IBPS4 Cognitive SAQ+ERQ
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
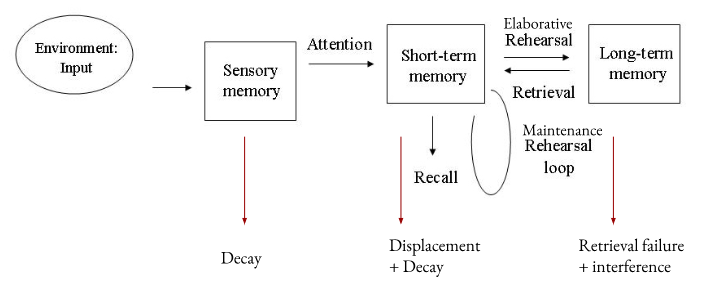
MSM (atkinson & shiffrin)
memory made up of 3 stores + 2 processes to transfer info. between stores (attention+ maintenance/elaborative rehearsal)
sensory: temp. store holding info from environment for 0.5-1s in the modal form it’s received. needs to receive attention to begin process of transferring to LTM - otherwise decays
modality specific
STM: if attention paid to stimuli, info enters thru SM. temp. store that can hold 7 “chunks” of info for 30s. if info. rehearsed, it’s transferred to LTM. if not rehearsed/more info disrupts rehearsal, info. may be displaced
maintenance rehearsal loop for temp. immediate use
encoded acoustically
LTM: if rehearsed in STM thru elaborative rehearsal, memory stored here. unlimited capacity + duration, can retrieve info. from LTM → STM when needed to b recalled (providing retrieval failure/interference doesn’t occur)
encoded semantically
glanzer & cunitz (serial position curve) — MSM
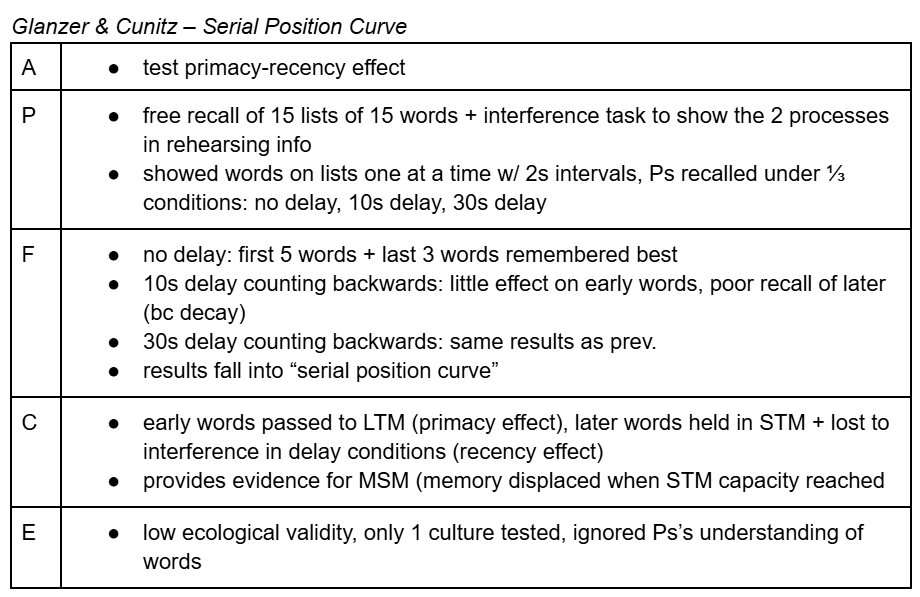
…exhibits 2 types of rehearsal that hold/transfer info between stores
high internal validity → strongly demonstrates how it was the delay that influenced recall due to other Vs being controlled
milner’s case study of HM — MSM

demonstrates how info. could stay in STM but couldn’t be transferred to LTM via elaborative rehearsal → evidence of separate stores existing by showing how memory formation not possible in HM’s case
findings can be transferred IRL to ppl w/ brain dmg to understand better
longitudinal → studied change over time in HM’s brain
bartlett (war of the ghosts) — schema theory
[A] investigate how schemas influence recall + demonstrate role of culture in schema processing
[P] British students presented w/ unfamiliar Native American story → allocated Ps to either serial/repeated reproduction to retell it
[F] no sig. diff. in conditions. recited version left out/replaced details relating to NA culture (e.g. canoe → boat). Ps filled gaps in memory w/ own cultural schemas (assimilation). word count went from 330 → 180 (levelling). added emotion to convey main themes (sharpening)
[C] remembering is active: info. changed to fit into existing schemas to create meaning (such as B boys changing NA tale to make it more logical to them). more complex elements of info. distorted/forgotten (word count dec). we try to find familiar patterns in new experiences using our existing cultural schemas (derived from prior knowledge + exp.).
tversky & kahneman — dual processing model
[A] investigate how heuristic influences estimation of math problem (even when Ps aware of sequence) to demonstrate system 1 thinking
[P] highschoolers asked to estimate 8! in 5s, split into ascending/descending condition. theorised that 1st no. would bias estimate (due to insufficient time to apply logical thinking)
[F] median for ascending group 512, descending 2250. both underestimated (actual = 40 000)
[C] first number created anchor that affected estimation → shows anchoring heuristic (a result of system 1). hence irrelevant values can bias decision when using quick, system 1 thinking. if used system 2…
landry & bartling — WMM
[A] investigate if articulatory suppression affects recall accuracy of serial recall of dissimilar letter sequences
[P] undergrad psych students divided into experimental (articulatory supression) and control groups (silent recall). saw list of dissimilar 7-letter sequences (5s), 5s wait, then write. experimental repeated 1,2 aloud while doing the task. avg % correct recall was calculated
[F] experimental group had lower recall accuracy (76% vs 45%) bc phonological loop was disrupted by verbal interference
[C] articulatory suppression prevents rehearsal bc phonological loop overloaded, leading to less recall accuracy
WMM (baddeley and hitch)
STM more complex than just one single store, made up of multiple stores
CE: directs attention (at automatic/supervisory level) and allocates info. based on modality. very limited capacity. can focus/divide/switch attention
PL: limited capacity. auditory info. + written/spoken lang. store
phonological store → inner ear (holds words heard). can receive info from SM/LTM/articulatory process
articulatory process → inner voice (holds words heard/seen, repeats it)
VsS: limited capacity. visual/spatial info. store from SM or LTM
visual cache → form/colour info.
inner scribe → process spatial/movement info
EB: links info. to form integrated memory w/ time sequencing + moves it to LTM e.g. memory of event
schema theory (piaget)
organise knowledge, assist recall, guide behaviour, predict situations, make sense of events
derived from prior knowledge/experience. simplify reality + culture specific
scripts → schemas about events in time. if don’t go according to expectations, we get annoyed/confused/angry
children learn using existing schemas that are accommodated (existing schema replaced) or assimilated (info. added to schema)
levelling (omitting minor details)/sharpening (exaggerating certain details) to fit into schema
schemas can influence memory at all stages (encoding/storage/retrieval) - brewer & treyens
brewer & treyens
[A] investigate role of schema in encoding/retrieval of episodic memory
[P] independent sample of 86 uni students seated in office room w/ congruent objects e.g. paper, coffee pot and incongruent objects e.g. skull. asked to wait here, then after 35s called into another room + asked what they remembered under ⅓ conditions: written recall + verbal recog., drawing, verbal recog. only
[F] Ps more likely to recall schema congruent objects in writing/drawing + often changed nature of objects to match schema. in verbal, more likely to identify incongruent + congruent objects not in room.
[C] schema played role in encoding + recall of memory
dual processing model (systems 1/2) (thinking/decision making)
system 1 → ignores absent evidence, focuses on what it sees, “automatic”, based on schemas. quick, prone to errors, generates impressions, takes heuristics
done bc:
humans are cognitive misers (lazy)
when task too difficult, experience ego depletion
too much stuff going on → cognitive load too high
= law of least effort
system 2 → requires concentration/effort, works w/ abstract concepts, reliable but slow, uses conscious reasoning + logic