7 Phyla of Animals: Bilateria
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Major features of bilateria
tripolasitc, bilateral symmetry, anterior/posterior axis, cephalization
cleavage
in the early stages of cell division after zygote formation, resulting in multiple cells (blastomeres), and an establishment of a longitudinal axis (animal-vegetal axis)
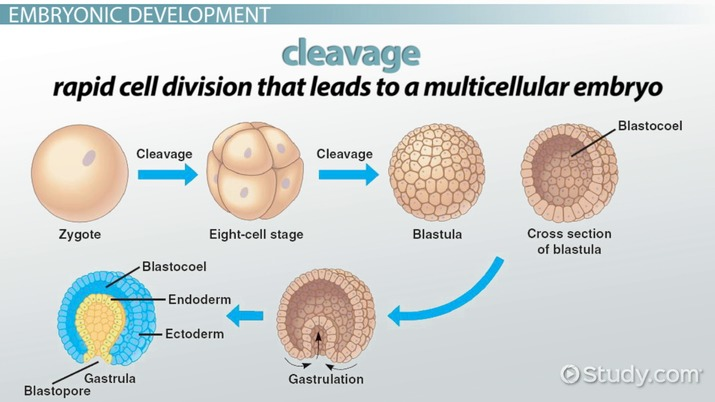
radial cleavage
right angles, symmetrical pattern
spiral cleavage
oblique angle, derived condition that characterizes the clade lophotrochozoa (mollusks and annelids)
if the mesoderm itself creates the cavity inside itself, this is what the cavity is called
coelem
Two major groups of bilateria are differentiated by
blastopore fate.
protostomes—blastopore becomes mouth.
deuterostomes—-blastopore becomes anus first.
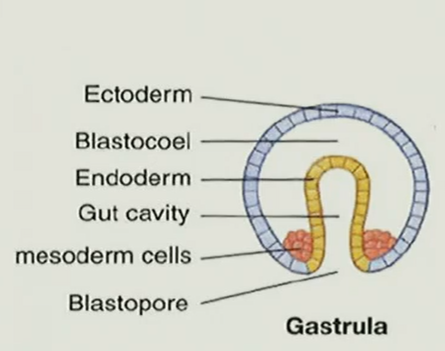
proteosome or deuterostome
proteosome because the mesoderm cells form near the lips of the blastopore—if a coelom is present, its from the splitting of the mesoderm.
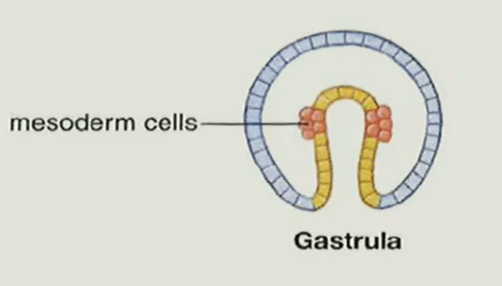
proteosome or deuterostome
deuterostome because the mesoderm cells and coelom form from outpocketing of cell wall
acoelomate plan
lack a true body cavity (coelum)
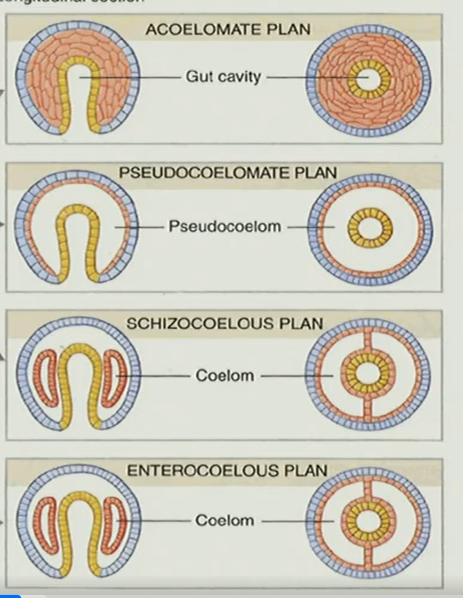
flatworms and roundworms are examples of __________. Earth worms are________.
acoelomates; true coelomates
traits associated with bilateral symmetry
segmentation, increased sensory and locomotor ability,