unit 2 flashcards: blood
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
second class gaining momentum,,.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
why is blood classified as connective tissue
arise from mesenchyme, made of cells+extracellular matrix
ave pH of blood? ave vol of blood?
ave pH: 7.4
ave vol blood: 5L
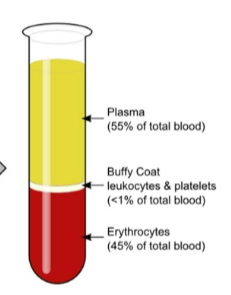
what are the percentages of plasma, erythrocytes, and leukocytes and platelets in the blood
plasma: 55%
erythrocytes: 45%
buffy coat - leukocytes & platelets: <1%
what are the fxns of blood
transportation - O2 → cells, CO2 → lungs, nutrients GI → cells, waste from cells → kidn, hormones
regulation - body temp, body pH, fluid balance
protection - wbc- disease, blood proteins - antibodies, prevents loss - blood clots
name plasma proteins (in order of abundance)
albumin, globulins, fibrinogens, regulatory proteins
albumin
most abundant at ~58%, prod by liver
acts as carrier to shuttle certain molecules thru circulation, such as bilirubin, hormones, metals, vitamins; important blood buffer (resists changes in pH) major blood protein contrib to plasma osmotic pressure (pressure that helps keep water in bloodstream)
globulins
alpha + beta-globulins primarily transport hydrophobic molecules and hormones, some metals, and ions (Cu)
gamma-globulins (immunoglobs/antibodies) involved in defense - prod by type of immune cells
fibrinogens
prod by liver, forms fibrin threads that form blood clot
regulatory proteins
includes enzymes + hormones
what is erythropoiesis and what triggers it?
it is erythrocyte (rbc) prod, takes 3-5 days
that is triggered by hormones (erythropoietin); depends on adequate supplies of Fe, folic acid, amono acids, certain B vits - B12 needed for complete maturation of RBC
what organ is in charge of monitoring blood and prod hormone? what organ does this hormone target?
kidneys monitor blood and produce blood-making hormone, erythropoietin (EPO)
erythropoietin targets the red bone marrow
patients w advanced kidney disease often have anemia. explain this connection
their kidneys don’t prod enough erythropoietin (EPO), leading to fewer rbc
what is a hematocrit? give normal vals
percentage of total erythrocyte volume in blood (“blood fraction”)
males: 47% +_ 5%
females: 42%
life span of erythrocytes? what happens when they age? what organ known as erythrocytes “graveyard”
life span 100-120 days
lose flexibility, become inc rigid + fragile, contained hemoglobin begins to degenerate
spleen bc small circ channels. try to squeeze them rupture
what is hemoglobin? how many O2 can each Fe and each hemglob molecule carry?
transported by rbc, protein that makes them red
binds easily and reversibly w oxy, transports oxy and co2
each iron holds 1 O2, each hemglob holds 4 Fe
what is hemoglobin made of?
heme: pigment, source of iron in body
globin: (responsib for structure) 4 polypeptide chains, mother cells in bone marrow, 2 α 2 β; any abnorms in chains can alter phys character of hemglob
when erythro destroyed, body processes three components of hemoglobin. list them
globin: amino acids, heme: iron + porphyrin → bilirubin
explain what ultimately happens to globin (non-protein)
breaks into amino acid, can be reused to prod other proteins
explain what ultimately happens to heme (protein) (Fe, organic lattice)
iron: removed and recycled in spleen
porphyrin: converted to bilirubin
what are norm vals of hemglob in humans?
14-20 g/100mL in infants
13-18 g/100mL in adult males
12-16 g/100mL in adult females
what determines whether blood is light or dull red? what do the colors mean?
oxyhemoglobin- oxy binds to iron
deoxyhemoglobin (reduced hemoglobin)- detaches from iron
can hemglob carry only oxy? explain
hemoglobin can carry O2, CO2
know blood types and what they mean in terms of what antibodies (agglutinins) and what agglutinogen (antigen) is present in erythrocytes
RBC A: Anti-B antibodies (agglutinins), A antigen (agglutinogen)
RBC B: anti-A antibodies, B antigen
RBC AB: no antibodies, A and B antigens
RBC O: anti-A and B antibodies, no antigens
RBC Rh (D): if Rh protein present, blood type +; if absent, Rh -
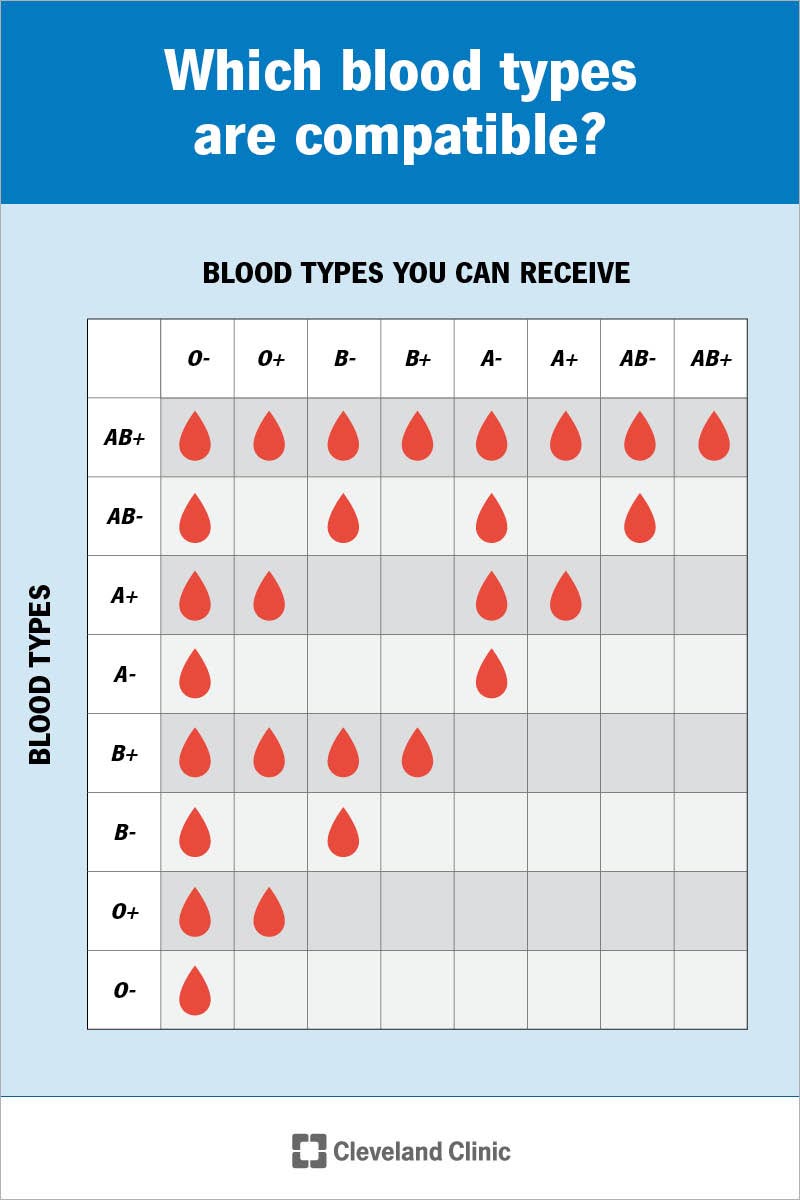
blood type donation
O can donate to anyone, can only receive O
A can donate to A and AB, but only receive A and O
B can donate to B and AB, but receive from B and O
AB can donate to AB, but can receive from anyone
pos Rh can donate to Rh+, can receive both Rh+ and -
neg Rh can donate to Rh+ and -, only receive Rh-
difference between antibodies and antigens
antigens are markers on the surface of the rbc that ID them to immune syst
antibodies are proteins prod by immune syst to recognize and attack foreign substances
which type of blood is the universal donor/recipient in the USA? (ABO and Rh)
universal donor: O-
universal recipient: AB+
which blood cells are the only ones considered cells and which ones are not? explain why
white blood cells are the only ones considered cells because they have a nucleus and usual organelles
classify leukocytes into granulocytes and agranulocytes and why they are classified as such
granulocytes: basophils, neutrophils, eosinophils - they have membrane-bound cytoplasmic granules
agranulocytes: lymphocytes, monocytes - they lack membrane-bound cytoplasmic granules
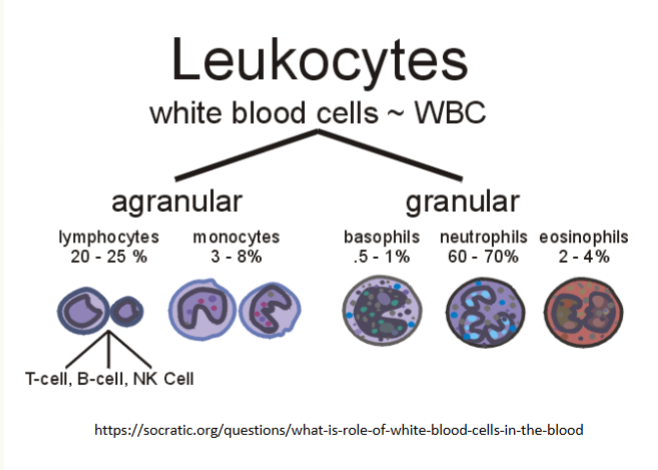
which white blood cells are the most common? least common?
most common: neutrophils (50-70%)
least common: basophils (0.5 - 1%)
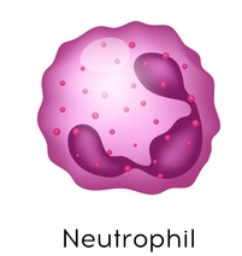
granulocyte: desc neutrophils and their fxn
twice as large as rbc; stain pale lilac w v fine granules that are hard to see
granules lilac bc “neutro=neutral, phils=loving.” their granules take up both basic (blue) and acidic (red) dyes
nuclei consisting of 3-6 lobes; active in phagocytes (eat bacteria/dead cells); respond quickly to tissue destruction by bacteria or fungus; they are body’s bacterial slayers; numbers inc during acute bacterial infections
granules - lysoszyme: kill bacteria; oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide; defensins - poke holes
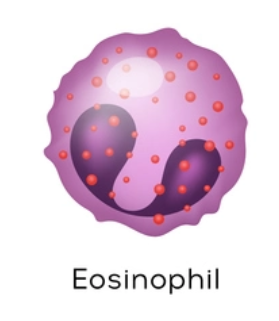
granulocyte: desc eosinophils and their fxn
usually found in tissues besides blood/bone marrow, place w most is GI
~ same size as neutrophils; deep red w 2 lobes, large granules stain red
lysosome-like but lacking enzymes specifically for digesting bacteria; parasitic worms - release enzymes from cytoplasmic granules onto parasite’s surface, digesting it away
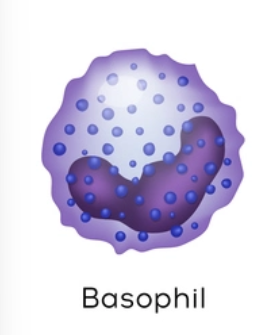
granulocytes: desc basophils and their fxns
large histamine-containing granules; similar fxn to mast cells - bind to IgE (immunoglobulin), causes cells to release histamine. release of histamine intensifies inflammatory rxns
affinity for basic dyes so they stain purplish black (baso=basic); deep purple nucleus w U or S shape and 2/3 lobes

agranulocytes: desc lymphocytes and their fxns
small, round w large, round, dark nucleus
B Lymphocytes - attack bacteria, viruses, toxins; plasma cells→antibodies (Ig=immunoglobin); memory cells
T cells/lymphocytes - manage + direct immune response; some directly attack foreign cells + virus-infected cells
NKC - natural killer cells; attack abnorm + infected cells
recirculate - blood→interstitial space→lymphatic fluid→blood

agranulocytes: desc monocytes and their fxns
have abundant pale-blue cytoplasm + a darkly staining purple nucleus, which is distinctively U/kidney shaped; take longer to get there but arrive in larger nums; destroy more microbes; migrate from blood into tissues where they enlarge + become macrophages (phagocytic)
what molecules enhance the prod of leukocytes?
messengers
interleukins: numbered (eg IL-3, IL-5)
colony-stimulating factors (CSFs): named for the leukocyte pop they stim (granulocyte-CSF (G-CSF) stims prod of granulocytes)
what is leukocytosis and what is its significance?
it is a high white blood cell count: 11,000
usually a sign of the body’s immune system being activated, often due to infection or inflammation
what are platelets?
essential for clotting process that occurs in plasma when bvs rupture/their lining is injured; by sticking to damaged site, platelets form temp plug that helps seal break
since they are anucleate (w/o nucleus), age quickly and degen in ~10 days if not involved in clotting; in meantime, they circulate freely, keeping mobile but inactive
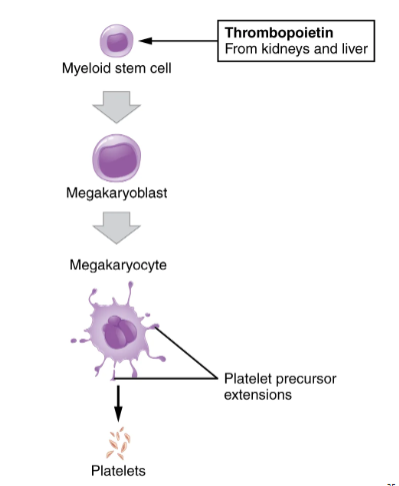
what cells give rise to platelets?
stem cells: megacaryoblasts
precursor cells: megacaryoblasts
platelets are cellular fragments of megakaryocytes
what is hemostasis? what are the steps and their order? what is needed to prod fibrin?
hemo=blood, stasis=halting = sequence of responses that stop bleeding
3 steps: (1) vascular spasms (bv constrict), (2) platelet plug formation, (3) coagulation, blood clotting
fibrinogen (plasma protein), thrombin
vascular spasms
serotonin → leads to blood vessel constriction (vasoconstrict vessel) → 20/30 mins - less blood loss during clotting
platelet plug formation
exposed collagen fibers, platelets attach → platelet activates → release granules content → serotonin (leads back to vasc spasm)
release granules content → ADP → adhesion (sticky) → temp platelet plug
coagulation (clotting)
extrinsic → tissue factor, outside the blood vessel, faster; intrinsic → all clotting factors are in blood, slower
→ prothrombin activator → prothrombin (inactive); → thrombin (inactive) → fibrinogen
thrombin → fibrin → permanent clot
compare and contrast extrinsic and intrinsic hemostatic pathways
extrinsic: tissue factor, outside the blood vessel, faster (external tissue damage)
intrinsic: all clotting factors are in blood, slower (internal tissue damage)
what is serum
when platelets contract, they pull on surrounding fibrin strands, squeezing serum, compacting the clot and drawing the ruptured edges of the bv closer together
(plasma w/o clotting factors)
what is clot retraction
when platelets contract, they pull on surrounding fibrin strands, squeezing serum, compacting the clot and drawing the ruptured edges of the bv closer together; as clot retraction occurring, vessel healing is taking place
what is plasmin? what does it do?
activated plasminogen; breaks down fibrin; body tissues + blood contain substances that activate plasminogen to plasmin