CH 3: Cell Biology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
cell
basic unit of life
three basic parts of a cell (CNC)
CELLS HAVE THESE COMPONENTS
Nucleus
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
organelles
SPECIFIC STRUCTURES that PERFORM UNIQUE FUNCTIONS
Typically in EUKARYOTES
e.g, mitochondria, ribosomes, Golgi body, ETC
cell membrane
This is OUTER LAYER of the cell that REGULATES WHAT GOES IN/OUT of the cell
There’s a PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER, meaning that certain molecules can diffuse or use different proteins to go in/out
It DETERMINES WHAT GOES IN/OUT OF THE CELL
cell membrane structure
Made of Lipids and Proteins
Phospholipid Bilayer
GLYCOCALYX (a combination of glycolipids and glycoproteins)
Glycolipids are fats that contains sugar molecules (carbohydrates) which are attached to a lipid component
Glycoproteins are proteins attached to the lipids outside the cell memebrane
function of cholesterol in the cell membrane
It’s used to STABILIZE THE AND HOLD THINGS TOGETHER WITHIN THE CELL MEMBRANE
Since there are many things that happen within the cell membrane (like many cells going in/out), the cell membrane is very destabilized. In order to keep things from going crazy, the cholesterol molecule (a steroid — lipid) would help and hold things together within the cell membrane
cytoplasm
The liquid WITHIN THE CELL MEMBRANE that SUSPENDS THE ORGANELLES, ALLOW MOVEMENT of organelles and material, and MAINTAINS CELL SHAPE
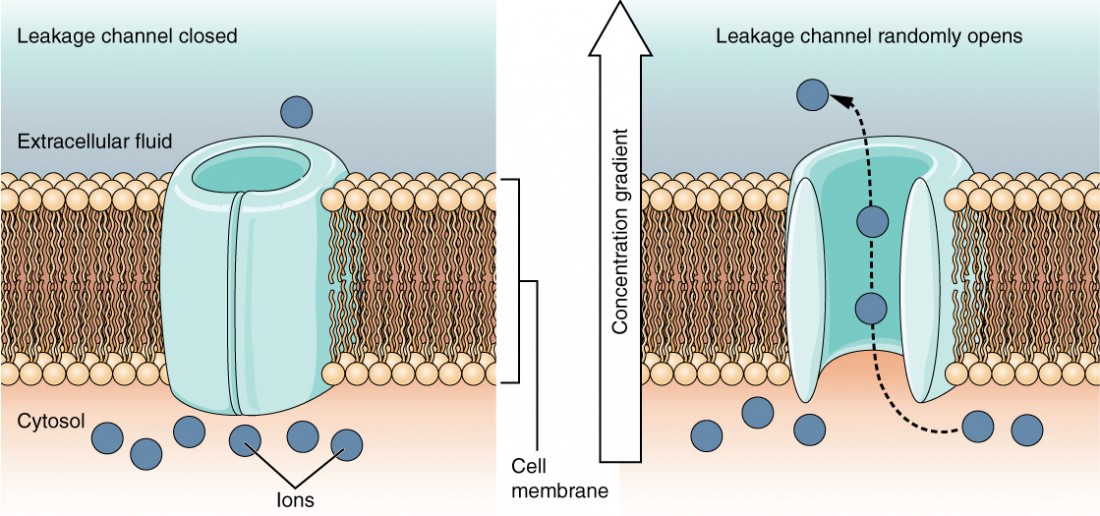
leak channels
These are CHANNELS that are ALWAYS OPEN and ALLOWS SPECIFIC SUBSTANCE TO ENTER THROUGH CONSTANTLY
e.g, K+ leak channels are always open to K+ ions (but it’s not going to allow other types of molecules to enter through because it’s specific to one substance)
ligand-gated channels
These are channels that ONLY OPENS/CLOSES WHEN LIGAND BINDS to it
lock and key motion
e.g, insulin-glucose ligand channel
insulin is the ligand that needs to bind to the channel in order for glucose to enter through the channels
If there’s no ligand that attaches to the protein, it’s not going to open and let things in
ATP powered pumps
These are pumps that NEED ATP to MOVE IONS/MOLECULES AGAINST CONCENTRATION GRADIENT
e.g, Na+/K+ pumps
these pumps are used to maintain a certain concentration on the outside and inside of the cell in order to stay in equilibrium
when there’s ATP, Na+ and K+ bind to the pumps because the pumps CHANGED SHAPES, and 3 Na+ goes OUT of the cell (making the outside more electronegative) while 2 K+ goes IN the cell (making the cell more electropositive)
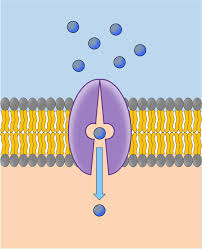
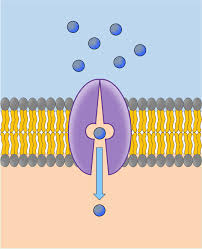
carrier protein
Type of proteins that ALLOW SPECIFIC MOLECULES TO ENTER THROUGH MEMBRANE based on their shape
REGULATES WHAT GOES IN/OUT
endomembrane system
These are many organelle systems that WORK TOGETHER to CREATE, CHANGE, AND EXPORT CELL PRODUCTS
Different organelles within the system:
ER
Golgi
Mitochondria
Nucleus
ER
This is like an EXTENSION OF THE NUCLEUS that’s INVOLVED IN PROTEIN/LIPID PRODUCTION. It contains CISTERNAE which are CANALS WITHIN THE ER
The cisternae allows ribosomes to move through the ER
rough ER
appears rough because of ribosomes; functions in the synthesis and transport of proteins
There’s going to be A LOT OF ROUGH ER IN THE MUSCLES because muscles need proteins
smooth ER
no attached ribosomes; functions in the transport of lipids and DETOXIFICATION
lots of smooth ER in the liver because it’s more involved in detoxification
ribosomes
function in protein synthesis; found in cytoplasm and ER; composed of protein and RNA; help produce proteins; made in the nucleolus
golgi apparatus
This RECEIVES, MODIFIES, SORTS, AND PACKAGES the PROTEINS and ships it off somewhere else
Proteins either stay inside the cell and get used OR it gets shipped out of a cell (through a transport vesicle) to get used somewhere else
mitochondria (image)
ATP MAKER; Contains the OUTER MEMBRANE, INNER MEMBRANE (with the CRISTAE and MATRIX)
Cristae are the INFOLDINGS of the mitochondria
Matrix are the spaces inside but between the cristae
nucleus
CONTAINS DNA; CONTROL CENTER (directs and control the cell on what to do)
The CHROMOSOMES ARE INITIALLY CHROMATIN BEFORE CELL DIVISION
Chromatin would CONDENSE and turn into different chromosomes
NUCLEOSOMES would wrap and condense the chromatin into chromosomes
nucleolus
CREATES RIBOSOMES
chromatin
Substance IN CHROMOSOME THAT HAS DNA AND PROTEINS
concentration gradient
MOVEMENT OF ENERGY (from high to low)
endocytosis
Molecules are EATEN INTO THE CELL
exocytosis
Molecules are SECRETED OUT of the cell
Typically going out through a vesicle
pinocytosis
LIQUID GOES IN
phagocytosis
SOLIDS GOES IN
receptor-mediated endocytosis
the cell USES SPECIFIC RECEPTORS to detect whether there are molecules in the receptor. When there are molecules that bind, it FORMS A VESICLE and takes it in
Receptors detects specific molecules, it surrounds the receptor and molecule into a vesicle and eat it
cell cycle
SERIES OF CHANGES a cells goes through until it reproduces
mitosis
two identical daughter cells produced
interphase (name and describe the 4 phases)
period of growth and reproduction of DNA; synthesizes
G1 phase - CREATION OF NEW ORGANELLES TO INCREASE PROTEINS
S phase - DNA REPLICATION HAPPENS
G2 phase - CONTINUATION OF CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION
G0 phase - MAINTENANCE PHASE (Cells DON’T REPLICATE in this phase)
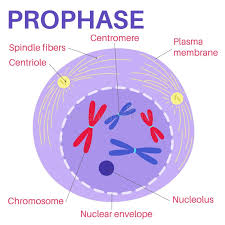
prophase
CHROMATIN TURNS INTO CHROMOSOMES
SPINDLE FIBERS GROW FROM CENTRIOLES
CENTRIOLES MOVE TO OPPOSITE SIDES/POLES OF THE CELL
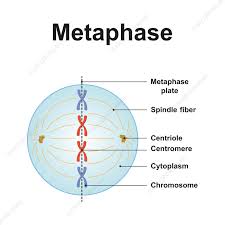
metaphase
ATTACHMENT OF SPINDLE FIBERS TO CHROMOSOMES
The CHROMOSOMES LINE UP IN THE MIDDLE OF THE CELL
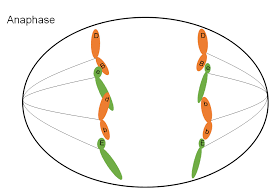
anaphase
spindle fibers shorten and pSEPARATION OF CHROMOSOMES and PULLS SISTER CHROMATIDS IN OPPOSITE SIDESull chromatids apart
telophase
CREATION OF NEW NUCLEAR ENVELOPE AROUND SEPARATED CHROMOSOMES
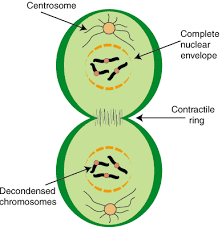
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm