Unit 1 Thinking Geographically Vocabulary
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:56 PM on 4/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
reference Maps
A map that shows geographic locations on Earth's surface, such as the locations of cities or oceans.
2
New cards
physical map
A graphical representation of physical locations of landmarks or markers.
3
New cards
political map
A map that shows the spatial organization of the countries and territories on the entire globe at a given point in time.
4
New cards
thematic maps
A map that emphasizes the spatial patterns of geographic statistics or attributes, and sometimes the relationships between them.
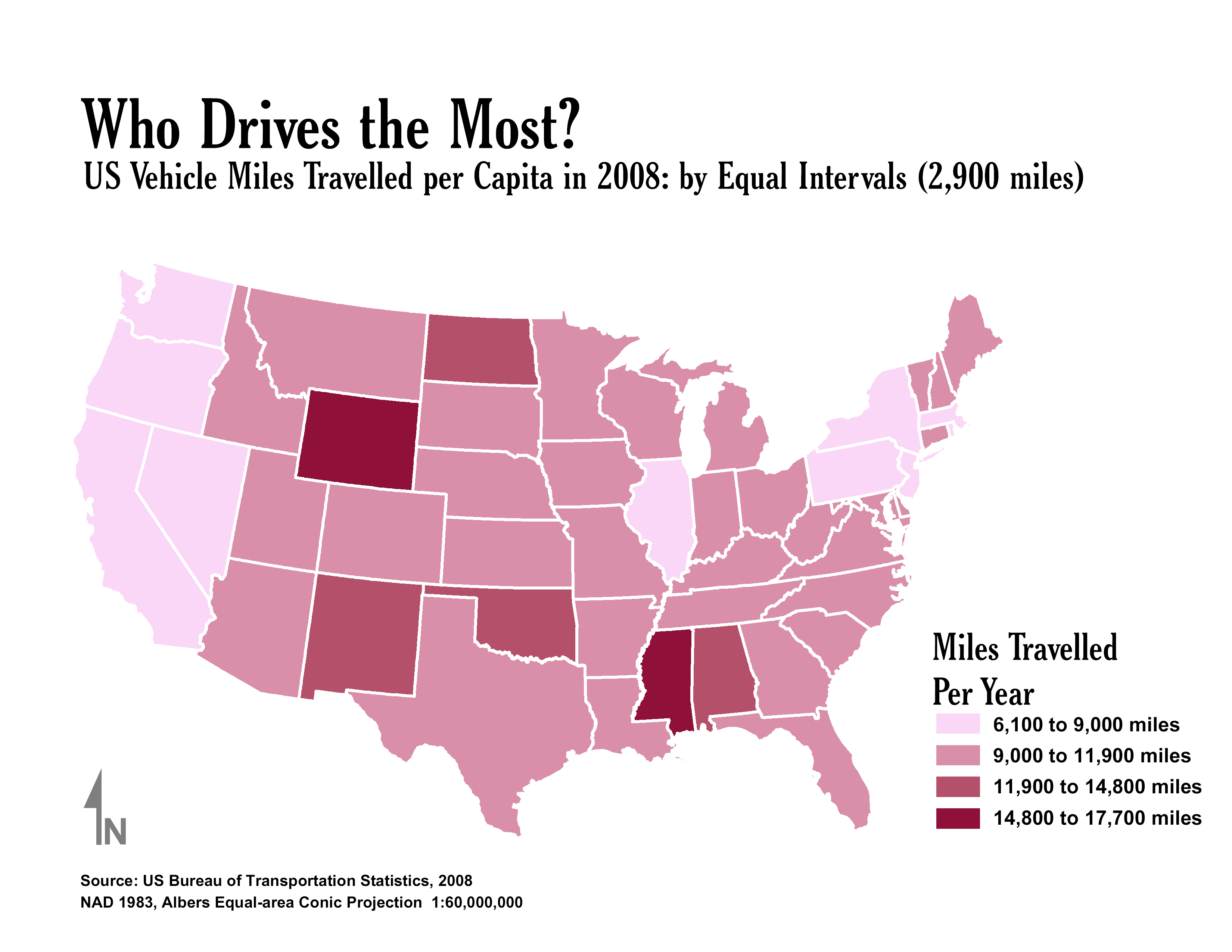
5
New cards
cartogram
A map that distorts the geographic shape of an area in order to show the size of a specific variable; the larger the area this map, the larger the value of the underlying variable.
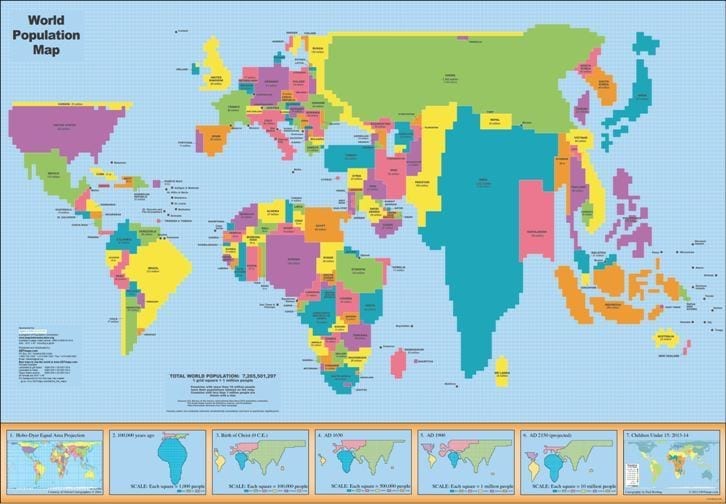
6
New cards
choropleth map
A thematic map that shows data aggregated for a specific geographic area, often using different colors to represent different values.
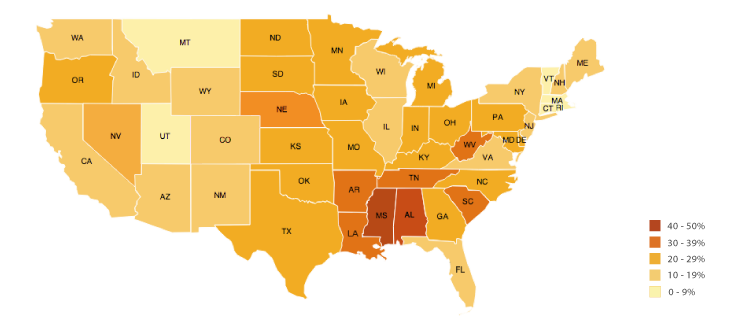
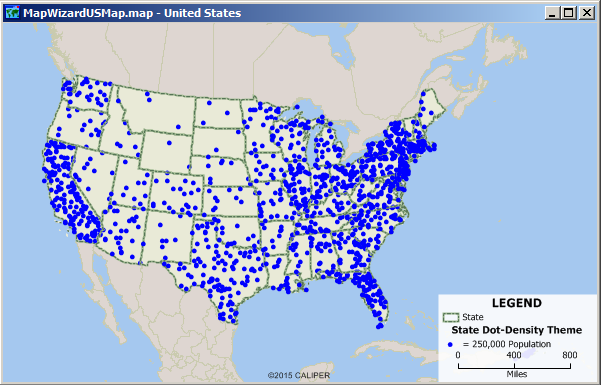
7
New cards
dot density map
A map that uses dots to represent objects or counts; the dot can represent one object (a one-to-one dot density map) or it can represent a number of objects (a one-to-many dot density map).
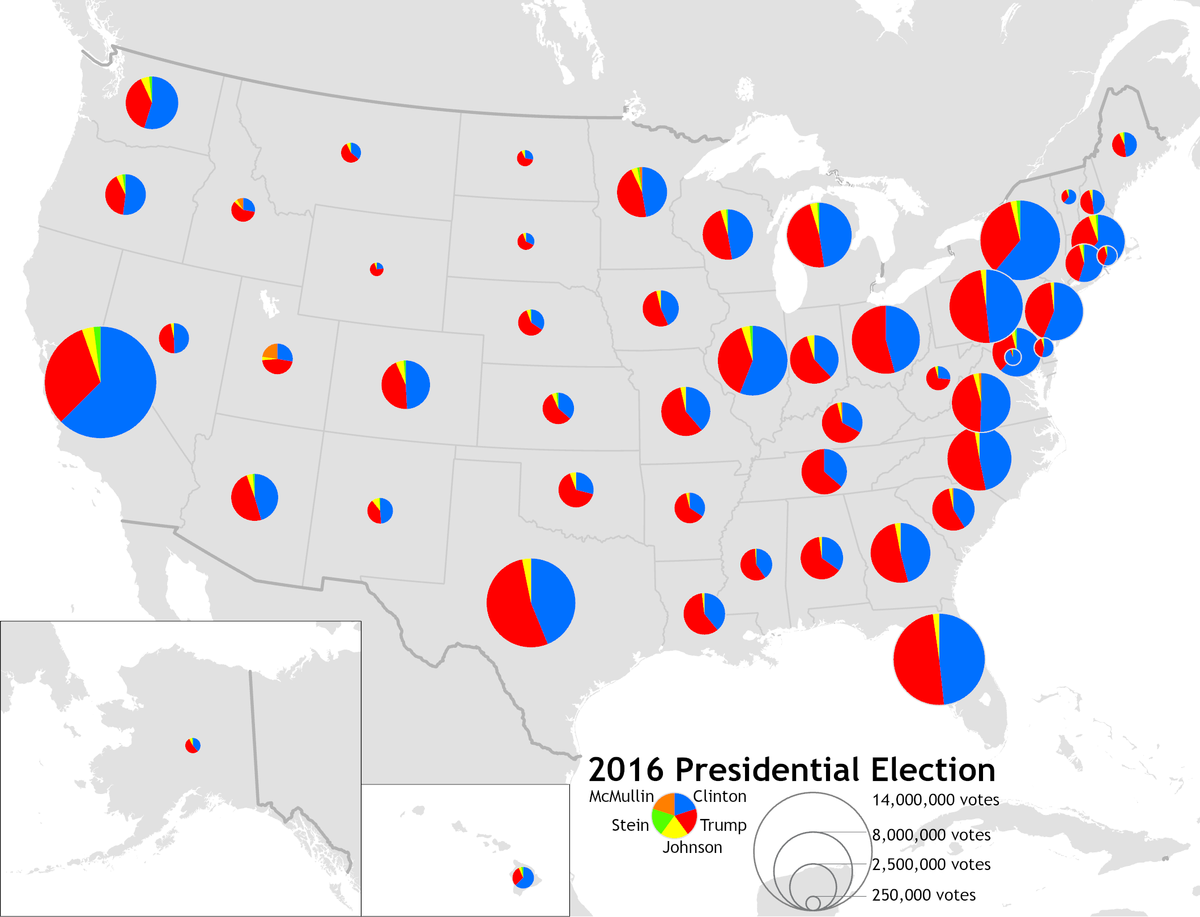
8
New cards
graduated symbols map (proportional)
A type of thematic map that uses map symbols that vary in size to represent a quantitative variable.
9
New cards
symbols map
A map that uses symbols (such as circles or dots) of different sizes to represent numerical values.
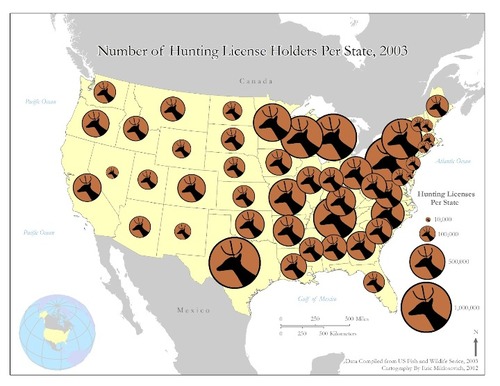
10
New cards
mental map
A personal representation of a portion of Earth's surface.
11
New cards
cylindrical map
A map projection in which the surface features of a globe are depicted as if projected onto a cylinder typically positioned with the globe centered horizontally inside the cylinder.
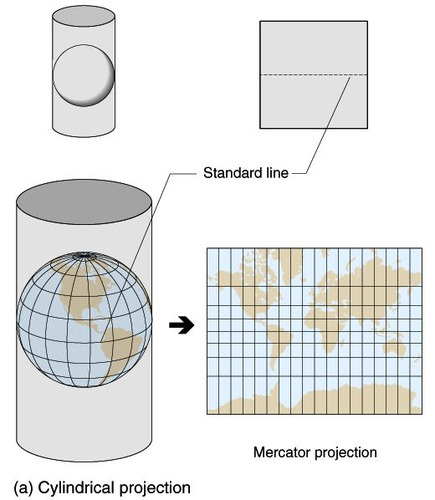
12
New cards
conic map
A map projection in which the surface features of a globe are depicted as if projected onto a cone typically positioned so as to rest on the globe along a parallel (a line of equal latitude).
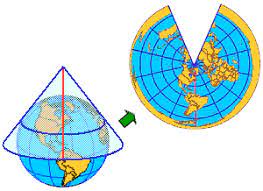
13
New cards
Planar/Azimuthal map
A map projection that transforms points from a spheroid or sphere onto a tangent or secant plane.
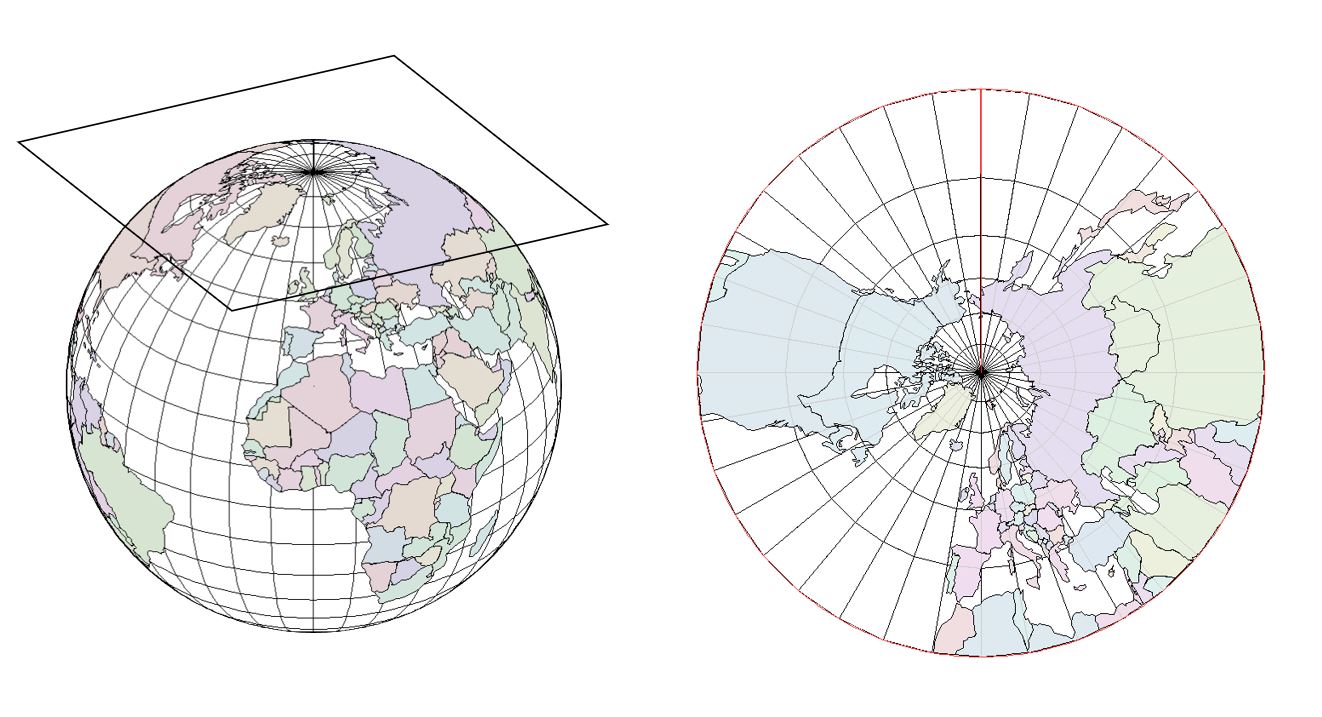
14
New cards
Oval map
A map projection used for world maps largely in the late 16th and early 17th century. It is neither conformal nor equal-area but instead offers a compromise presentation.
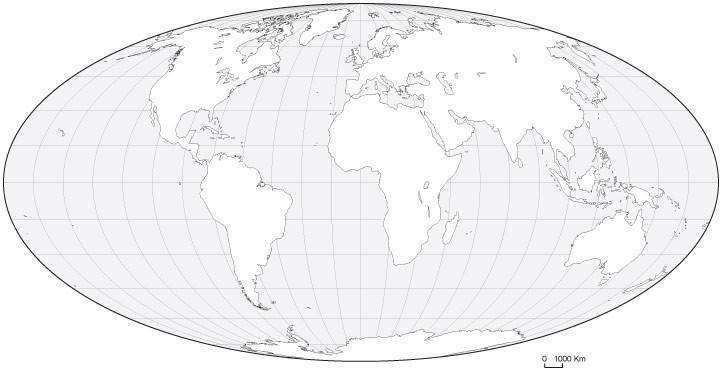
15
New cards
Isoline map
On a map, a line that connects or links different places that share a common or equal value, such as elevation.
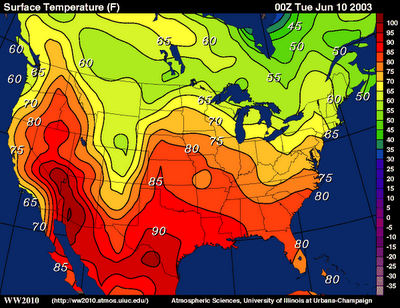
16
New cards
absolute distance
The distance that can be measured with a standard unit of length, such as a foot, yard, mile, or kilometer.
17
New cards
relative distance
A measurement of the level of social, cultural, or economic similarity between places despite their absolute distance from each other.
18
New cards
absolute direction
Corresponds to the direction on a compass: north south, east, and west and combinations such as northeast and southwest.
19
New cards
relative direction
A direction that can be described as position, such as in front of or behind, to the left or to the right.
20
New cards
spatial pattern
The placement or arrangement of objects on Earth's surface; also includes the space between those objects.
21
New cards
clustering
The method of grouping a set of spatial objects into groups called "clusters".
22
New cards
dispersal (distribution)
The arrangement of a phenomenon across the Earth's surface and a graphical display of such an arrangement is an important tool in geographical and environmental statistics.
23
New cards
Elevation
Distance above sea level.
24
New cards
Geospatial technology
Discipline concerned with the collection, distribution, storage, analysis, processing, presentation of geographic data or geographic information.
25
New cards
Geography data
Data and information having an implicit or explicit association with a location relative to Earth.
26
New cards
GIS(geographic information system)
A software application for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on Earth's surface; allows the rapid manipulation of geospatial data for problem-solving and research.
27
New cards
Satellite navigation systems
A system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning.
28
New cards
Remote sensing
The scanning of Earth by satellite or high-flying aircraft in order to obtain information about it.
29
New cards
Scale of Analysis
Patterns and processes at different scales that reveal variations in, and different interpretations of, data.
30
New cards
absolute location
A precise position on Earth's surface.
31
New cards
relative location
The position of one place (or person) in relation to the position of another place (or person).
32
New cards
space (geography)
The areas we occupy as humans; it has no value until the people who occupy make it their own.
33
New cards
place
How we modify space based on who we are as a group of people.
34
New cards
pattern
The geometric or regular arrangement of something in an area.
35
New cards
human-environment interaction
The effect that humans have on their environment and the effect that the environment has on humans.
36
New cards
distance decay
The interaction between two locales declines as the distance between them increases.
37
New cards
time-space compression
The decreasing distance between places, as measured by travel time or cost; often summarized by the phrase "the world is shrinking".
38
New cards
time-space convergence
The decline in travel time between geographical locations as a result of transportation, communication, and related technological and social innovations.
39
New cards
movement (geography)
Mobility of people, goods, and ideas across the surface of the Earth. Region.
40
New cards
Globalization
The process by which businesses and other organizations develop international influence or start operating on an international scale.
41
New cards
network
A set of interconnected nodes without a center.
42
New cards
Sustainability
The group of practices that meet the needs of the present without compromising future generations' ability to meet their needs.
43
New cards
Economic
The total value of goods and services, including income received from abroad, produced by the residents of a country within a specific time period, usually one year.
44
New cards
Social
It may include wealth, religion, family size, and structure, education level, population density, etc.
45
New cards
Environmental
A natural resource is considered a renewable resource if nature can reproduce it within a human lifetime.
46
New cards
Natural resource
Materials or substances that occur in nature and can be used for economic gain.
47
New cards
Environmental determinism
The belief that the physical environment is the dominant force shaping cultures and that humanity is a passive product of its physical surroundings.
48
New cards
Possibilism
The belief that any physical environment offers a number of possible ways for a society to develop and that humans can find ways to overcome environmental challenges.
49
New cards
Region
A geographical unit based on one or more common characteristics or functions.
50
New cards
Regionalism
Describing an area in terms of its individual characteristics, such as a shared language or cultural identity, that make that place unique.
51
New cards
Formal/uniform
A geographical area inhabited by people who have one or more traits in common.
52
New cards
Functional/Nodal
A geographic area that has been organized to function politically, socially, culturally, or economically as one unit.
53
New cards
Perceptual/vernacular
A geographic area that is perceived to exist by its inhabitants, based on the widespread acceptance and use of a unique regional name.
54
New cards
Regional boundaries
Transitional and often contested and overlapping boundaries.