17X: Block 5: Mission Assurance: ALL
1/240
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
241 Terms
What does OT stand for?
Operational Technology
What does OT encompass? *FS
Technologies involving interconnected devices and computers that monitor or control physical processes.
Devices include fuel/pump stations, electricity generation/metering/distribution, water distribution, etc.
What does IT encompass? *FS
Systems that focus on the flow of information and data.
Devices include PCs, cell phones, database systems, routers, and switches.
What does CPS stand for?
Cyber Physical Systems
What are some other terms for CPS?
Industrial Control Systems (ICS)
Embedded Systems
What is the purpose of CPS?
These systems enable OT.
What components do CPS typically have? *FS
1. Sensors
2. Actuators
3. Controllers
4. Communication Network
What is the purpose of a sensor in a CPS? *FS
It senses or monitors changes to the physical world.
What is the purpose of an actuator in a CPS? *FS
It makes changes to the physical world.
What is the purpose of a controller in a CPS? *FS
It makes decisions/controls processes based on sensed data.
What is the purpose of a communication network in a CPS? *FS
It handles communication among the sensors, actuators, and controllers.
How do the components of a CPS interact?
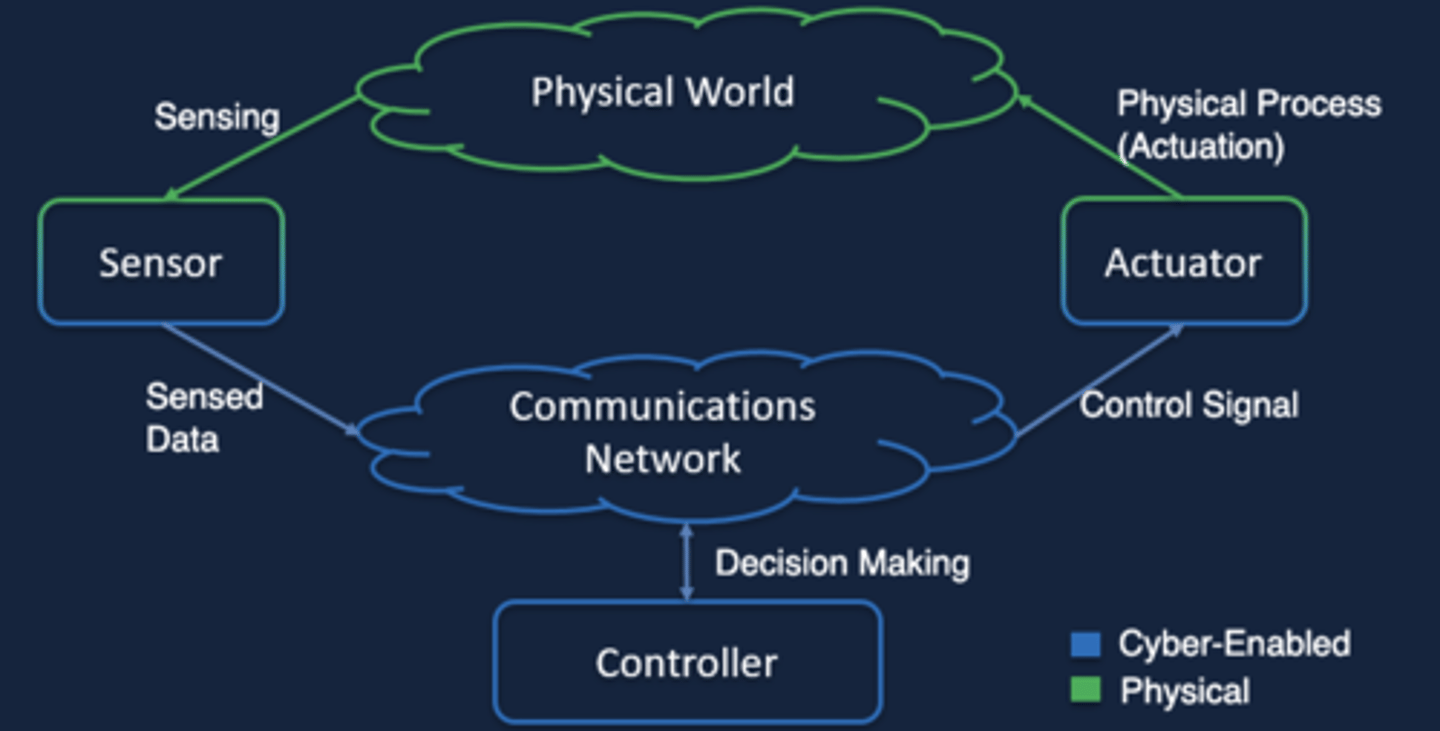
What is an open loop CPS? *FS
A system that operates without real-time feedback from the environment to adjust its behavior.

Are toasters and light switches examples of open or closed loops?
Open loops.
What is a closed loop CPS? *FS
A system that operates with real-time feedback from the environment to adjust its behavior.
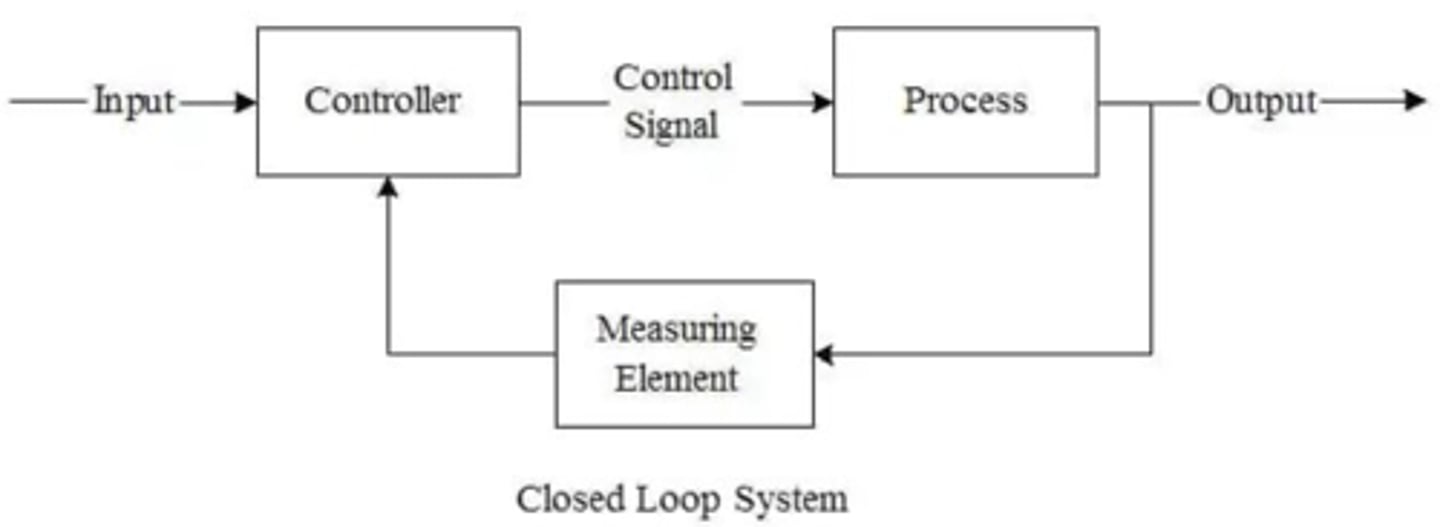
Are smart washers and HVACs examples of open or closed loops?
Closed loops.
What are the CPS Security Goals? *FS
1. Interoperability
2. Security
3. Dependability
4. Sustainability
5. Reliability
6. Predictability
What are examples of the types of CPS? *FS
1. SCADA: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
2. DCS: Distributed Control Systems
3. PLCs: Programmable Logic Controllers
4. HMI: Human Machine Interface
5. RTU: Remote Terminal Units
6. IED: Intelligent Electronic Devices
What is Critical Infrastructure?
It is the systems, assets, and networks that are so essential to a society, economy, or government that their disruption, degradation, or destruction would have a significant impact on national security, public safety, economic stability, or public health and welfare.
*NT: no formal definition in the slides
How many Critical Infrastructure categories did Presidential Policy Directive (PPD) 21 establish? *FS
16 categories.
What are the strategic goals of PPD 21?
1. Refine and Clarify Functional Relationships across the Federal Government
2. Enable Efficient Information Exchange for the Federal Government
3. Inform Planning and Operational Decisions Regarding Critical Infrastructure
Which act elevated cybersecurity from DHS to a separate agency?
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) Act
What sorts of categories fall under critical infrastructure?
*FS by instructor: know what isn't on this list.... e.g., entertainment.
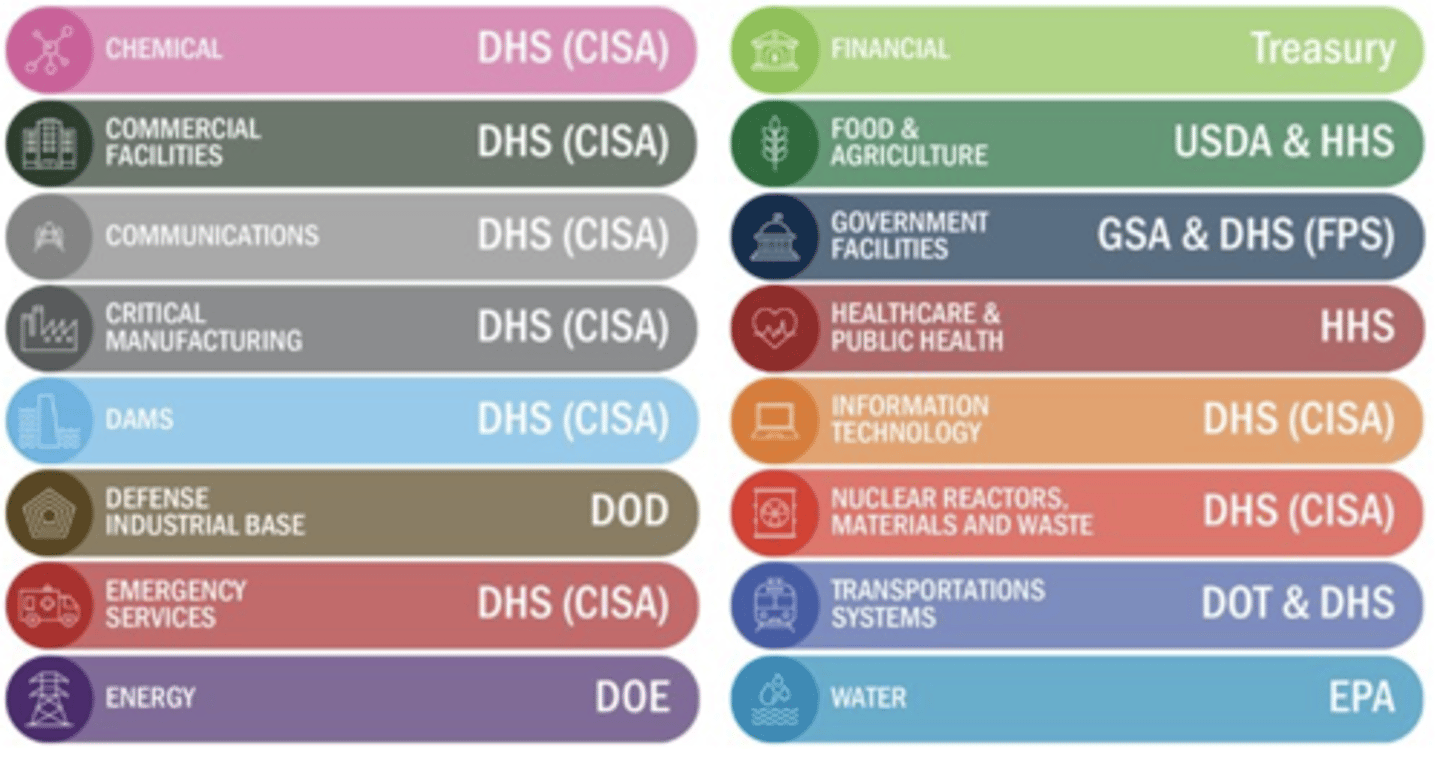
Which department/agency is the cybersecurity policy lead for the US government? *FS
DHS
Which department/agency is the cybersecurity operational lead for the US government? *FS
CISA
Which department/agency is the partner agency for unaffiliated critical infrastructure sectors?
DHS
Which department/agency handles partnership development, information sharing, incident management, and risk assessment & analysis?
CISA
Which department/agency develops and publishes cybersecurity standards (NIST) and handles small business cybersecurity training & awareness?
Department of Commerce
Which department/agency investigates cybercrime/ransomware and coordinates investigations/extradition with international law enforcement?
FBI
Which department/agency handles international information sharing/threat alerts and international cybersecurity cooperation?
Department of State
Which department/agency enforces sanctions and freezes foreign assets?
Department of the Treasury
Which department/agency coordinates computer crime prosecution with State, County, and Local governments?
Department of Justice
What is the purpose of other federal departments/agencies (HHS, DOE, etc) regarding critical infrastructure cybersecurity in the US Government?
They partner with regulated critical infrastructure sectors.
Which department/agency conducts persistent engagement of adversaries to defend and advance national interests at a level below armed conflict? *FS
DoD (USCYBERCOM)
Which department/agency defends/hunts forward to stop attacks on US and allied Critical Infrastructure at the source? *FS
DoD (USCYBERCOM)
What is the purpose of the NSA regarding critical infrastructure cybersecurity in the US Government? *FS
1. Develops OCO & DCO capabilities
2. Provides cryptography products & services
3. Conducts threat assessments on USG networks/IS
4. Provides reports on cyber intelligence and threats to USG and commercial partners (SIGINT)
What does IE stand for?
Information Environment
What is the definition of IE?
The IE is the aggregate of social, cultural, linguistic, psychological, technical, and physical factors that affect how humans and automated systems derive meaning from, act upon, and are impacted by information, including the individuals, organizations, and systems that collect, process, disseminate, or use information. It is an intellectual framework to help identify, understand, and describe how those often intangible factors may affect the employment of forces and bear on the decision of the commander. (JP 3-12, Cyberspace Operations)
What are the three dimensions of the IE model? *FS
1. Cognitive
2. Physical
3. Information
What is the focus of the Cognitive Dimension in IE?
It is human-centric.
What is the focus of the Physical Dimension in IE?
It is tangible/real-world.
What is the focus of the Information Dimension in IE?
It is data-centric.
Which dimension of IE is based on individual attitudes, beliefs, judgment, information processing, decision making, group identity, and norms?
Cognitive
Which dimension of IE is focused on how individuals assign meaning to or interpret images and actions?
Cognitive
Which dimension of IE is focused on material characteristics, both natural and manufactured, of the environment that create constraints and freedoms on the people and information systems that operate in it?
Physical
Which dimension of IE encompasses where and how information is collected, processed, stored, disseminated, and protected?
Information
Which dimension of IE is where the C2 of military forces is exercised and where the commander's intent is conveyed?
Information
Actions in which dimension of IE affect the content and flow of information?
Information
What does CO stand for?
Cyberspace Operations
What is the definition of CO? *FS
The employment of cyberspace capabilities where the primary purpose is to achieve objectives in or through cyberspace.
How does CO create strategic effects?
Through tactical actions: it uses links and nodes located in the physical domains and perform logical functions to create effects first in cyberspace and then, as needed, in the physical domains.
What are the three layers of the CO layer model? *FS
1. Physical Network
2. Logical
3. Cyber-Persona
What does the Physical Network Layer of the CO Layer Model encompass?
IT devices and infrastructure in the physical domain.
E.g., hardware, wireless and wired links, physical storage mediums, geography.
What does the Logical Layer of the CO Layer Model encompass?
Abstractions from the physical layer, based on the logic programming (code) that drives network components.
E.g., IP addresses, ports, protocols, services, operating systems, virtual machines, etc.
What does the Cyber-Persona Layer of the CO Layer Model encompass?
Digital representations of an actor or entity's identity in cyberspace.
E..g, user accounts, account roles/relationships.
Multiple users may have the same account and a single user may have multiple accounts (social media, email, banking, etc).
What are the three categories of ownership in cyberspace? *FS
1. Blue
2. Grey
3. Red
What is blue cyberspace? *FS
Cyberspace owned and/or protected by the US, its mission partners, and the DoD.
What is grey cyberspace? *FS
Unaffiliated/unaligned cyberspace.
What is red cyberspace? *FS
Cyberspace owned or controlled by an adversary.
What about cyberspace ownership leads to issues with attribution?
The lines between blue/grey/red are often blurry and unclear.
What factors help us attribute cyber attacks? *FS
The attacker's:
1. Geographic Location (IP address)
2. TTPs
3. Level of Sophistication
4. Political Goals/Interests
What does OIE stand for?
Operations in the Information Environment
How does CO relate to OIE? *FS
CO is an overlapping subset of OIE that can be executed independently to or in concert with other OIE missions.
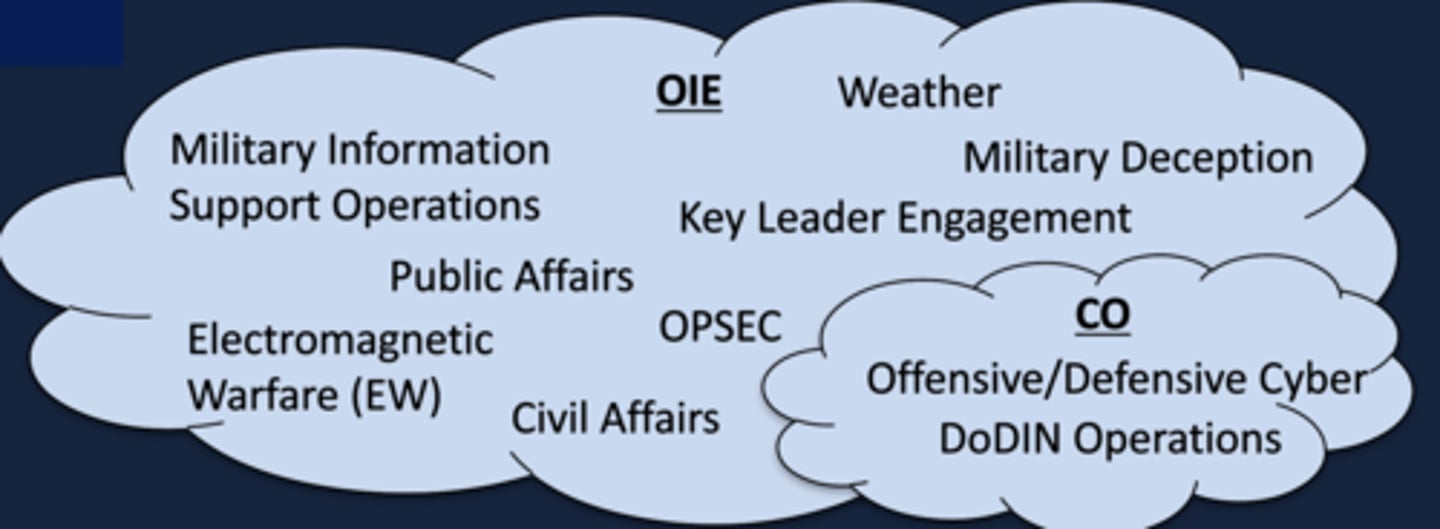
What are the three primary DoD cyberspace domains? *FS
1. NIPR
2. SIPR
3. JWICS
What does NIPR stand for?
Non-Classified Internet Protocol Router Network
What does the NIPR domain encompass?
Unclassified, up to CUI, used for daily operations by most DoD members.
What does SIPR stand for?
Secret Internet Protocol Router Network
What does the SIPR domain encompass?
Classified, up to SECRET//NOFORN, used for OCO/DCO and DoDIN Operations (threat response).
What does JWICS stand for?
Joint Worldwide Intelligence Communications System
What does the JWICS domain encompass?
Classified, up to TOP SECRET, all SCI categories, used by the Intelligence Community (IC) and for OCO/DCO.
What are the four threats to DoD Cyberspace? *FS
1. State Actors
2. Non-State Actors
3. Individuals
4. Accidents and Natural Hazards
What does APT stand for?
Advanced Persistent Threat
An APT is an example of what type of threat to DoD Cyberspace?
A state actor.
What are some examples of non-state actor threats?
1. Criminal Organizations
2. Violent Extremist Organizations (VEO)
A script kiddie is an example of what type of threat to DoD Cyberspace?
Individual
A hurricane is an example of what type of threat to DoD Cyberspace?
Accidents and Natural Hazards
What are the four challenges to DoD cyberspace? *FS
1. Geography
2. Technology
3. Private Industry and Public Infrastructure
4. Globalization
Why is geography a challenge to DoD cyberspace?
All of cyberspace is owned by someone, so there is no stateless maneuver space.
Why is technology a challenge to DoD cyberspace?
1. Using a capability may reveal how it functions.
2. There is no/low cost for replication of software-based capabilities.
3. Incomplete understanding and integration of new technologies (e.g., AI, IoT).
Why is private industry and public infrastructure a challenge to DoD cyberspace?
1. DoD relies on commercial infrastructure, such as ISPs and cloud computing services, for mission critical function.
2. DoD and Defense Industrial Base (DIB) rely on fragile global supply chains.
Why is globalization a challenge to DoD cyberspace?
The DoD procures many mission-essential IT products and services from foreign vendors, leading to both supply chain and operational security risks.
E.g., underseas fiber optic cables, foreign satellites.
What is the definition of mission assurance?
A process to protect or ensure the continued function and resilience of capabilities and assets, including personnel, equipment, facilities, networks, information and information systems, infrastructure, and supply chains, critical to the execution of DOD mission-essential functions in any operation environment or condition. (DODD 3020.40 – Mission Assurance)
What is the overall purpose/goal of MA?
The knowledge that the capability will occur when needed (on America's worst day).
It focuses on the protection, continued function, and resilience of capabilities and assets critical to supporting MEFs.
What is the first pillar of MA? *FS
Identify and prioritize critical missions, capabilities, functions, systems, and supporting assets.
What is the second pillar of MA? *FS
Develop and implement a comprehensive and integrated MA risk-management construct.
What is the third pillar of MA? *FS
Use risk-informed decision making to optimize risk reduction solutions.
What is the fourth pillar of MA? *FS
Partner with non-DoD entities, as appropriate and as permitted by law, to reduce risk.
Which pillar of MA identifies, characterizes, and prioritizes the assets and capabilities that are critical to performing MEFs, including mission-critical human, physical, information, supply chain, and supporting assets and capabilities?
Pillar 1
Which pillar of MA examines the inter-connectedness of DoD's critical assets and external dependencies?
Pillar 2
Which pillar of MA enables decision-makers to manage risk more effectively and efficiently?
Pillar 2
Which pillar of MA uses red-teaming, war-gaming, and alternative analysis to facilitate and inform this process and share assessment results, so that decision-makers can identify and address trends and strategic issues?
Pillar 2
Which pillar of MA leverages existing or establishes new integrative processes and advocacy forums to implement the mission assurance framework and provide inputs to the DoD’s existing planning, budgeting, requirements, and acquisition processes?
Pillar 3
Which pillar of MA focuses on protecting the system using planning, budgeting, and policy?
Pillar 3
Which pillar of MA focuses on nurturing relationships and enhancing information sharing with key external stakeholders at all levels of responsibility?
Pillar 4
Which pillar of MA addresses the fact that DoD MEF execution depends on public and private assets that the DoD does not own?
Pillar 4
What are the four processes in MA?
1. Identification
2. Assessments
3. Risk Management
4. Monitoring & Reporting
What does the identification process encompass in MA?
Determine what assets are important and why.
What does the assessments process encompass in MA?
Determine risk to identified assets through assessments.
What does the risk management process encompass in MA?
Develop plans to manage risk.
What does the monitoring & reporting process encompass in MA?
Monitor and report changes in risks and operational status.