CHM112 Exam 3
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chap 17 acids & bases. Chap 18 acid-base equilibria & solubility equilibria
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Strong acids
H2SO4 - Sulfuric
HI - hydroiodic
HBr - hydrobromic
HNO3 - nitric acid
HCl - hydrochloric
HClO4 - perchloric
“So I Brought No Clean Clothes”
Strong bases
Hydroxides of group 1 and 2 metals
Most common:
LiOH - lithium hydroxide
NaOH - sodium hydroxide
KOH - potassium hydroxide
Ba(OH)2 - barium hydroxide
Ca(OH)2 - calcium hydroxide
Arrhenius definition of acids and bases
Acid: A substance that produces hydrogen ions (H+) (aka
protons) in aqueous solution
Base: A substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) in
aqueous solution.
What’s a neutralization reaction?
a reaction between an acid and a base. Usually produces water and a salt. The overall result is the cancellation of the acid's and base's acidic and basic properties
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → H2O(l) + NaCl(aq)
Brønsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases
Acid is a proton (H+ ion) donor.
Base is a proton (H+ ion) acceptor.
Why is water considered amphiprotic?
Because it can either donate or accept a proton.
H2O(l) + H2O(l) ⇆ H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Acid Base
What is a conjugate acid-base pair?
If two species only differ by the presence or absence of
an H+ ion, they are a conjugate acid-base pair.
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇆ NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
base acid conj acid conj base
Dissociation of strong acids vs weak acids
Strong acids fully dissociate (completely forms H+)
Goes to completion (→)
ex: HCl → H+ + Cl–
Weak acids partially dissociate
Reaction is a chemical equilibrium (⇆)
ex: HF ⇆ H+ + F–
What determines the strength of an acid HA in terms of its dissociation?
Stronger acids (HA) more easily dissociate into H⁺ and A⁻.
How does electronegativity of atom A in HA affect acid strength
Higher electronegativity = share e- less equally = weaker H–A bond = easier to remove H⁺ = stronger acid.
What is an oxoacid?
An acid containing H, O, and a central nonmetal atom (ex. H₂SO₄).
How do double bonds in an oxoacid affect its acid strength?
More double bonds = more resonance structures = more stable conjugate base = stronger acid.
ex. H2SO4 stronger than H2SO3. Sulfuric acid has more double bonds
What functional group defines a the organic acid, carboxylic acid?
The carboxyl group (–COOH)
R - COOH
Are carboxylic acids weak or strong and how does this affect their ability to dissociate?
They are weak acids, and only partially dissociate, existing in equilibrium
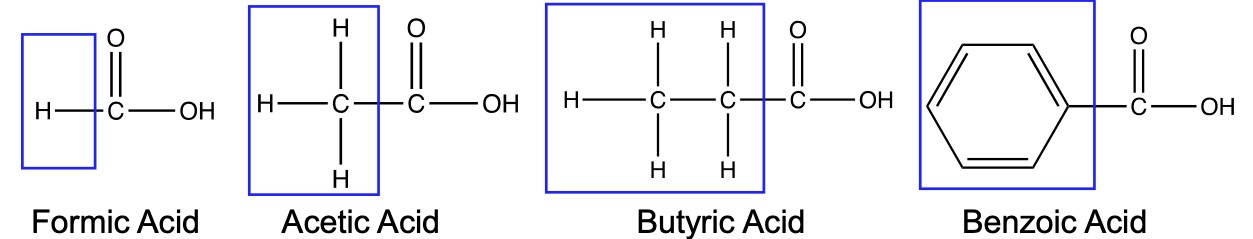
How does the R group of a carboxylic acid affect the acid strength
Electron-withdrawing groups (EWGs) pull electron density away from the COOH group (toward R group) → delocalize and spread out the negative charge = the negative charge on the conjugate base is more stable → stronger acid.
EWGs often have high electronegativity or resonance
Properties of strong bases vs weak
Strong: Tend to be ionic compounds (contains metal and hydroxide)
Fully dissociates (completely forms OH–)
Ex: NaOH → Na+ + OH–
Reaction goes to completion
Weak: Tend to be molecular compounds (contains all nonmetal)
Partially dissociates (partially forms OH–)
Ex: NH3 + H2O ⇄ NH4+ + OH-
Reaction is a chemical equilibrium
What ions are always soluble
Ammonium (NH4+)
Hydrogen (H+)
Alkali metals (group 1A)
Nitrate (NO3- )
Perchlorate (ClO4- ) & Chlorate (ClO3-)
Acetate (CH3COO-)
What ions are usually soluble and their exceptions
Halides/group 17 (F-,Cl-,Br-, I- )
Exceptions (insoluble if with):
Pb2+, Hg22+, Ag+
Sulfate (SO42-)
Exceptions (insoluble if with):
Pb2+, Hg22+, Ag+, Ba2+, Ca2+, Sr2+
What ions are sparingly soluble (insoluble) and their exceptions?
Sulfide (S2-)
Hydroxide (OH- )
Oxide (O2- )
Carbonate (CO32- )
Phosphate (PO43-)
Chromate (CrO42- )
Exceptions:
soluble if with any of
the cations listed in the
always soluble box
What functional group defines the organic base amine?
A nitrogen atom with a lone pair (ex. –NH₂, –NH–)
Ionic product constant of water (Kw)
Kw = Kc = [H3O+] [OH–] = 1.0 x 10-14 at 25°C
The pH scale and acidity/basicity
[H+] or [H3O+] pH Value Solution Type
> 1.0 x 10-7 pH < 7 Acidic
= 1.0 x 10-7 pH = 7 Neutral
< 1.0 x 10-7 pH > 7 Basic
pH/pOH and [H+]/ [OH-] calculations
pH = -log[H+]
[H+] = 10-pH
pOH = -log[OH-]
[OH-] = 10-pOH
equation for pKw
pKw = 14 = pH + pOH
Acid dissociation constant (Ka) of weak acids
HA (aq) ⇄ H+ (aq) + A– (aq)
Ka = [H+]eq[A-]eq / [HA]eq
Acid strength and acid dissociation constant
Ka↑ = pKa ↓ = ↑ weak acid strength
The greater the value of Ka, the stronger the acid
Percent ionization equation and acid strength
Percent ionization = (concentration ionized / original concentration) x 100 = (Δ[HA] / [HA]initial) x 100
The greater the percent ionization, the stronger the acid.
What is a polyprotic acid?
Acids that have more than one ionizable proton (ex. H2SO4, H2CO3, H3PO4)
How do weak polyprotic acids ionize?
In successive steps, each releasing one proton at a time.
H2CO3(aq) ⇄ H+(aq) + HCO3- (aq) Ka1
HCO3- (aq) ⇄ H+(aq) + CO32- (aq) Ka2
Ka values for ionization steps of a polyprotic acid
Each step has its own Ka
Easier to remove the first proton than the second, etc.
Ka1 > Ka2 > Ka3....
(Because after losing a proton, the conjugate base is more negatively charged and holds onto the next proton more tightly)
Successive equilibrium constants have less and less impact on pH
Relationship between Ka, Kb, and Kw
Ka x Kb = Kw = 1.0 × 10-14
Relationship between pKa and pKb
pKa + pKb = 14
Strength of conjugate acid/base if it’s formed from strong acids/base
extremely weak - cannot act as an acid/base
Strength of conjugate acid/base if it’s formed from weak acids/base
Conjugates of weak acids/bases are stronger than the original, but still weak and able to act as an acid/base
What is the composition of a salt?
An ionic compound composed of a metal cation and a nonmetal anion
Ex. NaCl, KCl, MgSO4
How to determine acidic/basic properties of a salt
Separate it into its constituent cation and anion. Then, identify the parent acid and base of each ion
How to Determine if an Ion is Acidic, Basic, or Neutral
Break the salt into its positive cation and negative anion.
Identify the base that would combine with the acid to form the cation.
Identify the acid that would combine with the base to form the anion.
Ex. NaCl
Na+ Cl-
Base: Acid:
NaOH HCl
Combined Effect of Cations and Anions in Salt Acidity/basicity
1) neutral + neutral = neutral.
2) neutral + acidic = acidic
3) neutral + basic = basic
6) Strong acid + strong base = neutral
7) Strong acid + weak base = acidic
8) weak acid + strong base = basic
9) weak acid + weak base = ?
if Ka > Kb, acidic
if Ka < Kb, basic
If Ka ≈ Kb, neutral
What is a buffer and what are its components
It is a solution that resists changes in pH
It's composed of a weak acid (base) and it's conjugate base (acid)
What does buffer capacity depend on and when is it most effective
The capacity depends on the concentrations of the weak acid and its conjugate base. more of each = greater buffer capacity.
It is most effective when the weak acid and conjugate base are in comparable amounts
What is the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation and what is it used for
Used for calculating the pH and pOH of buffer
pH = pKa + log [B]/[A] B = conj base, A = weak acid
pOH = pKb + log [A]/[B] A = conj acid, B = weak base
What types of substances can be mixed to make a buffer
1) A Weak acid and its conjugate base
- Ex. CH3COOH and CH3COONa
2) A weak base and its conjugate acid
- Ex. NH3 and NH4Cl
3) A strong acid and a weak base (with extra amount)
- Ex. HCl and NH3 H+(aq) + NH3(aq) → NH4+(aq)
4) A strong base and a weak acid(with extra amount)
- Ex. KOH, HF OH-(aq) + HF (aq) → F- (aq) + H2O(aq)
5) A weak acid and a weak base(either one in extra amount)
-Ex. CH3COOH, NH3
CH3COOH(aq) + NH3 (aq) → CH3COO- (aq) + NH3+(aq)
How to choose a buffer to maintain a specific pH
Choose a weak acid with pKa close to the desired pH
To reach the desired pH, adjust [A-]/[HA]
To make the buffer work best, [A-]/[HA] should be between 0.1 and 10
what is the equivalence point of a titration
the point where moles of acid = moles of base (reaction is stoichiometrically complete).
xFound on a pH curve as the steepest part of the curve
What is the endpoint of a titration and how is it different from the equivalence point
Endpoint: The point in a titration where the indicator changes color, signaling that the titration should stop. It is a visual cue. It is usually close to equivalence point.
The equivalence point is the theoretical point in a titration where the moles of the titrant exactly equal the moles of the analyte
pH of equivalence points between a
strong acid + strong base
weak acid + strong base
strong acid + weak base
strong acid + strong base
pH = 7
weak acid + strong base
pH > 7
strong acid + weak base
pH < 7
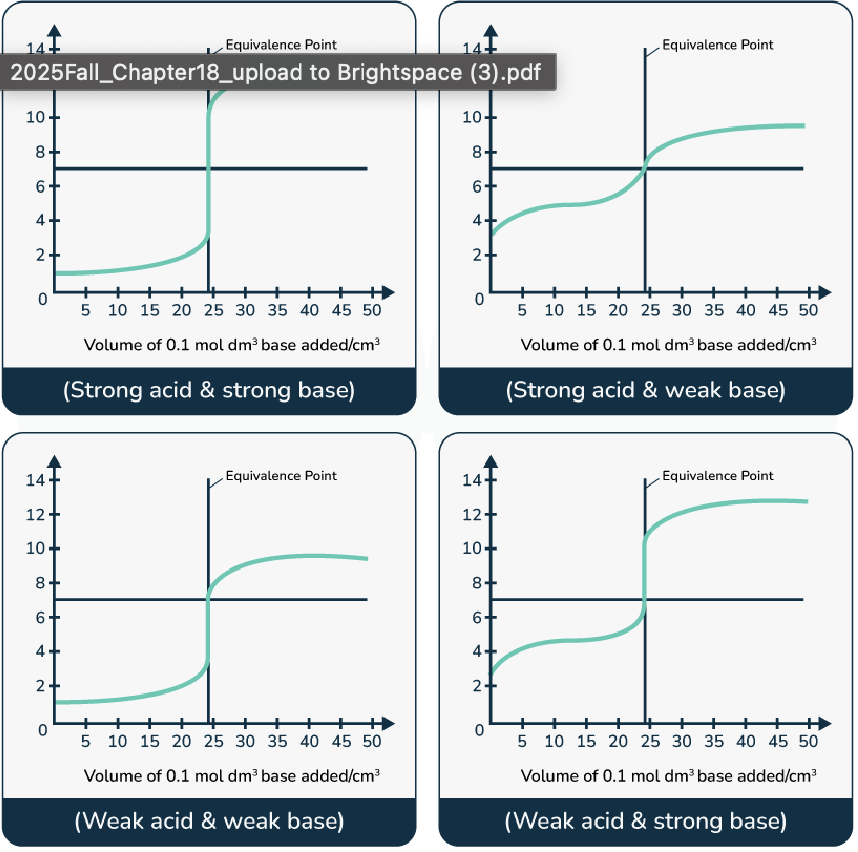
Why do we usually avoid using a weak acid or weak base as the titrant?
Because weak acids/bases do not fully ionize, they produce a smaller pH change near the equivalence point. This makes the titration less accurate and the equivalence point harder to detect with an indicator.
pH changes during titration of a weak base (NH₃) with a strong acid (HCl)
Beginning
Before equivalence point
At equivalence
After equivalence
Beginning: pH is set by weak base NH₃.
Before equivalence point: NH₃ + NH₄⁺ solution forms a buffer, controlling pH.
At equivalence point: All NH₃ is converted to NH₄⁺; NH₄⁺ hydrolysis lowers pH → pH < 7.
After equivalence point: Excess HCl controls pH; effect of NH₄⁺ is negligible.
*Buffer region is the region between first addition of HCl and equivalence pt
What is a polyprotic acid/base and characteristics of its titration
Polyprotic acids are acids that can donate more than one proton
Theres an equivalence point for each acidic proton.
What is the solubility product constant
Salt (s) ⇌ Cation+ (aq) + Anion- (aq)
Ksp = [Cation+][Anion-]
Ksp and solubility
Solubility tells you how much of a salt can dissolve in a
certain amount of water
Larger Ksp = more soluble
Amount of salt does not alter Ksp
The value of Ksp depends only on the temperature.
What is molar solubility? How is it different from solubility in g/L?
Molar solubility (M): Maximum moles of a solute that dissolve in 1 L of water.
Solubility (g/L): Maximum grams of solute that dissolve in 1 L of water.
Example: PbCl₂ (s) ⇌ Pb²⁺ + 2Cl⁻
Step | Pb²⁺ | Cl⁻ |
|---|---|---|
Initial (I) | 0 | 0 |
Change (C) | +x | +2x |
Equilibrium (E) | x | 2x |
Molar solubility = x
Solubility (g/L) = x · molar mass
What is the difference between Q and K, and how do they predict reaction direction?
K = equilibrium constant (describes the system at equilibrium).
Q = reaction quotient (describes the system at any moment).
Q = K → system at equilibrium (no net change).
Q < K → reaction shifts right (forms products).
Q > K → reaction shifts left (forms reactants).
How do you predict whether a precipitate will form using Qsp and Ksp?
Qsp = Ksp → solution is saturated → no precipitate
Qsp < Ksp → solution is unsaturated → no precipitate forms
Qsp > Ksp → solution is supersaturated → precipitate WILL form