Anterior Pituitary: Hormones
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What hormones does the pituitary secrete?
human growth hormone (hGH)
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
What is a tropic hormone?
hormone that acts on another gland to have secretions of another hormone
Human growth hormone (hGH)
or somatotropin
What is its target tissue?
targets the liver
Human growth hormone (hGH)
or somatotropin
Function?
How?
stimulates the liver to produce insulin-like growth factors (IGFs)
promotes protein synthesis, elevates blood glucose, breaks down fat, and growth of body cells
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
or thyrotropin
What is its target tissue?
Function?
Thyroid gland
causes the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones
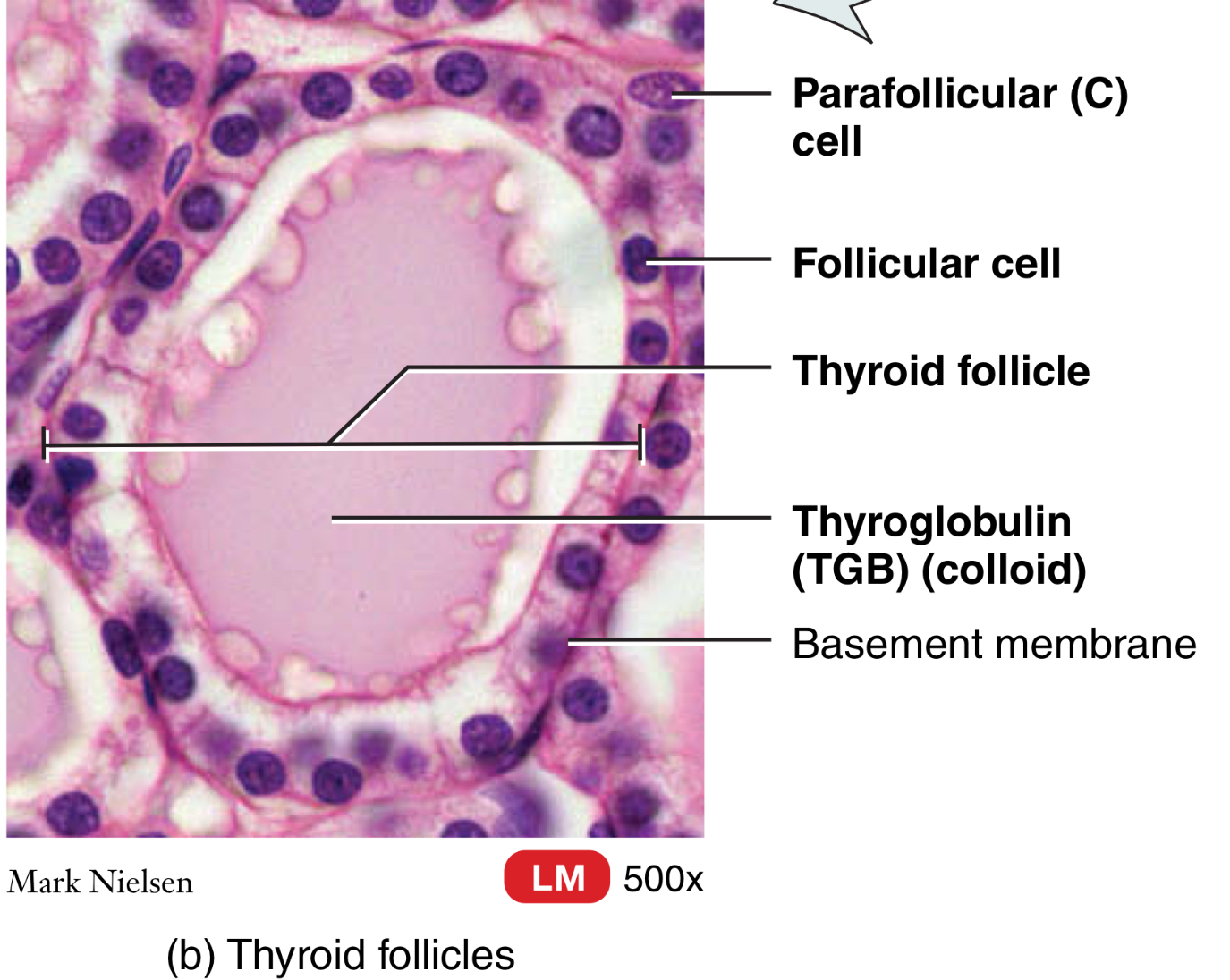
Thyroid gland:
What are the cells of the thyroid follicle?
parafollicular (C) cell
Follicular cell
Thyroglobulin cell (TGB)
Thyroid gland: What are thyroglobulin cells?
precursor to thyroid hormones

Thyroid glands: What are the hormones of the thyroid gland?
T3 and T4, and calcitonin (CT)
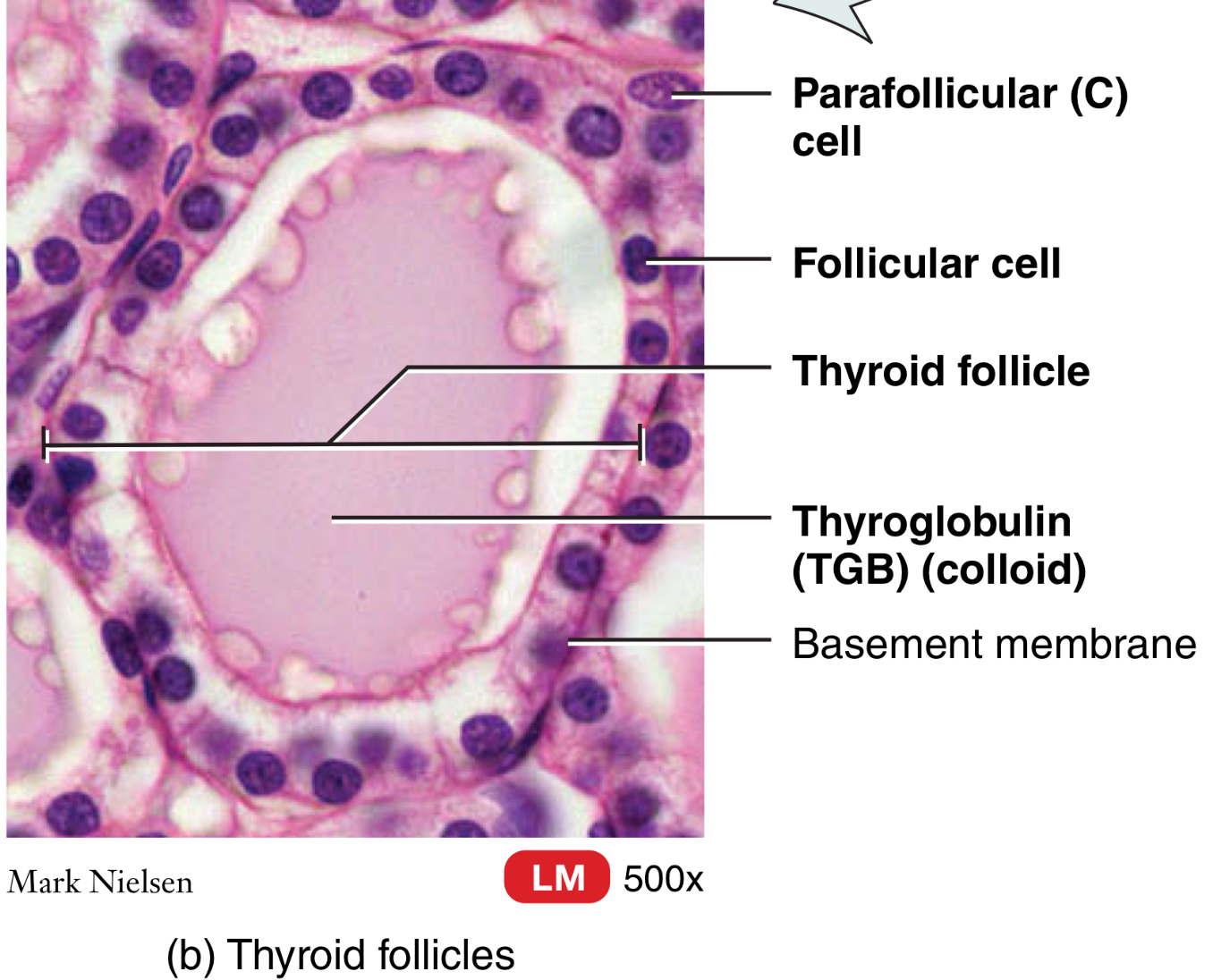
Thyroid gland:
T3 and T4
What are they called?
What cell produces them?
What are their functions?
Are thyroid hormones produce by the follicular cells
increase basal metabolic rate, blood glucose, lipolysis, and protein synthesis
Thyroid gland:
Calcitonin (CT)
What cell produces them?
What are their functions?
increasing?
Produced by parafollicular cells
reduces blood calcium levels and increases bone density
by inhibiting bone reabsorption by osteoclasts
increasing the uptake of calcium into the bone extracellular matrix
Parathyroid glands
What cell secretes it?
what do they produce and secrete
what are its functions
produces and secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH)
chief cells
increases blood Ca2+ levels by increases bone reabsorption of osteoclasts (breaking down bone)
What hormones are involved in calcium balance?
parathyroid hormone by the parathyroid gland
and
calcitonin by the thyroid gland
What are gonadotropins?
What are the types?
hormones that stimulate (act) the gonads
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
(GT) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
What are its target tissues?
effect on females?
effect on males?
T: ovaries and testes
F: development of the follicle for oocyte
M: stimulates the testes to produce sperm
(GT) Luteinizing hormone (LH)
What are its target tissues?
effect on females?
effect on males?
ovaries and testes
F: stimulates the corpus luteum to produce progesterone and estrogen
M: stimulates the production of testosterone
What are the sex hormones?
What stimulates their release?
estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone
stimulated for release by gonadotropins
(SH) Estrogen and Progesterone
what is it released by?
what are some of the tissues affected?
released by the ovaries
effects the breasts and uterus
(SH) Estrogen and Progesterone
What are its functions
what hormone is especially important for pregnancy? Why?
helps regulate the cycle
second sex characteristics of females
prepare uterus for pregnancy
prepare mammary glands for lactation
helps maintain pregnancy, especially progesterone, and assures that the uterus does not contract
(SH) Testosterone
what is it released by?
What are its functions?
released by the testes
maintain male secondary sex characteristics
sperm production
What hormones are needed to produce viable sperm?
FSH and testosterone
Prolactin (PRL)
what tissue does it affect?
what is its function
mammary glands
together with other hormones stimulates the production and secretion of milk
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
or corticotropin
what tissue does it affect?
what is its function?
the adrenal CORTEX
stimulates the secretion of glucocorticoids (mainly cortisol )
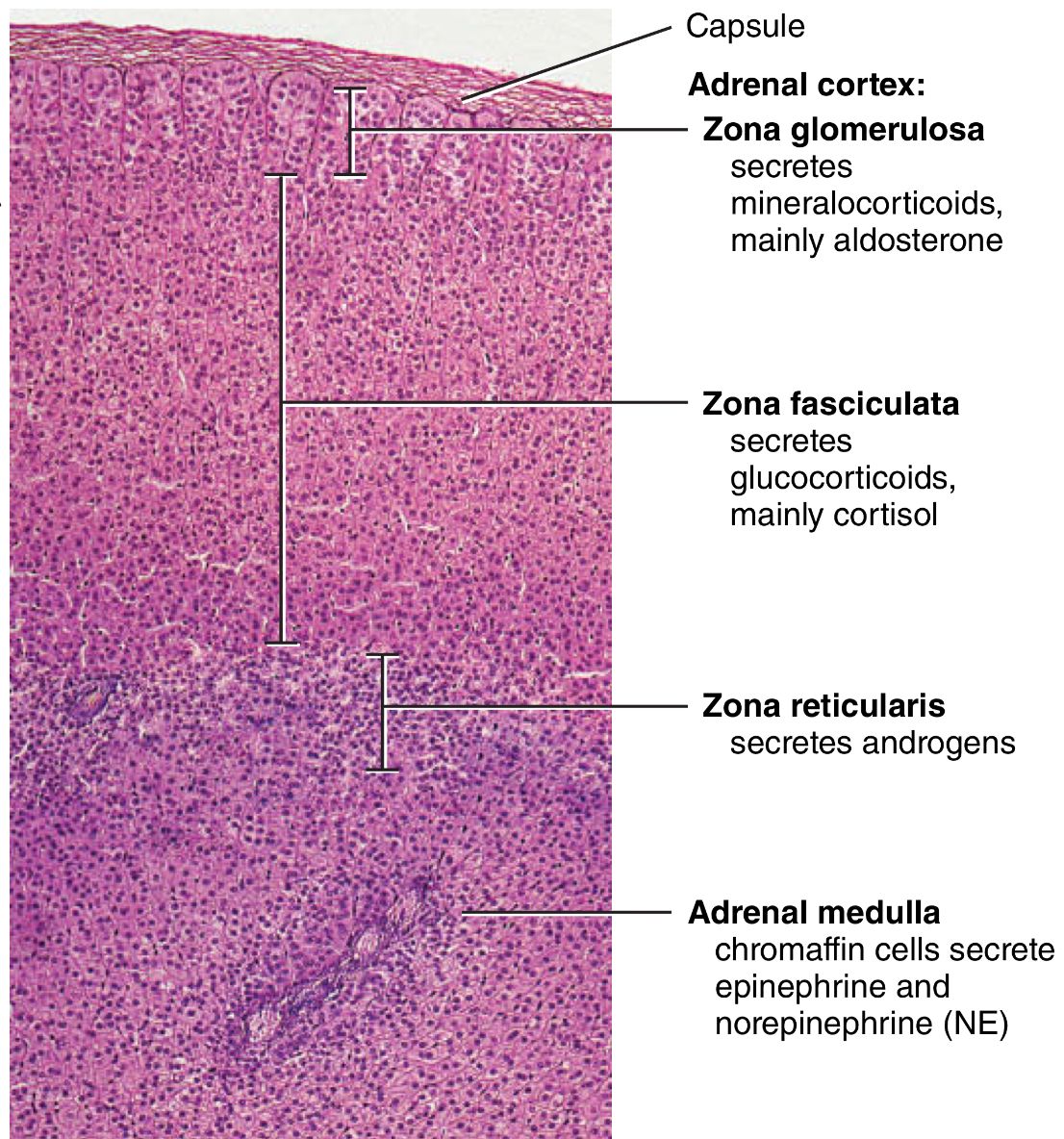
Adrenal cortex
What are its cells?
What do they mainly secrete?
“Go Find Rex, Make Good Sex”
zona glomerulosa
mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone)
zona fasciculata
glucocorticoids (mainly cortisol)
zona reticularis
sex hormones (androgens)
Adrenal Cortex: Mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone)
what are they secreted by?
what is their function
“Go, Make”
zona glomerulosa cells
important for neural signaling, increasing Na+ and water, and decreasing K+ blood levels; increasing blood pressure
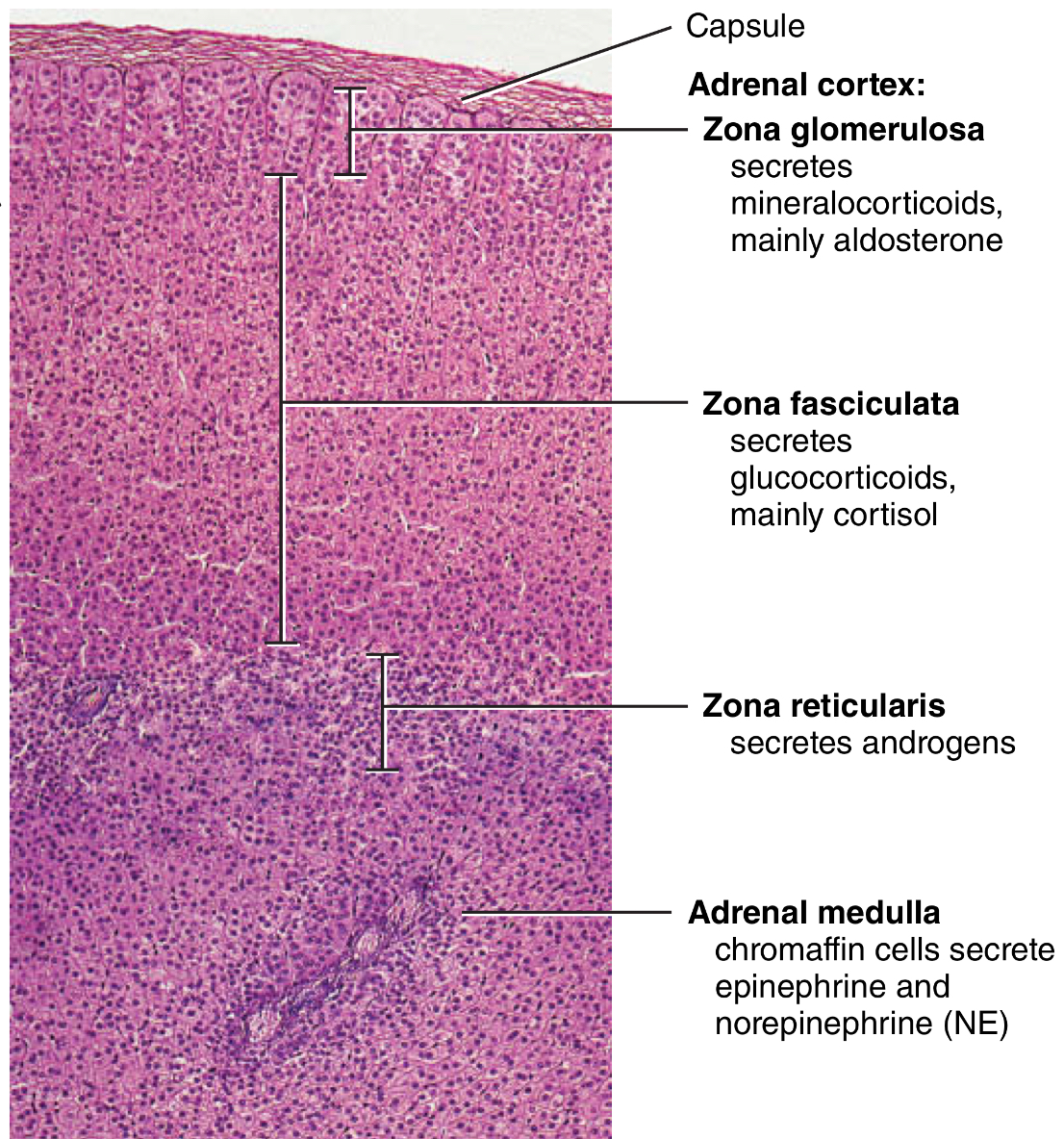
Adrenal Cortex: glucocorticoids (mainly cortisol)
what are they secreted by?
what is their function
“Find, Good”
zona fasciculata cells
stress hormone, increases protein breakdown, stimulates gluconeogenesis and lipolysis, dampens inflammation ,and depresses immune response
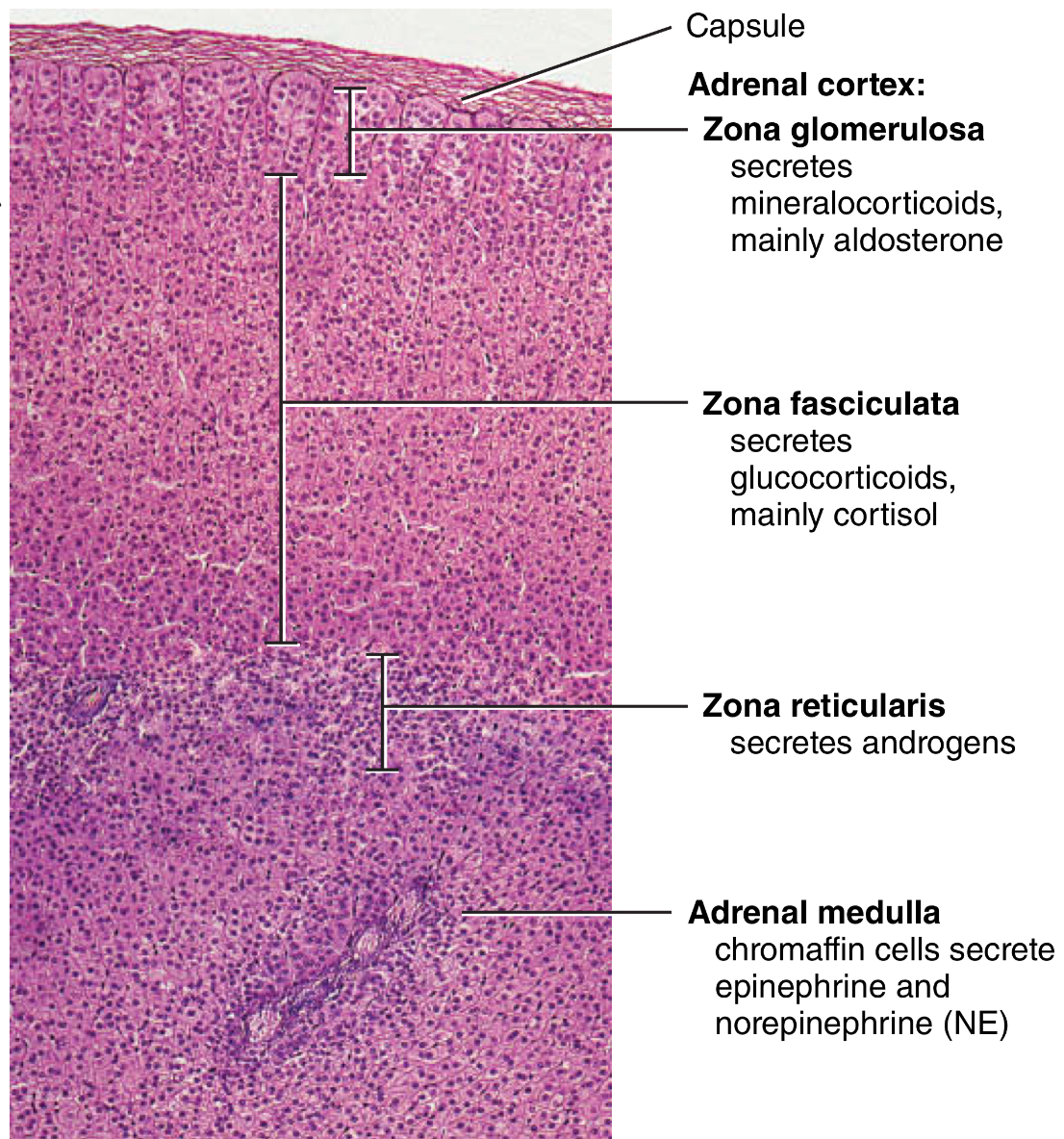
Adrenal Cortex: androgens
what are they secreted by?
what is their function
“Rex, Sex”
zona reticularis cells
Assist in the early growth of axillary and pubic hair in both sexes
A testosterone derivative in females contributes to libido and is a source of estrogen after menopause
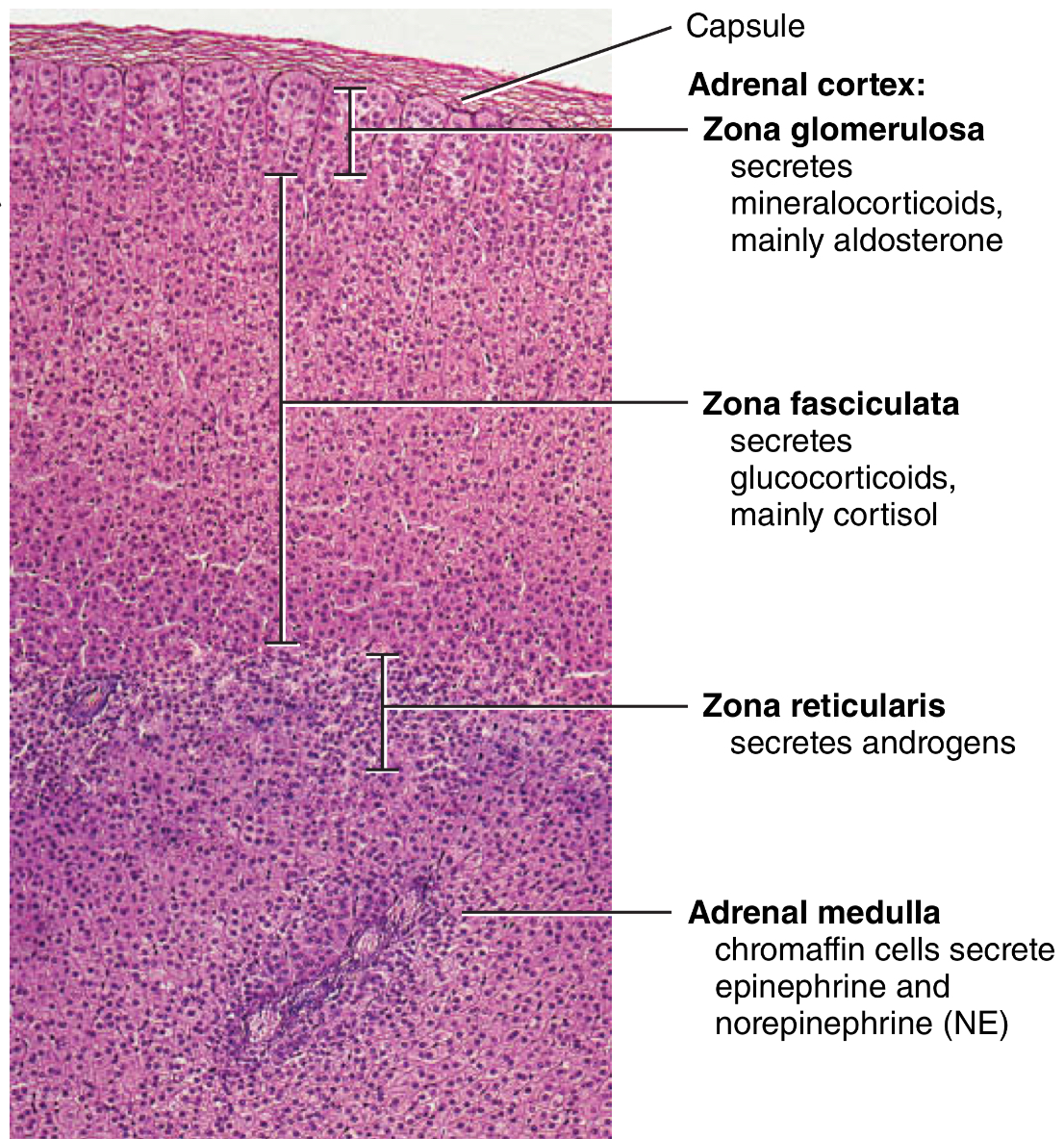
What does the adrenal MEDULLA secrete
What cells?
What is its effect?
Chromaff cells
secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
enhances the effects of the sympathetic division of the ANS during stress