitheaters to protect spectators against the sun.
Circus
A long U-shaped or enclosed arena for chariot and horse racing (equivalent to the Greek Hippodrome) with a central median strip called the spina (or euripus) separating the two lanes. The track is flanked by tiers of seating (cavea) for spectators

Circus Maximus, Rome
largest and earliest stadium in ancient Rome, known for hosting spectacles like chariot races and, at times, gladiator fights.
5 classes of Tombs
Coemeteria or subterranean vaults
Monumental tombs
Pyramidal tombs
Temple-shaped tombs
Sculptured Memorials
Triumphal Arch
A large arched monument constructed in a public urban place to commemorate a great event, usually a victory in war.
Cenotaphs
memorial monuments to persons buried elsewhere.
Quadriga
4-horsed chariot
Rostral Column
celebrates naval victories
Rostra: rows of captured ships
Palace of the Emperors, Rome
most commonly refers to the Palace of Domitian (also known as the Flavian Palace), a vast imperial residence that dominates the Palatine Hill, it was the official residence of the Roman emperors and served as the center of the empire for centuries.
divided into the Domus Flavia (public wing), the Domus Augustana (private wing), and a stadium.
3 types of Roman Houses
1. the domus or private house - Houses of the rich and the upper classes were large and lavish.
2. the villa or country house - Roman country house built for the upper classes
3. the insula or many-storeyed tenement -apartment building where ordinary people lived.
- It housed most people of lower- or middle-class status
atrium
most important part of the house, was where guests were greeted
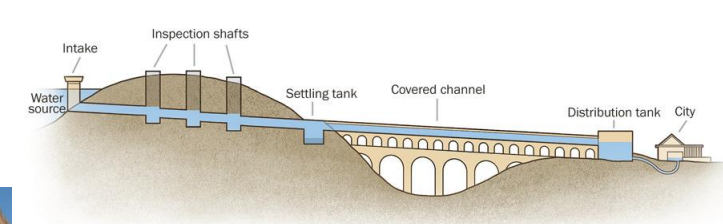
Aqueducts
Romans were able to live in large cities because they knew how to transport water for drinking, public baths and sewerage systems.
Aqua Appia
first aqueduct
Pont du Gard bridge in France
The tallest aqueduct still standing
Bridge of Augustus
best preserved and one of the finest ancient structure in Italy, with its stretch of five arches over the River Marecchia.
Trevi Fountain
designed by Nicola Salvi and completed by Giuseppe Pannini in 1762.
Roman Structures