Lecture 8: Aggression
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
definitions of aggression
-many different ways of defining aggression
-researchers struggle to agree on one definition
-makes it harder to define and compare between studies
Bandura (aggression definition)
-behaviour resulting in personal injury or destruction of property
Scherer (aggression definition)
-behaviour intended to harm another of the same species
Baron (aggression definition)
-behaviour directed towards the goal of harming or injuring another living being who is motivated to avoid such treatment
Baron & Byrne (aggression definition)
-intentional infliction of harm on others
Anderson & Bushman (aggression definition)
-behaviour directed towards another carried out with the proximate intent to cause harm
Baron & Branscombe (aggression definition)
-behaviour that is designed to harm others in some way
-broad definition combining other definitions
-but researchers can have different ideas of what aggression is whilst all falling under this definition
studying aggression
-measure aggression differently:
analogues of behaviour
signals of intention
ratings
observation
analogues of behaviour (studying aggression)
-substitutes for physical aggression
-needed to pass ethical approval as cannot have real aggression in the lab
-e.g., bobo dolls or pressing a button to deliver a fake shock
evaluation of analogues of behaviour (studying aggression)
-is this generalisable to real life settings?
-hitting a doll is not the same aggression as hitting a person
signals of intention (studying aggression)
-expression of willingness to behave aggressively
-ask how willing they would be to behave aggressively
evaluation of signals of intention (studying aggression)
-intention does not always translate to behaviour
ratings (studying aggression)
-self-report
-reports by others
-observation
evaluation of ratings (studying aggression)
-social desirability bias → aggression is not a desired social behaviour so people are more likely to lie
-observation → researcher may interpret behaviour in line with prior expectations/hypotheses
indirect (studying aggression)
-non-physical aggression, relational/psychological aggression
-is not objective as cannot see it
-measured more by rating scales or self report
evaluation of indirect (studying aggression)
-may inflate the prevalence of aggression if comparing to direct/physical measures of aggression
theoretical approaches
biological
-psychodynamic
-evolutionary
biosocial
-frustration and aggression
-excitation transfer
social
-social learning theory
psychodynamic approach (biological approach)
-have an unconscious drive known as ‘thanatos death instinct’
-over time this instinct builds up creating pressure which we cannot control and makes us do something aggressive
-we deal with this tension by redirecting it to other activities → catharsis
evolutionary approach (biological approach)
-aggressive behaviour is used to ensure genetic survival
-aggression must be linked to living long enough to procreate → can be seen comparing against animal behaviour
males fighting other males for mating rights, hunting for food, protecting territory or resources
mothers behave aggressively to protect their offspring
-among humans → obtain social and economic advantage to improve the survival rate other their children
evaluation of biological approaches
-unknowable and immeasurable → instinct can’t be measured or studied
-evolutionary tendencies develop over thousands of years - difficult to measure in the lab
-humans behave aggressively outside of situations when we need to defend ourselves/children
-doesn’t explain aggression towards our own relatives
-not informative for prevention or intervention → no modifiable factors for identifying ways to tackle aggression in real life
frustration and aggression hypothesis (biosocial approach)
-based on catharsis approach
-frustration is a precursor to aggression
frustration → individual is prevented from achieving a goal by some external factor
-aggression is a cathartic release of the build-up of frustration
-cannot always challenge the direct source of aggression
sublimation (frustration and aggression hypothesis)
-using aggression in acceptable activities
displacement (frustration and aggression hypothesis)
-directing our aggression outwards onto something or someone else
excitation transfer (biosocial approach)
-experience physiological arousal in different contexts
-arousal in one context can carry over to other situations and may increase likelihood of aggressive behaviour
-requires three conditions:
first stimuli produces arousal/excitation
second stimulus occurs before the complete decay of arousal from the first stimulus
there is misattribution of excitation to the second stimulus
strengths of biosocial approaches
-provides useful opportunities for interventions to target
-Marcus-Newhall → meta analysis, found that participants who were provoked but unable to retaliate directly against the source of their frustration were significantly more likely to aggress against an innocent party than people who were not provoked → supports the idea of displacement
limitations of biosocial approaches
-frustration/being aroused does not always lead to aggression → can be aggressive without these → too simplistic
-some types of arousal can also make us feel good → this reduces aggression
-Bushman → participants who vented their anger by hitting a punching bag became more angry and aggressive rather than less so → challenges the idea of displacement
social learning theory (social approaches)
-aggression can be learnt:
directly through operant conditioning
indirectly through observational learning and vicarious reinforcement
-if aggressive behaviour is rewarded, learnt to be socially acceptable
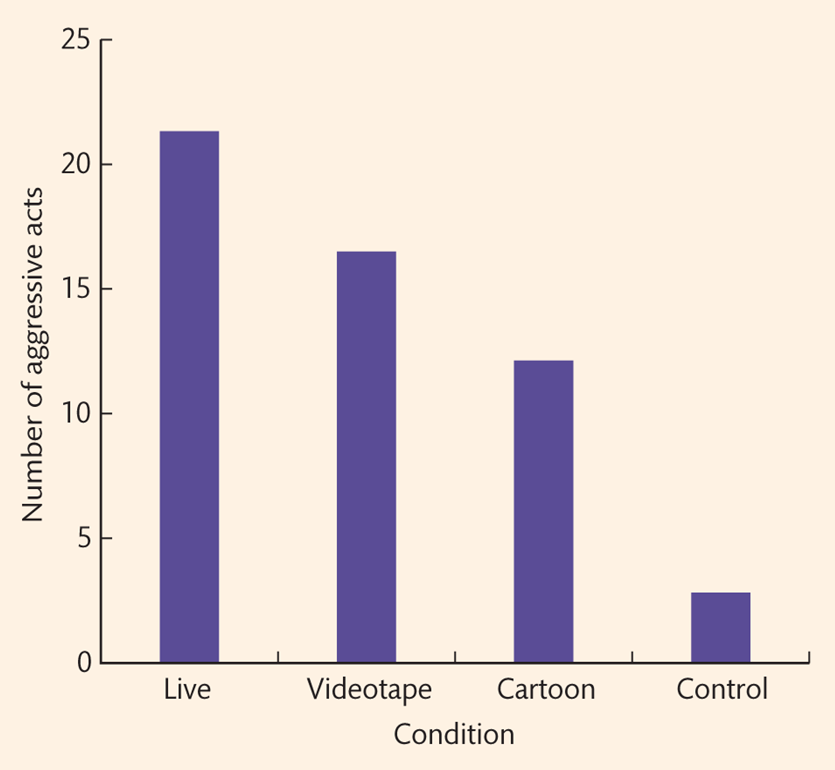
Bandura & Walters (social learning theory)
-nursery school children observe adult attack a ‘bobo doll’ when upset:
in person
videotaped
cartoon
control - saw nothing
-found children exposed to an adult displaying aggressive behaviour demonstrated increased number of aggressive behaviours when alone
-strongest effect for live observation
strengths of social learning theory
-accounts for how children learn from other people around them and the media
-empirical support from many studies
limitations of social learning theory
-many studies conducted in lab settings and this increased the problem of demand characteristics and external validity
-aggressive role models does not equal aggressive behaviour
-does not consider individual differences
-effect of violent media on aggressive behaviour not consistently replicated
-consistent finding in the bobo doll experiments is that boys show more aggression than girls regardless of the experimental condition -> so Bandura underestimated the importance of biological factors
gender (personal factors)
-men engage in aggressive behaviour more frequently than women
-individual variation in testosterone levels across genders
testosterone only has a weak positive relationship with aggression
-learn gender appropriate behaviours:
physical aggression socially unacceptable for women
indirect forms of aggression may be more socially acceptable for women
-predict that men and women would differ in the type but not the amount of aggression displayed
Denson (gender - personal factors)
-literature review of aggressive behaviour in women
-women are more likely to engage in indirect forms of aggressive behaviours
-women are less physically aggressive compared to men in lab studies
-gender differences in aggression may be due to socialisation
attachment (personal factors)
-meta-analysis examined the relationship between attachment security and offending
-offenders were less secure in their attachments than controls
-insecure attachment was strongly associated with all types of criminality
-did not include juvenile and female offenders
-measures of attachment differed across studies
alcohol (situational factors)
-alcohol present in 68% of incidents of physical aggression
-meta analysis showed that alcohol consumption increased aggressive behaviour in men in experimental studies
direct effects of alcohol (situational factors)
-compromises cortical control and increases activity in more primitive brain areas
-impairment in cognitive function → decision making → disinhibition hypothesis
-physiological arousal → in line with excitation transfer model
indirect effects of alcohol (situational factors)
placebo effects → expectations of receiving alcohol placebo increased aggressive behaviour
priming effect → activating thoughts of alcohol increased aggressive behaviour
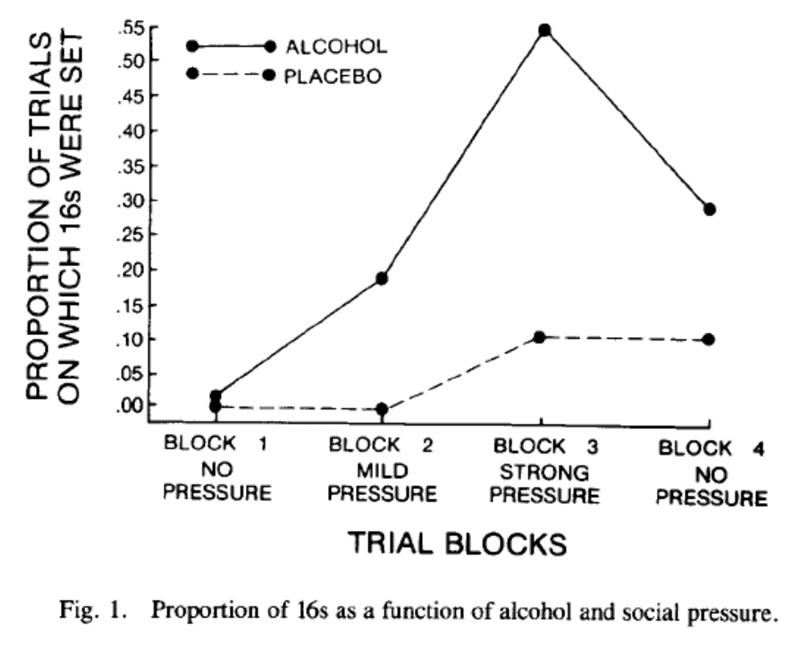
Taylor & Sears (alcohol - situational factors)
-alcohol vs placebo condition
-competitive task with another ppt involving reaction time
-loser received electric shock from opponent each time
-shock level ‘supposedly ‘ set by ppt delivering the shock → was actually kept constant by experimenter
-confederate applied social pressure to the ppt, sometimes encouraging them to increase the shock level
-those in the alcohol group were more susceptible to this pressure to commit an aggressive act
crowding (situational factors)
-population density linked to crime rates
increases stress, irritation, frustration and physiological arousal
-anonymity in crowds:
disinhibition
deindividuation
disinhibition (crowding - situational factors)
-when the usual social forces that restrain us from acting anti-socially are reduced in some way
deindividuation (crowding - situational factors)
-feeling unidentifiable among many others means we think we are unlikely to face consequences for aggressive acts
-football hooliganism, online bullying
disadvantaged groups (societal factors)
-may engage in aggression if they believe:
they are unjustly disadvantaged
cannot improve their disadvantaged position
-rates of homicide and non-lethal violence is higher among young, urban, poor and ethnic minority males → likely due to mix of social and ecological factors
relative deprivation (disadvantaged groups - societal factors)
-discontent coupled with feeling that chances of improving conditions through legitimate means is minimal
-vandalism, assault, violent protests
violent media (societal influences)
-easy access to sanitised versions of aggression/violence in the media has been argued to desensitise viewers
-aggressors often depicted as unpunished heroes
-SLT argues that viewers will copy such reinforced acts
-catharsis hypothesis argues it will release tension and reduce aggression
evidence to support violent media and aggression (societal influences)
-viewing a violent film increases aggression scores compared to watching a non-violent film
-meta analysis suggests that violent video games increase aggression
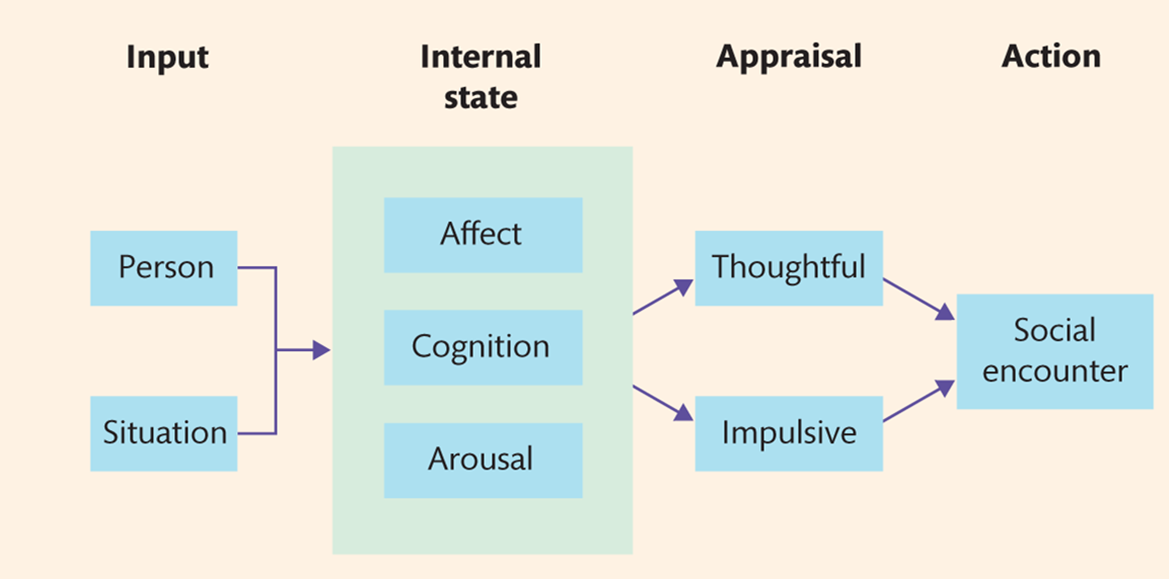
general aggression model (GAM)
-interplay between personal and situational variables
-influences 3 internal states:
cognition
affect
arousal
-affecting our appraisal/decision processes → which influence aggressive outcomes
-applied in many contexts
-used to inform interventions to reduce aggression and violence
GAM process
person and situation factors increase or decrease the likelihood of aggression through their influence on internal state variables
person/situation variables can affect our moods/emotions, aggressive thoughts and arousal which affects our appraisals → alters the likelihood of aggression
internal states influence the appraisal of the situation
the behavioural script that was activated during the appraisal is then enacted → leading to the social encounter
explaining temperature effects (GAM)
-measured hostile affect, hostile cognition, perceived arousal and physiological arousal
-played video games while room temp was controlled
increasing temperature → increased hostile affect, hostile cognition and physiological arousal
-hot temperatures increase aggressive tendencies by 3 separate routes (internal states)
-excitation transfer process may then increase the likelihood of biased appraisals of ambiguous social events → increased likelihood of aggression
institutions
-places with strict rules that give little choice to members of that institution
institutional aggression
-aggressive behaviours adopted by members of an institution
examples of institutional aggression
-25% of prisoners are victimised by violence each year
-4-5% of prisoners experience sexual violence
-1-2% are raped
-30% of all students annually experience aggression at school
dispositional factors (causes of institutionalised aggression)
-personalities of the institution’s members
-importation model → aggressive features of the institution members that they bring into the institution
-e.g., gender, personality, past experience
situational factors (causes of institutionalised aggression)
-situation in which the members find themselves
-deprivation model → features of the institution causes aggression
-e.g., crowding, loss of freedom