Topic 1 Biology : Cell biology
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
what’s a Eukaryotic cell
a cell that contains its genetic material in a nucleus
what’s a prokaryotic cell
a cell that does not have a nucleus. doesn’t contain its genetic material in a nucleus
What is the role of a nucleus
contains DNA, genetic material
where do prokaryotic cells contain their DNA
A single loop of DNA & Plasmids
micrometer size & standard form
1 millionth of a meter. 1×10^-6
nanometer size & standard from
1 billionth of a meter. 1×10^-9
what does 1 order of magnitude mean
10x
what are mitochondria
where aerobic respiration takes place
what are ribosomes
sites of protein synthesis
what is cytoplasm
where chemical reaction takes place
what is the cell membrane
controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell
shape of plant and animal cells
plant cells = regular shape
animal cells = irregular shape
what are chloroplasts
Contain chlorophyll and are the sites of photosynthesis
what is the cell wall
made from cellulose. Strengthens the cell
what is a permanent vacuole
Vacuole gives the plant cell its shape. filled with cell sap
How is a sperm cell specialised
Long tail helps them swim to the Ovum
They are streamlined to help with swimming
Contrail lots of mitochondria which provides energy needed for swimming
Contain enzymes that allow them to digest their way through the outer layer of the ovum
how is a nerve cell specialised
Long, so they can conduct nerve impulses between different areas of the body
dendrites allowing nerve cells to communicate with other nerve cells
myelin speeds up nerve impulse transmission
how are muscle cells specialised
contain protein fibres that slide over eachother to allow contraction
lots of mitochondria to release energy for contraction
how are root hair cells specialised
Root hairs increase surface area. rate fo osmosis is greater
don’t contain chloroplasts
thinner walls than other plants for a shorter diffusion distance
how are xylem cells specialised
doesn’t contain any organelles allowing free passage of water
walls contain lignin, providing support for the plant
no end walls providing long hollow tube for water & dissolved minerals
how is a phloem cell specialised
very few sub-cellular structures to help flow of materials
contain companion cell that provides mitochondria to the phloem vessel cell
role of xylem and phloem
xylem = carry water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves
phloem = carry dissolved sugars up and down the plant
problems with light microscopes
limited resolution
limited magnification
advantages of electron microscope
Greater resolution
Greater magnification
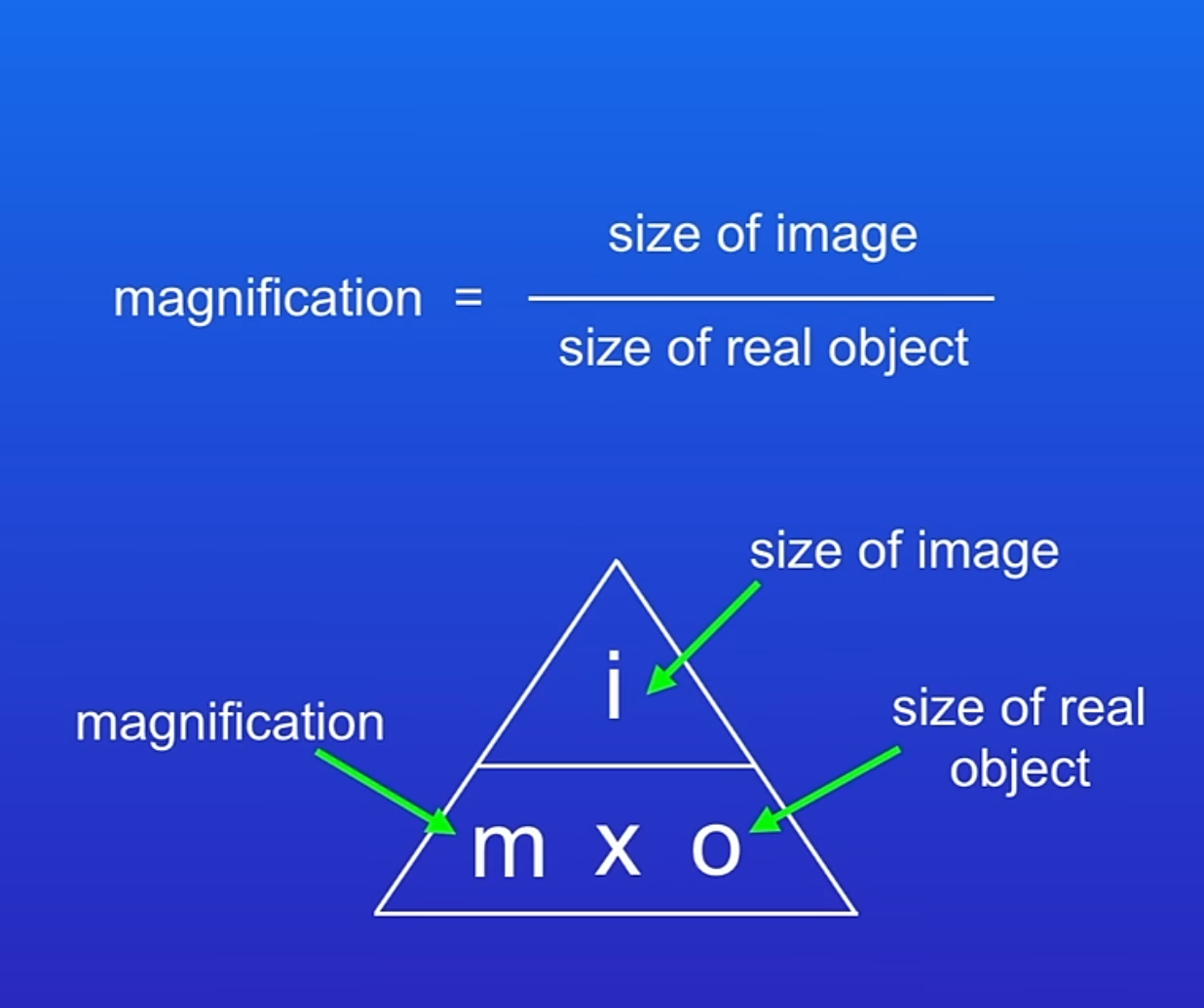
magnification equation
what is binary fission
one bacterial cell splitting into two bacterial cells
how often can bacteria carry out binary fission
once every 20 minutes
formula for bacterial division
2^n n = number of rounds of division
what happens in the first stage of mitosis
DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome
what happens in the second stage of mitosis
mitosis takes place.
One set of chromosome is pulled to each end of the cell. nucleus also divides
what happens in the final stage of mitosis
cytoplasm and cell membrane divide to form two identical cells
3 functions of mitosis
growth and development of multicellular organisms
when an organism repairs itself
during asexual reproduction
where can we find stem cells (what can they differentiate into)
early stage embryos - any thor of cells
in bone marrow - blood cells
describe a bone marrow transplant (for leukaemia)
patients existing bone marrow is destroyed using radiation
patient receives a transplant of bone marrow from a donor
stem cells in bone marrow decide to form new bone marrow & blood cells
why do some people reject therapeutic cloning
ethical or religious objections
plant stem cell
meristems
what is diffusion
the spreading out of particles resulting in a movement of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
what can affect the rate of diffusion
concentration gradient
temperature
surface area
what is osmosis
diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution though a partially permeable membrane
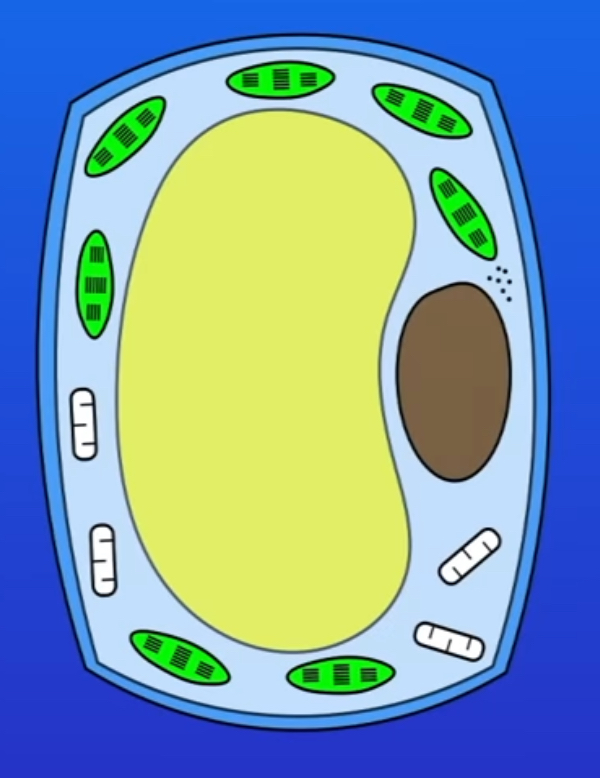
what happens if you place a plant cell in water
water moves into the cell by osmosis and cell will expand. this is called turgid
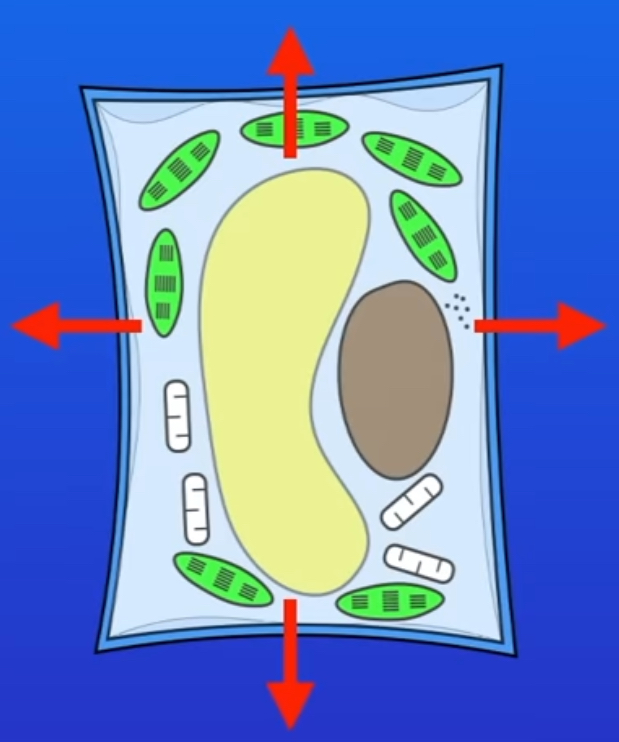
what happens if you place a plant cell in a concentrated solution
water moves out of the plant cell it will cause the plant to shrink. flaccid
what is active transport
moves substances against the concentration gradient. requires energy from respiration