psychometrics midterm
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What are the 4 levels of measurement?
nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio
What is the definition of nominal?
Numbers are assigned to represent labels or categories of data only.
What is the definition of ordinal?
Numbers are assigned to rank-order data. However, the distances or values between numbers are not equal; they can vary.
What is the definition of interval?
Numbers are assigned to rank-order data and the distances between numbers is judged to be equal. However, there is no absolute zero point (a number that indicates the complete absence of what is measured)
What is the definition of ratio?
Numbers are assigned to rank-order data, and the distance between numbers is also equal, and there is a point of absolute zero?
Gender, ethnicity, eye color, and blood type are examples of what level of measurement?
Nominal
Income level (low, middle, high), Level of agreement (completely agree-completely disagree), and political orientation (far left-far right) are examples of what level of measurement?
Ordinal
Credit scores, standardized test scores, and Fahrenheit temperature are examples of what kind of level of measurement?
Interval
Weight, height, length, and time are examples of what kind of measurement?
Ratio
What is reliability?
How consistent is the measurement of a test.
What is inter-rater reliability?
Is a score of a measurement consistent between different evaluators?
When data for inter-rater reliability is nominal or ordinal, what statistic should be used?
Cohens kappa
What is test-retest reliability?
A method of testing reliability that aims at observing the stability of scores over time by readministering the test to the same sample at a later date.
With test-retest, how long should you wait to give the second administration?
No longer than 6 months. less for children (developmental changes).
What is the greatest issue with test-retest?
Practice effects (and random fluctuations of performance)
What is split-half reliability?
A method of establishing internal consistency through cutting the test in half and administering each half. only used for homogenous test.
What are the different ways of splitting test?
Right in half or by odd/even numbered questions.
When using split-half reliability on a short test what statistical correction should you use?
Spearman brown correction
When using split-half reliability on a test with definite right or wrong answers, what statistical measure do you use?
KR-20
When using split-half reliability on a test with multiple potential correct answer for questions (example, rating scale) what statistical measure do you use?
Cronbach's alpha
What are the 3 measures of central tendency?
Mean, median, mode
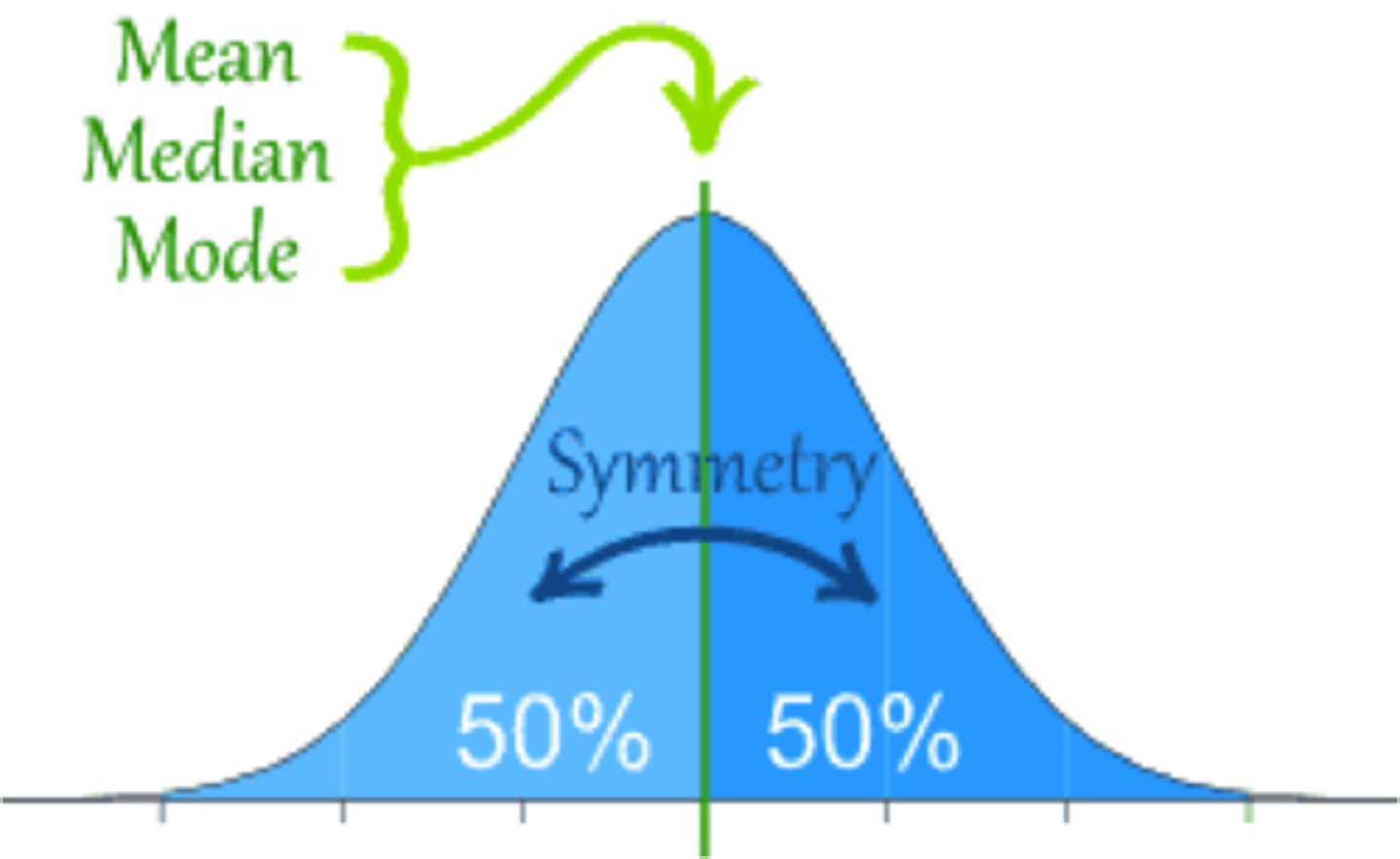
the mean, median, and mode are all the same in a symmetrical distribution. True or false?
true
Where is the "tail" of a positively skewed distribution?
To the right.
Where is the "tail" of a Negatively skewed distribution?
To the left.
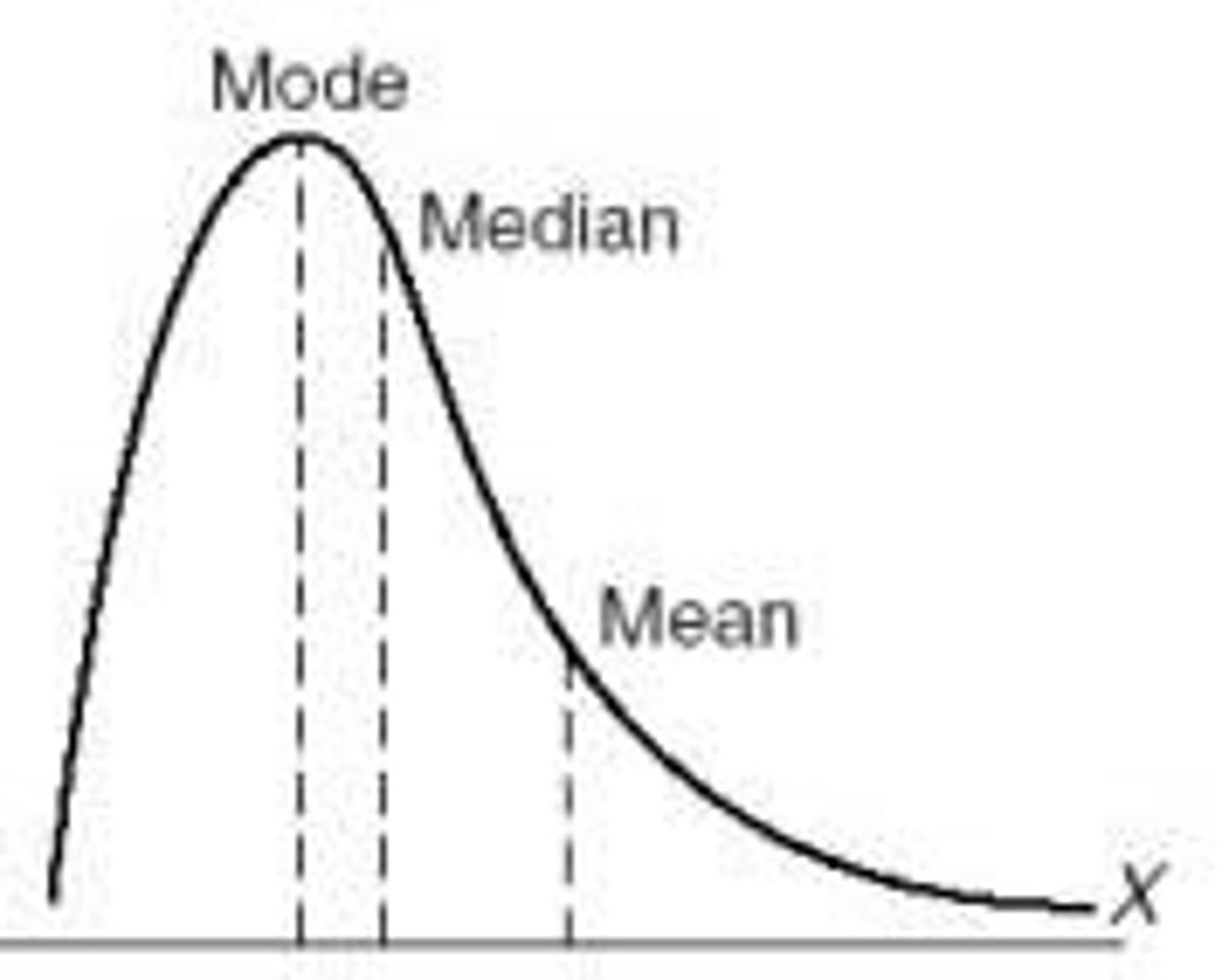
Know what a positive skew looks like and where mean, median, and mode are.
positive skew.
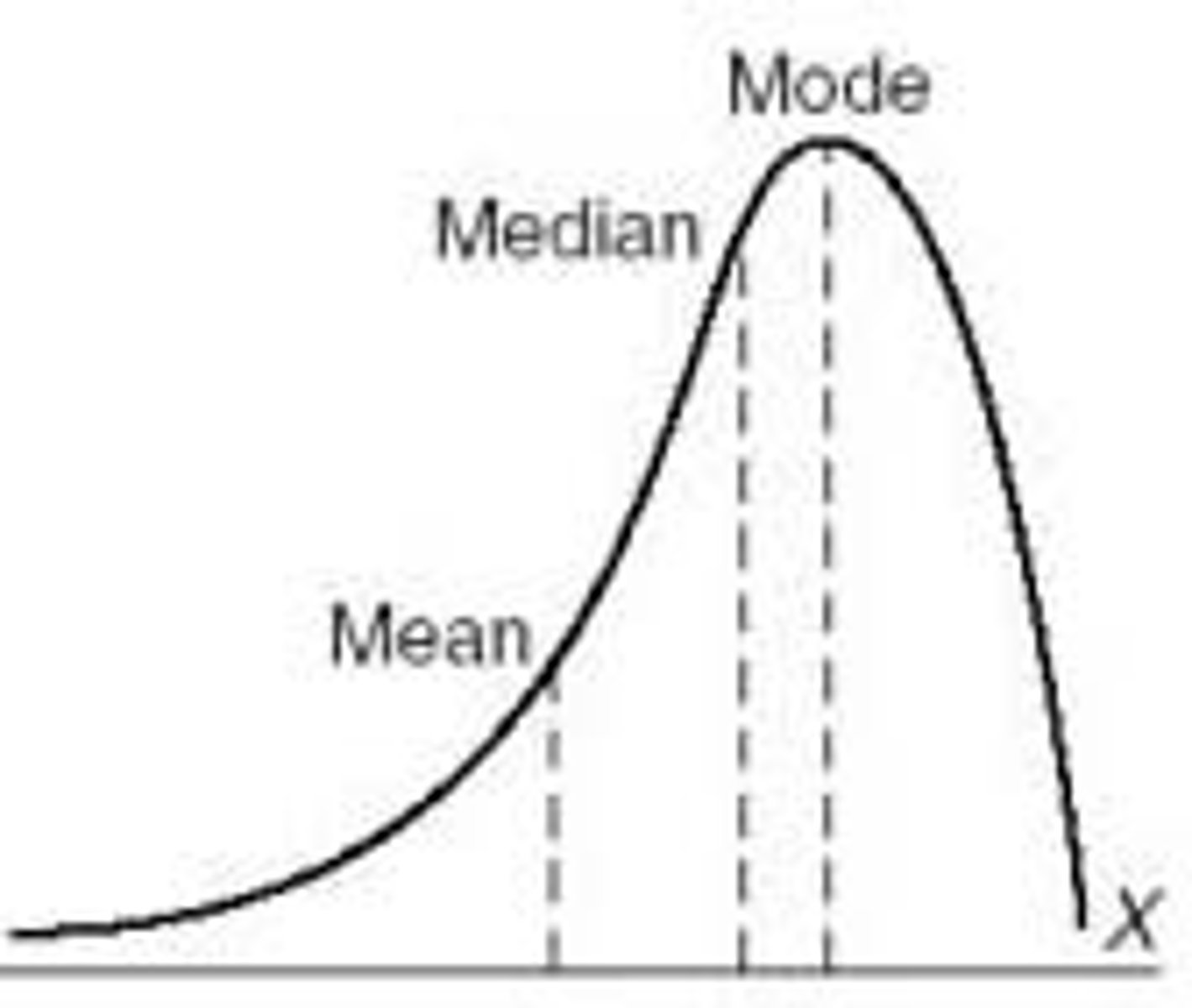
Know what a negative skew looks like and where mean, median, and mode are.
Negative skew.
Know what a symmetrical distribution looks like and where the mean, median, and mode are.
Symmetrical distribution
What is variance?
The average distance scores vary from the mean. Gives information on how spread out scores in a distribution are (how flat or skinny a distribution is).
What is the formula for variance?
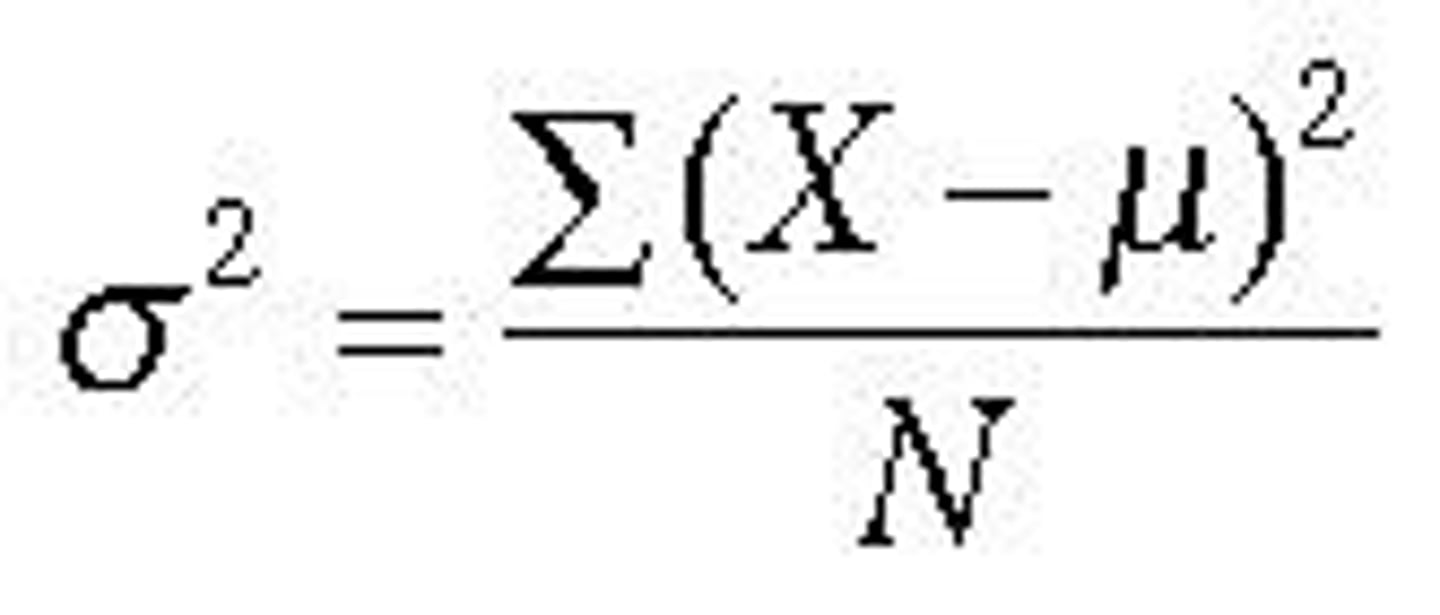
What is standard deviation?
Most commonly used measure of variability in a distribution of test scores.
What is the formula for standard deviation?
Notes: square root variance. Also, when inferring the SD of a population use n-1 instead of n
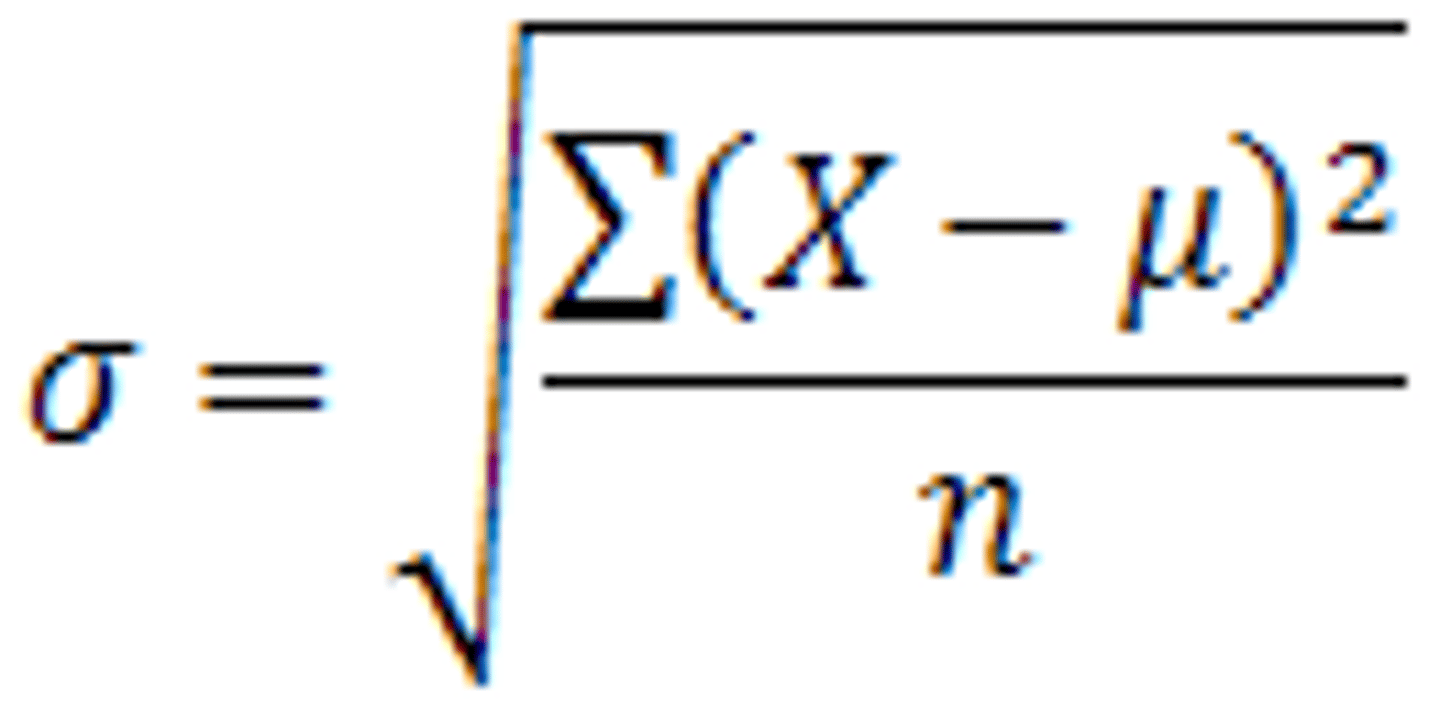
What are standard scores?
Standard scores are different methods of converting raw scores into more meaningful scores used for interpretation.
What are the different kinds of standard scores?
linear transformations and area transformations
What are the different methods of linear transformation?
Percentages and standard deviation units (z scores and t scores)
What are the different methods of area transformations?
Percentiles and stanines
How do you calculate z scores?
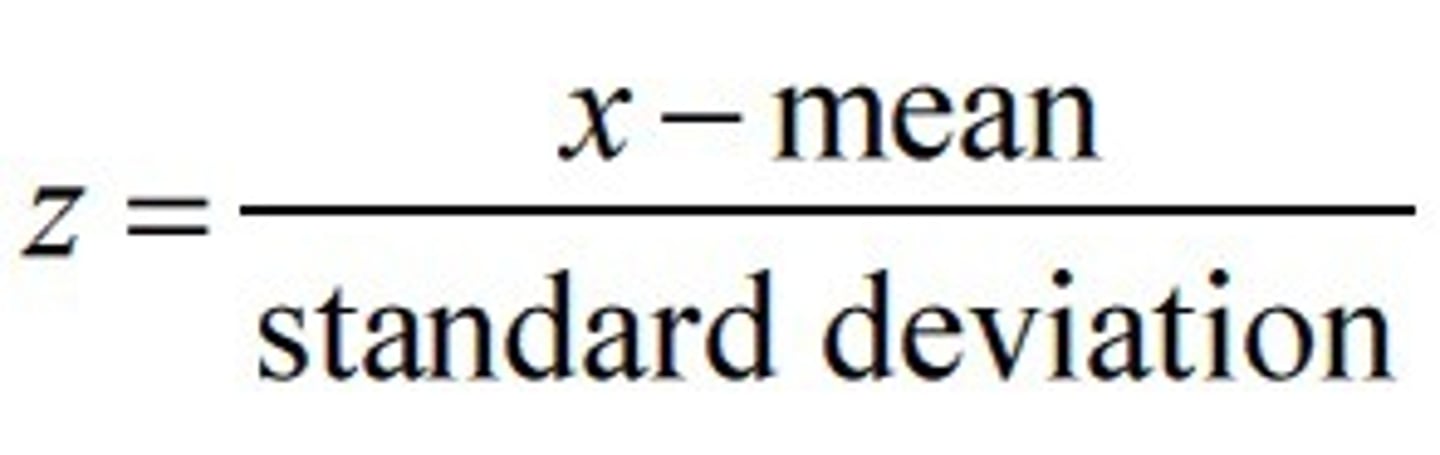
when should you use z scores?
Normally distributed data and large samples.
How do you calculate t scores?
T = ( Z * 10) + 50
What is the mean and standard deviation of z scores?
Mean of 0 and standard deviation of 1.
What is the mean and standard deviation of t scores?
Mean of 50 and standard deviation of 10.
When do you use t scores?
Smaller samples or when standard deviation is unknown.
How do you calculate percentage?
raw score divided by total possible score time 100. Think of how you find out your grade on a test. Example, on a 100 question test I got 90 correct answers. (90/100= .90) (90*100= 90).
How do you calculate percentiles?
((B+ .5E)/N)*100. B = number of scores below the individual score, E number of scores equal to the individual score, N the number of people who took the test.
Why would you use stanines?
It is easier to describe in words to clients the meaning of their scores. Scores range from 1-9.
1, 2, 3 USUALLY BELOW THE MEAN
4, 5, 6 MEAN (OR CLOSE TO)
7, 8 USUALLY ABOVE THE MEAN
9 EXCEPTIONAL
What is classical test theory?
Explains how much of an observed score is due to error.
What is the formula for classical test theory?
Observed score = true score - measurement error. Focuses or random error.
Can a true score be calculated?
No
Can measurement error be measured?
No, it can only be estimated.
What are the types of error?
Random error and systematic error.
What is random error?
Error due to environmental or extraneous factors such as the room, the administrator, what you ate for breakfast, motivation, how much you slept. Influences reliability.
What is systematic error?
A single source of error that always increases or decreases a score. Example, a body weight scale ALWAYS off by 2 pounds. Does not effect reliability because the measure is consistent (just consistently wrong).
What can contribute to error?
TEST LENGTH, HOMOGENEITY OF QUESTIONS, TEST-RETEST INTERVAL, TEST ADMINISTRATION, SCORING, COOPERATION OF TEST TAKERS
How would you increase the reliability of a test?
Increase the number of questions
Improve the quality of questions
- Are they clear?
- Is everyone interpreting them the same?
- Are they homogenous?
Decrease interval of administrations (be careful of practice effect)
Administer test in standardized manner
Care in scoring
cooperation of test takers
What is standard error of measurement (SEM)?
The amount of error in an individual test score.
How is standard error of measurement calculated (SEM)?
r is the reliability coefficient of the test.
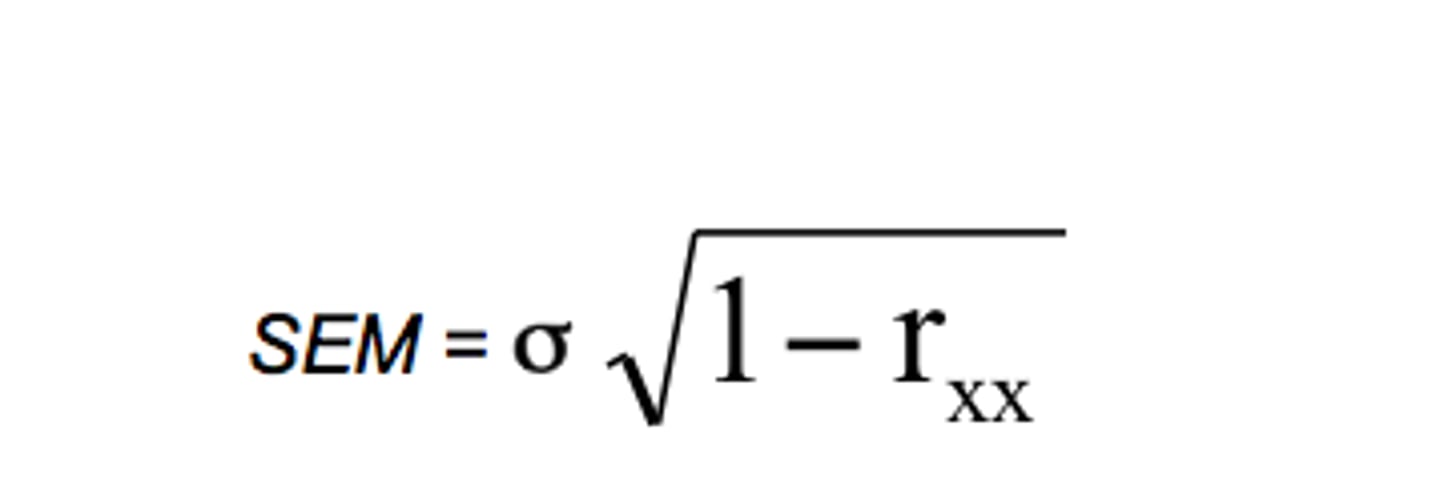
What are confidence intervals?
A range of score that we are confident will include the test takers true score. Example, a test takers IQ score on the WAIS was 122. if we set out p value to .95 we would obtain a confidence interval of 115-127. This means we are 95% certain that the test takers IQ score lies between 115-127.
What is generalizability theory?
Recognizes that there are different sources of variability for any measure. Can we generalize the reliability of test from one situation to another? Focuses on systematic error.
What is validity?
Is a test measuring what it is meant to measure?
What are the different kinds of validity?
Content, Construct, and Criterion
What is content validity?
Does the content of a test represent the concepts the test is trying to measure. Example, A math test including history question would have poor content validity.
What is criterion validity?
Does the test predict what it is meant to predict. Example, does the SAT predict college performance?
What is construct validity?
Does the test make inferences on the theoretical construct it is trying to measure? Example, is a test that is supposed to measure anger actually measuring anger?
What is face validity?
Whether a test "on its face" looks like it is measuring what it says its measuring. For example, are the questions of a test measuring depression asking you questions about how much and how often you are sad.
When is it better to have poor face validity.
When you want the purpose of the test to be hidden from test taker to prevent malingering.
What are threats to content validity?
When a test includes content irrelevant to the construct and when a test fails to include content expressing the full range of the construct.
What is a test of maximal performance?
A test that is aimed to test performance of a particular well defined task such as IQ, mechanical ability, and driving test.
What are behavioral observation tests?
Test observing individuals behavior in particular context. Unlike maximal performance, the individual is unaware their behavior is being measured. Examples, Job performance or clinical interviews.
What are self-report test?
Test where the test taker describes their feelings, beliefs, opinions, or mental states. Example, personality inventories.
What are standardized test?
test to measure a specific construct where the scores are compared to a larger group of similar test takers. Example, SAT and ACT.
What are nonstandardized test?
Test measuring a specific construct where there are no standardized sample to compare individual scores to. Examples, exams in high school and college.
What are objective test?
Test where there are predetermined right and wrong answers requiring little subjective judgement. Quantitative. Example, Stanford-Binet intelligence scale
What are Projective test?
Test where test takers are asked to respond to unstructured and ambiguous stimuli. More subjective and qualitative (some level of measurement). Examples, Rorschach and TAT.
What is the Flynn effect?
Observation that each generation has a significantly higher IQ than the previous generation. It is thought that this is due to newer generation being more adapted to abstract thinking rather than being more intelligent.
What is Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient?
Statistical technique to find the correlation between 2 variables. Symbolized by r for sample and P (rho) for population (almost always r).
What is the range of r (correlation coefficient)?
-1 to 1
Is a correlation coefficient of r= -0.5 positive or negative?
Negative
Is a correlation coefficient of r= 0.62 positive or negative?
positive
What is a negative correlation?
The increase of one variable is associated with a decrease of the other variable.
What is a positive correlation?
The increase of one variable is associated with the increase of the other. Also, the decrease of one variable is associated with the decrease of the other.
What is the equation of the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient?

What determines a strong or weak correlation coefficient (r)?
The closer to -1 or 1 the stronger the correlation. The closer to 0 the weaker the correlation.
When do you use nominal or ordinal scales?
Primarily with qualitative analysis.
When do you use interval and ratio scales?
Primarily with quantitative analysis.
What is a test user?
A person or party who is involved in purchasing, administering, interpreting, or using the results of a psychological test.
What is a test taker?
a person who responds to test questions or whose behavior is measured.
Where to find test takers right?
page 73 of the book. too much to type :(
What the 4 issues regarding test taker rights?
1. Right to privacy
2. Right to informed consent
3. Right to know and understand results
4. Right to protect from stigma
What is informed consent?
Process of explaining to individual such things as why they are being tested, the purpose of a test, if and how third parties might be involved, if and what fees might be involved, and limits to confidentiality.
Parents of a minor give informed consent, while the minor themselves give (blank)?
Assent
When is informed consent not required?
when assessing the capacity of a person to make decisions (normally in competency evaluation forensic psyc) or mandated by law.
True or false: Test user should rely on test results only and not other collateral data when making clinical judgements.
False
How did the Rehabilitation act of 1973, the Americans with disabilities act of 1990, and the Education for all handicapped children act of 1990 influence educational and psychological testing standards?
Test users should ensure that the test outcomes indicate the intended skills or attributes accurately and that the test scores have not been altered because of disabilities.
True or false: When clinicians are testing clients with disabilities, they have to accommodate or modify the testing process for their disabilities.
True
True or false: Test users have to consider the norm group of a test when choosing what test to administer to a client of a racial or ethnic diverse background.
True
True or false: Scores of test takers who are culturally different from the norm group of a test rarely differ.
False
What is the Pygmalion effect?
the phenomenon whereby higher expectations lead to an increase in performance and lower expectations lead to lower performance.
What are the responsibilities of test users?
MAINTAIN TEST SECURITY
AVOID STIGMATIZING LANGUAGE IN RESULTS
USE THE TEST FOR WHAT IT IS INTENDED FOR
FOCUS ON FACTS
TEST TAKERS HAVE A RIGHT TO RECEIVE FEEDBACK
Test taker special population include:
Physical/mental disability
- sensory
- motor
- cognitive
When is informed consent implied?
When test taker voluntarily engages in a test required for educational purposes (SAT, ACT) or job applications.
True or false: Labels do not affect clients.
False