Final Exam Study Guide; Psych 101
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Psychology
scientific study of behavior and mental processes
Theory
the way to explain relationships among observed events or experimental findings in ways that make them more understandable and predictable
Basic Research
acquiring knowledge without direct practical application
Applied Research
research that aims to find solutions to specific problems
interneurons and sensory neurons
two kinds of motor neurons that transmit information from the sensory organs, muscles, and inner organs to the spinal cords and brain
Dendrites
rootlike structures at the end of axons that receive neural impulses from neighboring neurons
Axons
tubelike part of a neuron that carries messages away from the cell body toward other neurons
Soma (Cell Body)
contains the nucleus of the cell and carries out the cell’s metabolic functions
Cerebral Hemispheres
each of these controls feelings and movement on the opposite side of the body
Corpus Collosum
thick band of fibers that connects to the left and right hemispheres of the brain
left, right
The right side of the body is controlled by the _____ hemisphere, and the left side is controlled by the ____ hemisphere.
Sensation
process by which we receive, transform, and process stimuli from the outside world
Perception
process by which the brain integrates, organizes, and interprets sensory impressions to create a representation of the world
Gestalt Principles of Perceptual Organization
Figure and group, proximity, similarity, continuity, closure, connectedness
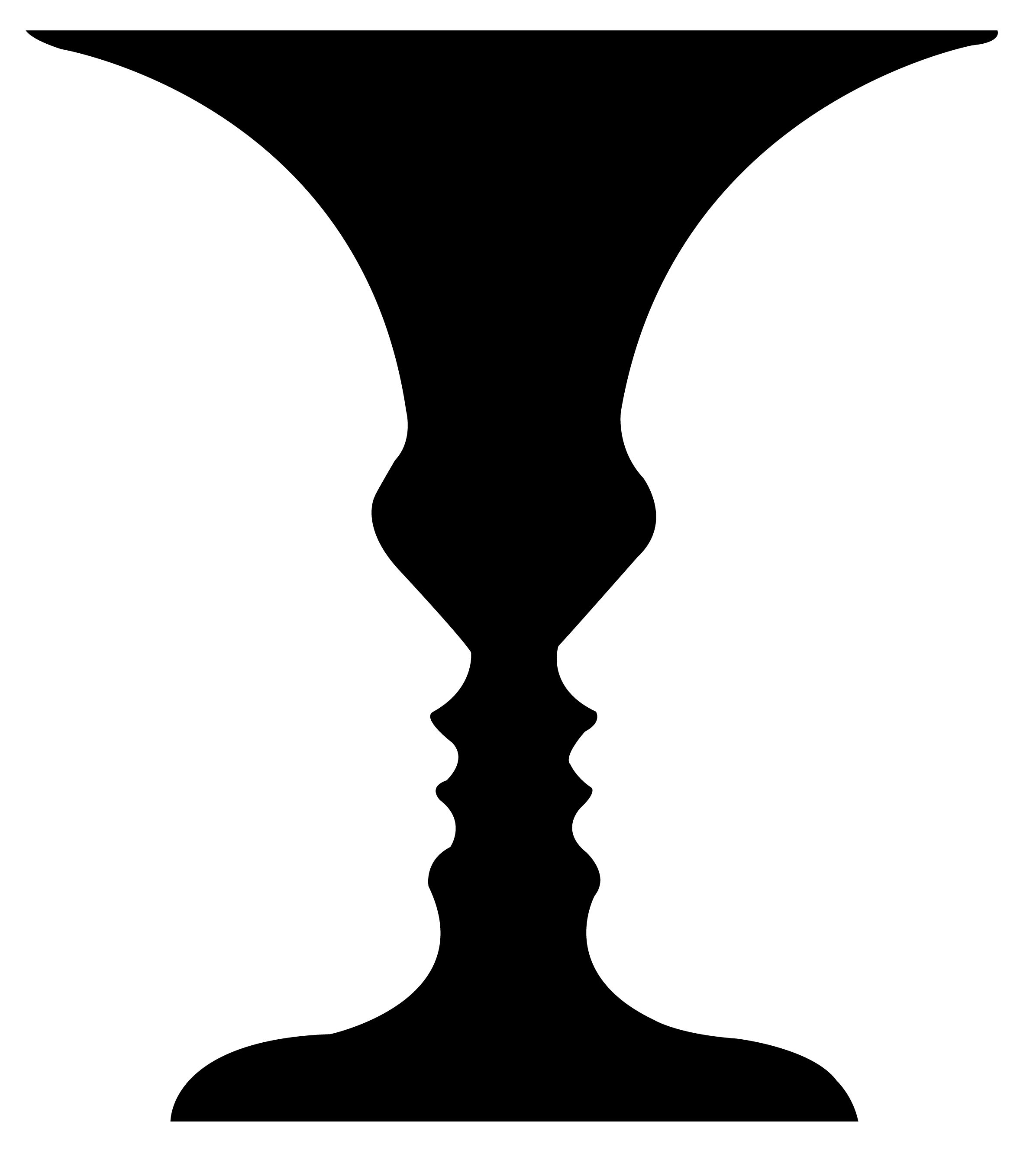
Figure and Group
gestalt principle that figures have definite shapes, but the ground is shapeless. We perceive objects as figures when they have shapes or other traits like distinctive coloring, which is set against a backdrop of the ground on which they appear

Proximity
gestalt principle that objects that are near each other will be perceived as belonging to a common set
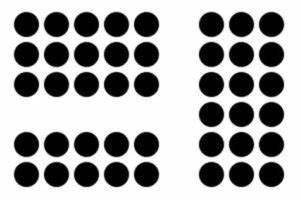
Similarity
gestalt principle that objects that are similar will be perceived as belonging to the same group

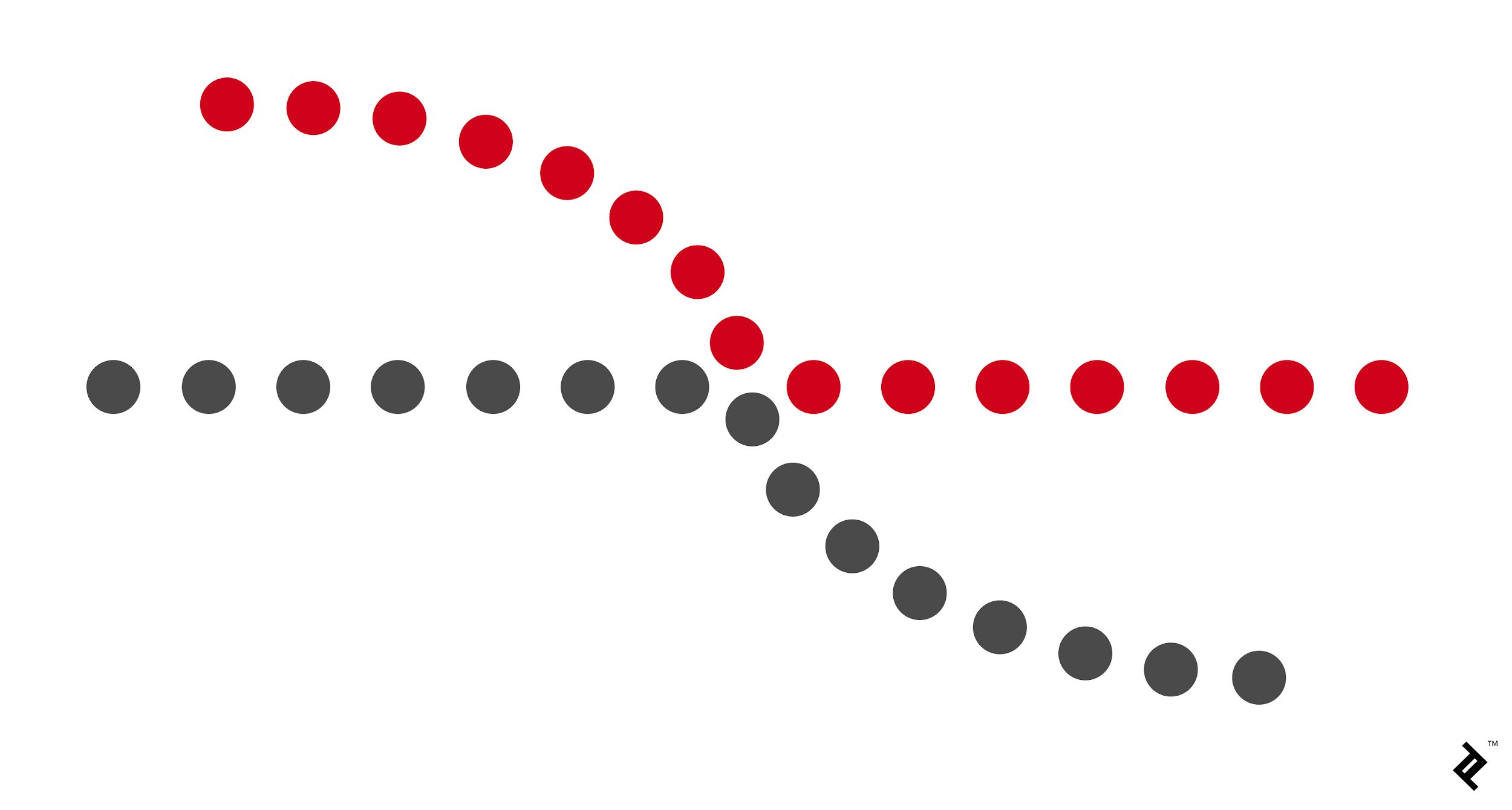
Continuity
gestalt principle that a series of stimuli will be perceived as representing a unified form

Closure
gestalt perceptional principle that people tend to piece together disconnected bits of information to perceive whole forms
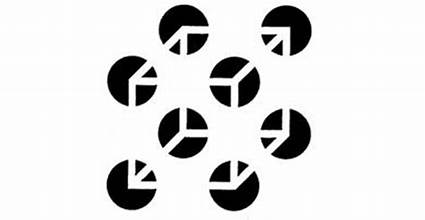
Connectedness
gestalt principle that objects positioned together or moving together will be perceived as belonging to the same group
reasons that we sleep
protective function - keeps organism out of harms way
restorative function - helps the brain restore and recover
memory consolidation - freshly formed memories become last ones
Manifest Content
events that happen in a dream
Latent Content
underlying meaning of a dream
Activation-Synthesis Hypothesis
dreams represent an attempt by the cerebral cortex to make sense of random discharges of electrical activity in the brain during REM sleep
Neo dissociation Theory
believes that there are multiple levels of awareness that can become split off or dissociated from one another
Operant Conditioning
process of learning where the consequences of a response determine the probability that the response will be repeated
Positive Reinforcement
strengthening a response by giving a desired stimulus
Negative Reinforcement
response is strengthened by taking away an unpleasant stimulus
Positive Punishment
weakening a behavior by giving an undesired stimulus
Negative Punishment
weakening a behavior by taking away a desired stimulus
Behavior Modification
the systematic application of learning principles to strengthen adaptive behavior and weaken maladaptive behavior
Extrinsic Motivation
reflects the desire for external rewards, like wealth or respect from peers
Heuristic
a rule of thumb for solving problems or making judgments or decisions
Cognitive Pyshcology
branch of psychology that focuses on mental processes like thinking, problem-solving, decision-making, and the use of language
Interpersonal Intelligence
ability to understand and interact effectively with others
Interpersonal Intelligence
psychologists, therapists, and social workers have high
_________ _________.
Crystallized Intelligence
form of intelligence associated with knowledge or wisdom
Intrinsic Motivation
motivation reflecting the want for internal gratification, like self-satisfaction for completing a goal
William Masters and Virginia Johnson
What 2 people pioneered the research indicating a physical response from the body to sexual stimulation
Self-actualization
Esteem
Love and Belongingness
Safety
Physiological
What are Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs (top of pyramid to bottom)
Drive Theory (Clark Hull)
belief that behavior is motivated by drives that come from biological needs that demand satisfaction (and who’s theory is it?)
General Adaptation Syndrome (Hans Selye)
term for the general pattern of bodily responses to various forms of stress (and who coined the term?)
Reciprocal Determinism (Bandura)
model where cognitions, behaviors, and environmental factors influence and are influenced by each other (and who’s model is it?)
Psychotherapy
verbal therapy derived from psychological framework that consists of one or more treatment sessions with a therapist
Eclectic Therapy
therapeutic approach that draws on principles and techniques from different schools of therapy
Cognitive Therapy
helps clients identify and correct faulty styles of thinking
Humanistic/Gestalt Therapy
helps clients develop of unified sense of self by bringing true feeling and conflicts with others to the awareness
Psychoanalysis
Freud’s method of psychotherapy that focuses on uncovering the unconscious conflicts and desires at the root of the patients problems
Free Association
technique in psychoanalysis where the client is encouraged to say anything that comes to mind
Dream Analysis
technique is psychoanalysis where the therapist analyzes the latent content of the client’s dreams
Resistance
in psychoanalysis, the blocking that happens when therapy touches upon anxiety-inducing thoughts or feelings
Transference
in psychoanalysis, the tendency of the client to reenact their conflicting relationships in the relationships they have with their therapist
John Watson
who is known for their studies of behavior and emotions?
John Watson
who believed that loud sounds naturally make infants cry and shudder with fear?
Freud’s theory of personality
theory of personality that personality and behavior are shaped by unconscious forces and conflict
Wilhelm Wundt
who was interesting in studying mental experience?
Introspection (Wundt)
attempt to directly study consciousness by having people report on what they are consciously experiencing (and who’s method is it?)
Classical Conditioning
process of learning where a previously neutral stimulus comes to evoke a response identical or similar to one that was originally evoked by another stimulus due to being paired or association of the two stimuli
Albert Bandura
who believed that children become more aggressive after observing aggressive models on TV
Observational/Social Cognitive Learning
Law of Effect (Edward Thorndike)
responses that have satisfying effects are strengthens and become more likely to be repeated while responses that lead to undesired effects become weakened and are less likely to reoccur (and who’s idea is it?)
B.F. Skinner
who believed that operant conditioning is the process of learning where the consequences of a response determines the probability that the response will be repeated?
Charles Spearman
Who’s theory believed that intelligence involves general cognitive ability, or “g”
Lev Vygotsky
who’s theory emphasizes the roles of social and cultural factors in development, or cognitive development
Triarch Theory of Intelligence (Robert Sternberg)
proposes 3 aspects of intelligence: analytic, creative, and practical (and who’s theory is it?)
Zone of Proximal Development (Jean Piaget)
the range between a child’s present knowledge and their potential knowledge if taught (and who’s idea is it?)
Lawrence Kohlberg
who developed a methodology where he presented subjects with hypothetical situations involving conflicting moral values and moral dilemmas?
Erik Erikson
Who believed that psychosocial development progresses through stages that begin in early childhood and continue through adulthood and that personalities are shaped by how we deal with various psychological crises or challenges?
Henry Murray
who developed the thematic apperception test?
Thematic Apperception Test
test where a set of pictures of ambiguous scenes is shown that can be interpreted differently. Subject is asked to tell a story about that scene, what led to it, and the outcomes.
Carl Rogers
who was an optimist that believed in the essential worth and goodness of human nature
Carl Jung
who believed that people possess both a personal unconscious (repressed memories and impulses) and a collective unconscious (repository of accumulated ideas and images, as well as archetypes)
Raymond Cattell
who believed that the structure of personality had 2 levels: surface traits and deeper level traits
Individual Psychology (Alfred Adler)
psychology with emphasis on the unique potential of each individual (and who’s theory was it?)