Fluid & Electrolyte Balance
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Methods of fluid and electrolyte balance
-Oral and gastric feedings
-Parenteral therapy
How is choice of fluid therapy chosen?
Type and severity of imbalance
Patient's overall health status and age, renal and CV status
Usual maintenance requirements
Diffusion
Solute molecules move from high to low concentration
Osmosis
Solvent molecules move from low to high solute concentration
Osmolarity
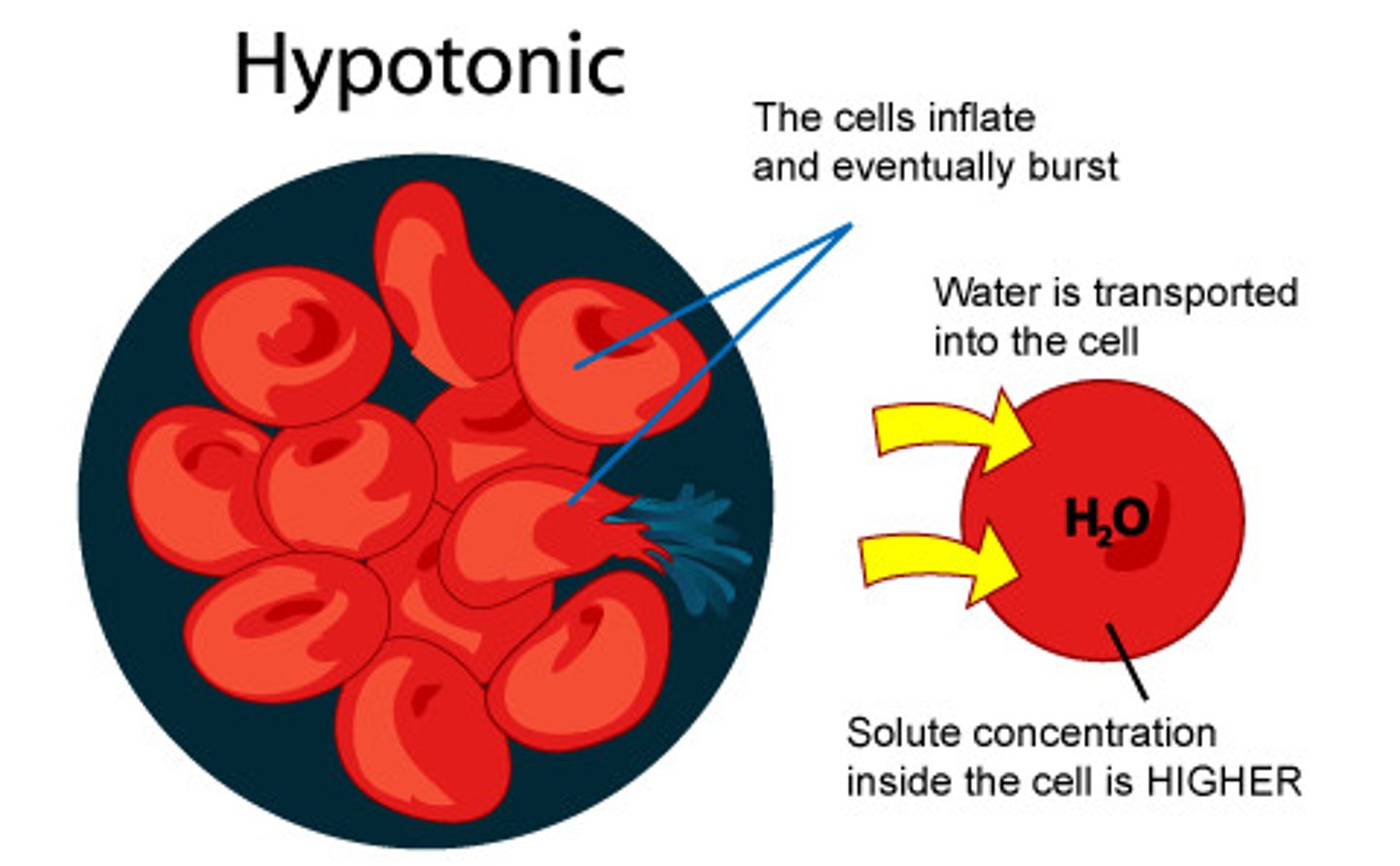
Hypotonic
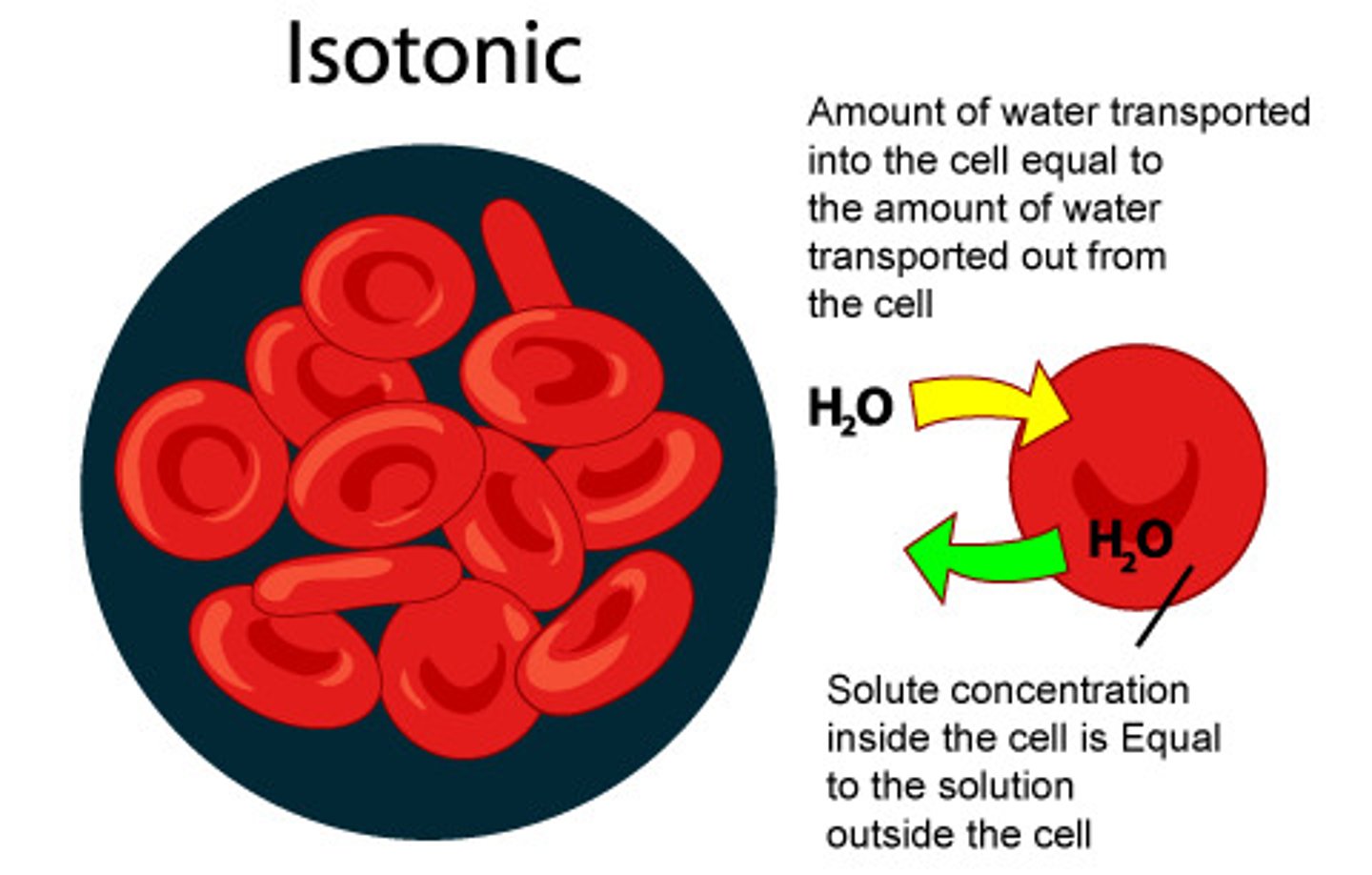
Isotonic
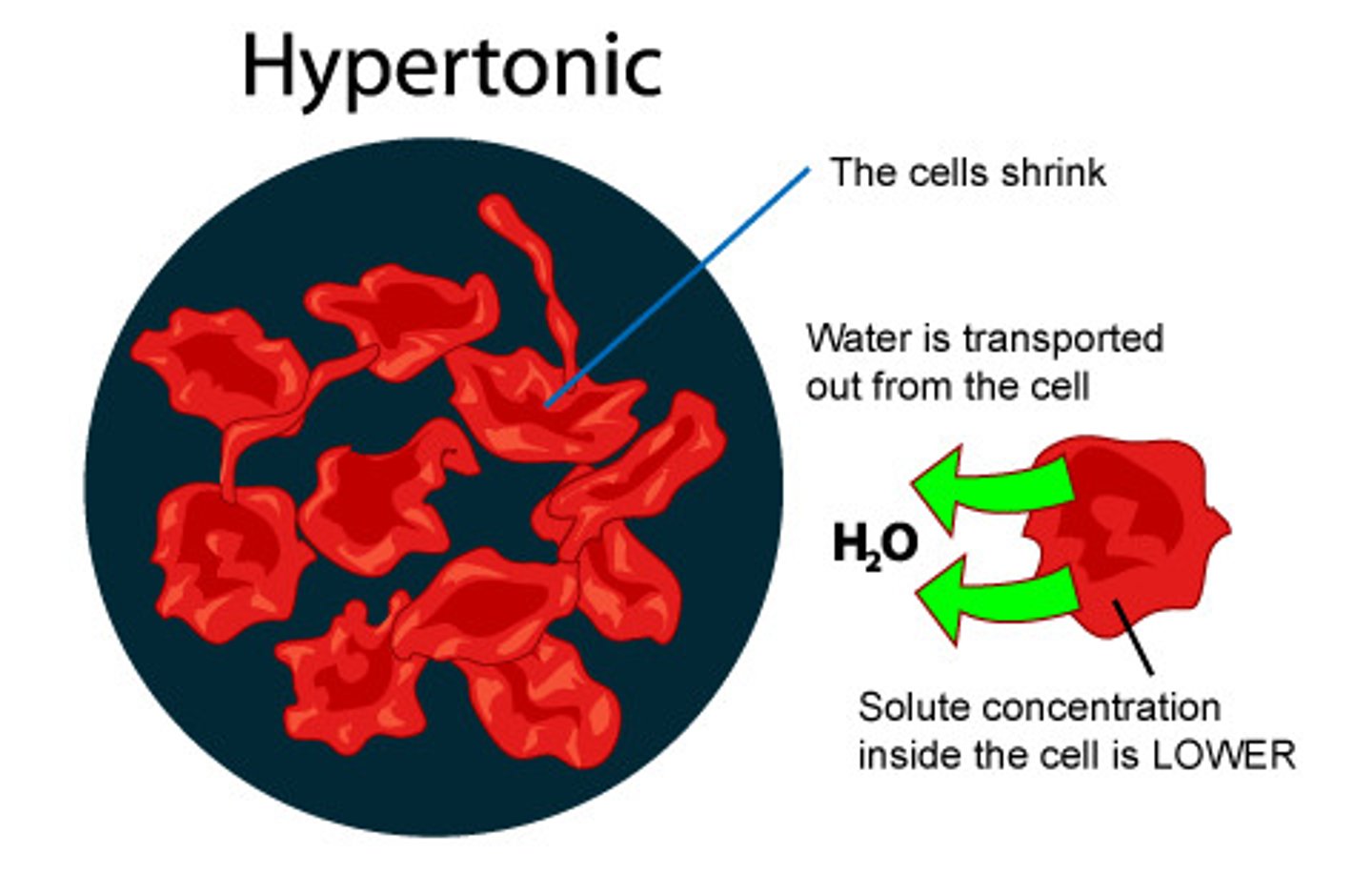
Hypertonic
Isotonic
-The concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside the cell
-Solution that has some tonicity as plasma, does not cause movement of solution in or out of the cell
Hypotonic
-Solution with lower osmolarity than plasma (<275)
-Draws water into cell from ECF
-Cell swells
Hypertonic
>295 osmolarity
-Draws water out of the cell into more highly concentrated ECF
-Cell shrinks
Isotonic IV fluid example
0.9% Normal Saline
LR
Hypotonic IV solution
0.45% Normal Saline
D5W (Dextrose)
Hypertonic IV solution
3% Saline (example of use: pulls fluid from the brain)
D5N5
D10W
D5LR
D50
Nursing process: Implementation replacement of fluids and electrolytes
-Daily weights
-i&o
-Enteral fluid replacement OR restriction of fluids
Oral replacement therapy
-Semi or high fowlers to avoid aspiration
-Maintain accurate i&o records
-Daily weight
-Monitor serum sodium levels, BUN levels, and serum osmolality
-Pt teaching
Why do we need to know about Lab Diagnostics?
-Patient education: explaining to pt and ensure accuracy
-Patient prep: diet restriction, sequencing procedures, protective barriers
-Data interpretation
What variables can affect lab test results?
-Age (peds, middle and older adults)
-Gender (muscle mass, hormones)
-Race has little effect on lab values but greater effect on genetic disease
-Pregnancy
-Food ingestion
-Posture
-Altitude
What lab changes may occur in middle and older adults?
Albumin and total protein decrease
Cholesterol & triglyceride increase
Venipuncture
-Usually in a superficial vein in antecubital fossa of arm
-Collection tubes and tourniquet
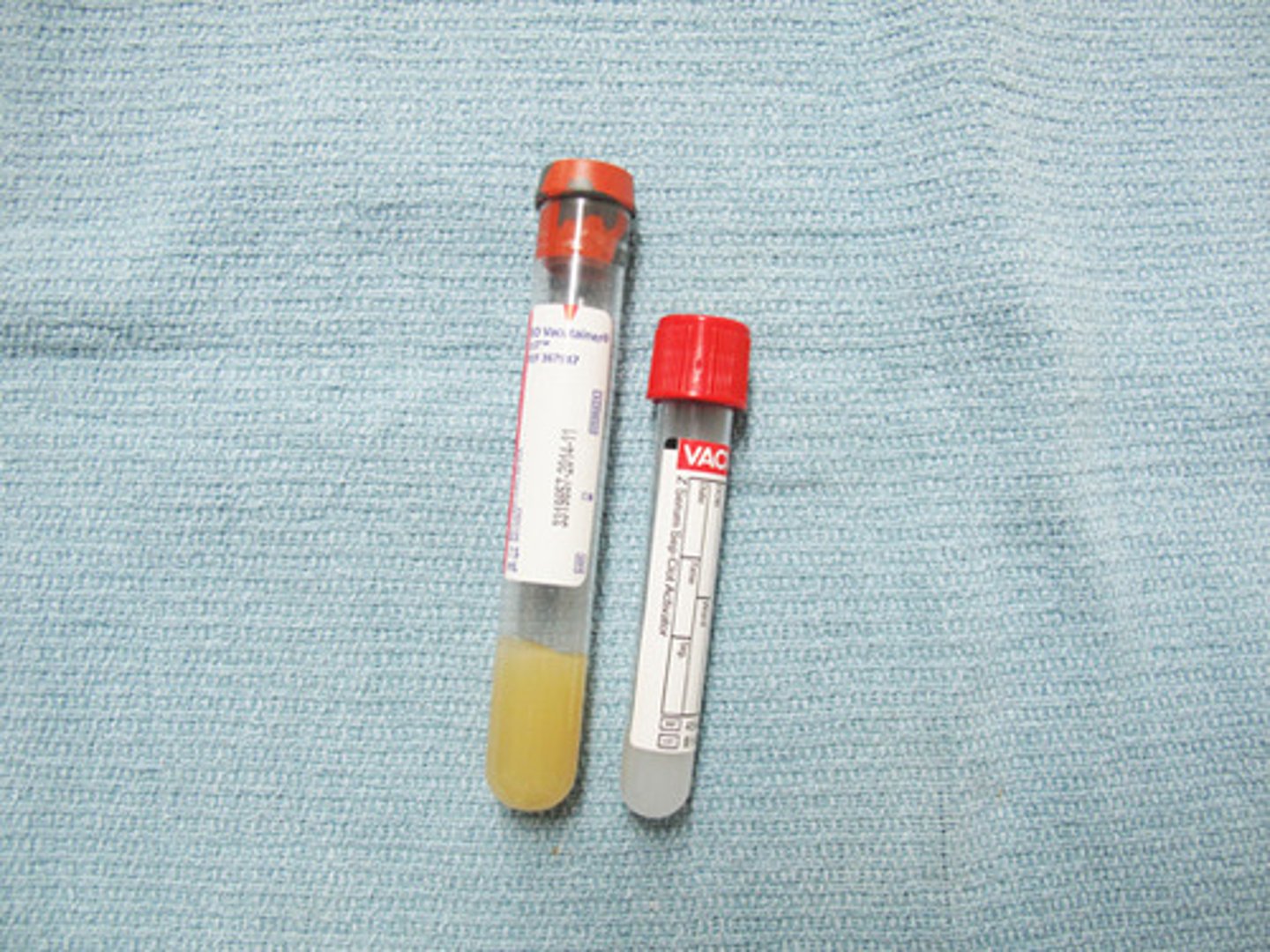
Red top collection tube
Allows blood to clot
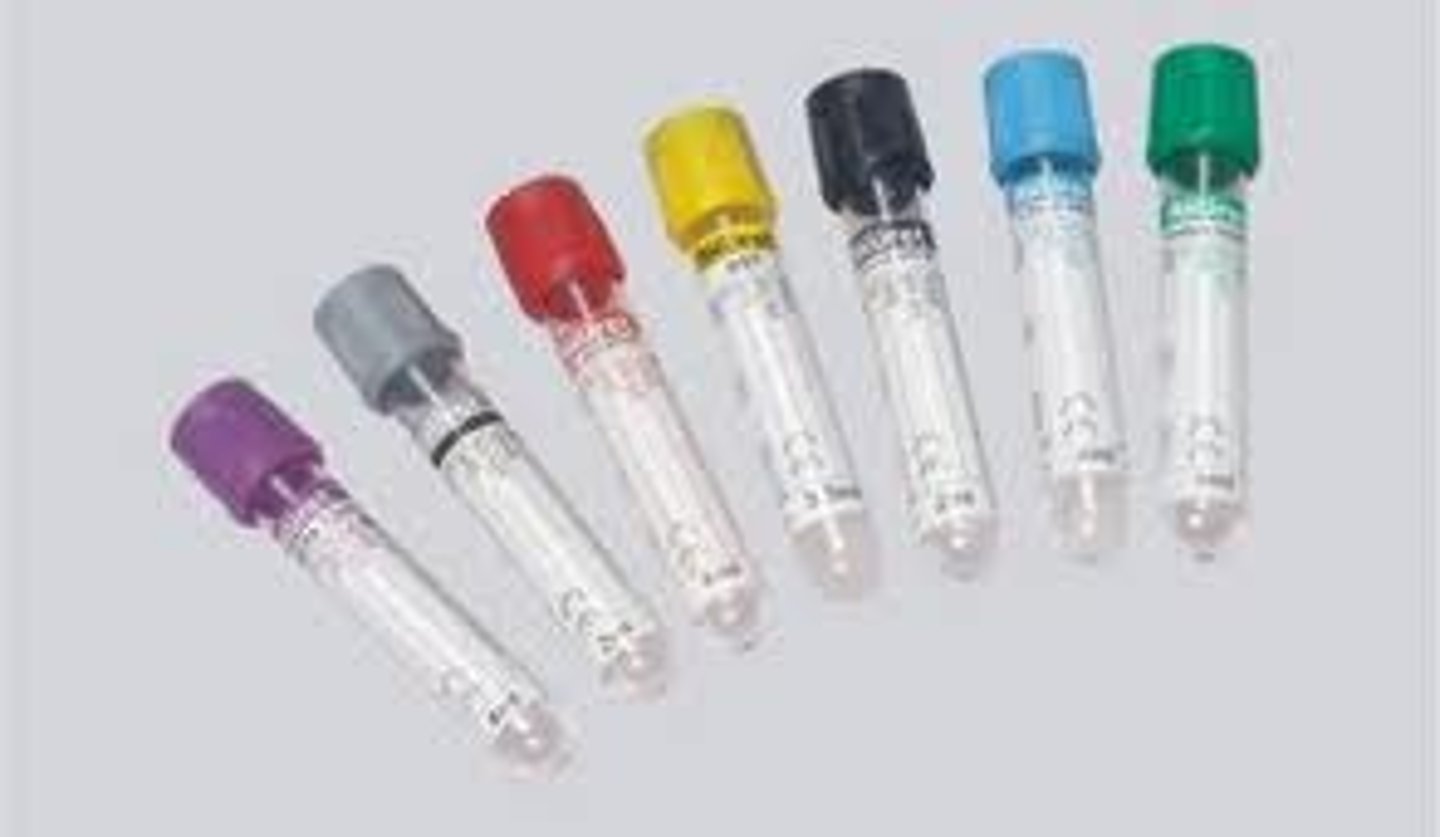
Blue, green, or lavender collection tube
Prevents blood from clotting
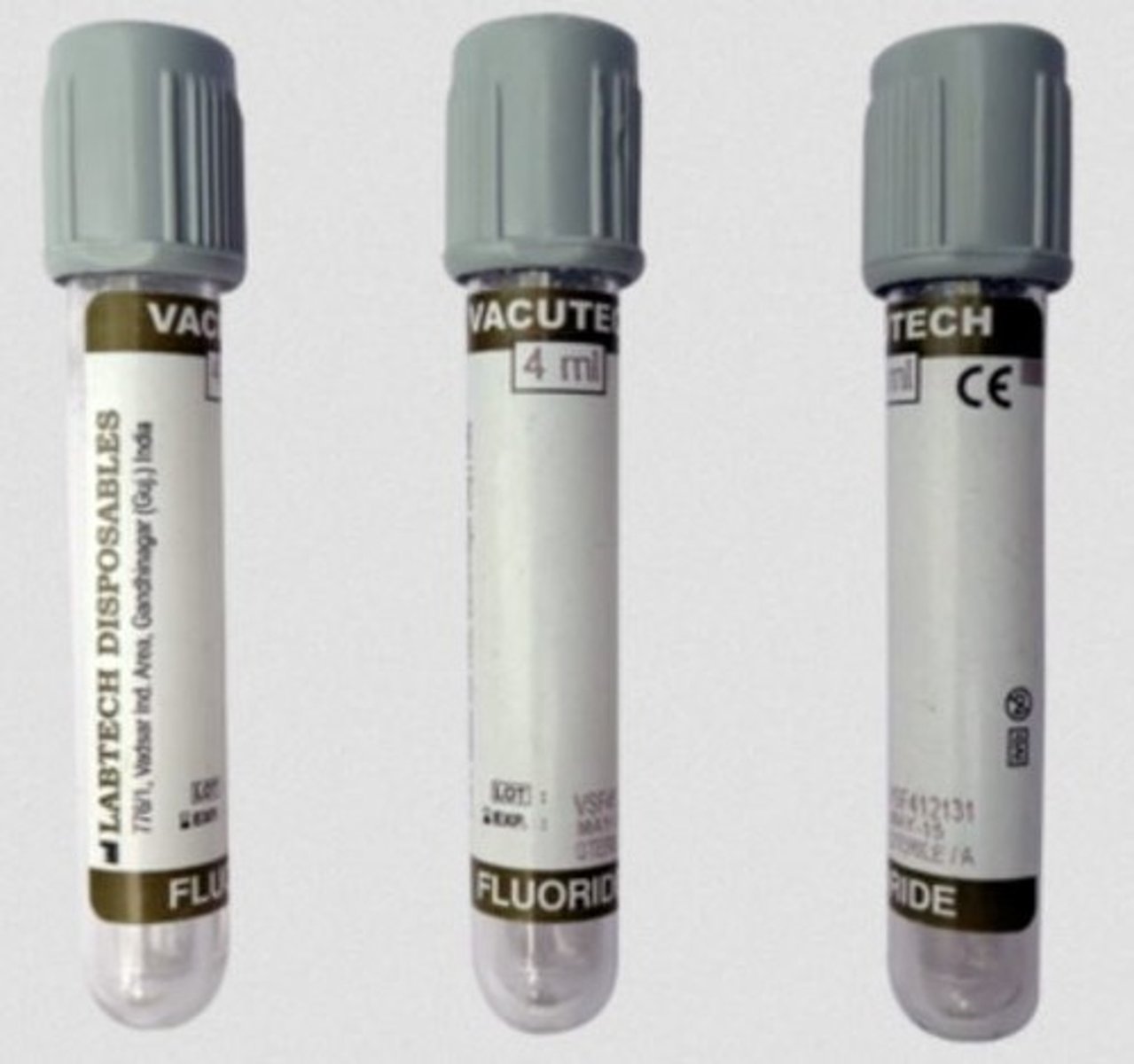
Grey top collection tube
Prevents glycolysis
Venipuncture order of blood draws
-Blood cultures (sterile)
-Light blue (Coag studies)
-Red (chem)
-Red speckled (chem)
-Green (chem)
-Light green
-Lavender (CBC)
-Yellow
-Gray
"Stop Light Red Stay Put, Green Light You Go"
CBC
RBC: What's left after white cells excluded
WBC: Gross count of cells not red
Hbg: Oxygen carrying capacity of blood
Hct: % of total blood volume that is RBC's (Approx 3x Hgb)
High WBC
-Generally points to infection
-Indicates something is wrong somewhere
-Differential WBC is a more detailed analysis of WBC's (neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils)
Sepsis WBC
Extremely high
Leukopenia
WBC count <4500
-Bone marrow failure from chemo/radiation
-Overwhelming infections of autoimmune disease
WBC Interfering factors
-Eating, physical activity, stress
-Pregnancy and spleenectomy
-Time of day
-Age
-Drugs
What can cause electrolyte imbalances?
Illness, burns, or trauma
Na reference values
135-145 mmol/L
K ref value
3.5-5.0 mmol/D
Cl ref value
95-105 mmol/L
CO2 ref value
25-40 mmol/L
BUN ref value
5-23 mg/dl
Creatinine ref value
0.6-1.2 mg/dl
Na panic values
<125 or >150
Hyponatremia <135
-Results from excessive loss of sodium or excessive water gain, diuretic therapy, excessive drinking of water, endocrine disorders
-S/s: HA, N, V, confusion, muscle twitching, tremors, weakness, irritability
-Tx: oral sodium supplements, restrict fluid intake
Hypernatremia >145
-Results from sodium gain in excess water or most commonly water loss in excess of sodium, severe insensible water losses, severe vomiting, sodium excess
-S/s: extreme thirst, restlessness or agitation, anorexia, N, V, dry sticky tongue and oral mucosa, disorientation, hyperactive reflexes, oliguria or anuria, lethargy
-Tx: prescribed oral/IV therapy and sodium restricted diet
K panic values
<2.5 mmol/L
>7.0 mmol/L
80-90% of body K is excreted by kidneys
Hypokalemia
<3.5 mmol/L
Results from excessive GI losses, chronic renal disease, certain drugs/diseases
-S/s: muscle weakness, leg cramps, paresthesia, fatigue, cardiac irregularities, GI complains, EKG changes, decreased reflexes
-Tx: oral K supplements, IV K chloride
Hyperkalemia
>5.0 mmol/L
Results from reduced excretion by kidneys, oliguria due to shock or severe dehydration, potassium-sparing diuretics, certain disease
S/s: irritability, paresthesia, numbness in extremities, skeletal muscle weakness, cardiac arrthymias
Tx: Kayexalate (cation exchange resin, orally or enema)
CO2
CO2 is venous CO2, not to be confused with PCO2 which is arterial
Elevated CO2
Alkalotic (cause: vomiting, gastric suction)
Decreased CO2
Acidotic (cause: chronic diarrhea, loop diuretics, renal failure, diabetic keto)
Elevated BUN and creatinine
Kidney Dysfunction
Increased BUN
Normal Creatinine
Dehydration
Decreased BUN
Normal creatinine
Overhydration
Nutrition Labs
K
Phos
Hgb
Mg
Ca
Alb
Fluid balance labs
BUN
Na
Cl
Hct
Patho labs
BUN/Cr
K
Ca
Phos
Mg
Albumin levels
3.5-5 g/dL
Total calcium levels
8.6-10.5 mg/dL
Ionized calcium levels
4.5-5.5 mg/dL
Mg levels
1.5-2.5 mg/dL
Phosphate levels
2.5-4.5 mg/dL
Total calcium panic values
<6.0 mg/dL
>14.0 mg/dL
Ionized calcium panic values
<2.8 mg/dL
>7.0 mg/dL
Hypocalcemia
<8.6 mg/dL
<4.6 mg/dL
Results from abnormal PTH, inadequate diet intake, excessive losses of bound, ionized, or total body calcium
Tx: calcium supplements PO or IV calcium gluconate or ca chloride
Hypercalcemia
>10 mg <5.5 mg/dL
Caused by increased intestinal absorption, renal abnormalities, pts with metastatic cancer
S/s: lethargy, muscle weakness/flaccidity, hyporeflexia, decreased muscle tone, polyuria, polydipsia, urinary calculi, arrhythmias, cardiac arrest
tx: adequate hydration, biphosphonates, ambulation
Mg panic values
<1.2 >4.9 mg/dL
What does Mg do?
-normal nerve and muscle function
-normal heart beat
-plays a role in almost all chemical processess
Hypomagnesemia <1.5 mg/dL
cause: excessive loss from GI and kidneys, chronic alcoholism, medications
s/s: neuromuscular irritability, weakness, tremors, dizziness, cardiac irritation, mood changes, tetany, convulsions
tx: orl Mg, iv Mg, rich Mg diet
Hypermagnesemia >2.5 mg/dL
causes: renal failure, adrenal insufficient, excessive intake, sepsis, Mg containing meds
s/s: feeling of warm/flushing, hypotension, SOB, drowsiness, hypoactive reflexes
tx: IV calcium gluconate, lasix, glucose, insulin
Phosphorous panic values
<1.5 mg/dL
Phosphorus use in body
-Building strong bones and teeth
-Needed for repair of all tissues/cells in the body
-Essential role in how the body stores and uses energy
Hypophosphetemia <2.5 mg/dL
causes: hyperparathyroidism, aluminum anacids, sepsis, ETOH, intoxication, NGT suctioning, diuretics, vitamin D deficiency
S/s: altered mental status, cardia arrhythmias, dyspnea, heart failure
tx: oral/iv phosphates, control the intake through diet
Hyperphosphatemia >4.5 mg/dL
causes: exercise, excessive enema usage, hypoparathyroidism, dehydration
s/s: tingling around mouth, fingertips, delirium, numbness, muscle cramps, tetany
tx: control intake through diet, acetazolamine (diamox)
Low albumin cause and risks
-inadequate protein intake for 14-20 days
-increase risk for pressure ulcers
-poor wound healing
Serum albumin level affected by
•Hydration
•Hemorrhage
•Renal or hepatic disease
•High-output wound drainage
•Steroid administration
•Albumin IV administration
•Age
•Trauma & stress: surgery, burns
Common labs indicating nutritional status
Serum albumin levels
Transferrin
Pre-albumin
Normal transferrin levels
>250 mg/dl
decreased can mean inadequate protein intake for 7-9 days
Pre-albumin normal levels
20-40 mg/dl
Decreased can mean inadequate protein for 2 days (Acute conditions, less sensitive to hydration status)
LFTs
bilirubin
SGOT/AST: aspartate aminotransferasae, found in many tissues
SGPT/ALT: alanine aminotransferase, found primarily in liver
Renal function tests
BUN and creatinine
Lipid profile tests
Total cholesterol
Triglycerides
LDLs
HDLs
Coagulation panel
PT: prothrombin time
PTT: partial
BUN test purpose
-Liver function and kidney excretion
BUN Increase meaning
-Azotemia/azotemic (elevated levels of urea and nitrogenous waste)
-Protein catabolism
-Dehydration
-Muscle breakdown
BUN Decrease meaning
-Decreased urea synthesis in liver
Creatinine test purpose
-Renal excretion
Causes of Creatinine increase
•Doubling indicates 50% ¯ in GFR
•Glomerulonephritis
•Pyelonephritis
•Acute tubular necrosis
•Urinary obstruction
•Meat Ingestion
Cause of Creatinine decrease
-Elderly and children d/t decreased muscle mass
How much total kidney function must be lost before BUN and creatinine appears outside the normal range?
Around 60% of total kidney function must be lost until BUN and creatinine are out of range
Creatinine clearance
•is a more accurate measure
•used whenever renal disease is suspected
•careful dosing of nephrotoxic drugs is required
GFR
Volume filtered from the renal capillaries into the Bowman's capsule per unit time to measure renal function
Factors used in determining GFR
‣Serum creatinine
‣Age
‣Race
‣Gender
‣Blood Urea Nitrogen
‣Albumin
Normal GFR
80-120
Mild GFR reduction
41-80
Moderate GFR reduction
30-40
Severe GFR reduction
<29
In chronic renal failure, what changes will be seen in urine lab values?
- decrease protein/na
- increase specific gravity
Chronic renal failure: changes in blood lab values
- increase: K, P, Mg, BUN, Creatinine
- decrease: ca, pH
- na may increase or decrease
platelet count
150,000-400,000
PT: prothrombin time
11.2-12.5 seconds
INR
International normalized ratio
therapeutic: 2-2.5 x normal
PTT: Partial Thromoboplastin time
Therapeutic: 1.5-2.5 X normal
Trough
Heparin therapy