Week One AIM Lectures
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
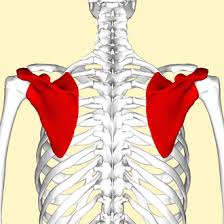
? and function
Scapula, Articulates with the humorous/clavical and connects the upper limb to the trunk
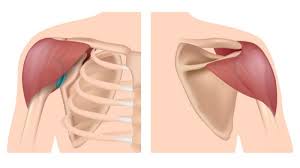
? and actions
Deltoid, AFE(Abducts, flexes, and extended the upper limb at the shoulder)
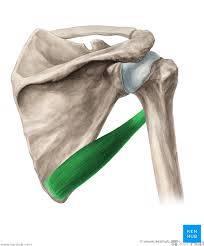
?
Teres Major
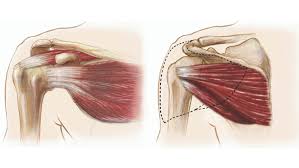
?, Parts, Set up, and Functions
Rotator cuff muscles, SItS(Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, tere minor, and subscapularis), Superspinatus highest, infraspinatus next, there minor next, and subscapularuis is flatter and under scapula, Stabilizes shoulder/rotates and abducts upper limb.
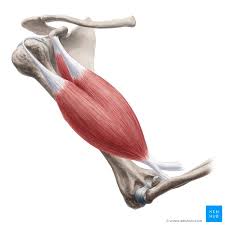
? and where
Anterior arm muscle, Biceps(2 head, originates from scapula and attaches to proximal end of radius)
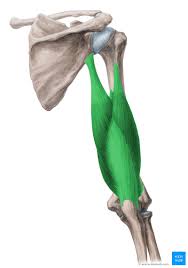
? and where
Anterior arm muscle, Brachialis(Little bulb, lies deep in biceps, originates from humerus and attaches to ulna)
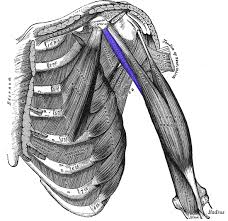
? and where
Anterior arm muscle, coracobracialis (superior to main head of bicep, thin and long)
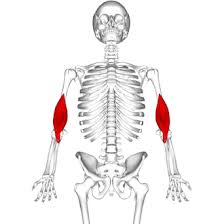
?, where, and function
Triceps Brachii, posterior arm, extends forearm at the elbow
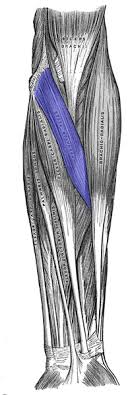
? and where
Pronator teres, anterior forearm
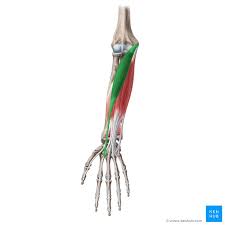
? and where
Flexor capri radialis, anterior forearm
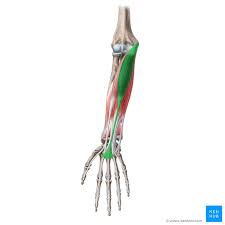
? and where
Palmaris Longus, anterior forearm
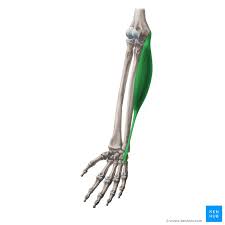
? and where
Flexor Capri Ulnaris, Anterior forearm
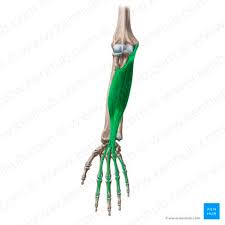
? and where
Flexor Digitorium Superficialis, Anterior arm
What is the tendon?
Where the muscle attaches to bone, e.g, Flexor Digitoriem Superficialis muscle has a tendon that attaches to the radius and ulna/humerus(Looks blue in pictures, not red like rest of muscle)
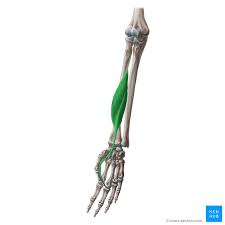
? and where
Flexor Policis Longus, anterior forearm

? and where
Flexor Digitorium Profoundus, Anterior Forearm
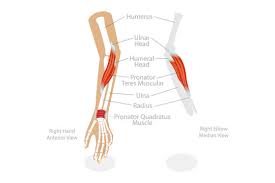
? and where
Pronator Teres(Top) and Pronator Quadratum(Inferior), anterior forearm
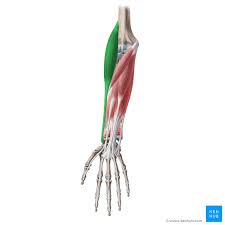
? and where
Brachioradialis, posterior forearm
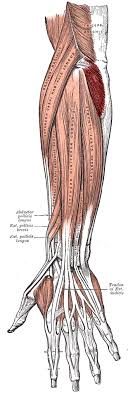
? and where
Anconeus, Posterior forearm
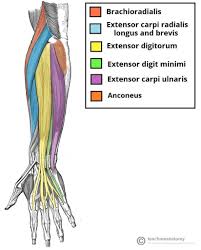
Functions and where
posterior forearm, Main function is to produce extension at the wrist and fingers
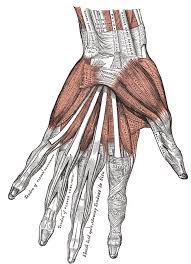
Thumb Musckles and where
Posterior, abductor polici longus on top and most lateral, extensor polices braves in middle, extensor polices longus on the bottom(Most medial)
Anatomical Position
Face Directed Forward
Arms at side
Palms of hands facing forward
Coronal Plane
Divides body into dorsal(back or posterior) and ventral(front or anterior)
Ventral
Front/Anterior
Dorsal
Back/Posterior
Adduction
Motion that pulls a structure toward the midline of the body or limb
Abduction
Motion that pulls a structure away from the mid line of the body or limb
Sagittal Plane
Divides body into right and left parts
Midsagittal
Divides the body into right and left parts through the midline
Flexion
Bending movement that decreases the angle between body parts
Extension
straightening movement that increases the angle between body parts
Transverse Plane
Divides the body into superior/cranal and inferior/caudal
Cranial
Towards head
Caudal
Towards tail
Rotations
The act of turning or twisting a body part, or the entire body, around an axis
Medial
Toward midline
Lateral
away from the midline
Anterior
Towards the front
Posterior
Towards the back
Proximal
Towards the trunk
Distal
Away from the trunk
Dorsal
Posterior hand/foot surface
Palmer
Anterior hand
Planter
Superior foot surface
Unilateral
One Side
Bilateral
Both sides
Ipsilateral
same sides
Contralateral
opposite sides
Internal/medial rotation
rotation towards midine
External/Lateral
rotation
Elevation
movement in a superior direction
Depression
movement in an inferior direction
Supination
palm anterior
pronation
palm posterior
Opposition
brings thumb and little finger together
reposition
brings thumb and little finger apart
Dorsiflextion
flex foot “up”(decrease angle between dorsal and ankle)
plantarflexion
point toes down(decrease angle between sole and back of leg)
Eversion
Sole of away from median plane(Exit sole)
Inversion
Sole of foot toward median plane (Roll ankle)
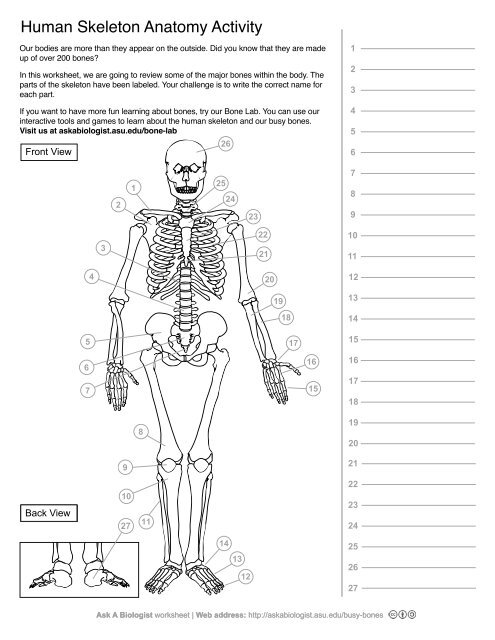
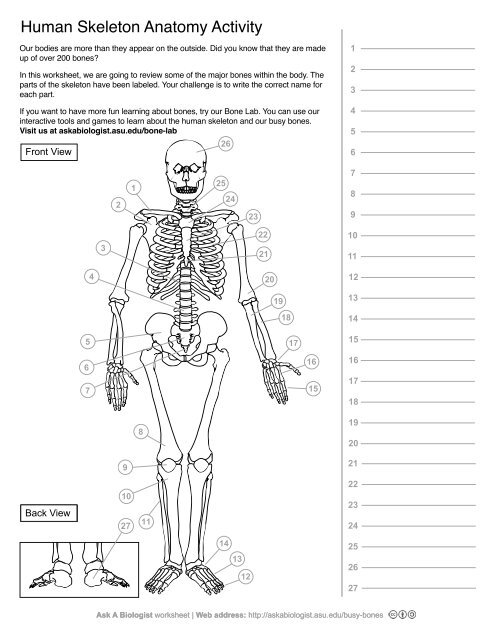
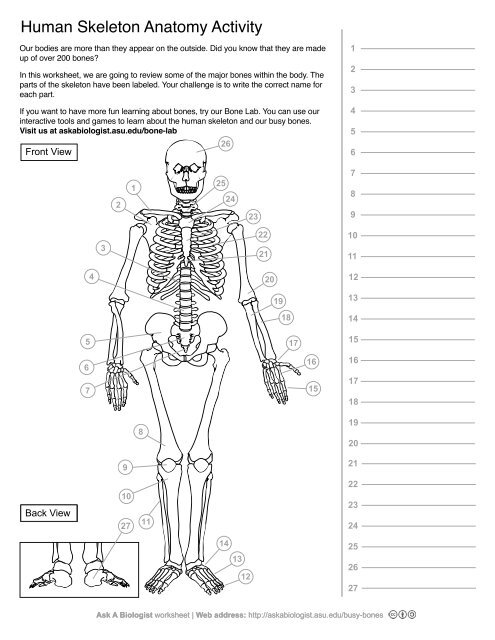
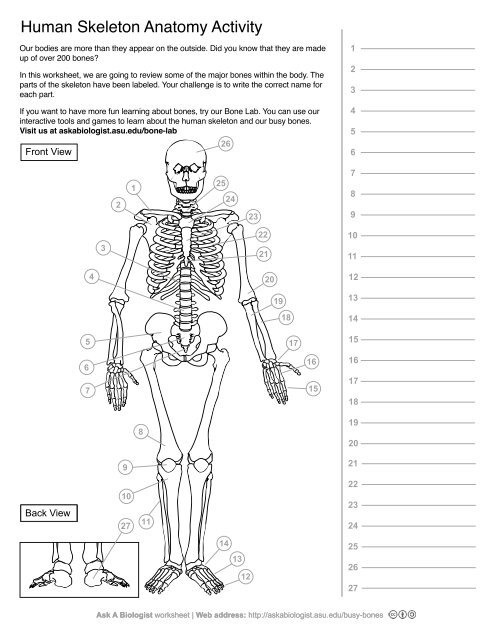
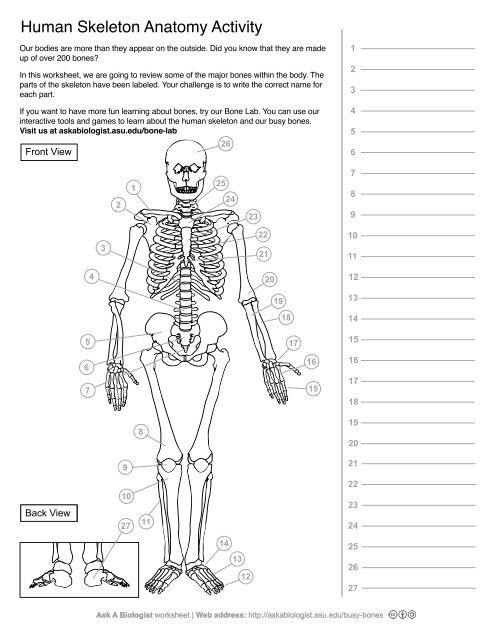
1
Clavical
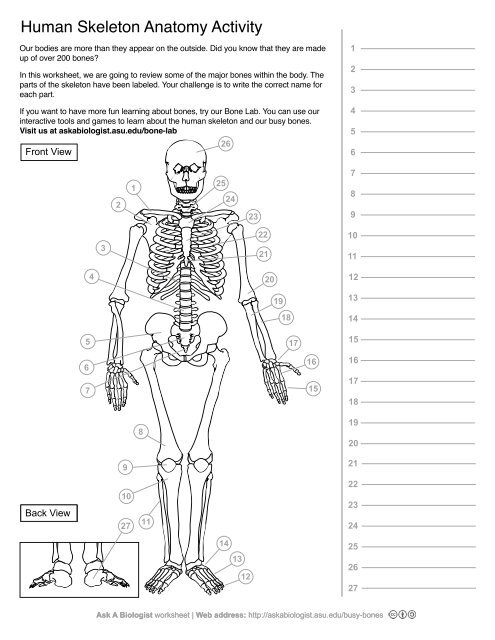
2
Scapula
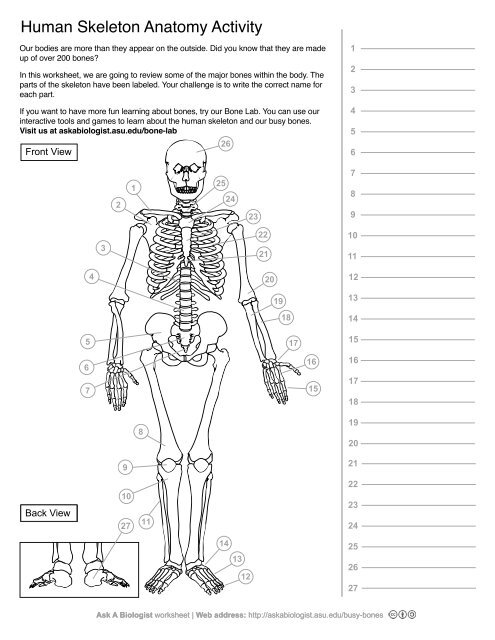
3
Thoracic Vertebrae
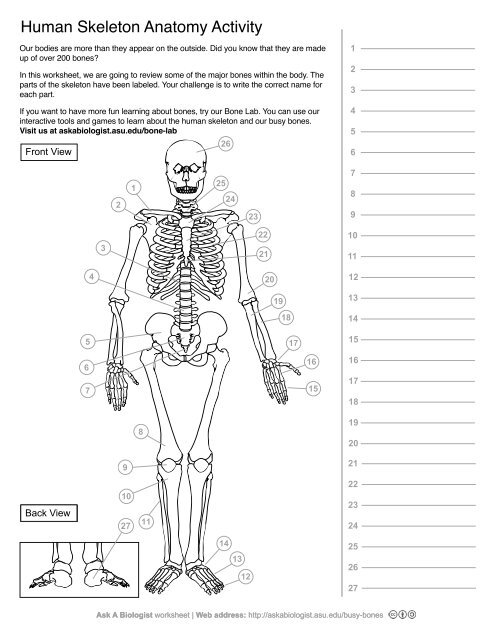
4
Lumbar Vertebrae
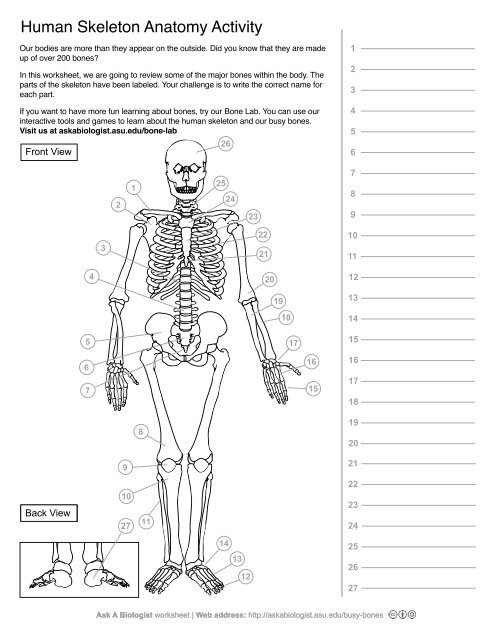
5
Pelvis
6
Sacrum
7
Coccyx
8
Femur
9
Patella
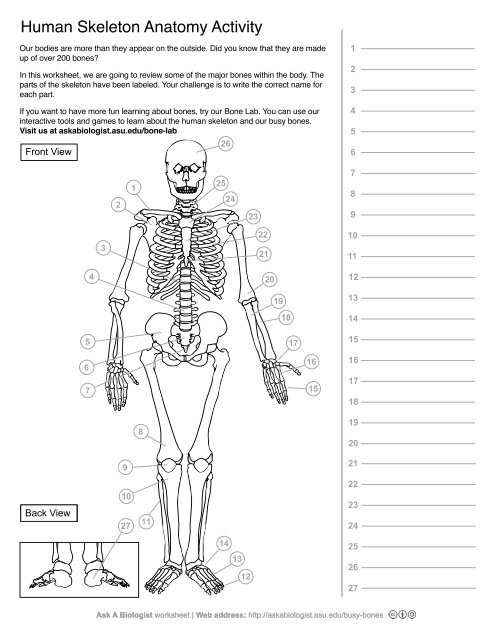
10
Tibia
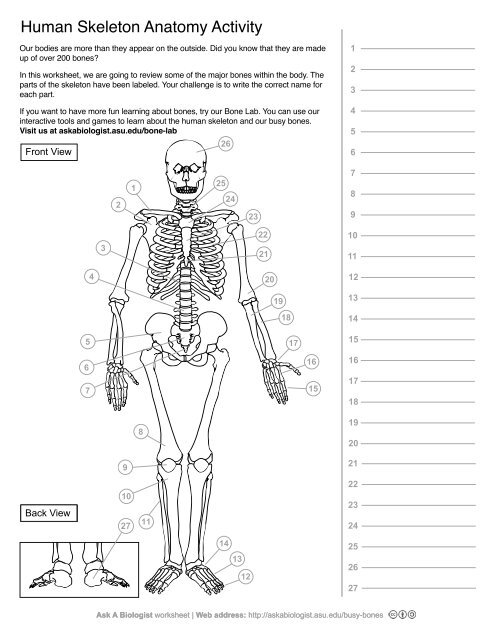
11
Fibula
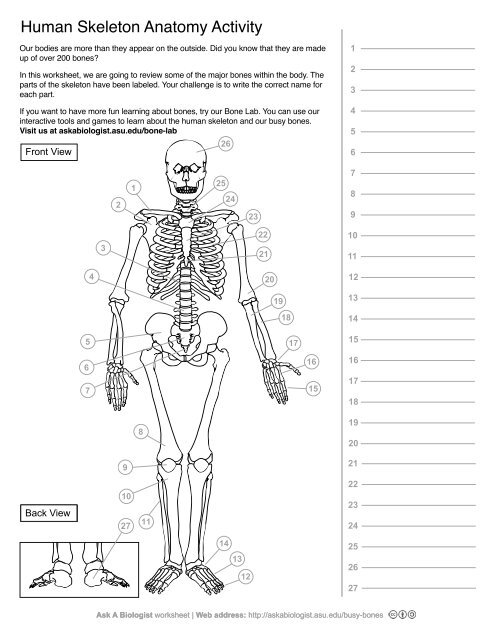
12
Phalanges
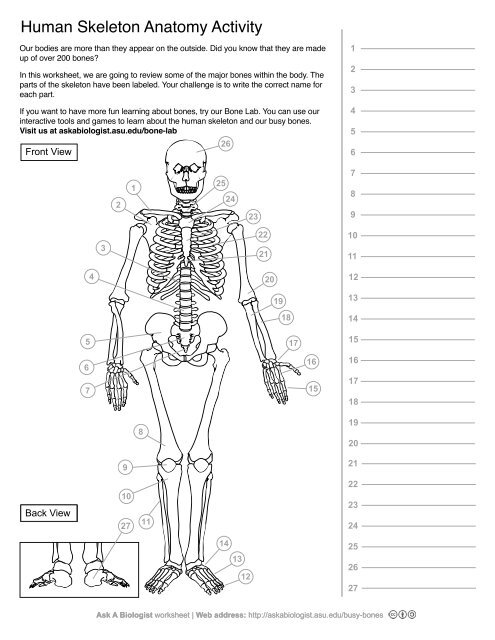
13
metatorsals
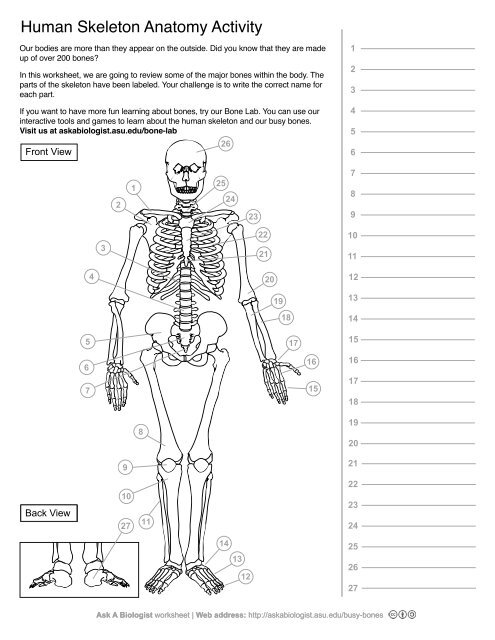
14
tarsals
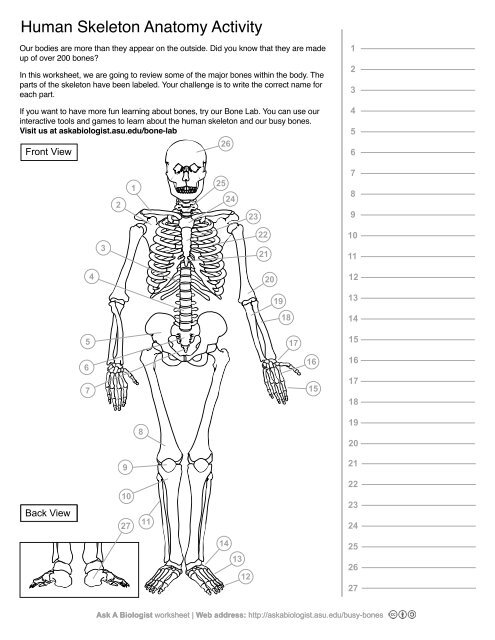
15
Phalanges
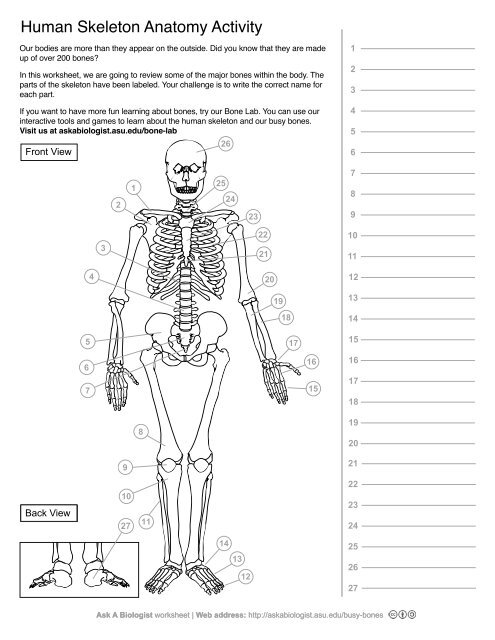
16
metacarpals
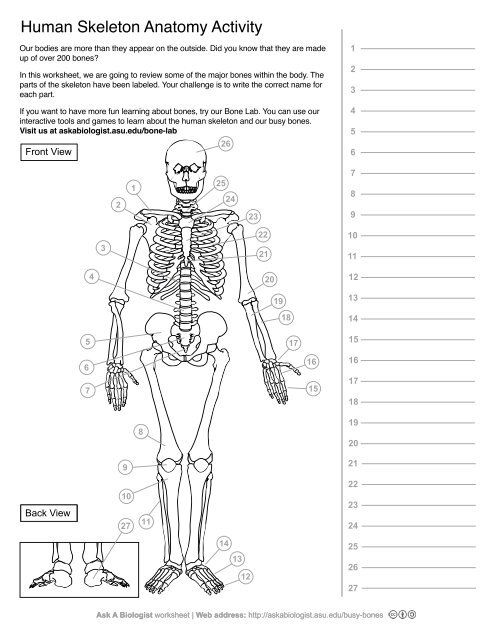
17
carpals
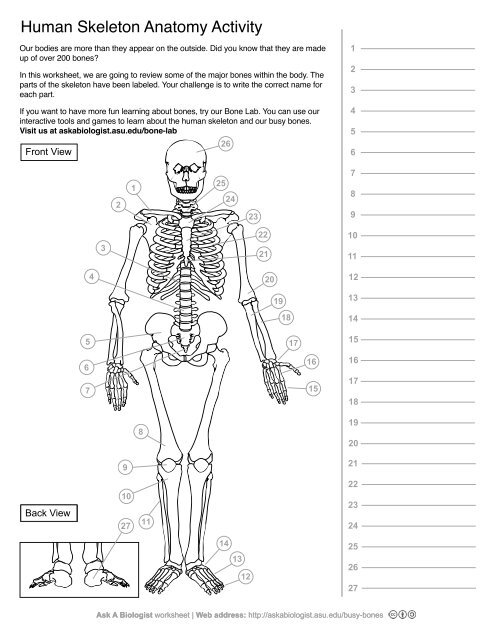
18
Radius(Lines up with thumb)
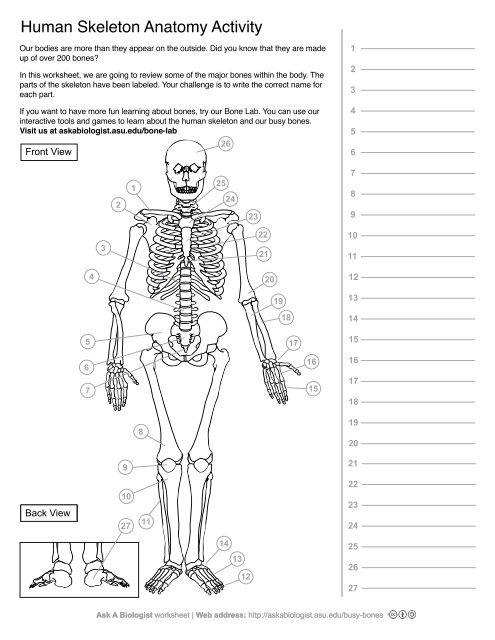
19
Ulna
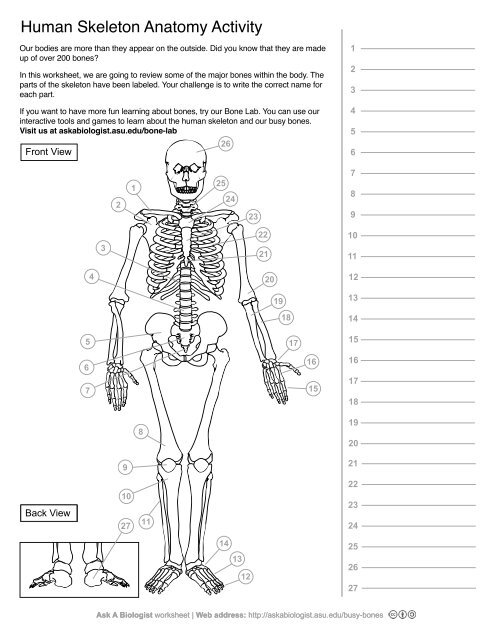
20
Humerus
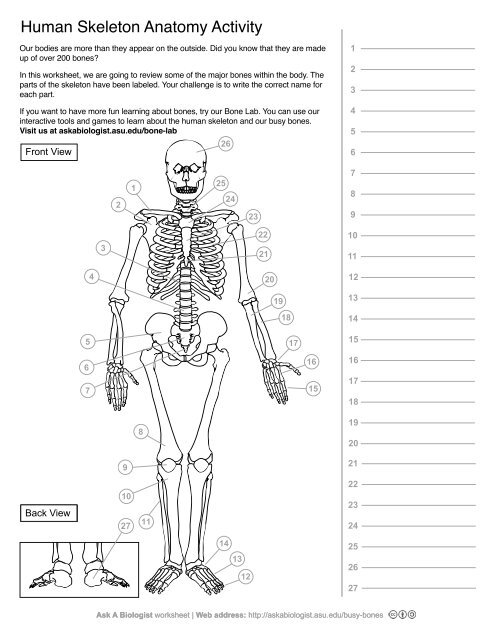
21
Xiphoid Process
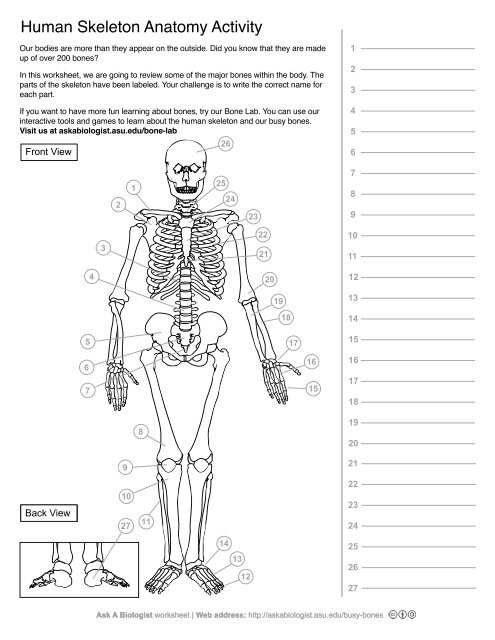
22
Ribs
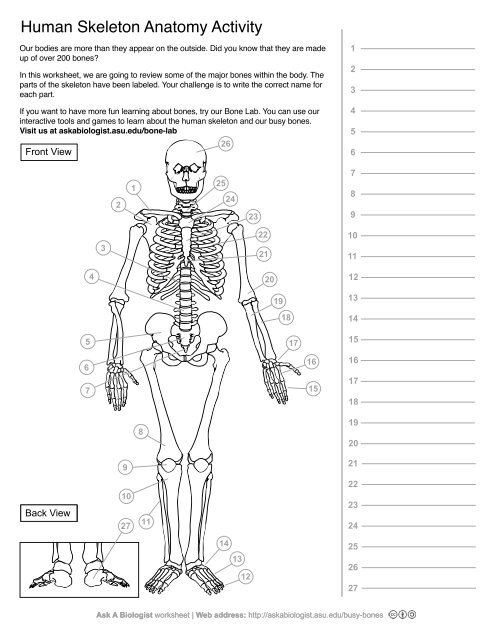
23
Sternum Body
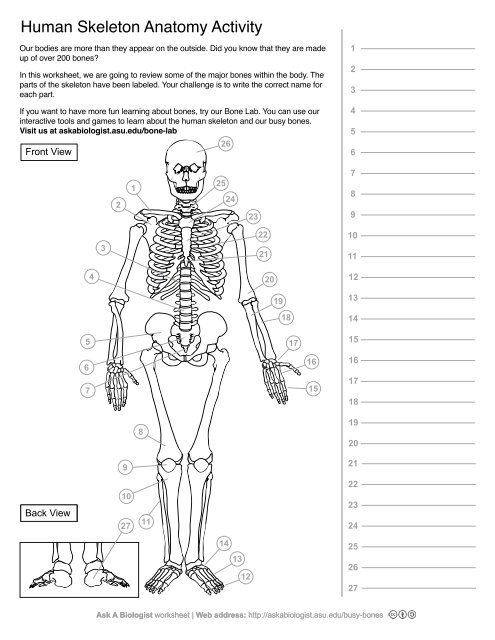
24
Mandibrium
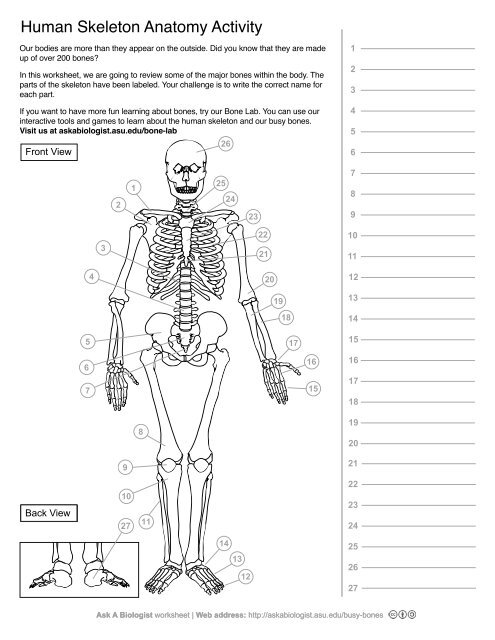
25
Cervical Vertebrae
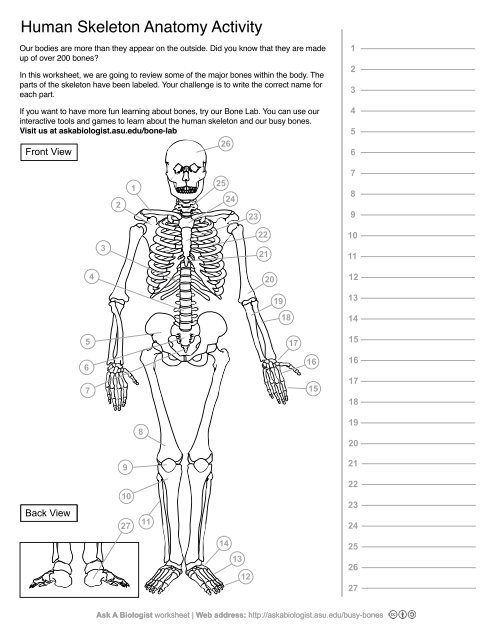
26
Cranium
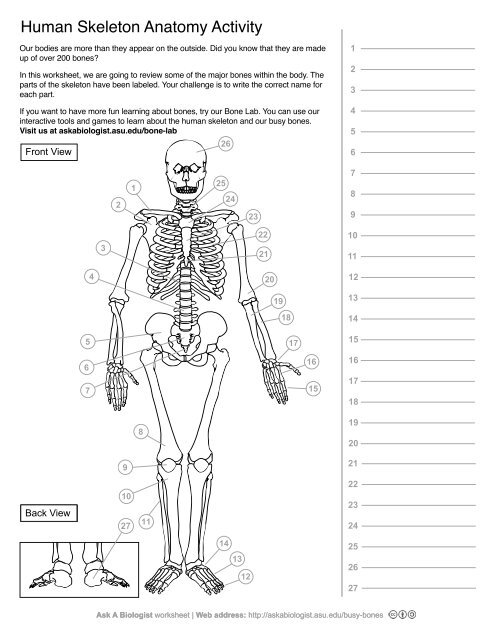
27
Calcaneus
Vertebral Column Functions
(SPAM)
Support:Carry weight of body parts above pelvis
Protection:Encloses and protects the spinal cord within the spinal canal
Axis:Forms the central axis of the body
Movement:Has roles in both posture and movement
Parts of spine(5 Parts)
(CTLSC)
Cervical(7)
Thoracic(12)
Lumbar(5)
Sacrum(5, fused)
Coccyx(4, fused)
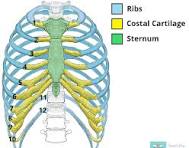
Ribs
12 total…
1-7 attached independently to the sternum
8-10 attached to the costal cartilage superior to them
11 and 12 do not have an anterior attachment and end in the abdominal musculature (Floating ribs)
Voluntary vs Involuntary Muscles
Voluntary= Consciously move
Involuntary= unconsciously move
Smooth muscle
an involuntary muscle found in the internal organs and blood vessels
Cardiac muscle
an involuntary muscle only found in the heart
Skeletal muscle
a voluntary muscle attached to the skeleton
Origin of muscle
Typically more proximal. Remains fixed during muscle contraction
Insertion of muscle
Typically more distal, moves closer to the origin during muscle contraction
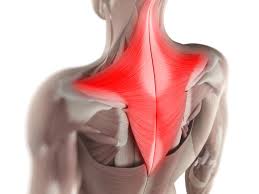
?
Trapezius
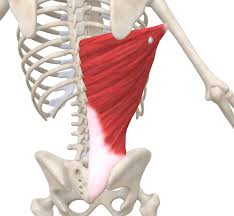
?
Latissimus Dorsi
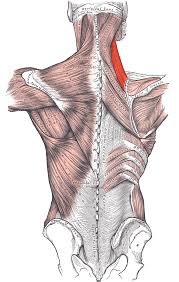
?(And Function?)
Lavator Scapulae, Elevates Scapulae
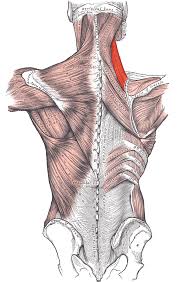
?
Rhomboid Minor