Connective Tissue Types: Histology, Composition, and Functions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the primary components of connective tissue?
Fiber component, ground substance, and cellular component.
What is the role of extracellular matrix in connective tissue?
It is the primary structural component and predominates over the cellular component.
What are the three types of fibers found in connective tissue?
Collagen, reticular fibers, and elastic fibers.
What is the most abundant fiber component in connective tissue?
Collagen.
How is collagen structured?
It is a triple helix of protein chains that forms longer structures called fibrils.
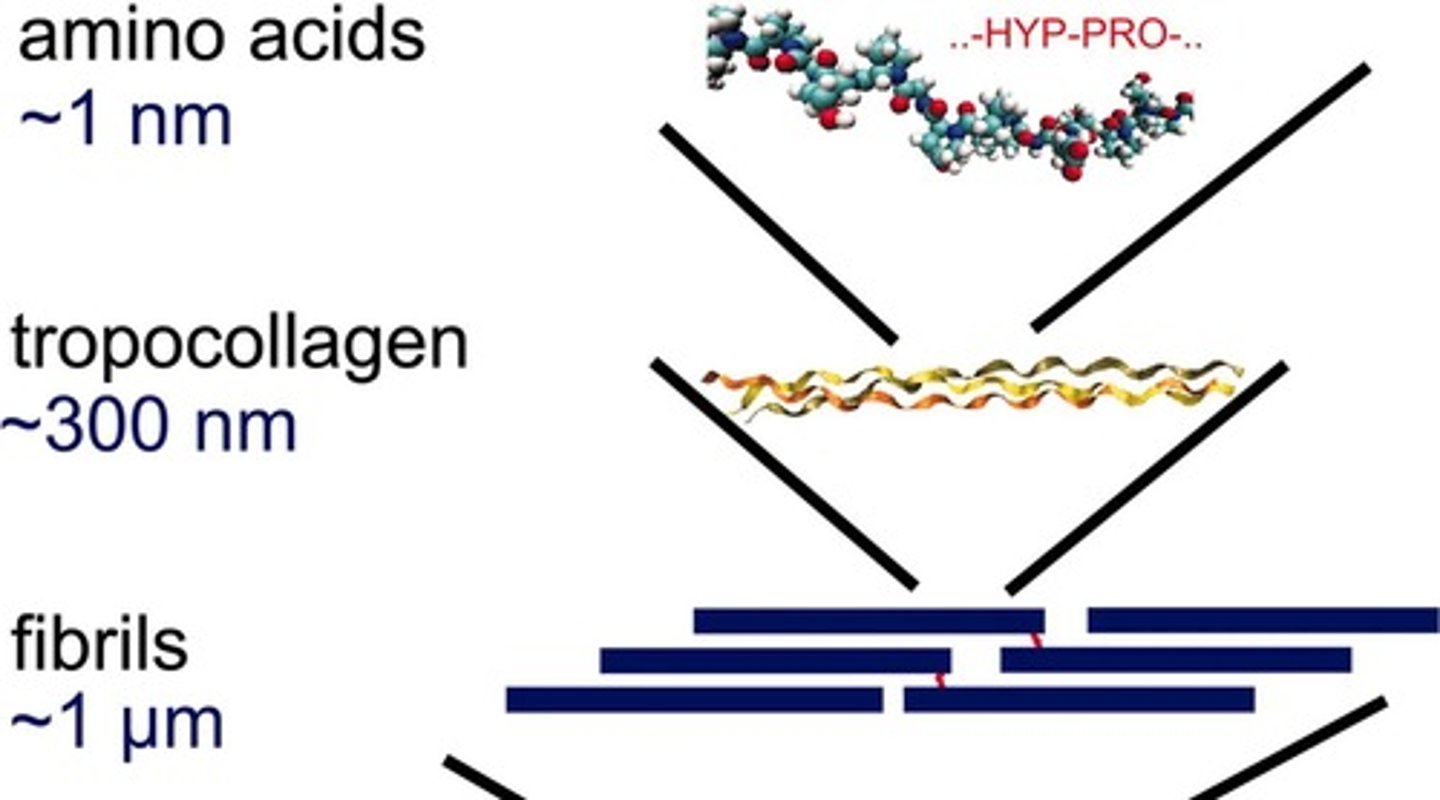
What types of connective tissue are formed by collagen type I?
Tendons and dermis (skin).
What is the unique characteristic of reticulin fibers?
They are delicate and unorganized, acting like a net to hold cells together.
What is the function of elastic fibers in connective tissue?
They provide the ability to stretch.
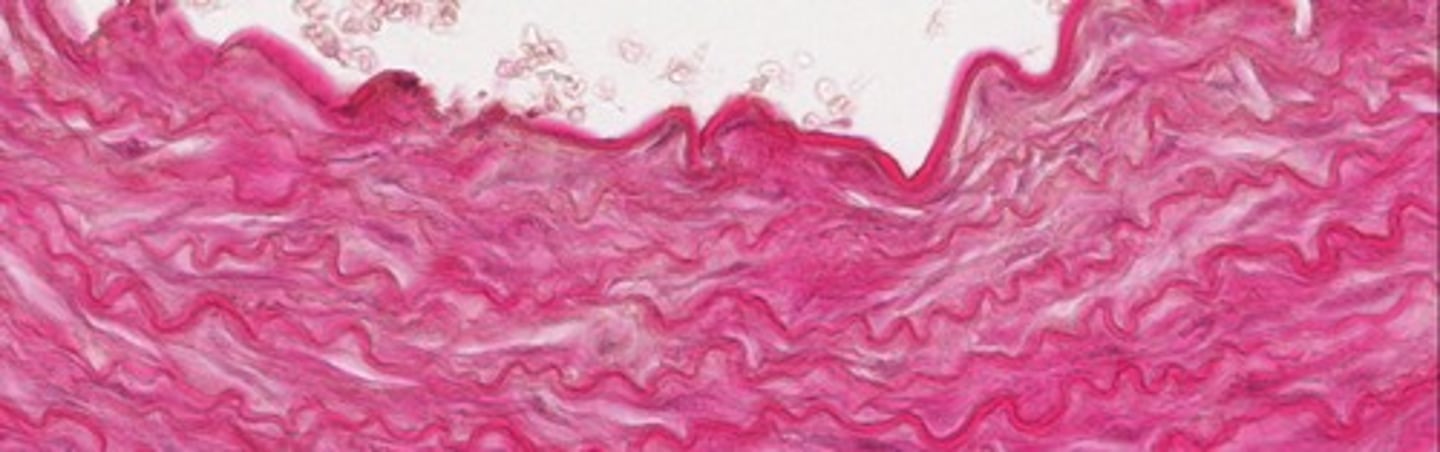
What is ground substance in connective tissue?
It is formed from glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans and acts like a sponge to hold water.
What are the primary cells found in connective tissue?
Fibroblasts, macrophages, leukocytes, and adipose cells.
How do fibroblasts differ from fibrocytes?
Fibroblasts are metabolically active and larger, while fibrocytes are smaller and inactive.
What is the function of macrophages in connective tissue?
They phagocytose debris and act as a surveillance system for the immune system.
What are the two main roles of adipose tissue?
To store energy in the form of lipid and provide insulation.
What are the two types of adipose tissue?
White adipose tissue (white fat) and brown adipose tissue (brown fat).
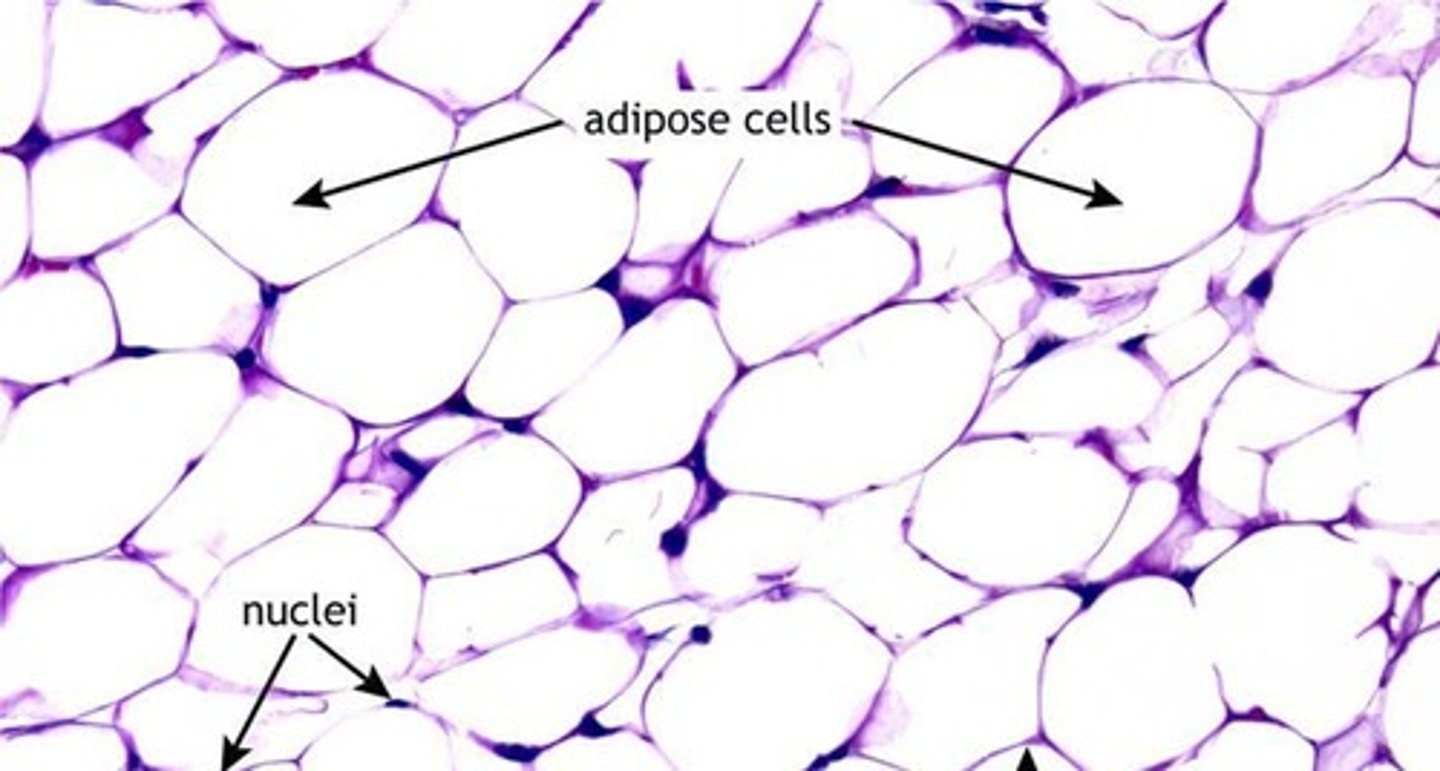
Where is white adipose tissue primarily located?
Subcutaneously (under the skin) and surrounding the viscera.
What is the histological appearance of brown adipose tissue?
It has smaller cytoplasmic vacuoles and eosinophilic cytoplasm.
What are the two forms of connective tissue morphology?
Embryonic connective tissue and fibrous connective tissue.
What is mesenchymal tissue?
A type of embryonic connective tissue with loosely arranged fibers and stellate cells.
What are the characteristics of loose (areolar) connective tissue?
A loose network of type I collagen and reticulin fibers with interspersed ground substance, cells, and vasculature.
What is dense fibrous connective tissue characterized by?
Closely packed collagen fibers with interspersed fibroblasts and fibrocytes.
What are the three major types of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage.
Where is hyaline cartilage primarily found?
On joint surfaces (articular cartilage).
What is the primary characteristic of fibrocartilage?
It has a higher collagen content than hyaline cartilage, making it tougher yet flexible.
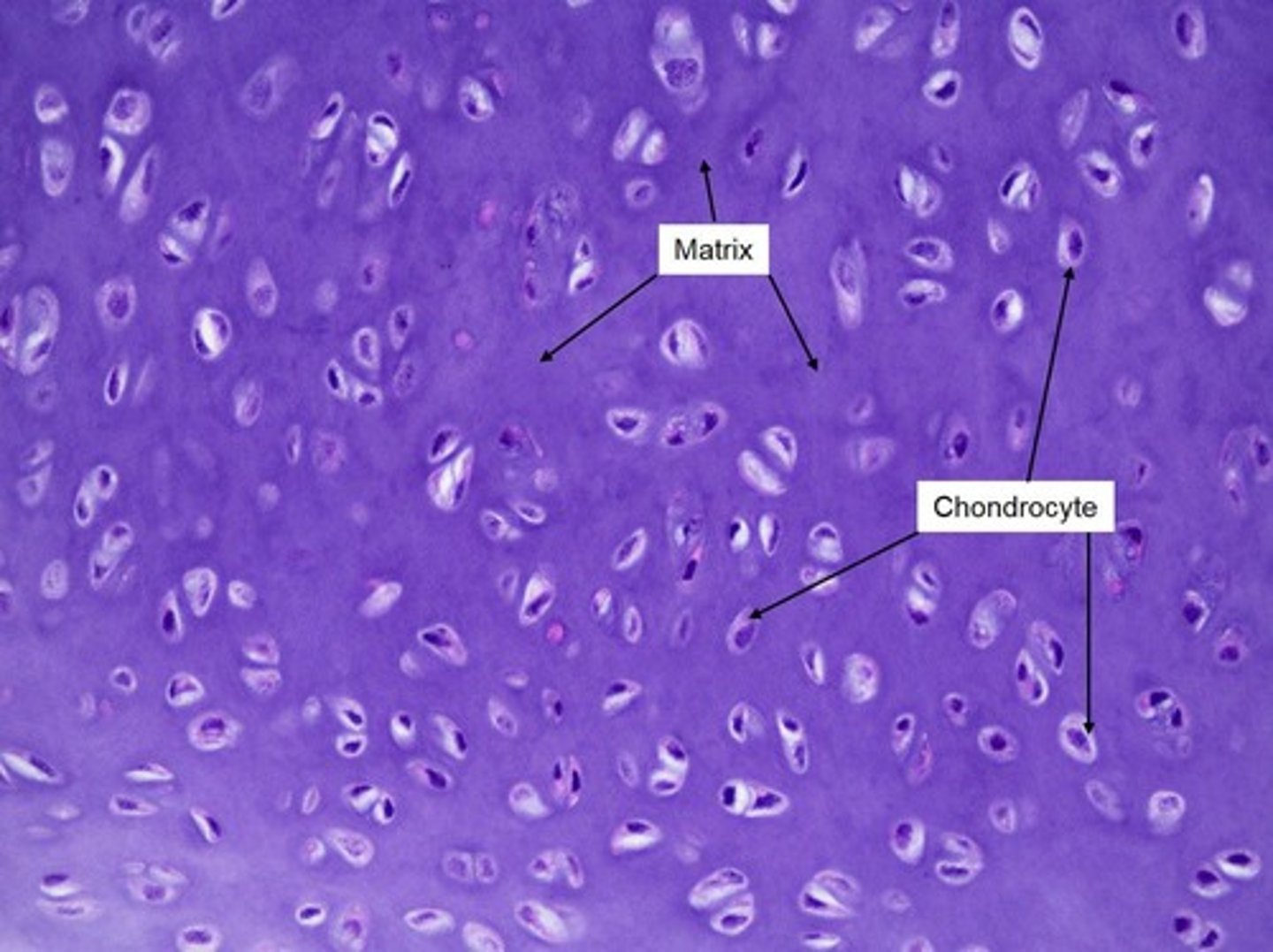
Where is fibrocartilage commonly found?
In intervertebral disks and the symphysis between certain bones.
What is the role of chondrocytes in cartilage?
They are the cells embedded in the extracellular matrix of cartilage.
What distinguishes elastic cartilage from hyaline cartilage?
Elastic cartilage contains elastic fibers, providing greater flexibility.
What is the function of reticular tissue?
It acts as a skeleton for organs with a high parenchymal component, such as the liver and spleen.