Anatomy and physiology chapter 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
Carbohydrates function
main source of energy (short term)
2
New cards
protein fuction
Some proteins control the rate of reactions, regulate cell processes, form important structures, transport various substances, and help fight disease.
3
New cards
Lipids fuction
source of long term energy
4
New cards
nucleic acid function
store and transmit genetic information
5
New cards
What do nerve tissues include?
neurons and glial (neurological) cells
6
New cards
What does pH measure?
acidity of alkalinity of a solution
7
New cards
What do fat cells make up?
Adipose Tissue
8
New cards
What is the power house of the cell?
mitochondria
9
New cards
What forms a smooth covering on the ends of long bones?
Hyaline cartilage
10
New cards
What are vesicles containing potentially dangerous enzymes?
lysosomes
11
New cards
similarities of cardiac and skeletal muscle
-both striated muscle tissue
12
New cards
differences of cardiac and skeletal muscle
* Cardiac muscle never stop working
* cardiac muscle is shorter
* cardiac muscles are single nuclei
* skeletal muscle pull on bones
* skeletal muscles are long and thin
* skeletal muscles have multiple nuclei
* cardiac muscle is shorter
* cardiac muscles are single nuclei
* skeletal muscle pull on bones
* skeletal muscles are long and thin
* skeletal muscles have multiple nuclei
13
New cards
3 types of muscle tissue
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
14
New cards
3 types of fibers found in connective tissue
collagen fibers, elastic fibers, reticular fibers
15
New cards
functions of connective tissue
physical protection, support and structural framework, binding of structures, storage, transport, immune protection
16
New cards
Which specific epithelial tissue makes up the esophagus?
Simple columnar- single layer long cells.
17
New cards
What do enzymes do?
speed up chemical reactions
18
New cards
Where are ribosomes located?
cytoplasm and rough ER
19
New cards
The monomers of nulceic acids
nucleotides
20
New cards
monomers of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
21
New cards
monomers of lipids
glycerol and fatty acids
22
New cards
monomers of proteins
amino acids
23
New cards
Nitrogenous bases in DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine (A-T, C-G)
24
New cards
2 types of nucleic acids
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA)
25
New cards
Elements in Carbohydrates and Lipids
C, H, O (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen)
26
New cards
elements in proteins
C, H, O, N (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen)
27
New cards
elements in nucleic acids
C H O N P (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus)
28
New cards
What types of bonds do water molecules form with each other?
Hydrogen bonds
29
New cards
What is a triglyceride?
a lipid made of one glycerol and three fatty acids
30
New cards
Histology
study of tissues
31
New cards
bone
osseous
32
New cards
Cartilage
a connective tissue that provides support and flexibility to parts of the skeleton
33
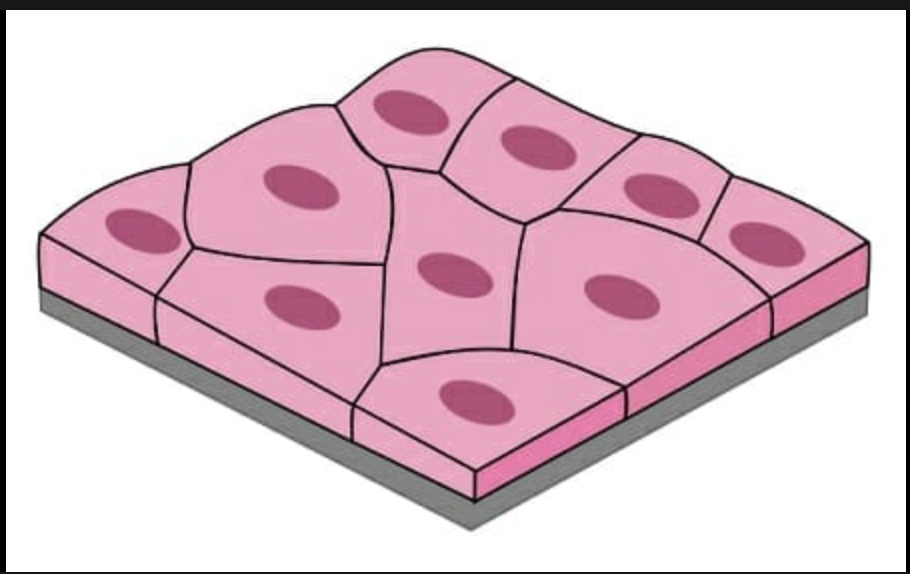
New cards
simple squamous
single layer of flat cells
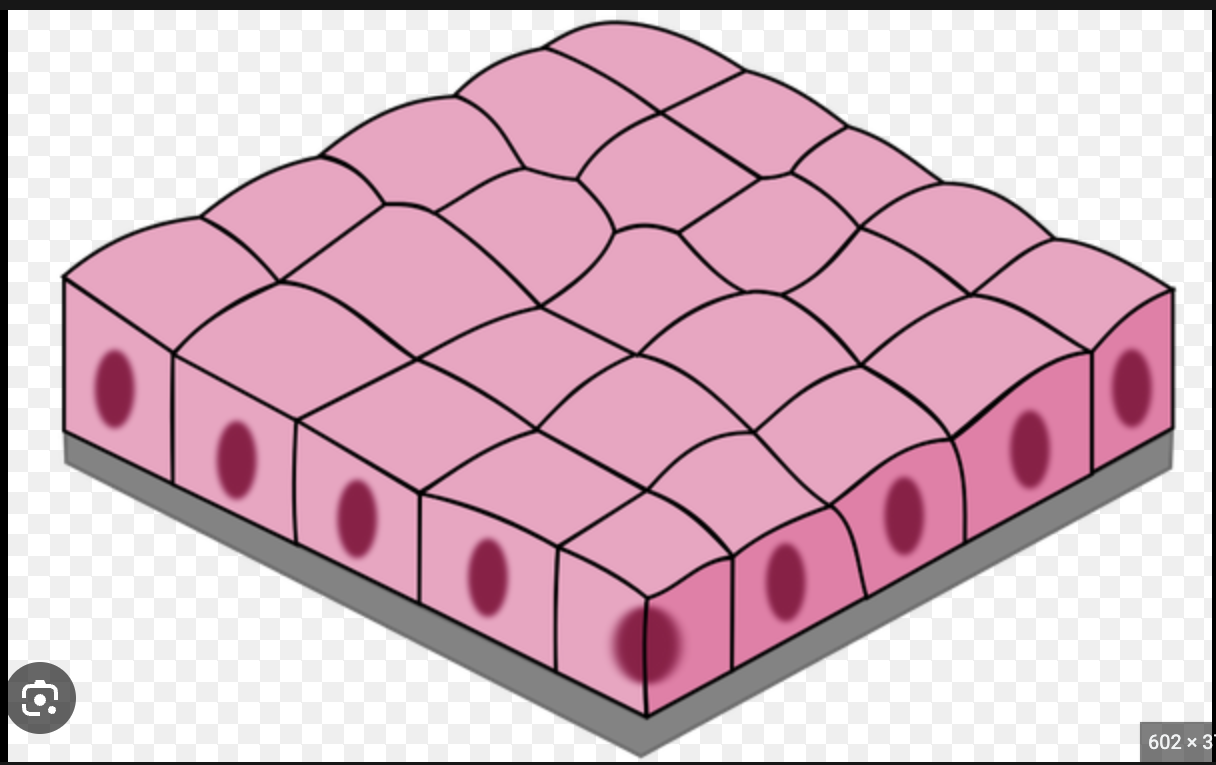
34
New cards
simple cuboidal
single layer of cube shaped cells
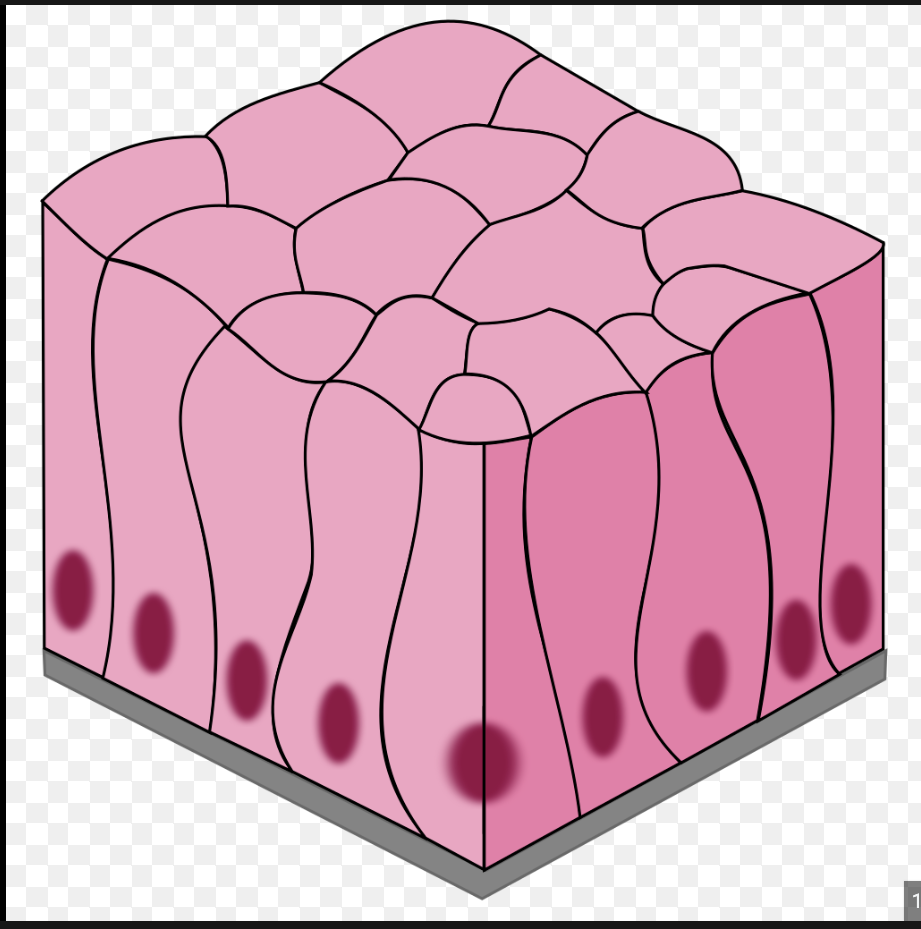
35
New cards
simple columnar
Single layer of tall cells
36
New cards
Stratidied squamous
Multi-layered, squamous cells
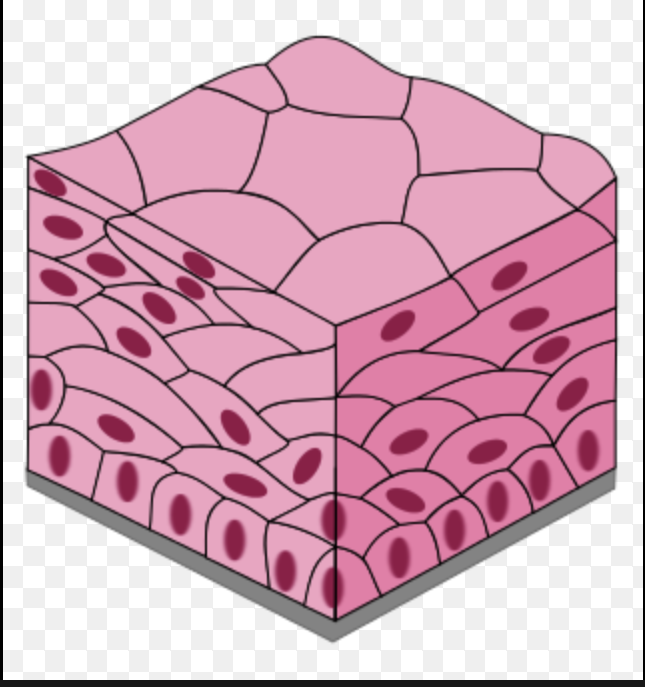
37
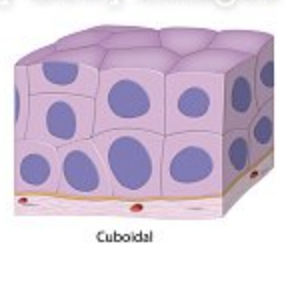
New cards
stratified cuboidal
Two layers of cuboidal cells
38
New cards
stratified columnar
Surface cells are columnar, cells underneath vary in size and shape.
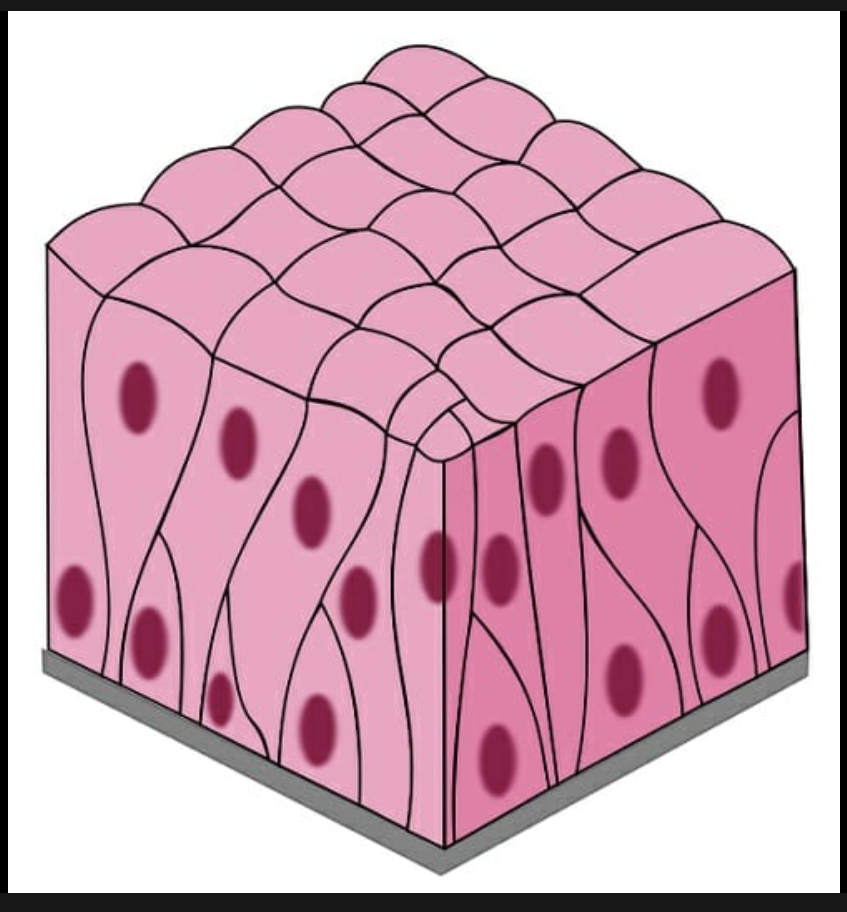
39
New cards
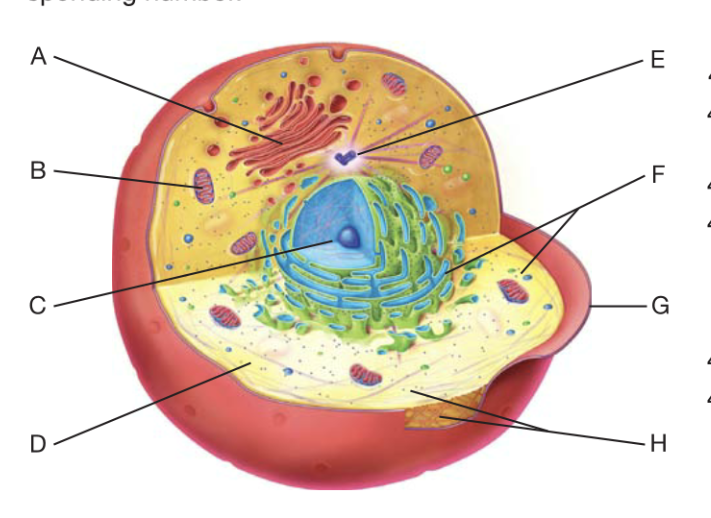
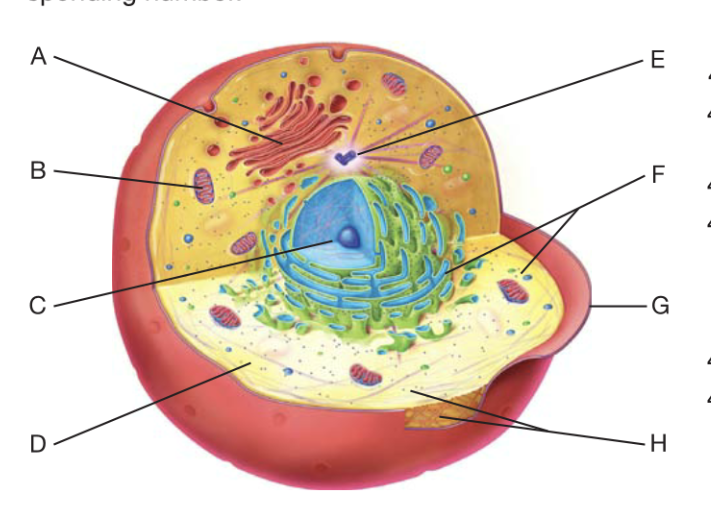
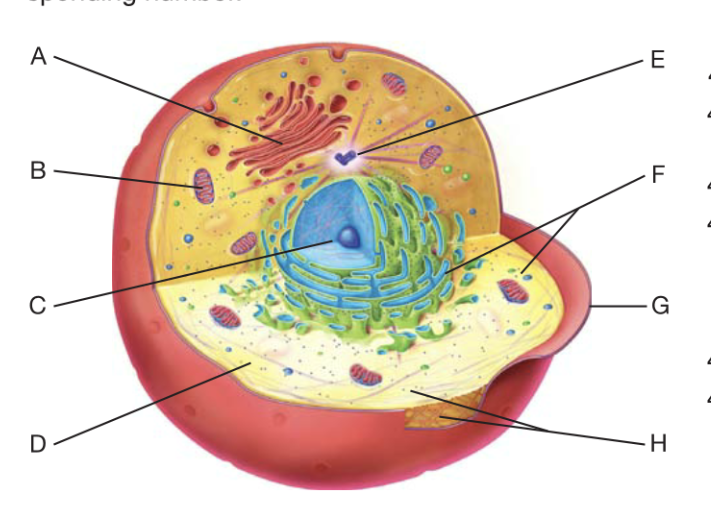
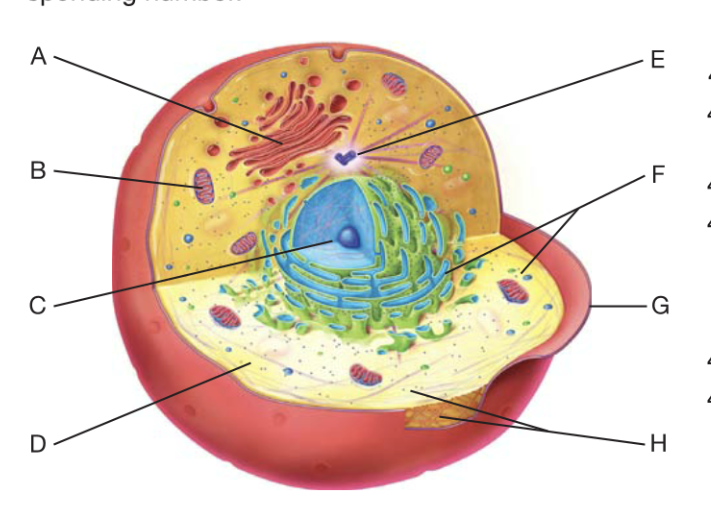
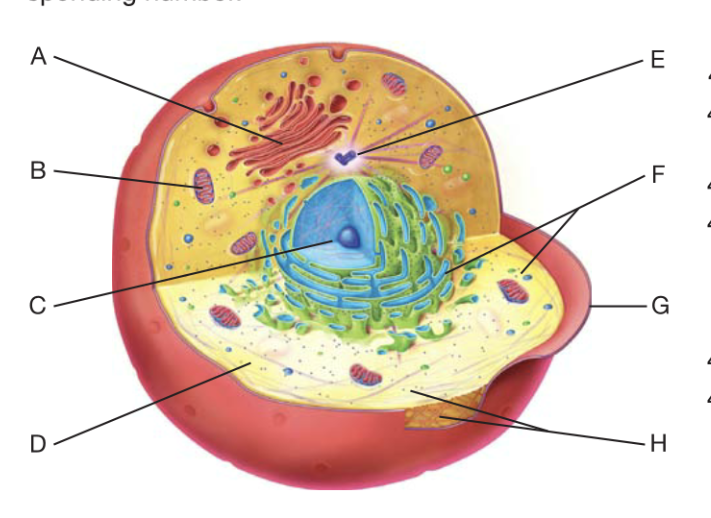
What is A?
golgi apperactus
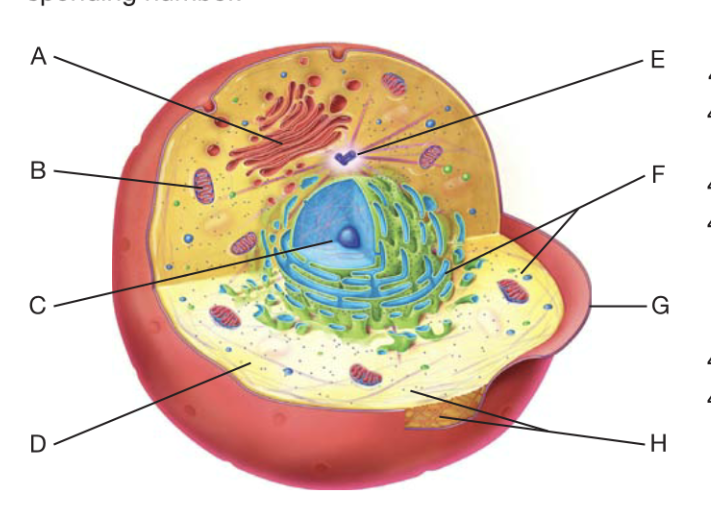
40
New cards
What is B?
Mitochondrion
41
New cards
What is C?
Nucleaus
42
New cards
What is D?
cytoplasm
43
New cards
What is F?
Ribosome
44
New cards
What is G?
plasma membrane
45
New cards
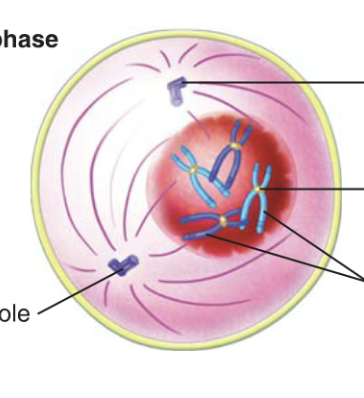
Prophase
\
46
New cards
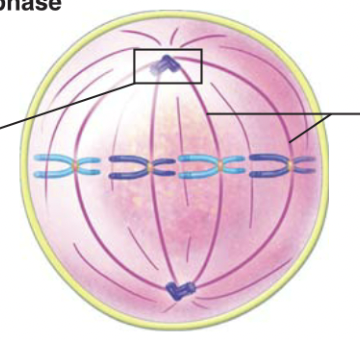
Metaphase
\
47
New cards
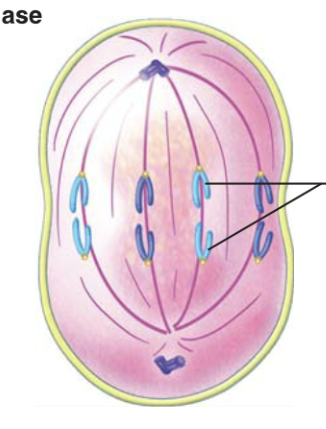
anaphase
\
48
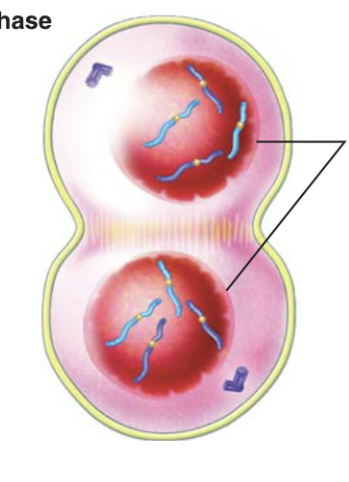
New cards
Telephase
\