Atomic Structure & the Periodic Table Exam Q Corrections
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Gallium was discovered six years after Mendeleev published his periodic
table.
Give two reasons why the discovery of gallium helped Mendeleev’s
periodic table to become accepted.
(gallium) fitted in a gap (Mendeleev had left)
(gallium’s) properties were predicted correctly (by Mendeleev)
allow (gallium’s) pr
Which scientist first suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances?
Bohr
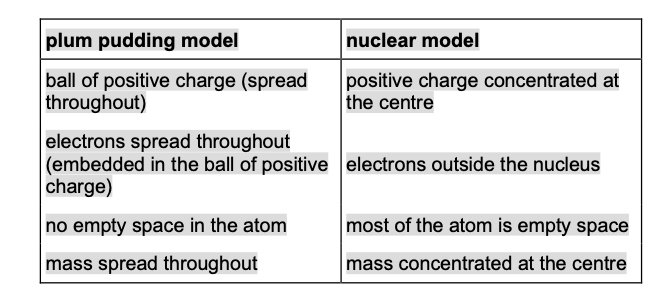
The plum pudding model did not have a nucleus.
Describe three other differences between the nuclear model of the atom
and the plum pudding model.
any three from: (nuclear model)
• mostly empty space
allow the plum pudding model has no
empty space
allow the plum pudding model is solid
• the positive charge is (all) in the nucleus
allow in the plum pudding model the
atom is a ball of positive charge (with
embedded electrons)
do not accept reference to protons
• the mass is concentrated in the nucleus
allow in the plum pudding model the
mass is spread out
do not accept reference to neutrons
• the electrons and the nucleus are separate
allow in the plum pudding model the
electrons are embedded
allow in t
The model of the atom changed as new evidence was discovered.
The plum pudding model suggested that the atom was a ball of positive
charge with electrons embedded in it.
Evidence from the alpha particle scattering experiment led to a change in
the model of the atom from the plum pudding model.
Explain how.
most (alpha) particles passed (straight) through (the gold foil)
(so) the mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus / centre
or
(so) most of the atom is empty space
some (alpha) particles were deflected / reflected
(so) the atom has a (positively) charged nucleus / centre
if not awarded for MP2 allow (so) the
mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus / centre.
The radius of an atom of element X is 1.2 × 10−10 m
The radius of the centre of the atom is 1/10000 the radius of the atom.
Calculate the radius of the centre of an atom of element X.
Give your answer in standard form.
1.2 × 10−10 × 1 × 10−4
1
= 1.2 × 10−14 (m)
an answer of 1.2 × 10−14 (m) scores 2 marks
a correct answer
Chadwick’s experimental work on the atom led to a better understanding of
isotopes.
Explain how his work led to this understanding.
Chadwick provided the evidence to show the existence of neutrons
allow Chadwick discovered neutrons
(this was necessary because) isotopes have the same number of
protons
allow (this was necessary because)
isotopes have the same atomic number
or
element
(this was necessary because) isotopes are atoms of the same
ignore isotopes have the same number
of electrons
but with different numbers of neutrons
allow but with different mass (numbers)
The plum pudding model of the atom was replaced by the nuclear model.
The nuclear model was developed after the alpha particle scattering
experiment.
Compare the plum pudding model with the nuclear model of the atom.
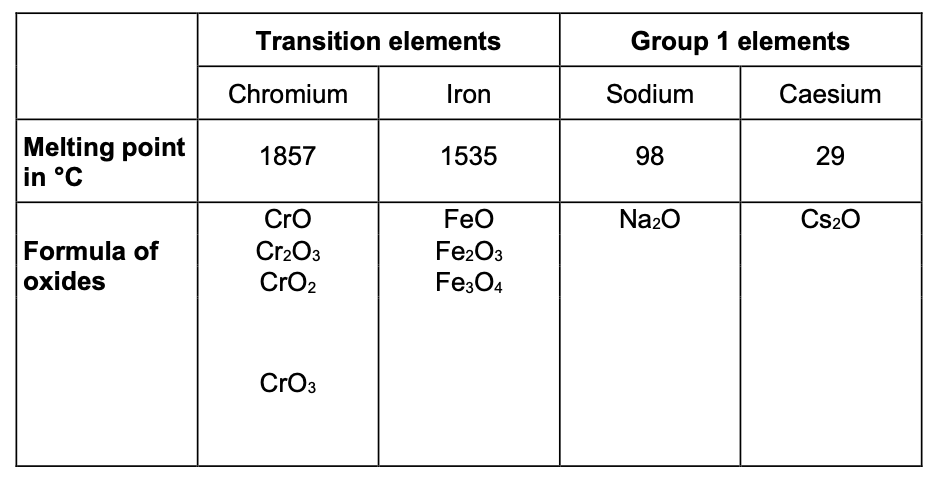
In the periodic table, the transition elements and Group 1 elements are
metals.
Some of the properties of two transition elements and two Group 1 elements are shown in the table below. Use your own knowledge and the data in the table above to compare the
chemical and physical properties of transition elements and Group 1
elements.
Physical
Transition elements
• high melting points
• high densities
• strong
• hard
Group 1
• low melting points
• low densities
• soft
Chemical
Transition elements
• low reactivity / react slowly (with water or oxygen)
• used as catalysts
• ions with different charges
• coloured compounds
Group 1
• very reactive / react (quickly) with water / non-metals
• not used as catalysts
• white / colourless compounds
• only forms a +1 ion
What is the test for chlorine gas?
Damp litmus paper turns white
A student tested a metal chloride solution with sodium hydroxide solution.
A brown precipitate formed.
What was the metal ion in the metal chloride solution?
Iron(III)
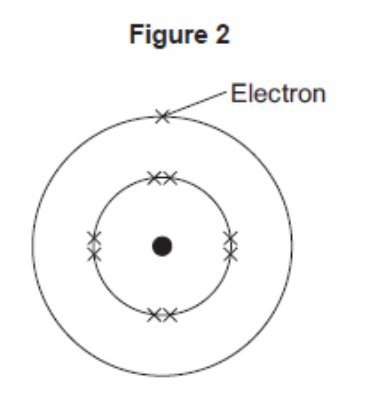
The electronic structure of a neon atom shown in Figure 2 is not correct.
Explain what is wrong with the electronic structure shown in Figure 2.
(iii) protons and neutrons
do not allow electrons in nucleus
(relative charge of proton) +1
allow positive
(relative charge of neutron) 0
allow no charge/neutral
ignore number of particles
too many electrons in the first energy level or inner shell
allow inner shell can only have a maximum of 2
electrons
too few electrons in the second energy level or outer shell
allow neon has 8 electrons in its outer shell or neon
does not have 1 electron in its outer shell
allow neon has a stable arrangement of electrons
or a full outer shell
neon does not have 9 electrons or neon has 10 electrons
allow one electron missing
allow fluorine has 9 electrons
ignore second shell can hold (maximum) 8
electrons or 2,8,8 rule or is a noble gas or in Group
max 2 marks if the wrong particle, such as atoms
instead of electrons
if no other mark awarded allow 1 mark
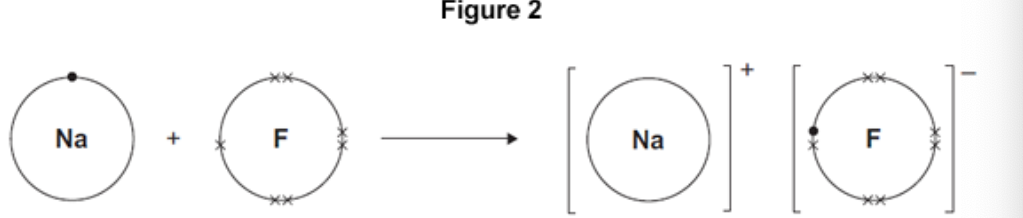
Figure 2 shows what happens to the electrons in the outer shells
when a sodium atom reacts with a fluorine atom.
The dots (•) and crosses (×) represent electrons.
Use Figure 2 to help you answer this question.
Describe, as fully as you can, what happens when sodium reacts
with fluorine to produce sodium fluoride.
sodium (atom) loses
fluorine (atom) gains
one electron
ions formed
allow sodium forms positive (ion) or fluorine forms
negative (ion)
allow form ionic bond
allow to gain a full outer shell of electrons
allow forms noble gas structure
max 3 if reference to incorrect particle / bonding
Sodium fluoride is an ionic substance.
What are two properties of ionic substances?
Dissolve in water
High melting point