Kaplan MCAT Biology Chapter 12: Genetics and Evolution
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Chromosomes
Contain genes in a linear sequence
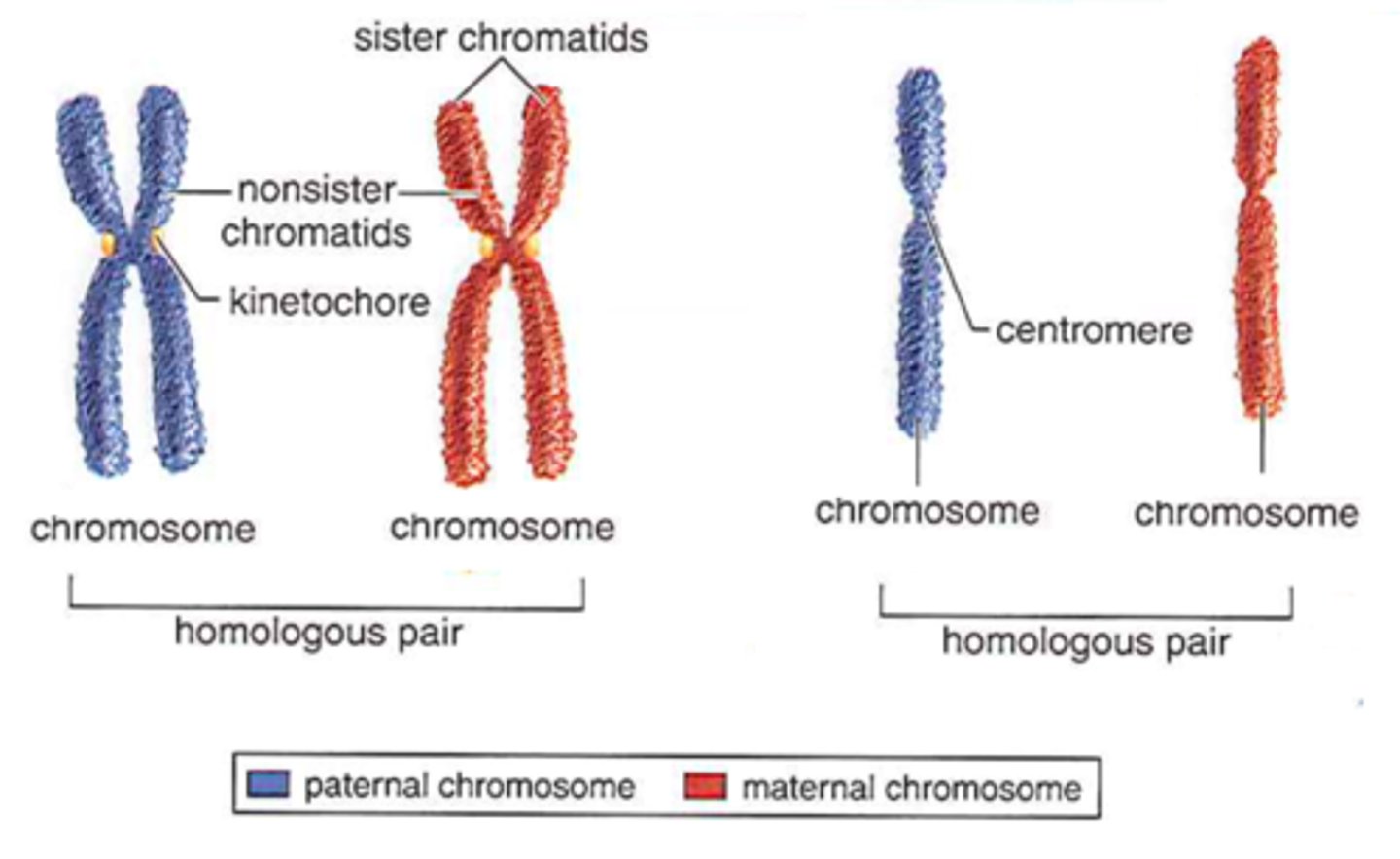
Carrier
Holds a recessive allele that is not expressed
Alleles (types)
Alternative forms of a gene
1) Dominate alleles
2) Recessive alleles
Dominate alleles
Require only one copy to be expressed.
Recessive alleles
Require two copies to be expressed.
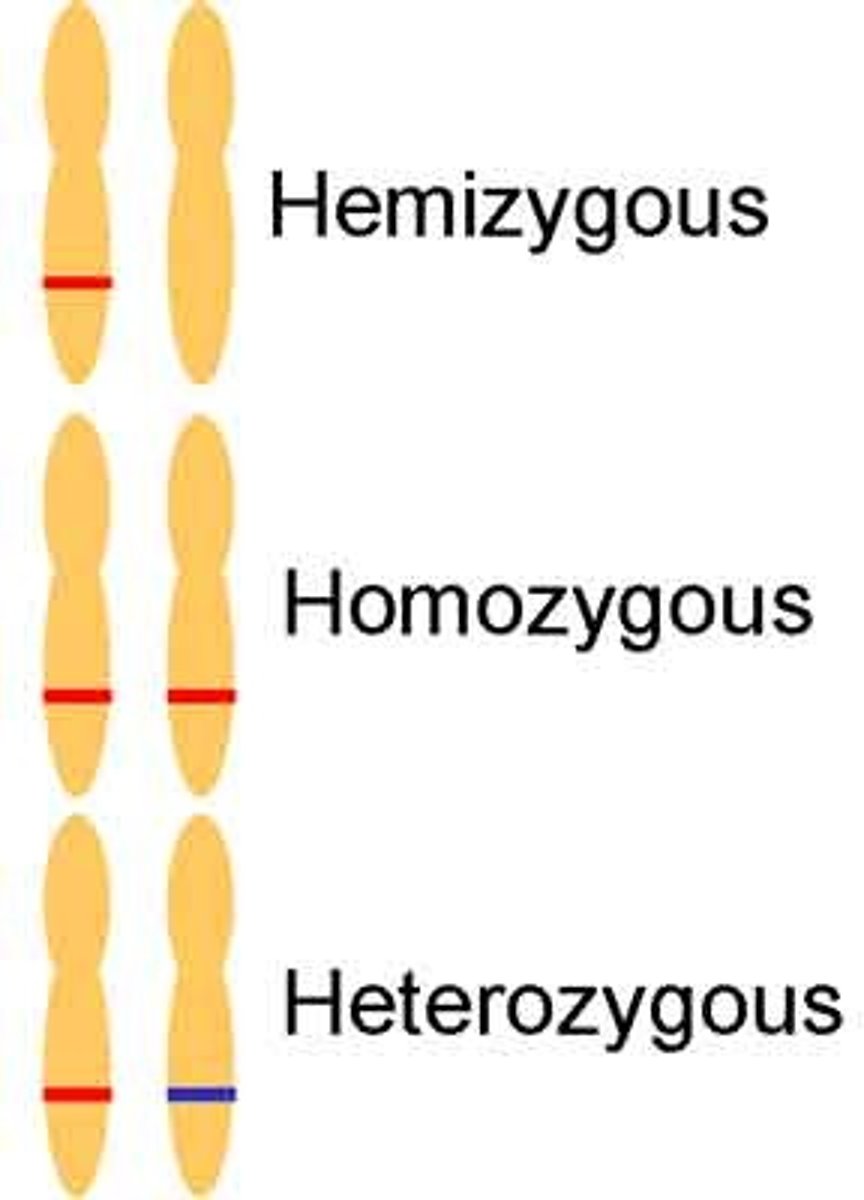
Genotype (types)
A combination of alleles one has at a given genetic locus.
Types:
1) Homozygous
2) Heterozygous
3) Hemizygous
Homozygous
Having two of the same allele
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles
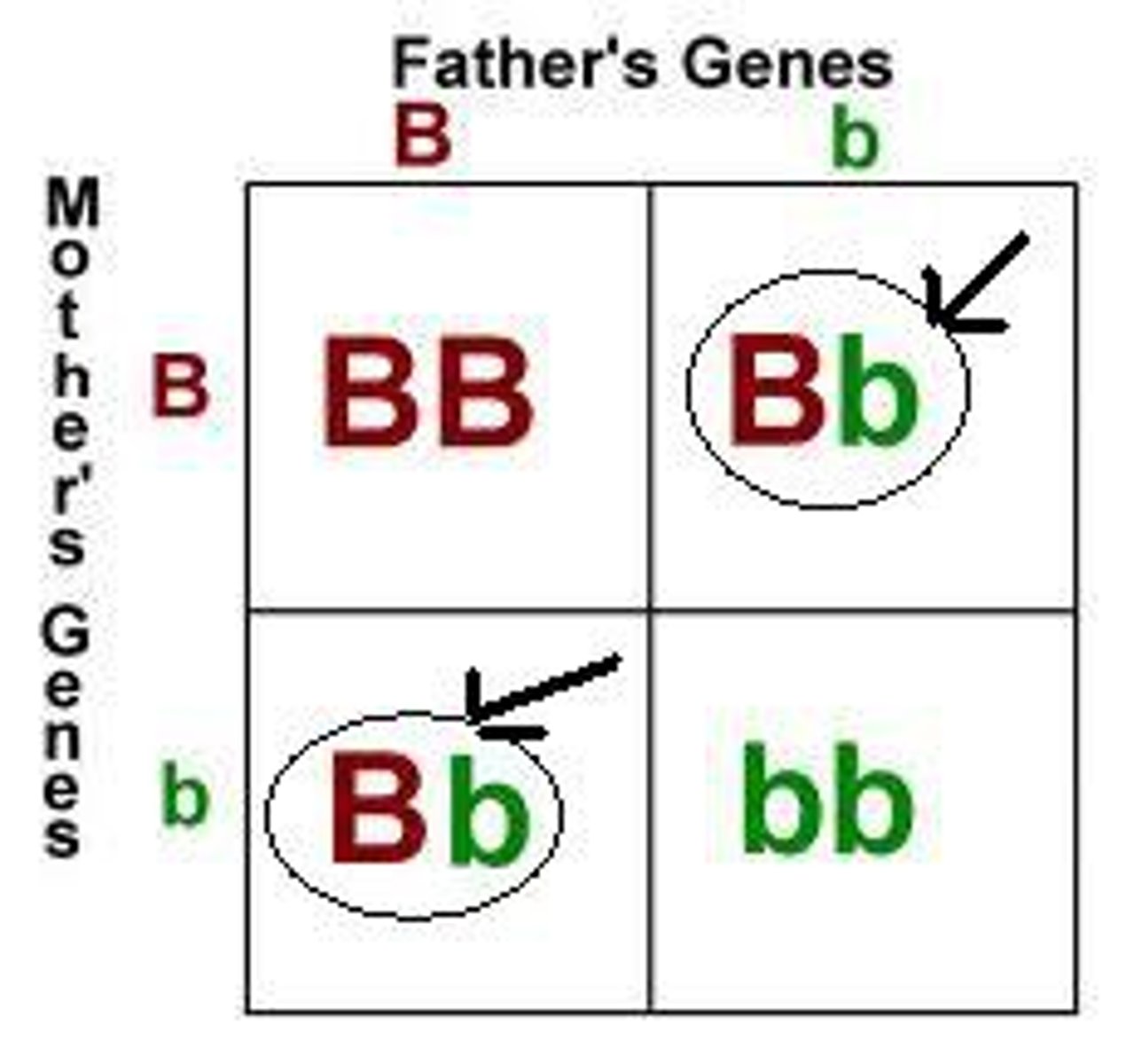
Hemizygous
Having only one allele (i.e. male-sex chromosome)
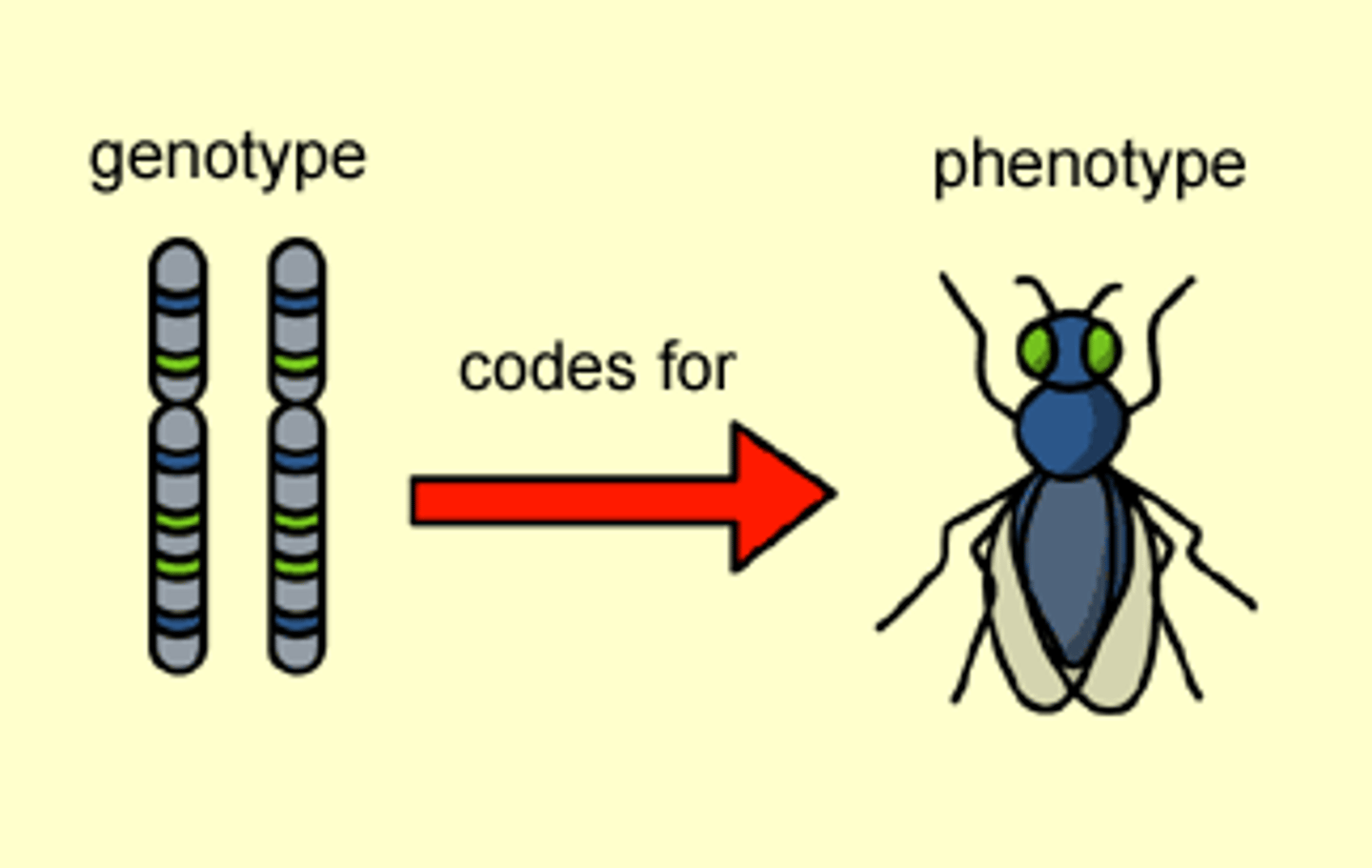
Phenotype
An observable manifestation of a genotype.
Patterns of dominance
Patterns:
1) Complete dominance
2) Codominance
3) Incomplete dominance
Complete dominance
One dominate allele and one recessive allele

Codominance
Has more than one dominate allele
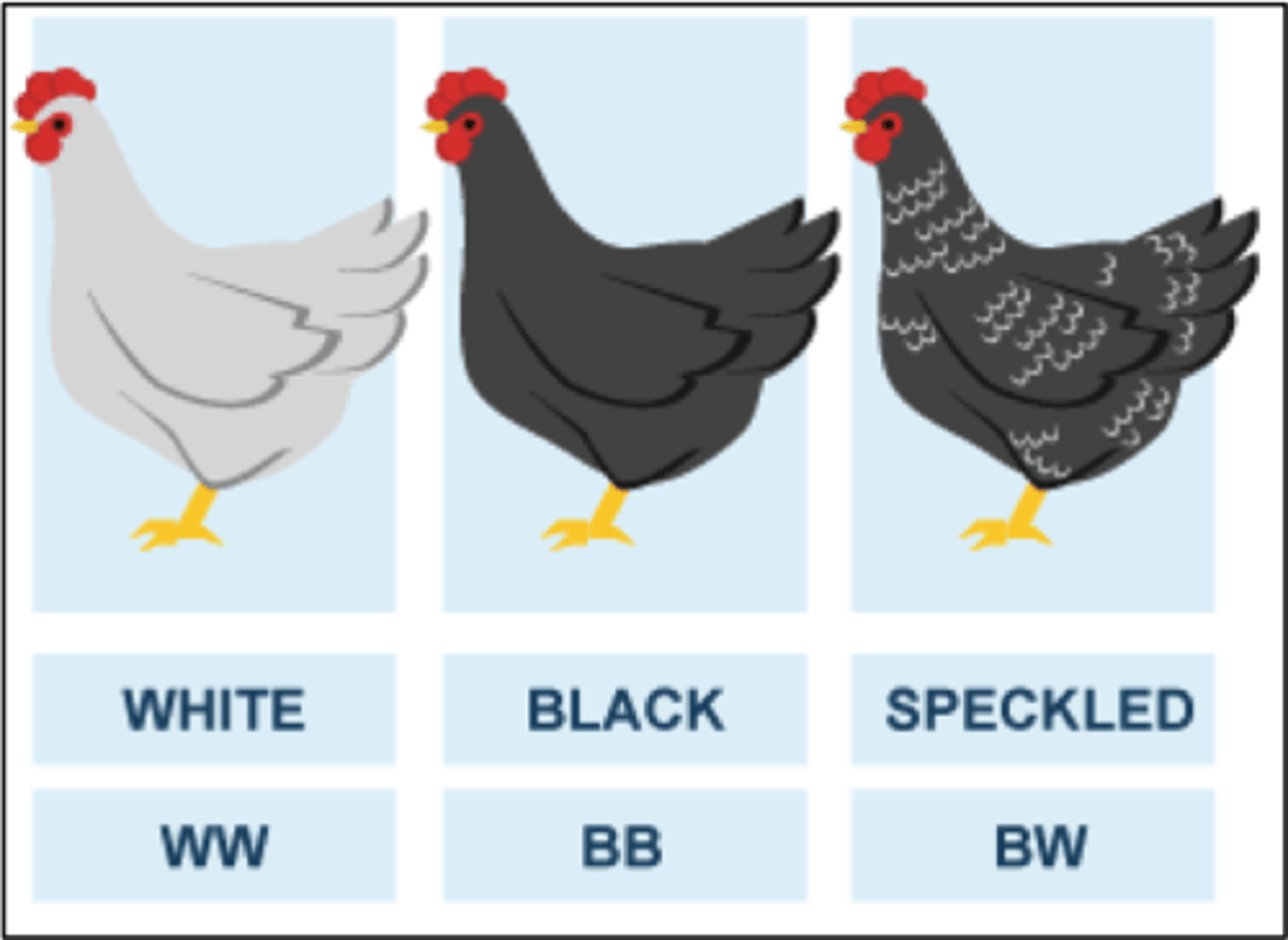
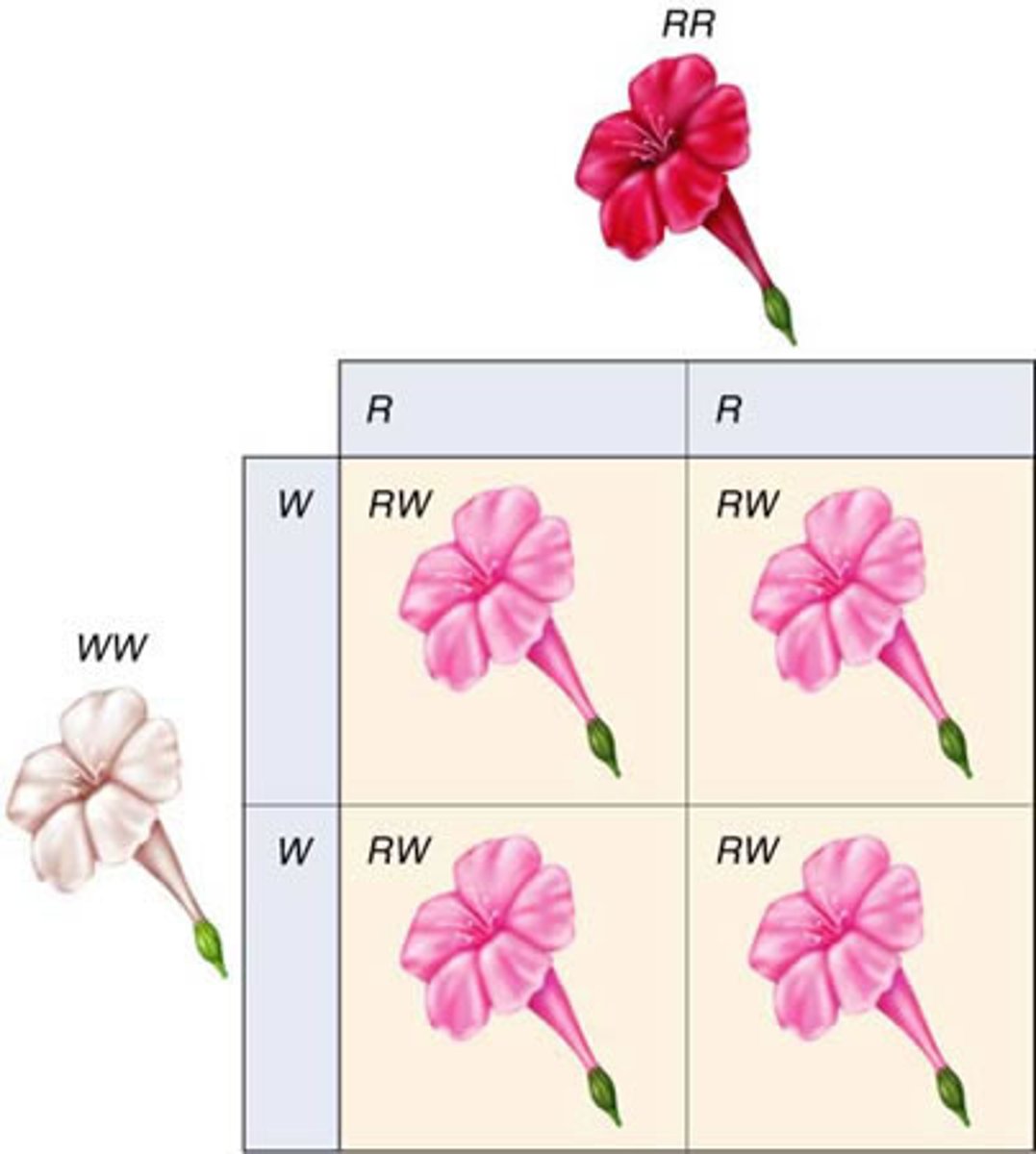
Incomplete dominance
Has no dominate alleles; heterozygotes have intermediate phenotypes.
Results in a mixture of the two alleles (i.e., pink flowers out of red and white)!
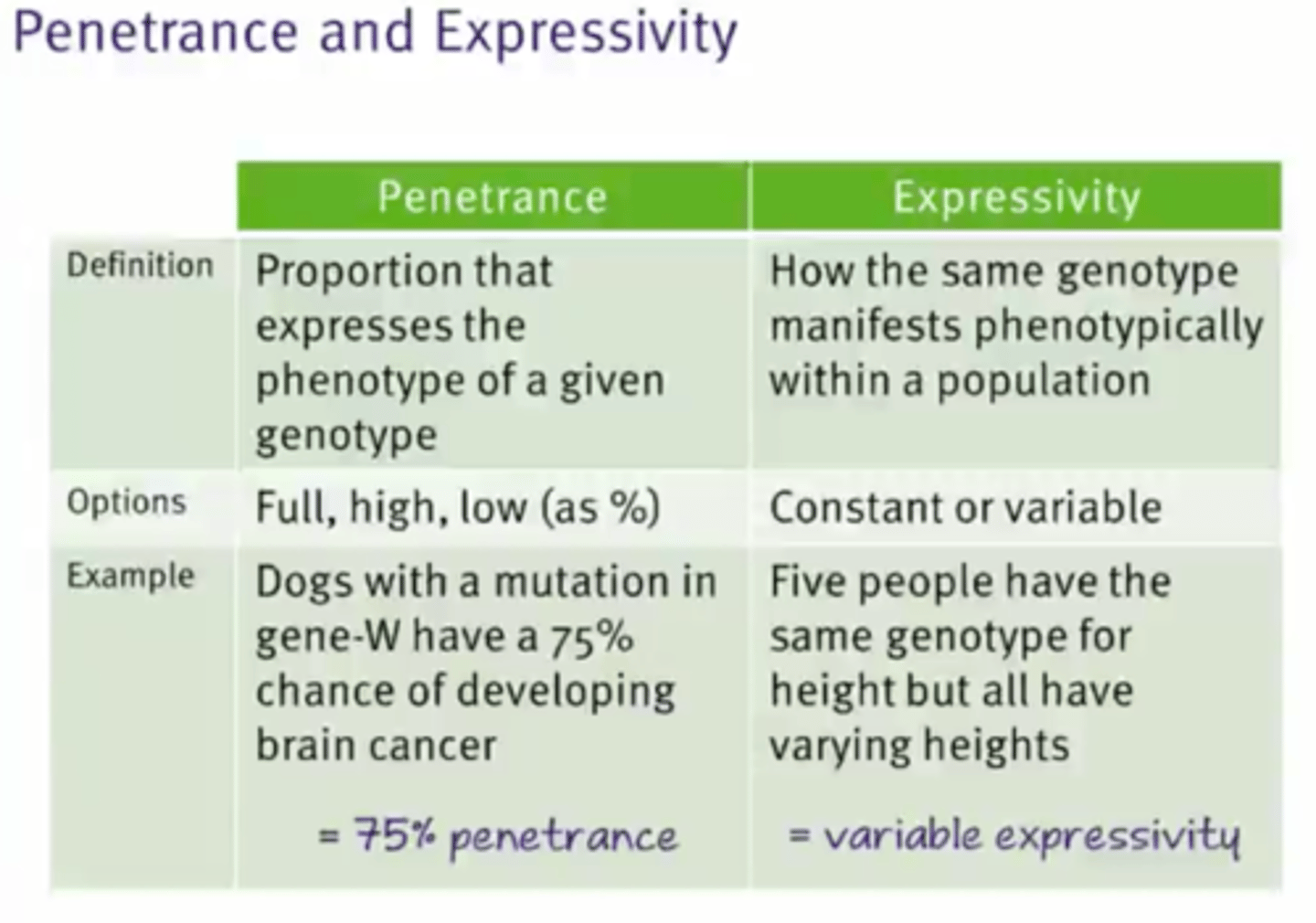
Penetrance
The proportion of the population with a genotype who express the phenotype
Expressivity
Refers to the varying phenotypic manifestations of a given phenotype.
Penetrance and Expressivity overview
Mendel's first law (of segregation)
States that an organism:
1) Has two alleles for each gene
2) Which separate during meiosis
3) Resulting in gametes
4) Carrying only one allele for a trait

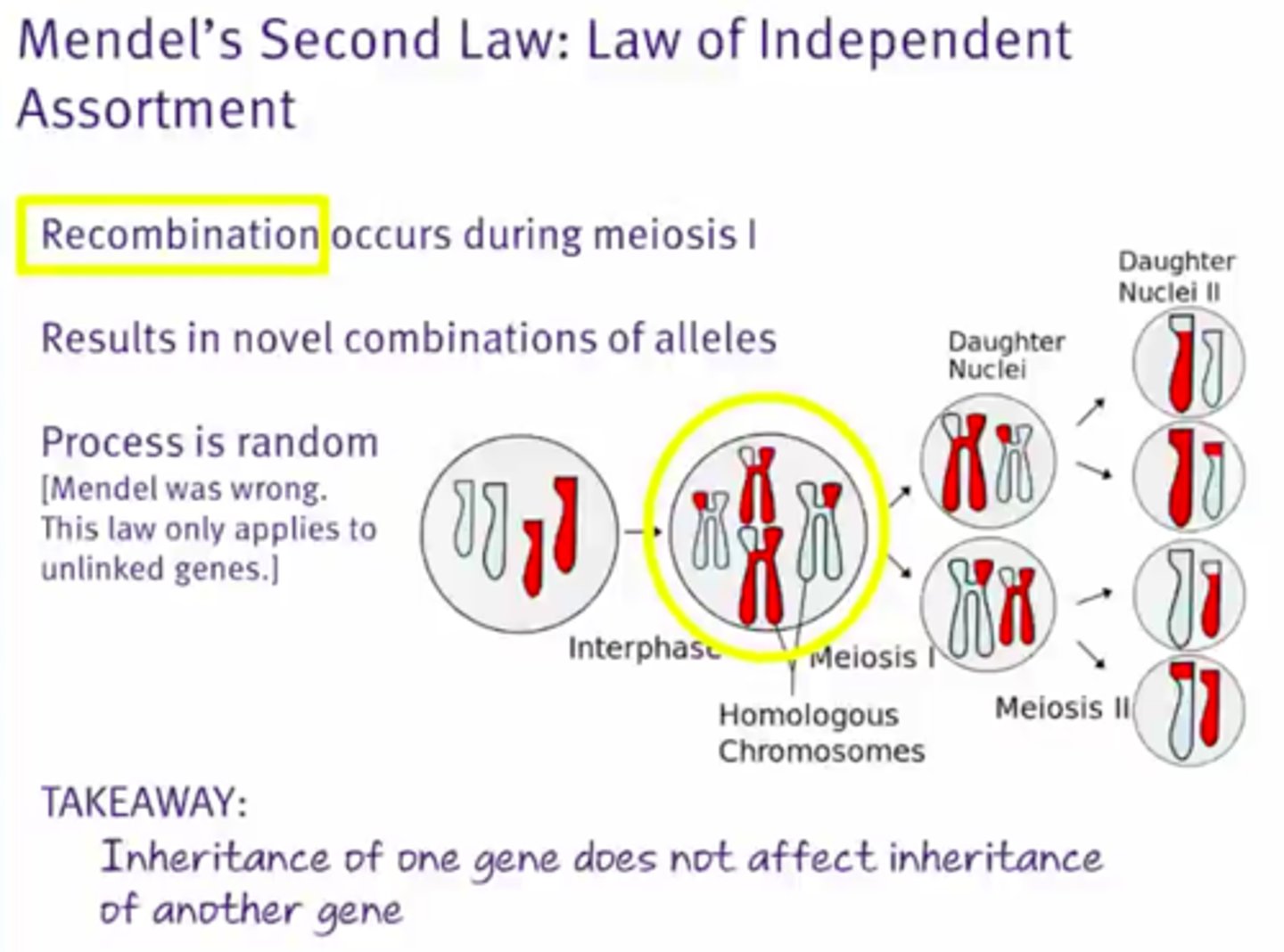
Mendel's second law (of independent assortment)
States that the inheritance of one gene does not affect the inheritance of another gene
Gene pool
All of the alleles in a given population
Mutations (Types)
Changes in the DNA sequence. Multiple types:
1) Point mutations
2) Frameshift mutations
3) Missense mutations
4) Nonsense mutations
Point mutations
A nucleotide mutation that involves the substituting of one nucleotide for another. Leads to silent mutations in wobble codon.
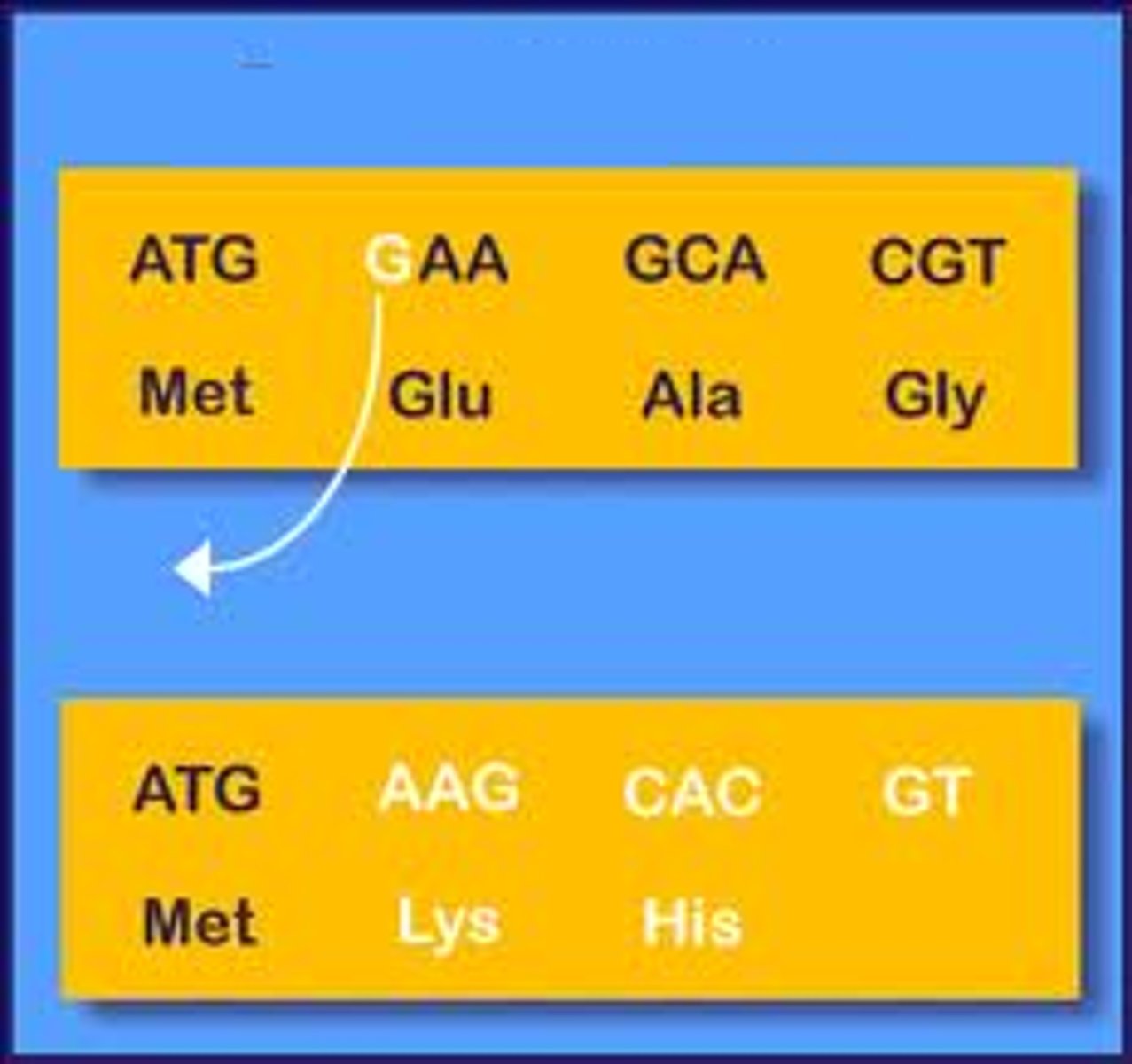
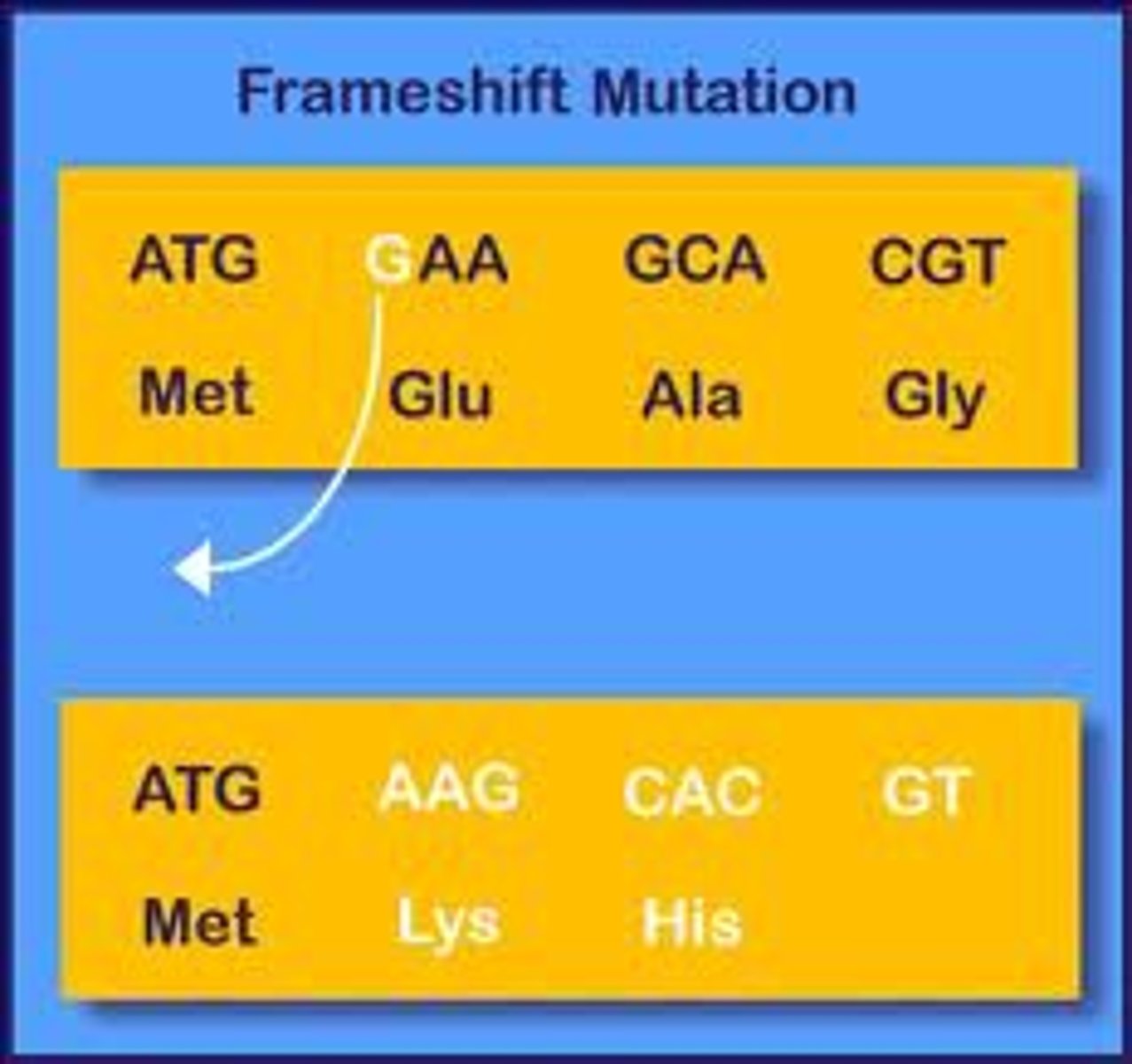
Frameshift mutations
Moving the three-letter transcriptional reading frame by inserting or removing a codon. Often causes a misfolded protein.
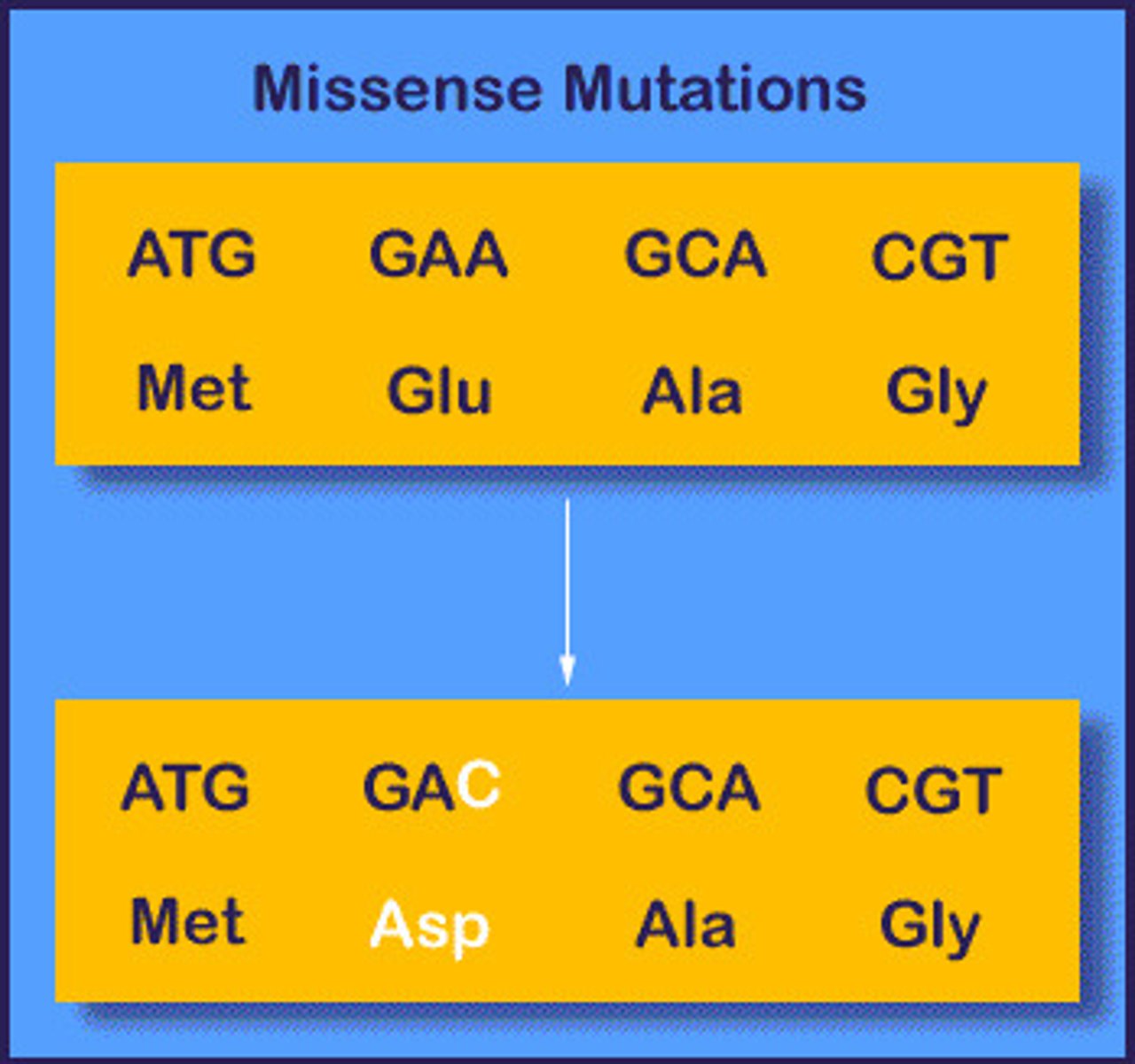
Missense mutations
Results in the substitution of one amino acid for another.
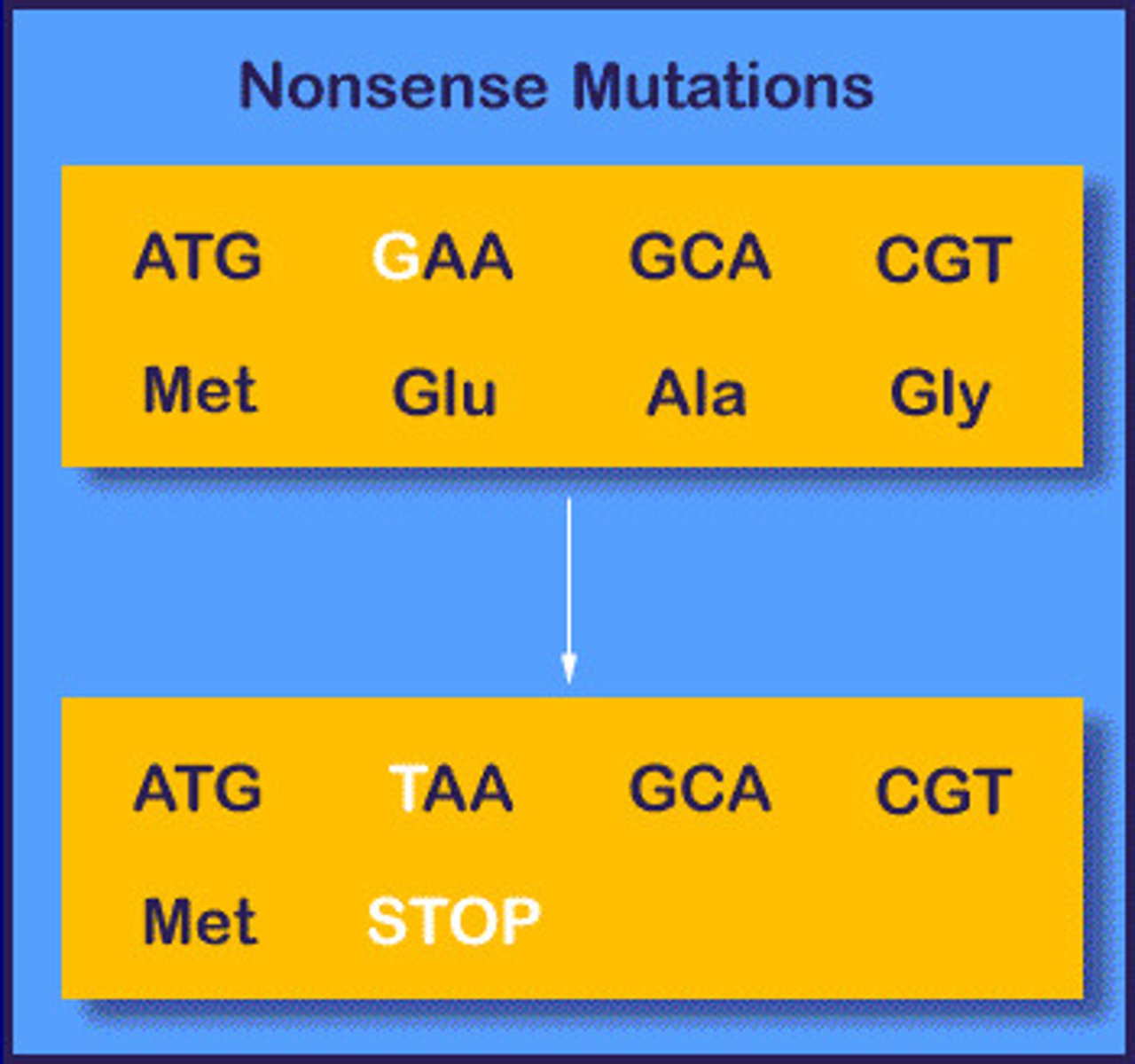
Nonsense mutations
Result in the substitution of a stop codon for an amino acid.
Chromosomal mutations (types)
Larger-scale mutations that affect whole segments of DNA.
Include:
1) Deletion mutations
2) Duplication mutations
3) Inversion mutations
4) Insertion mutations
5) Translocation mutations
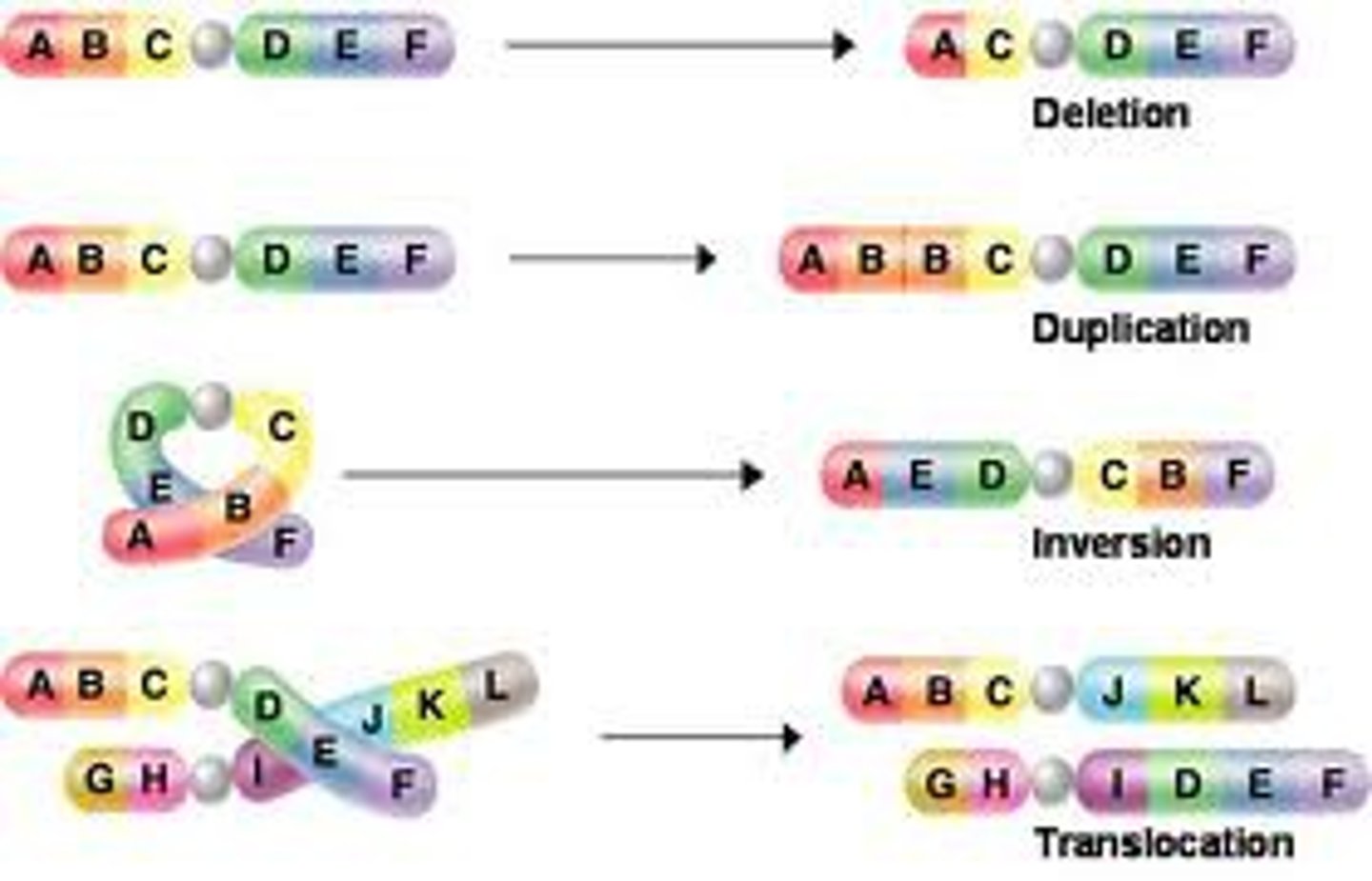
Deletion mutations
Occurs when a large segment of DNA is lost.
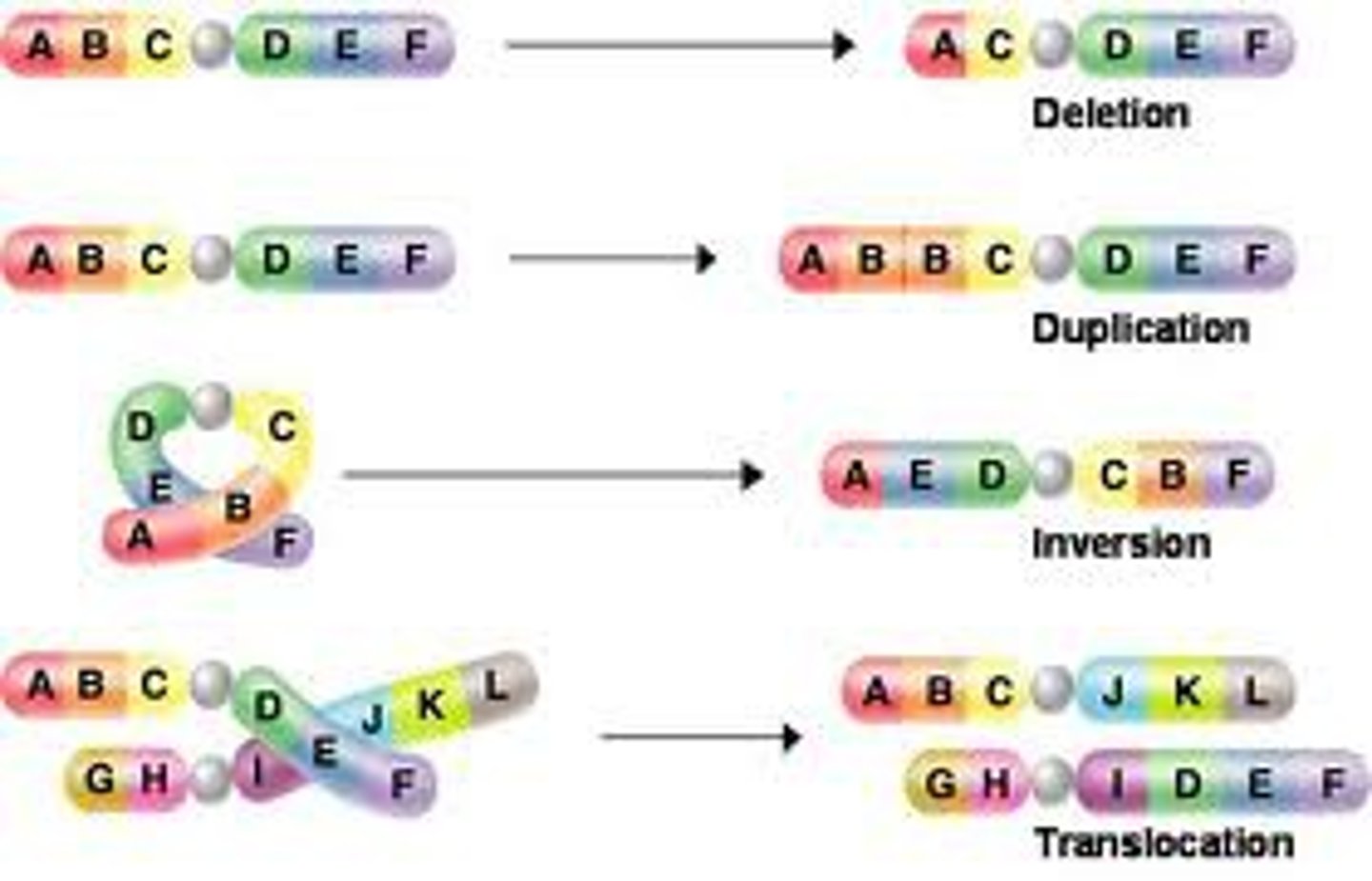
Duplication mutations
Occurs when a segment of DNA is copied multiple times.
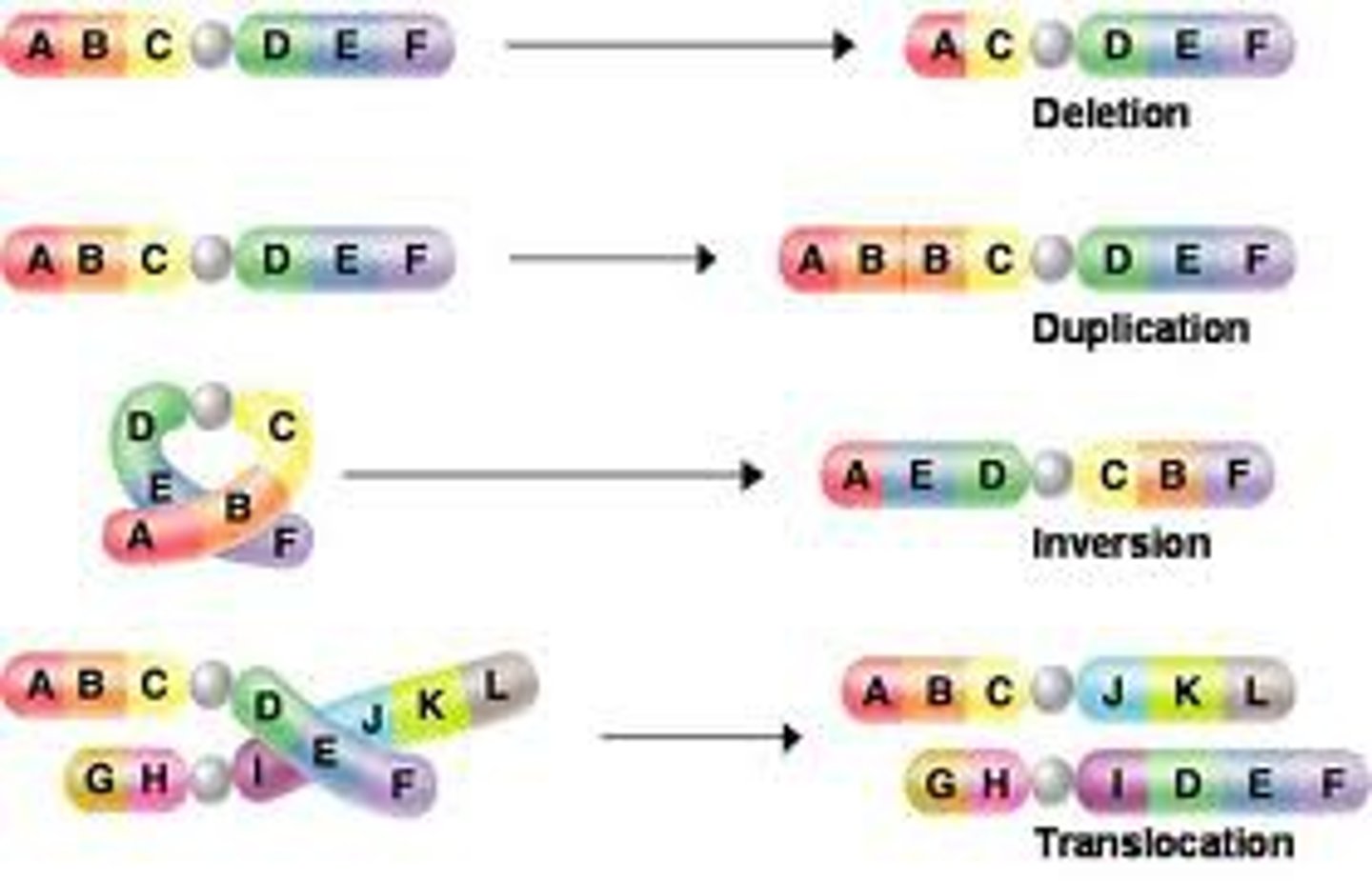
Inversion mutations
Occurs when a segment of DNA is reversed.
Least likely to cause an abnormality
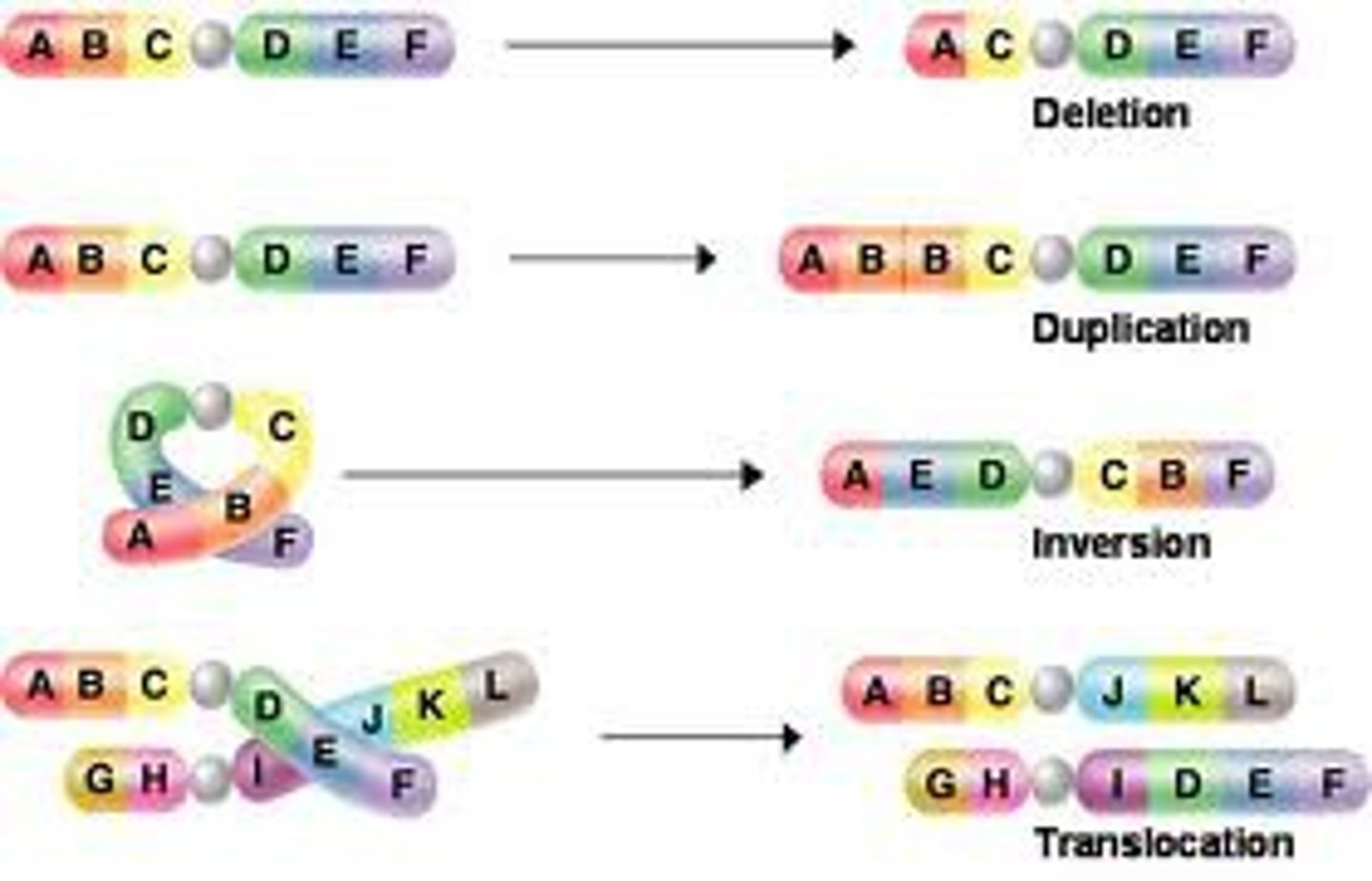
Insertion mutations
Occurs when a segment of DNA is moved from one chromosome to another.
Translocation mutations
Occurs when a segment of DNA is swapped with a segment of DNA from another chromosome.
Genetic leakage
The flow of genes between species through a hybrid offspring.
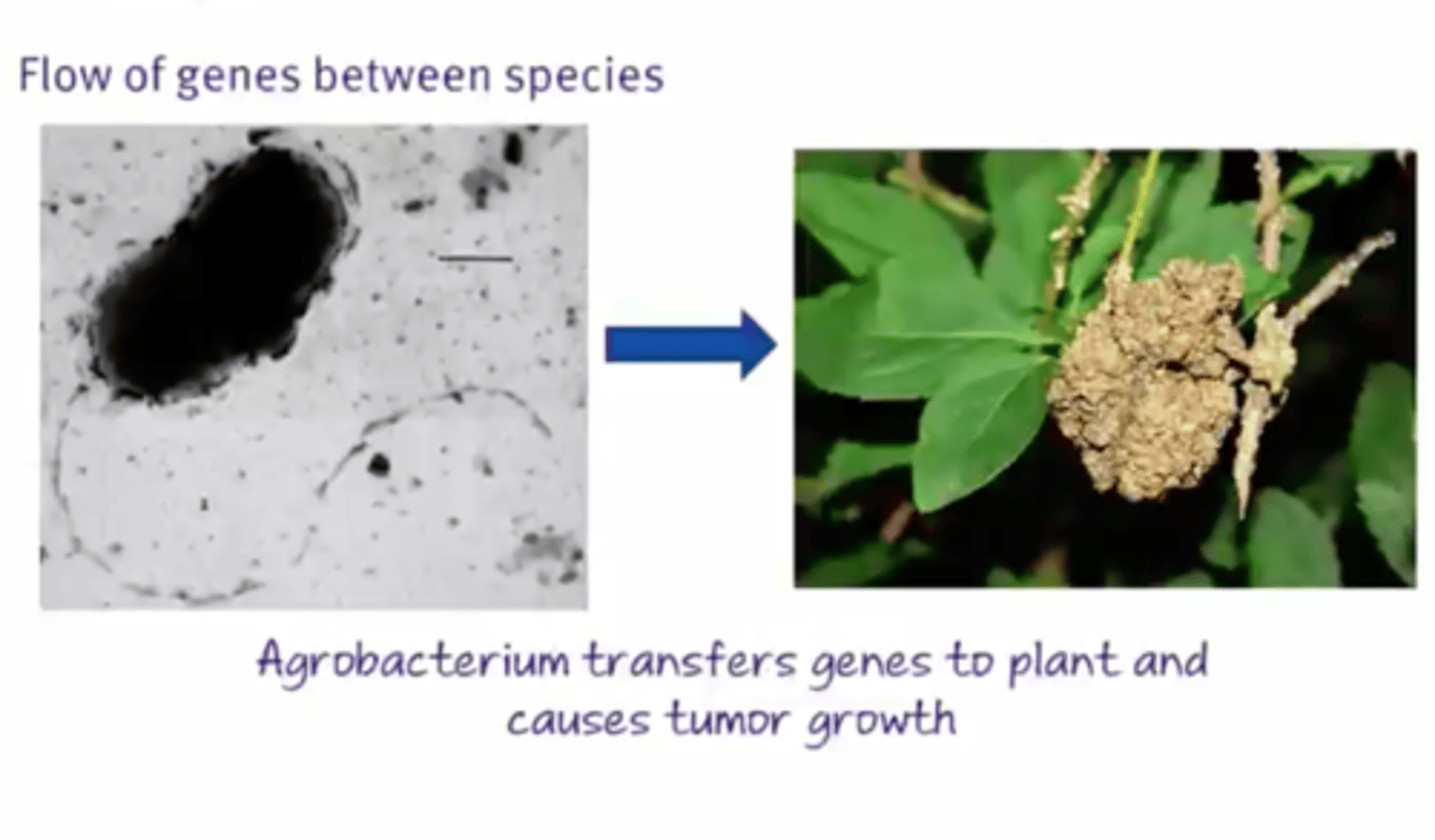
Genetic drift
Occurs when the composition of the gene pool changes as a result of chance.
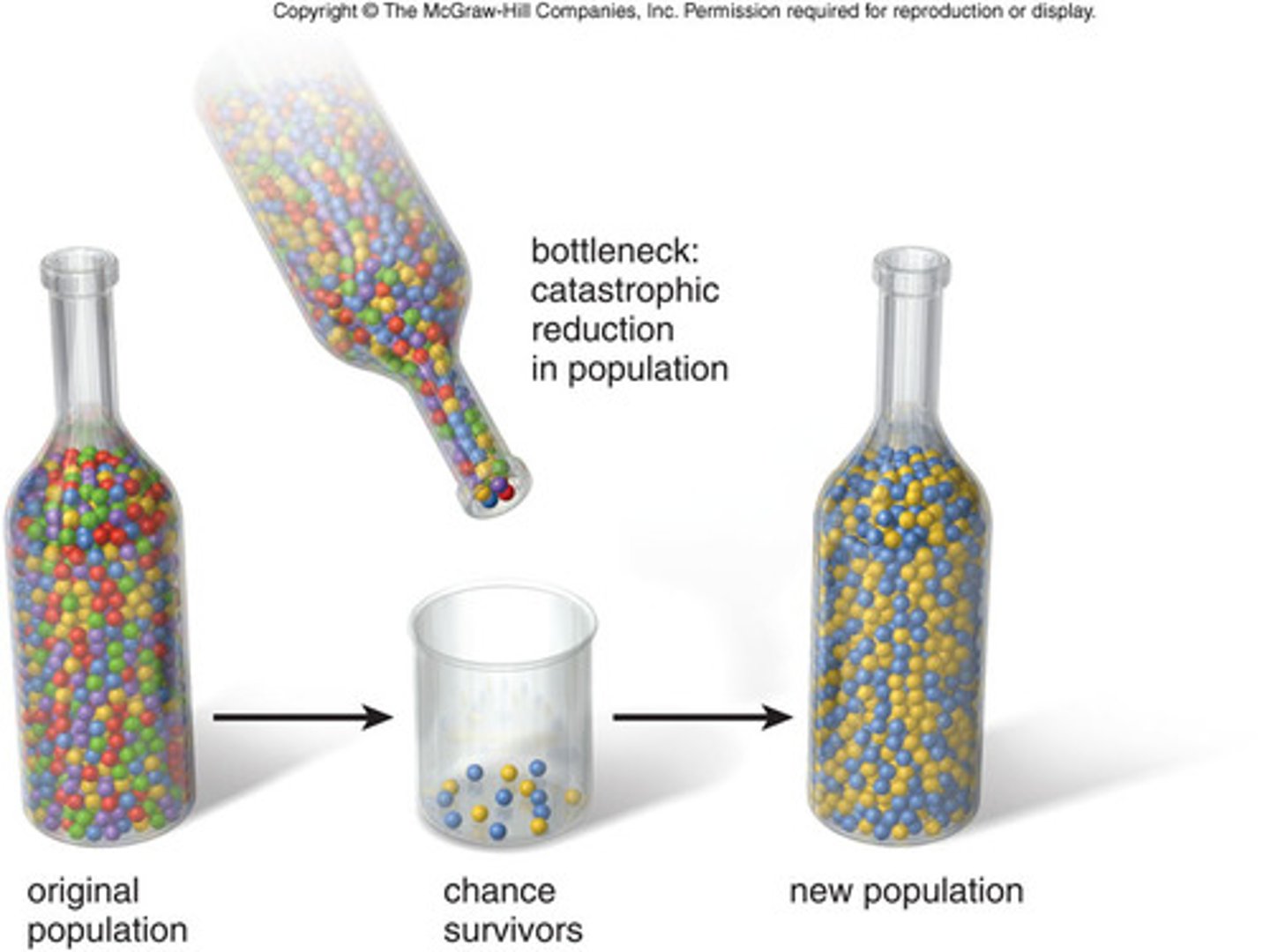
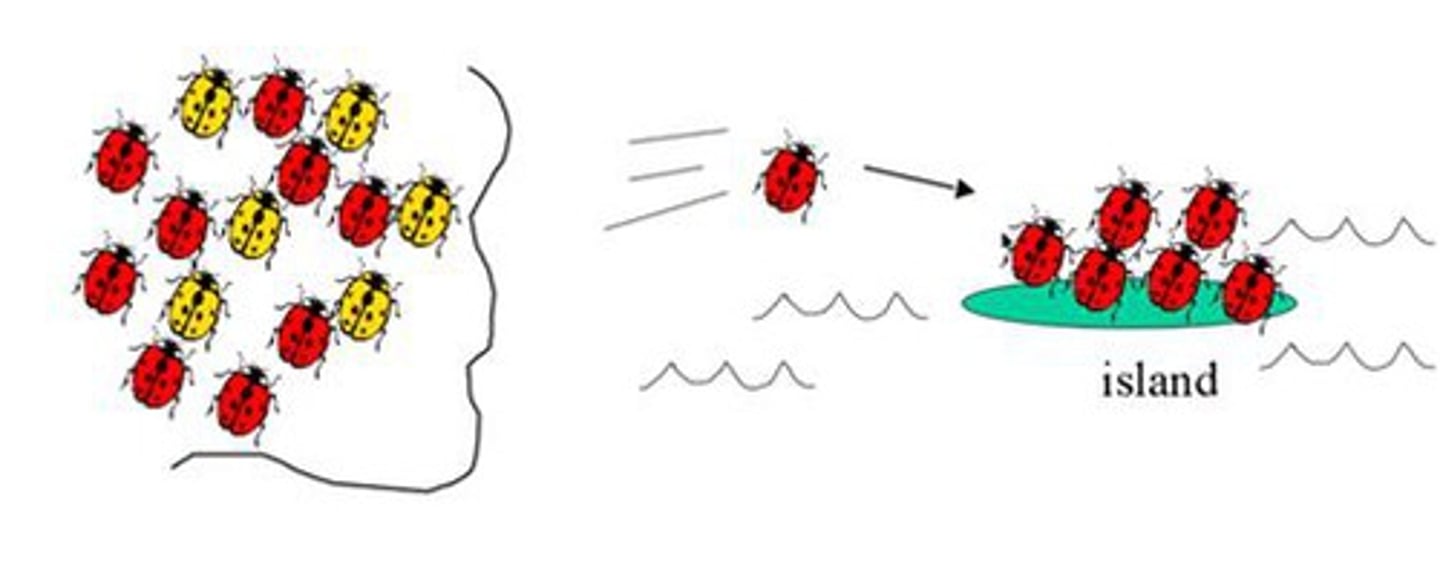
Founder effect
Results from a bottleneck that suddenly isolates a small population, leading to inbreeding and increased prevalence of certain homozygous genotypes.
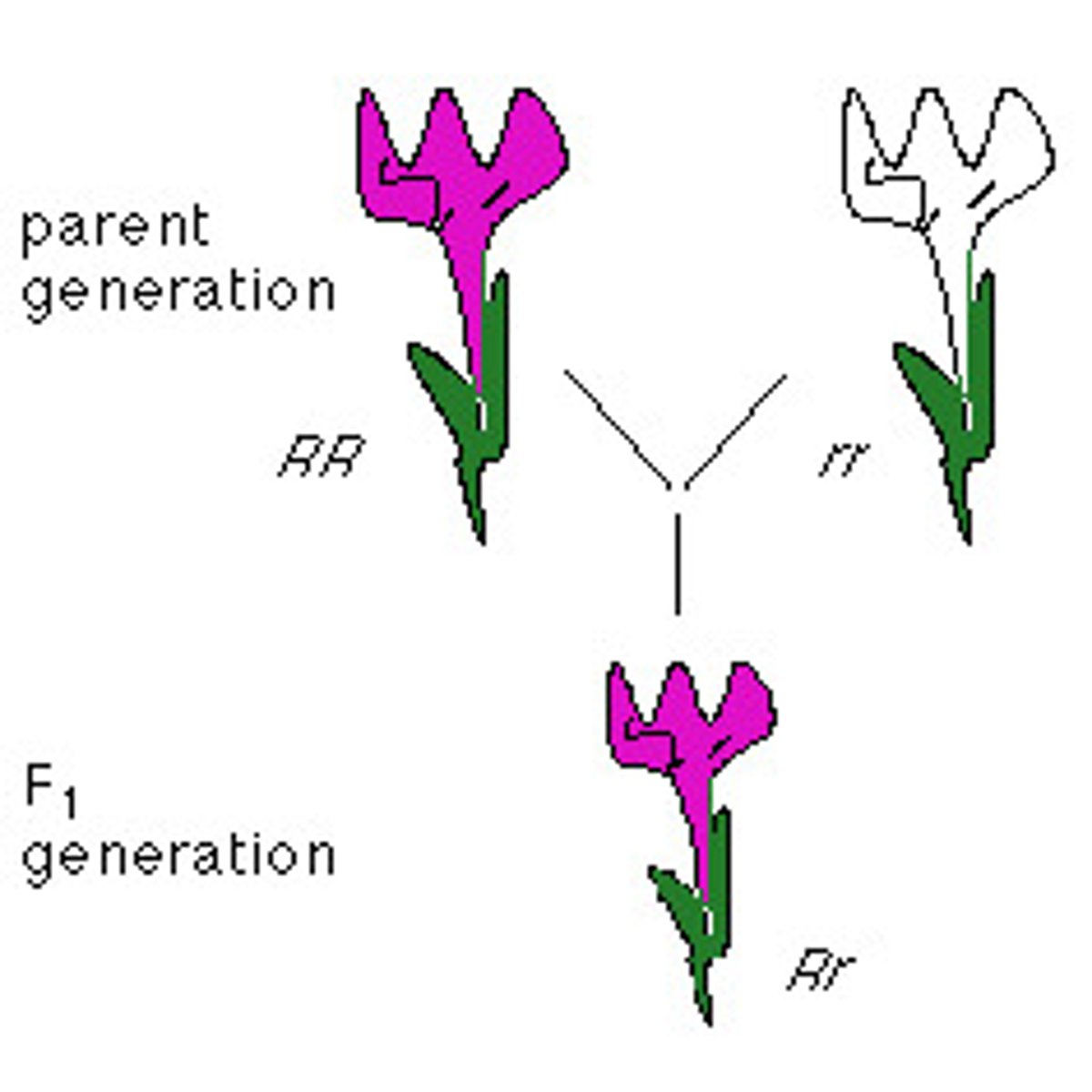
Parent generation
Represented by P1
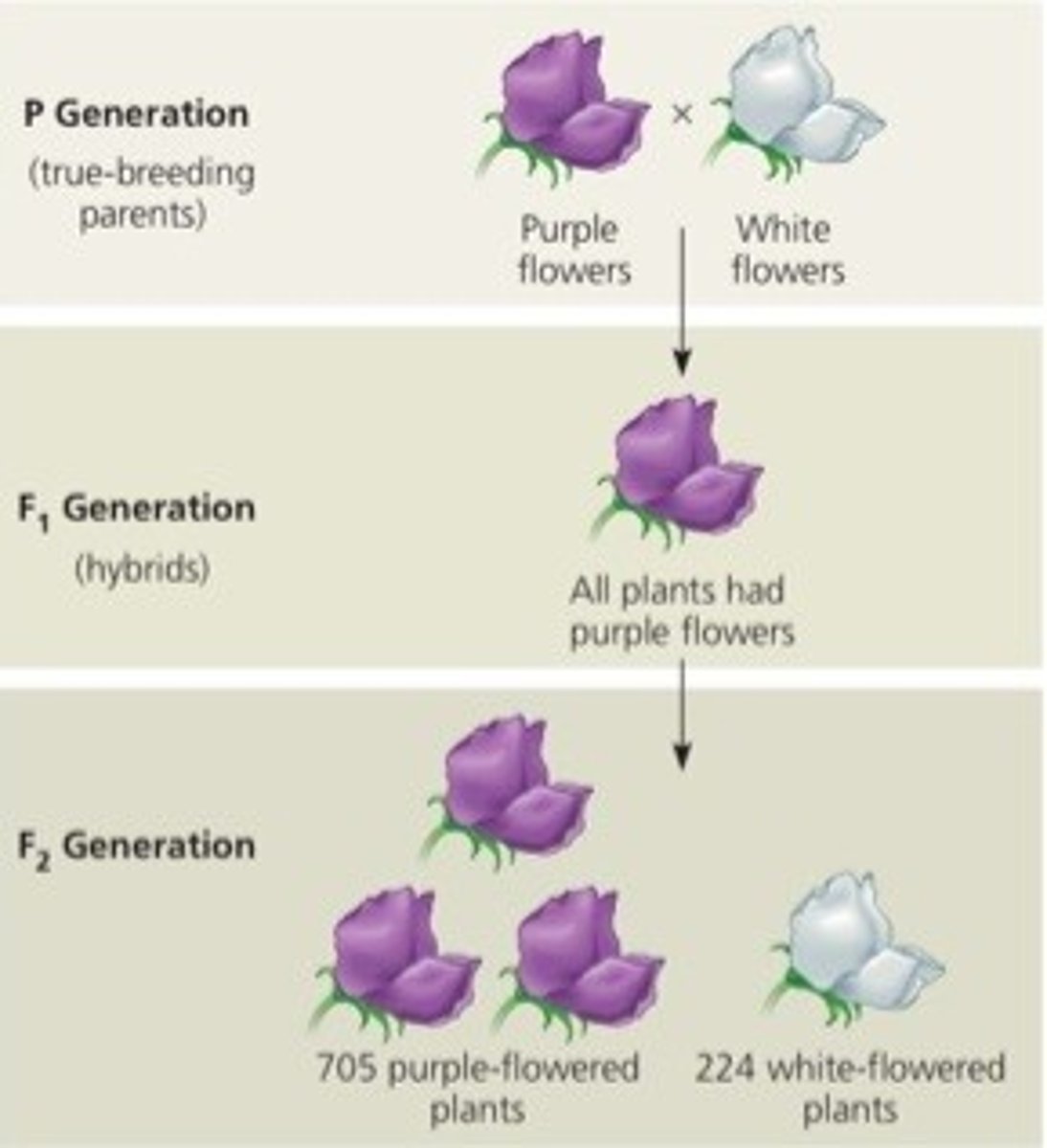
Filial (offspring) generations
Represented by F1, F2, and so on.
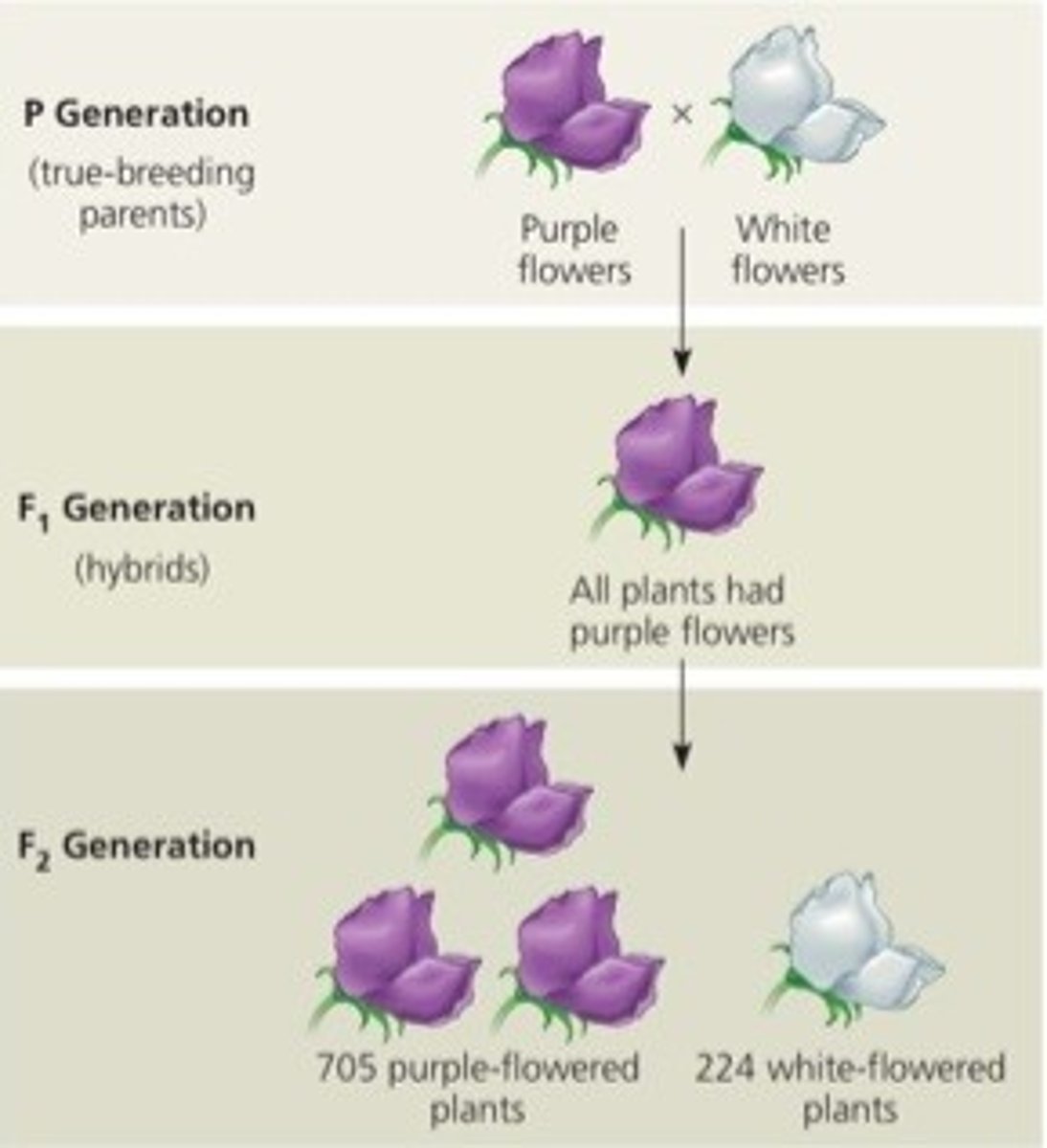
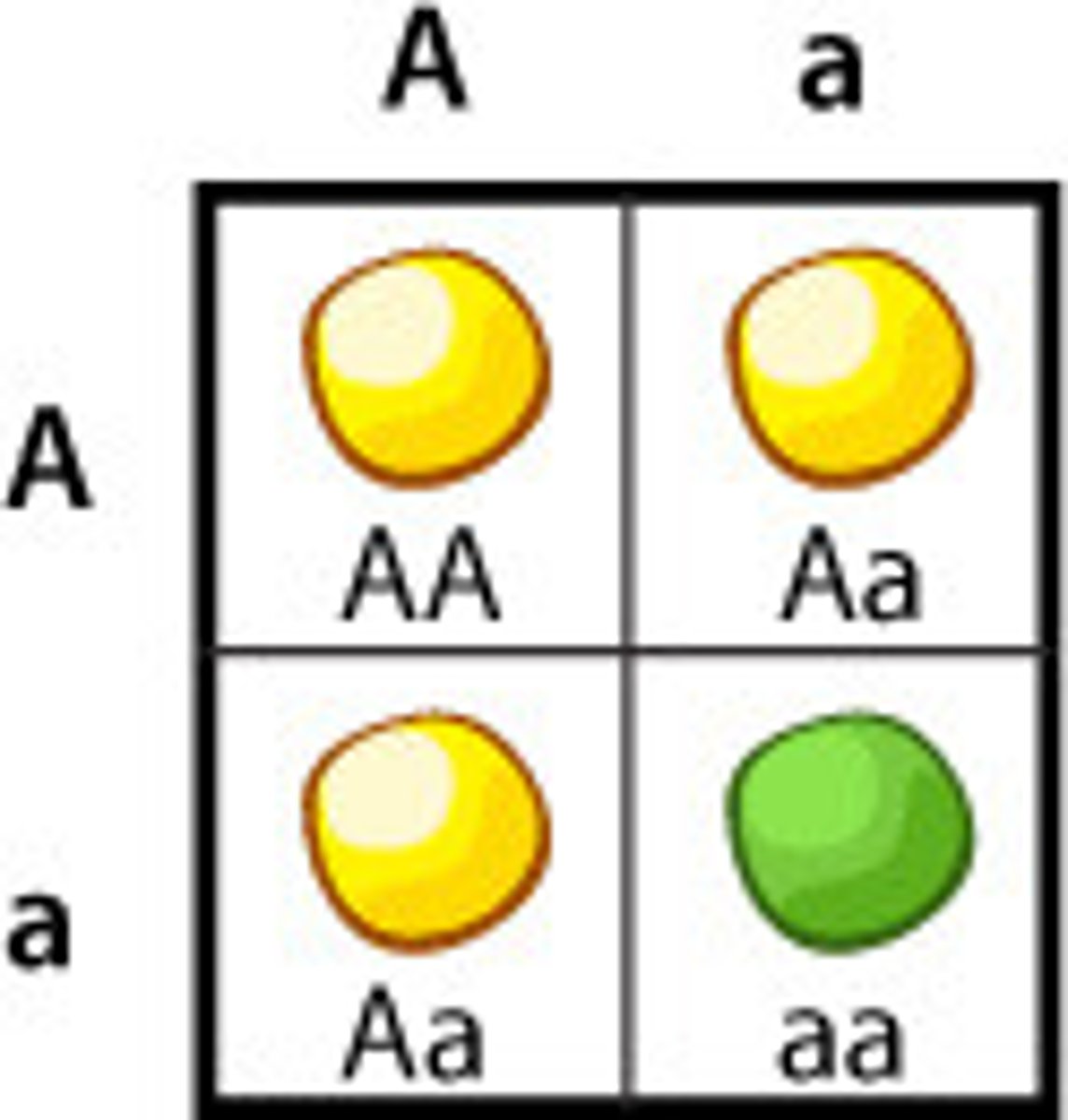
Monohybrid cross
Accounts for one gene
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
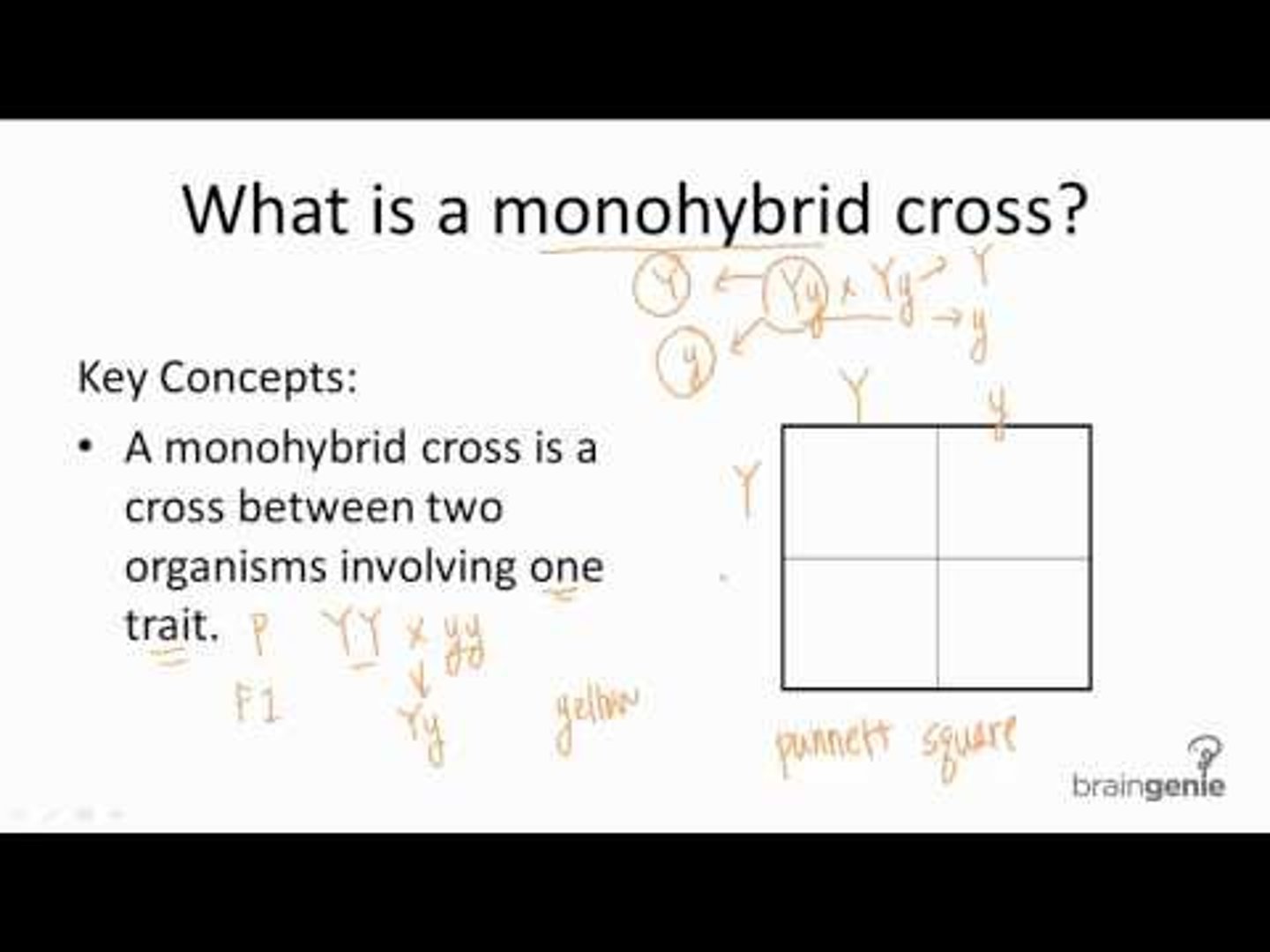
Phenotypic ratio for monohybrid cross?

Dihybrid cross
Accounts for two genes
Cross or mating between organisms involving two pairs of contrasting traits
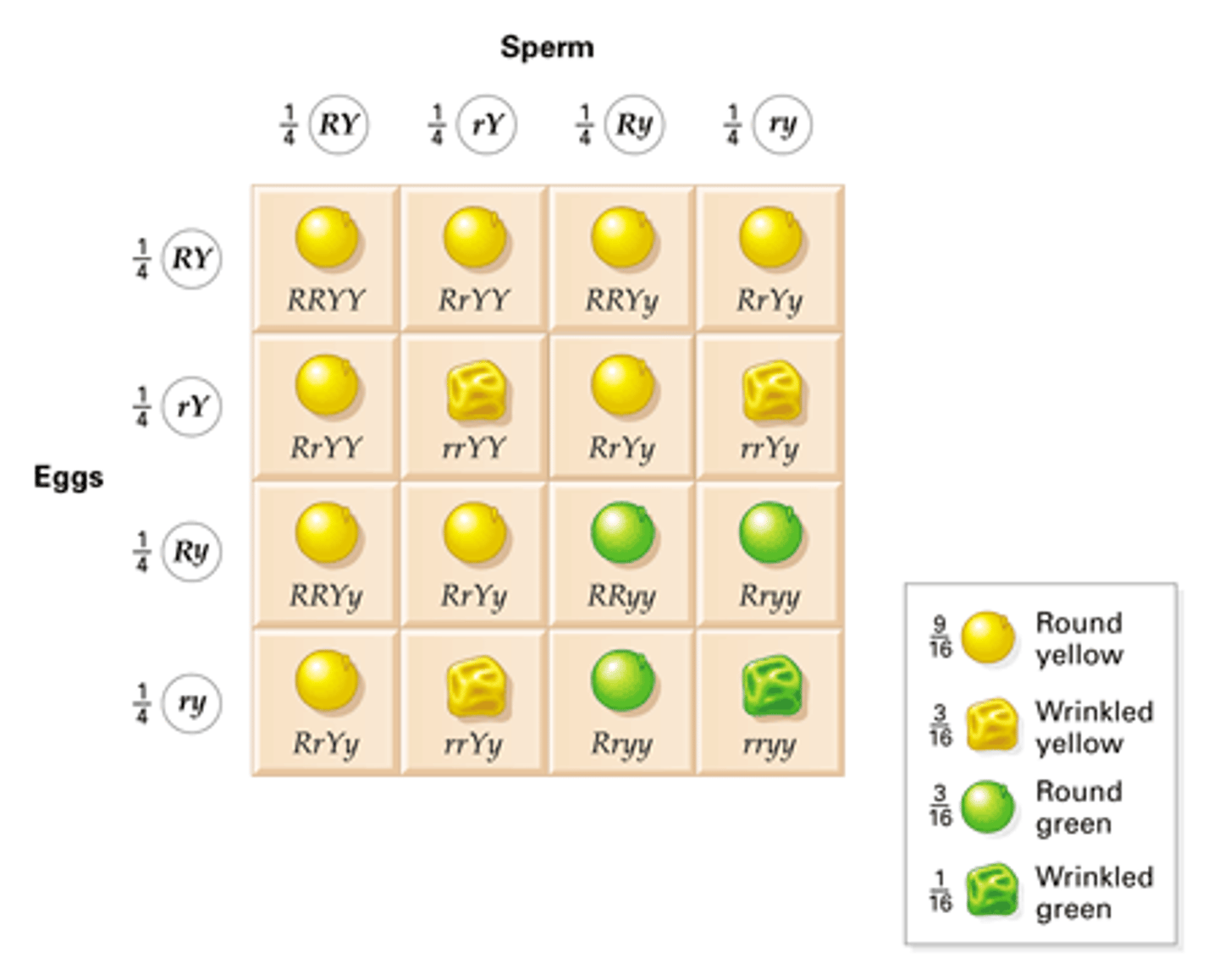
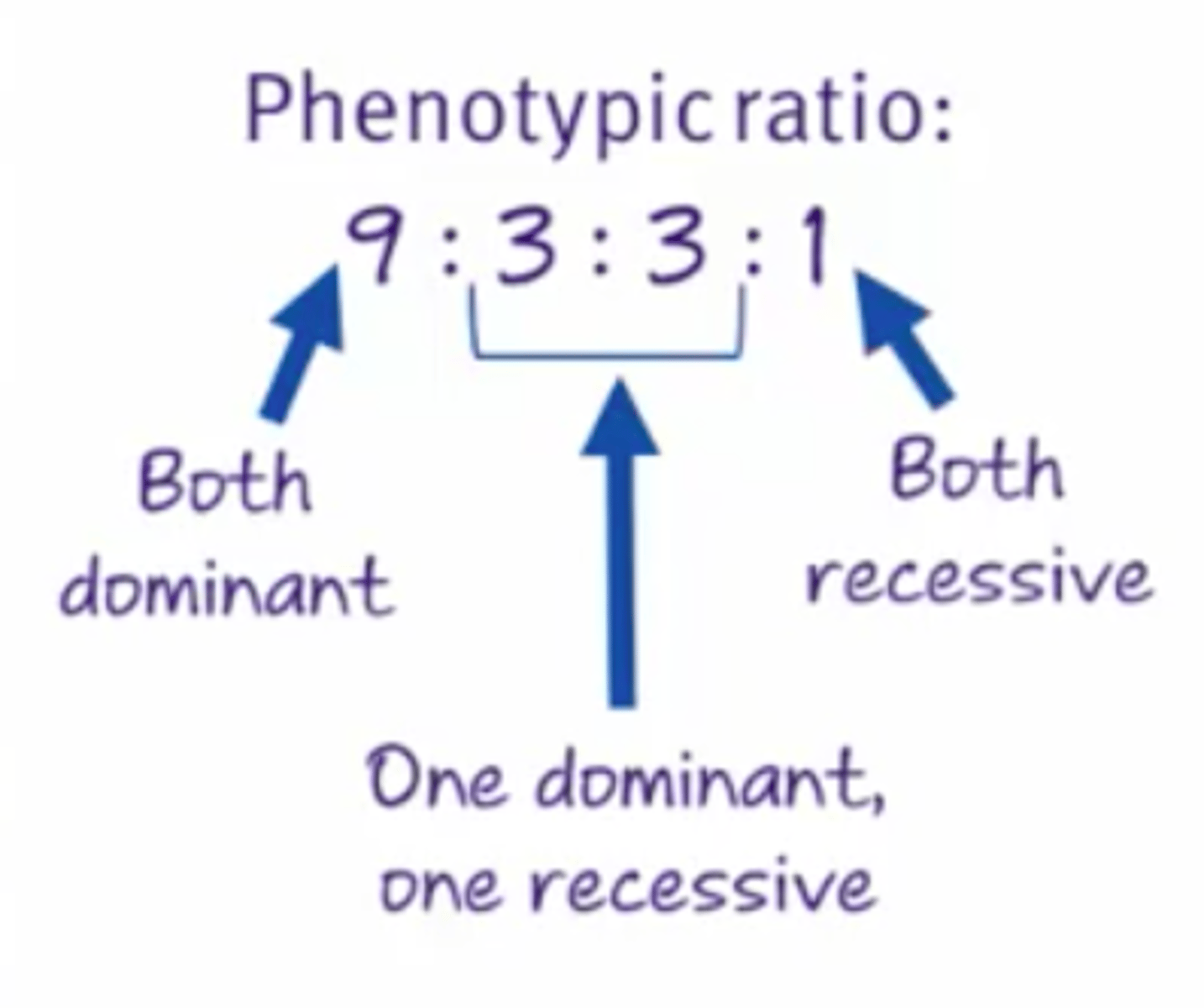
Phenotypic ratio for dihybrid cross?
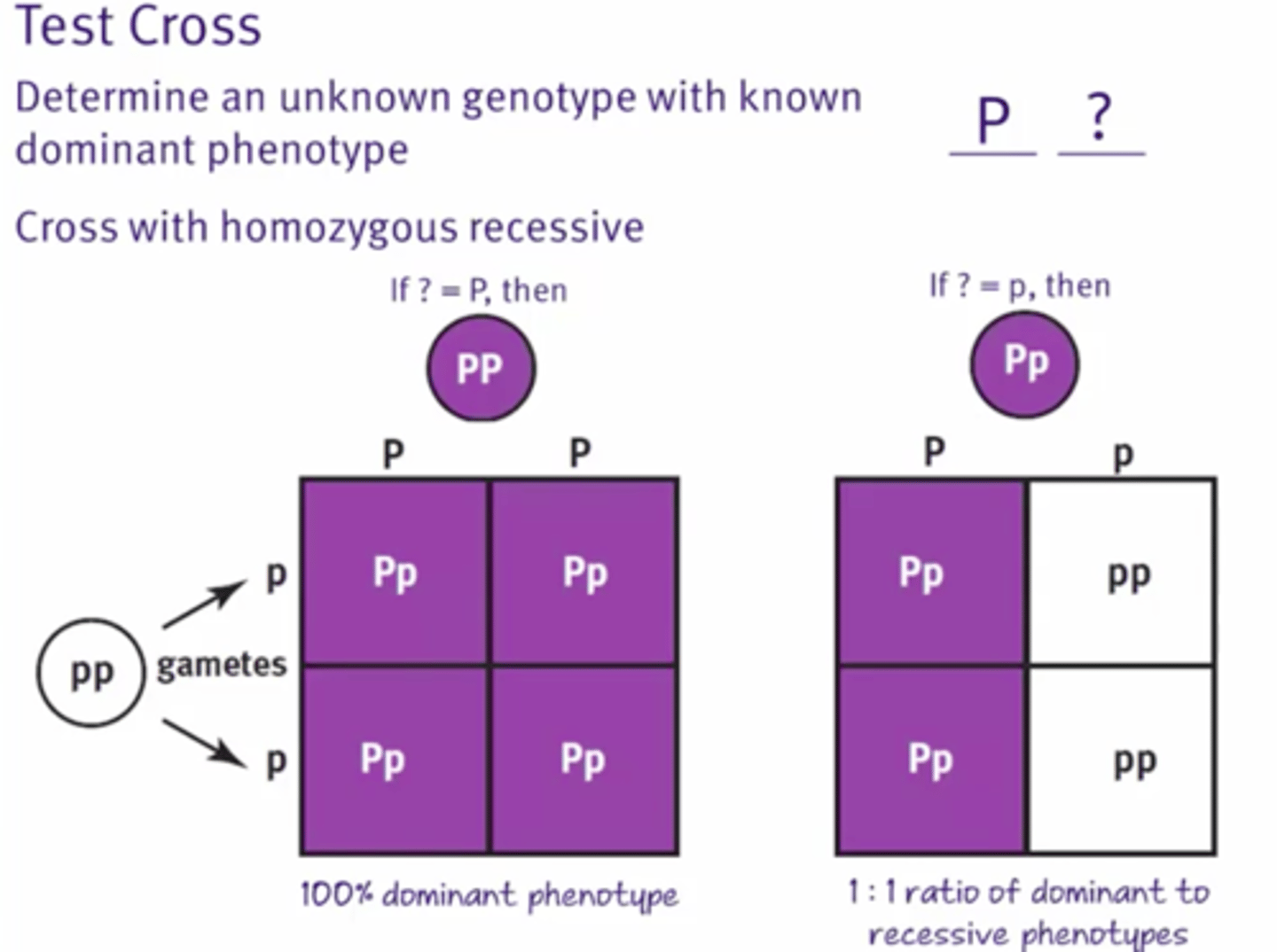
Test cross
Breeding the unknown parent with a homozygous recessive
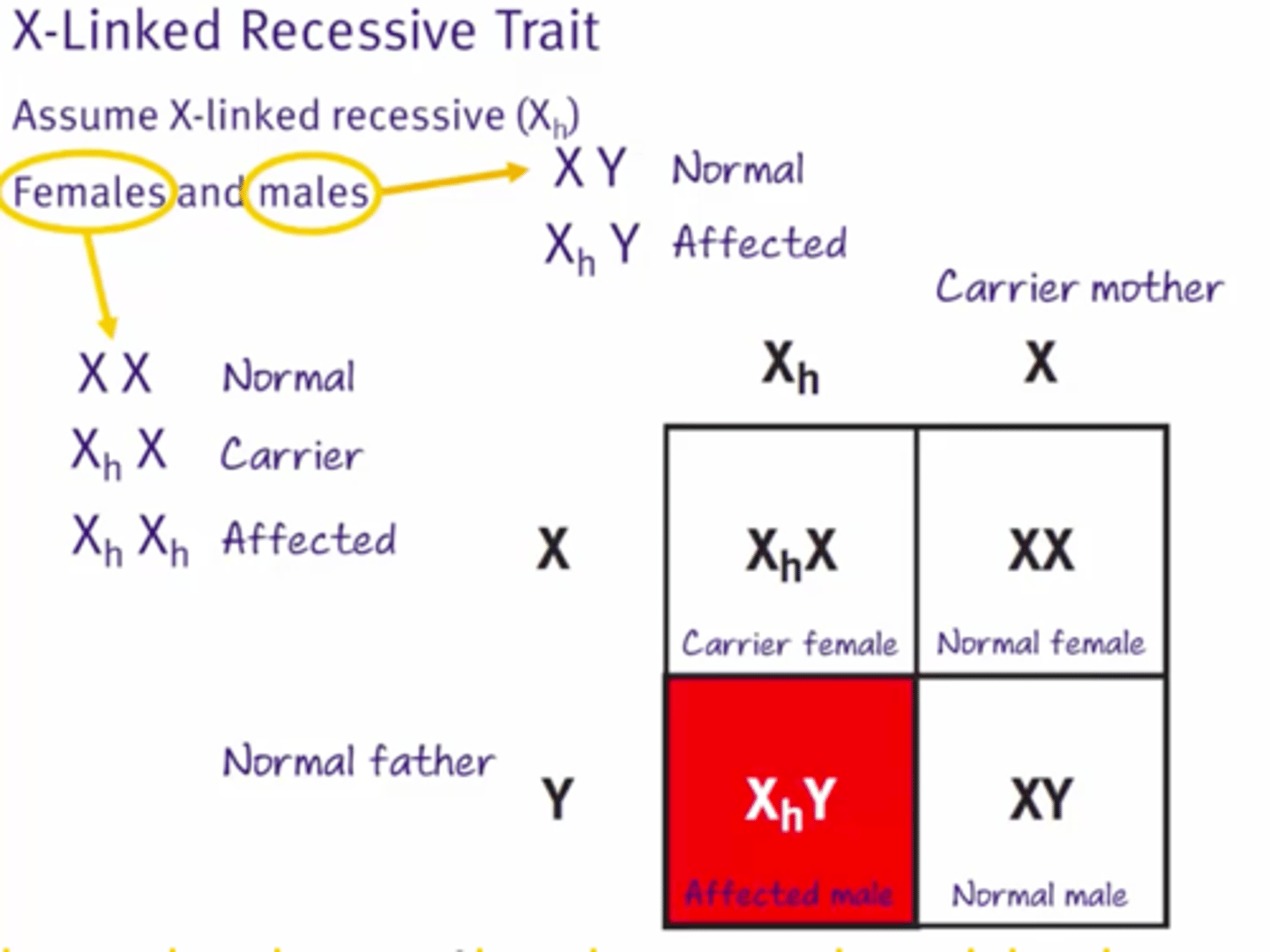
Sex-linked crosses
Sex chromosomes are usually used to indicate sex as well as genotype
SeX linked is X linked
X-linked trait is recessive
Recombination frequency
The likelihood of two alleles being separated during crossover by meiosis.
Genes that are close to each other have low recombination frequency because they are unlike to cross-over separately
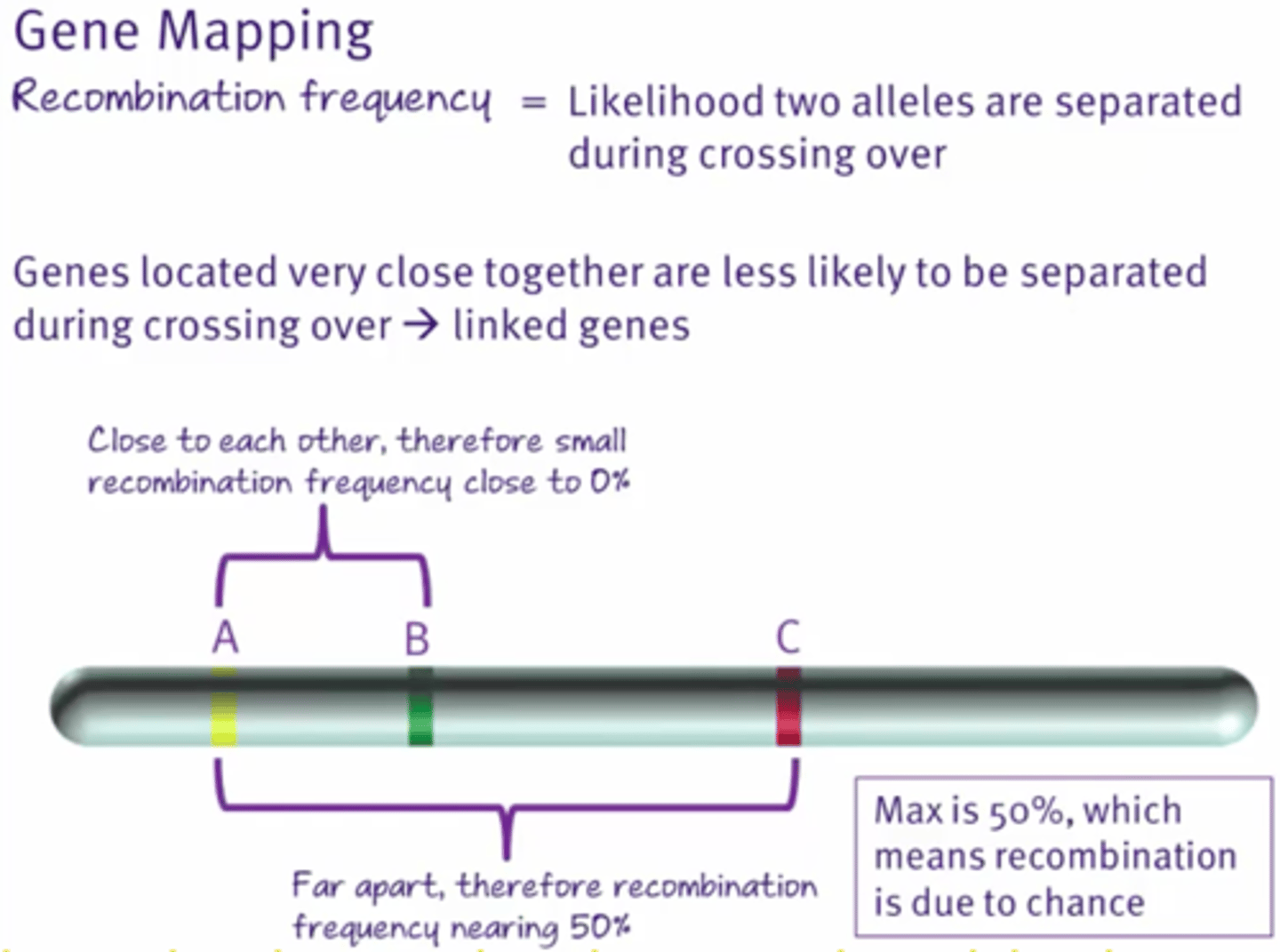
What is the maximum recombination frequency?
50% because it is a random process
Genetic maps
Maps made using recombination frequencies as the scale, in centimorgans.
Hardy-Weinberg principle
States that if a population meets certain criteria (aimed at a lack of evolution), then the allele frequencies will remain constant (Hardy-weinberg equilibrium).
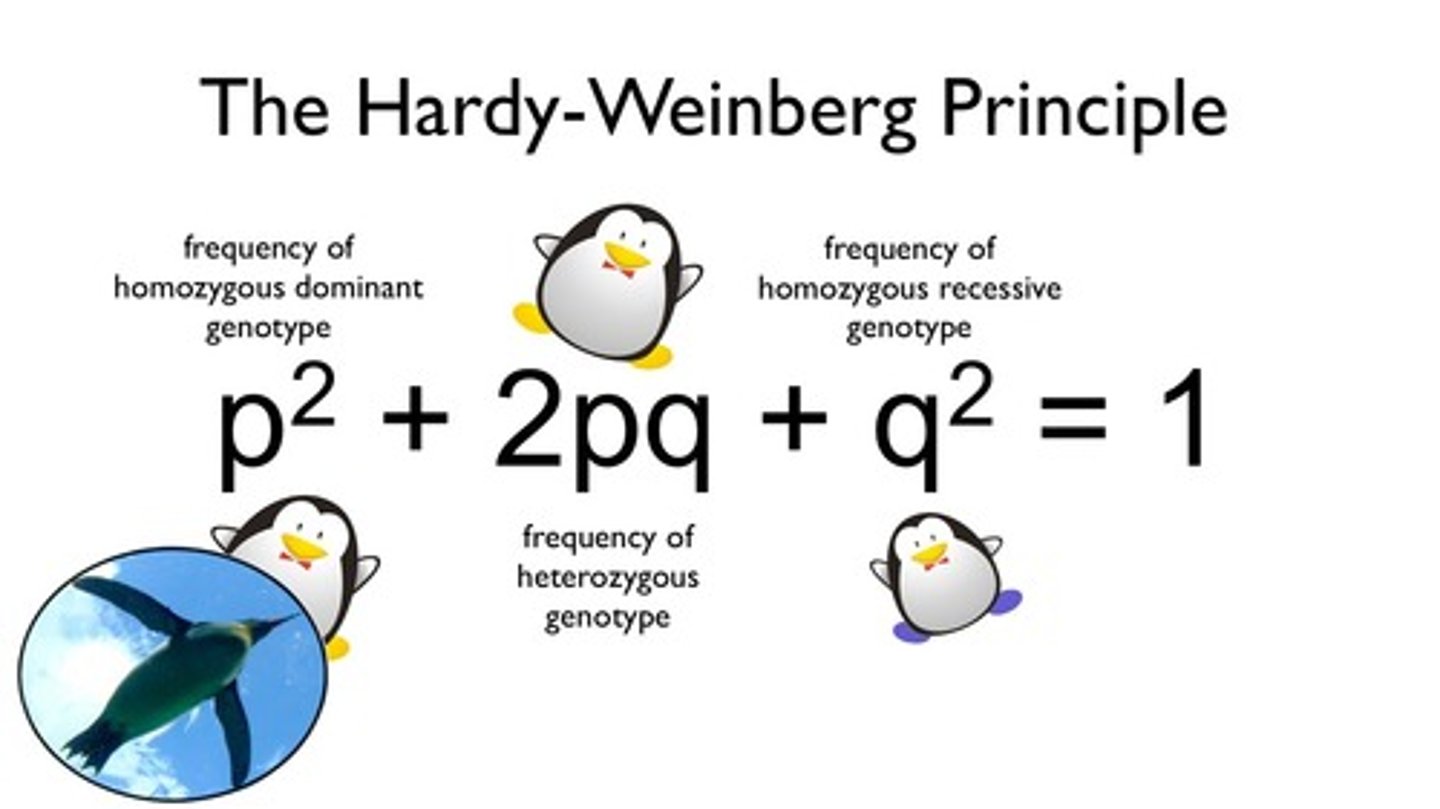
Hardy-weinberg equations
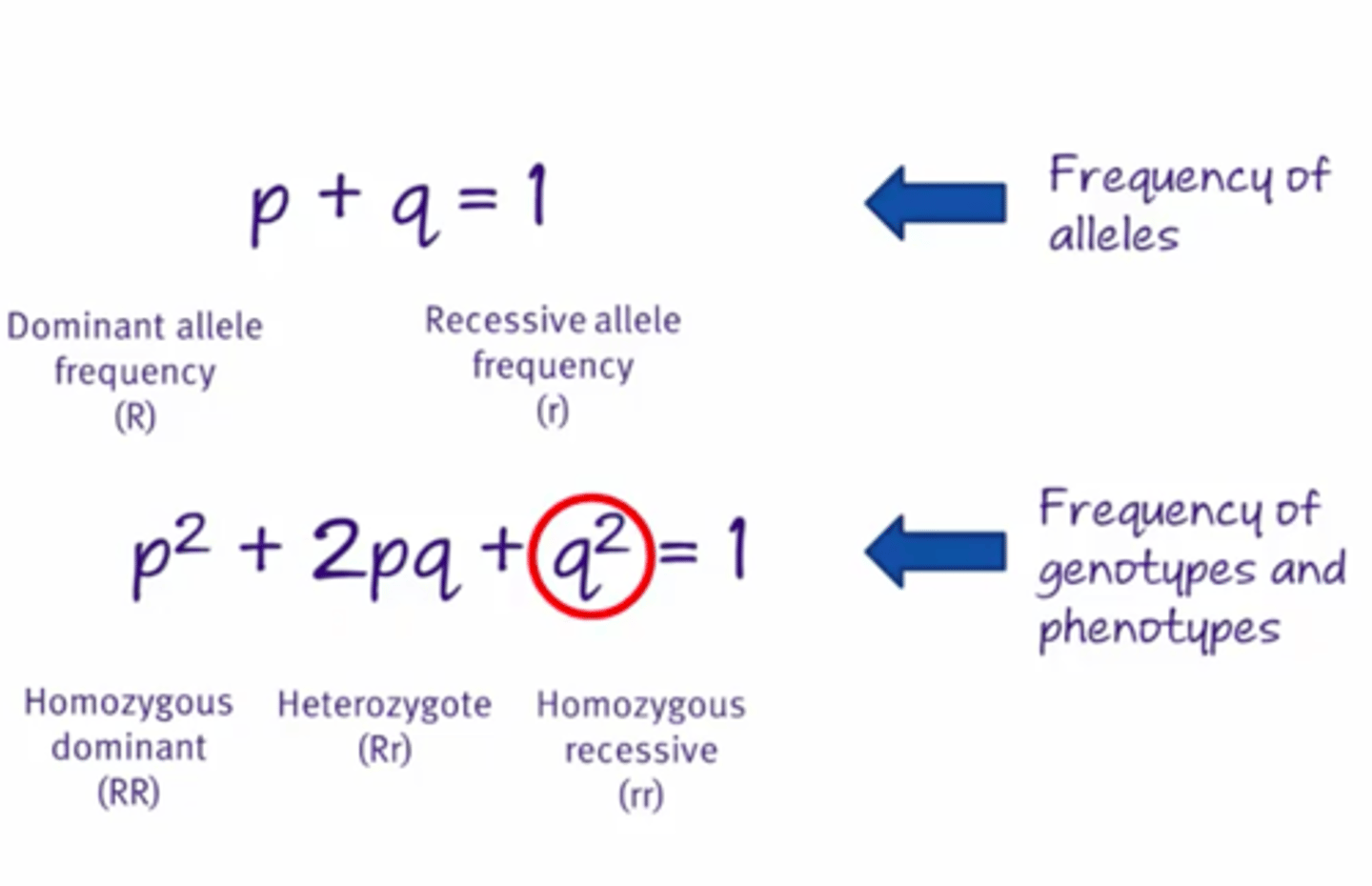
Hard-weinberg criteria
5 criteria:
1) Population is large
2) No mutations
3) Mating is random
4) No migration into/out of the population
5) No natural selection

Hardy-weinberg problem

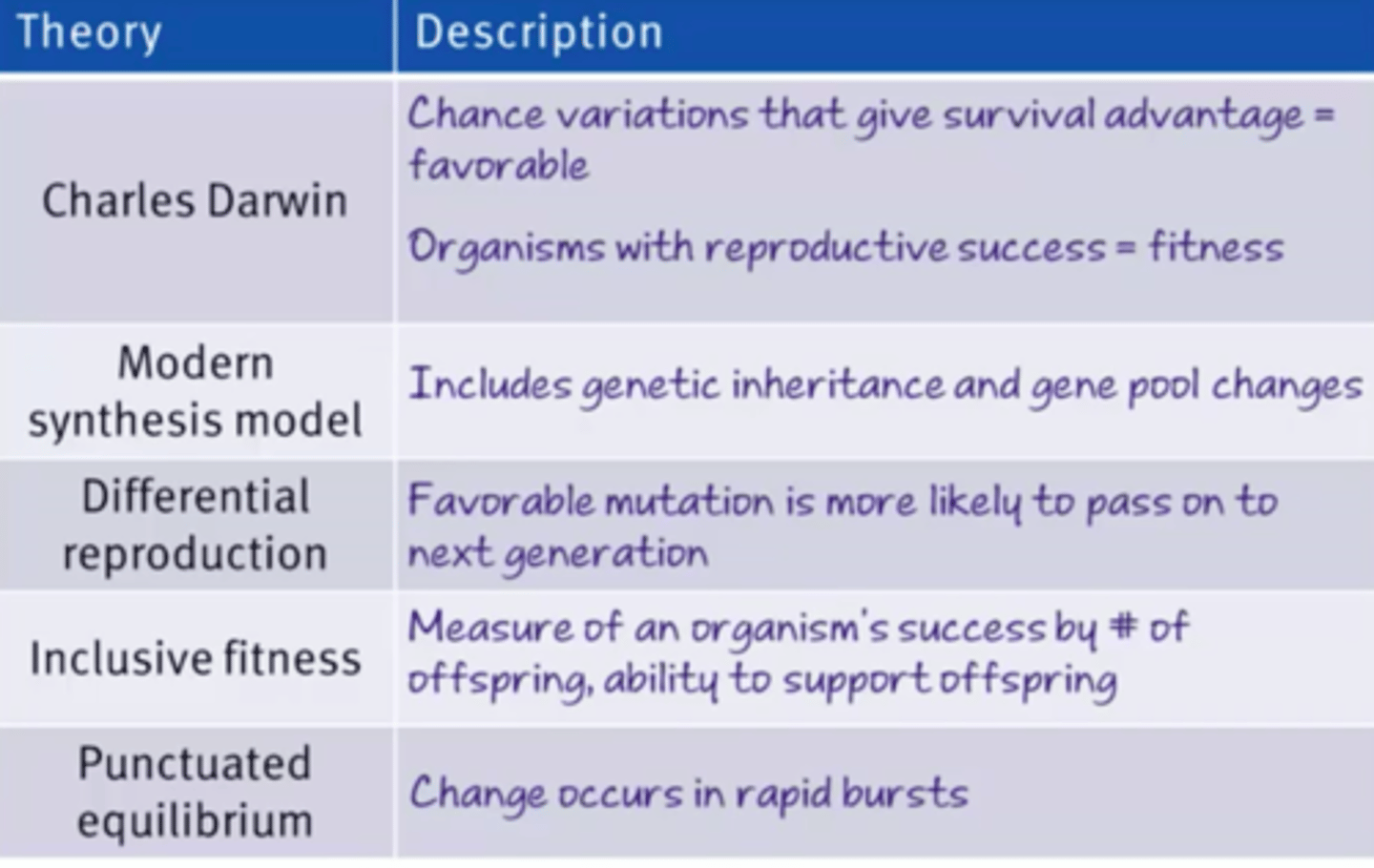
Natural selection
States that the chance variations that exist between individuals, and the advantageous variations-- those that increase an individuals fitness for the environment-- afford the most opportunity for reproductive success.
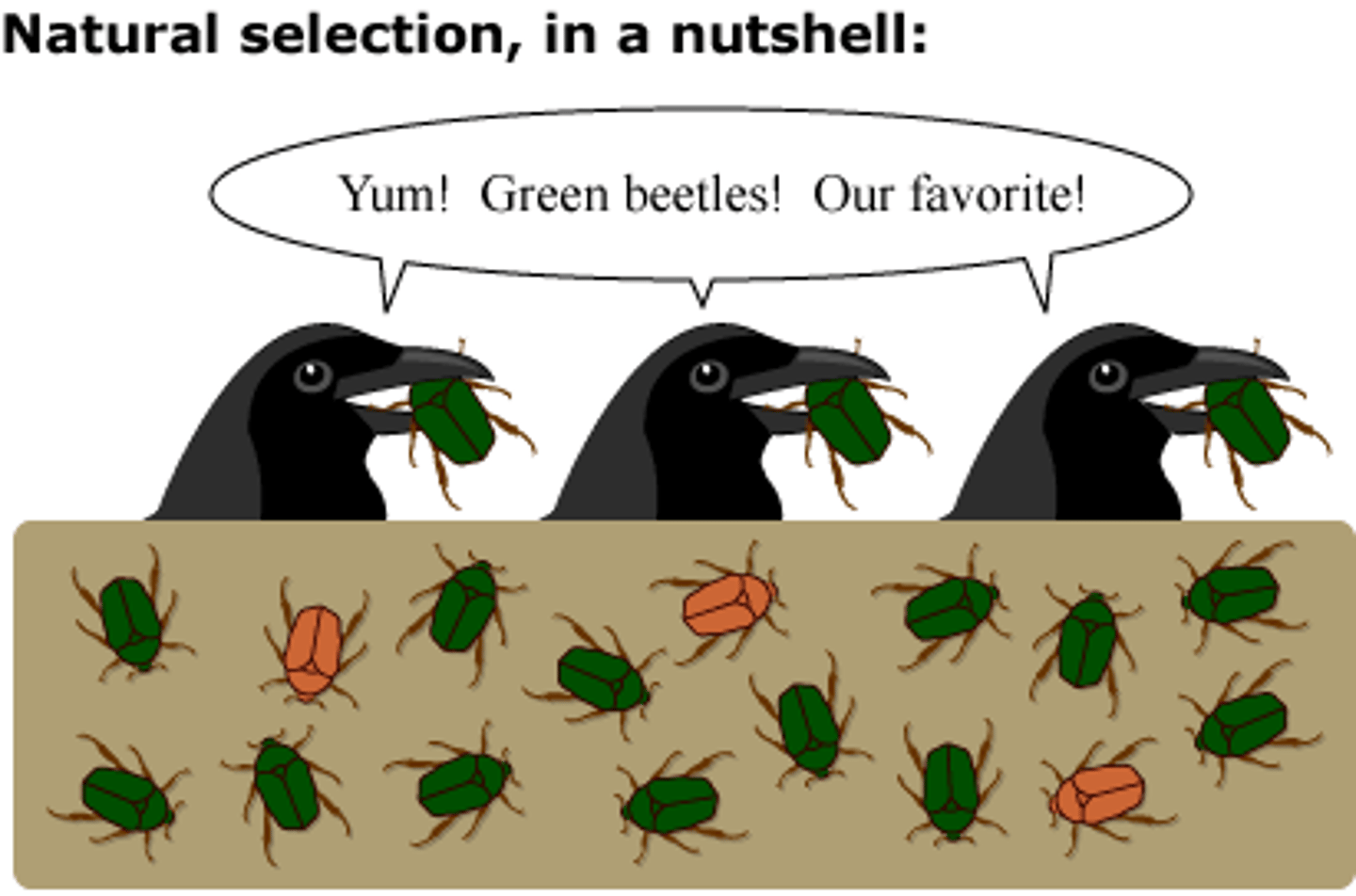
Modern synthesis model (net-darwinism)
Accounts for the mutation and recombination as mechanisms for variation and considers differential reproduction to be the mechanism for reproductive success.
Inclusive fitness
Considers an organisms success to be based on:
1) Number of offspring
2) Success in supporting offspring
3) Ability of offspring to reproduce
4) Survival of offspring
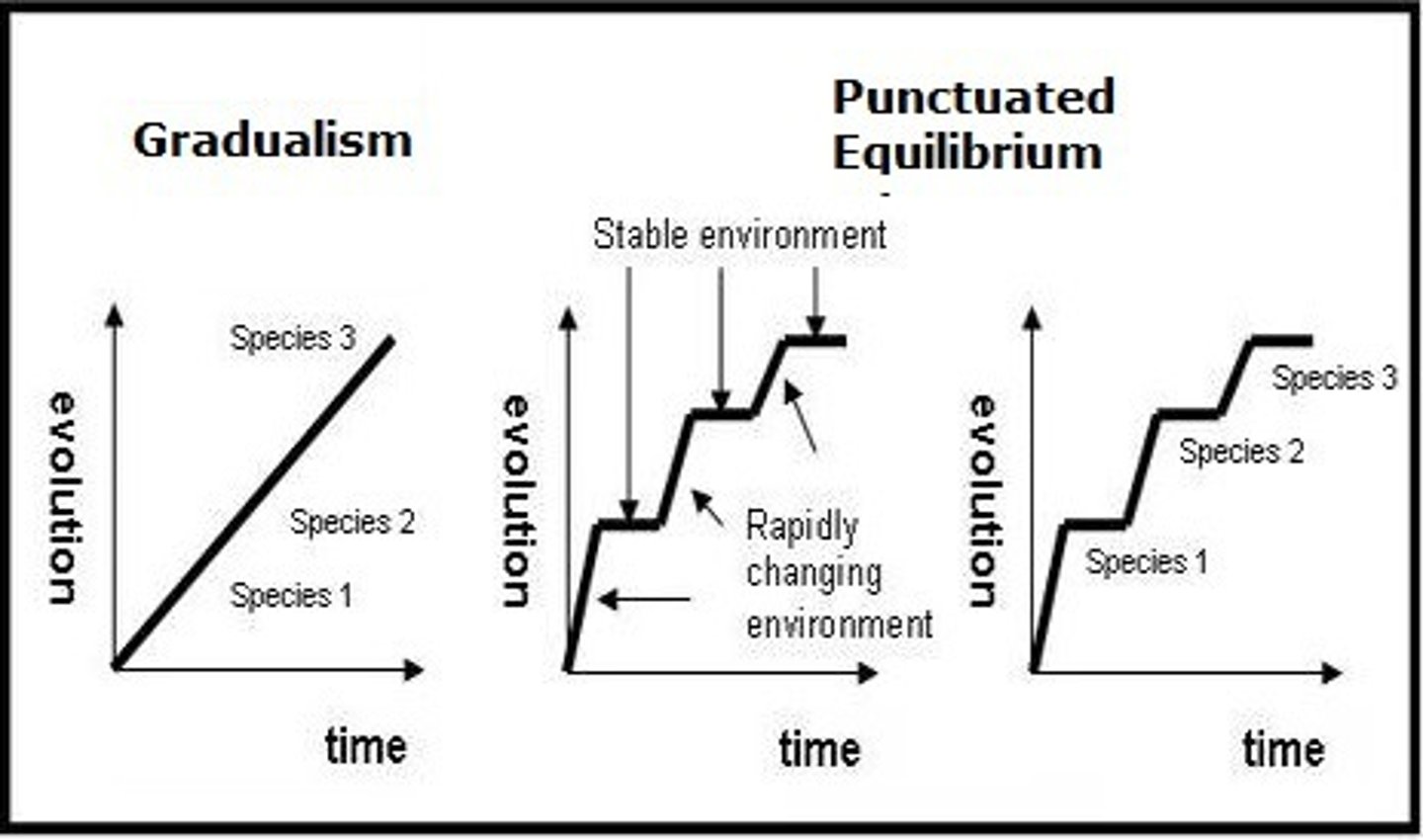
Punctuated equilibrium
Considers evolution to be a very slow process with intermittent rapid burst of evolutionary activity.
Evolution theories overview
Natural selection (types)
Different types of selection lead to changes in phenotype:
1) Stabilizing selection
2) Directional selection
3) Disruptive selection
4) Adaptive selection
Stabilizing selection
Keeps the phenotypes in a narrow range, excluding extremes.
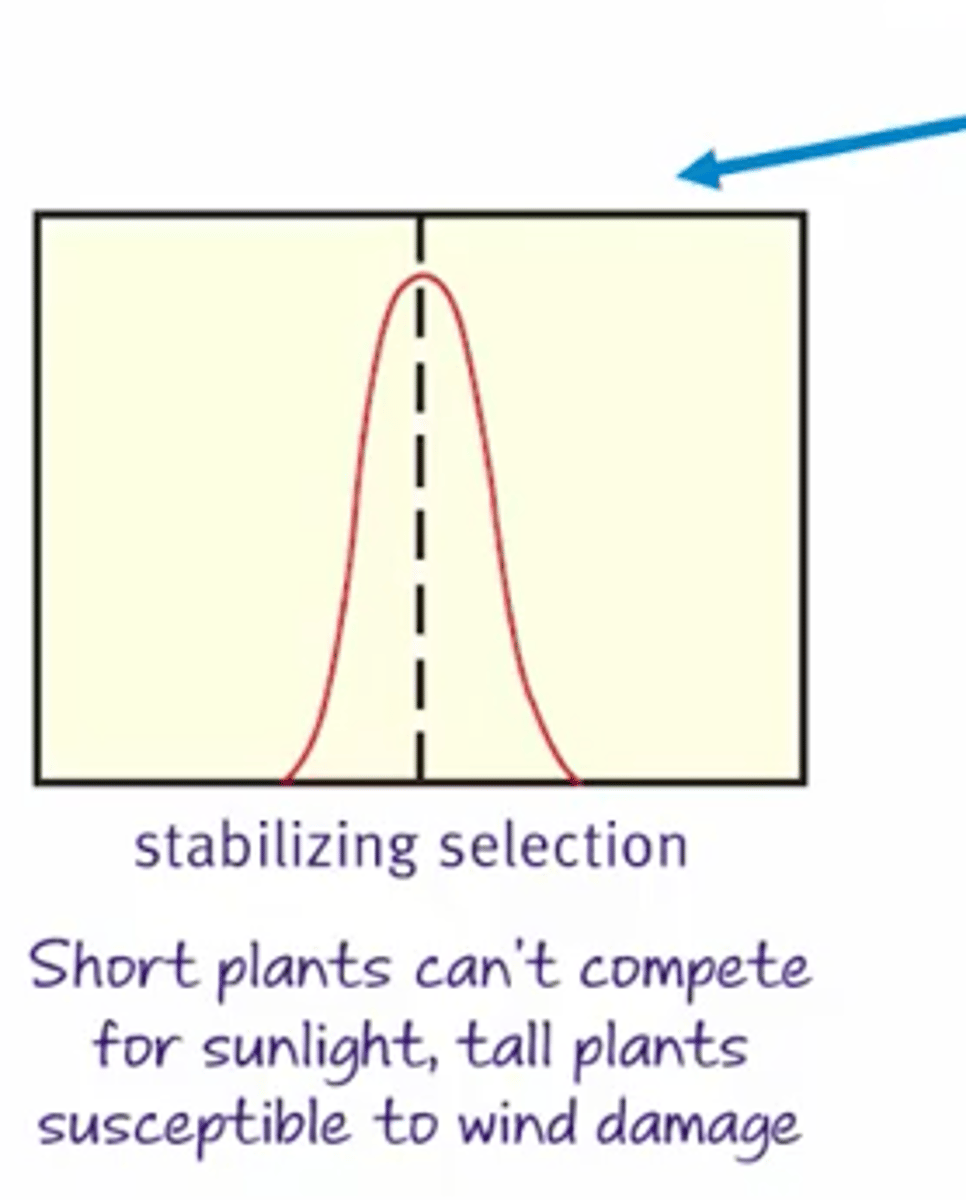
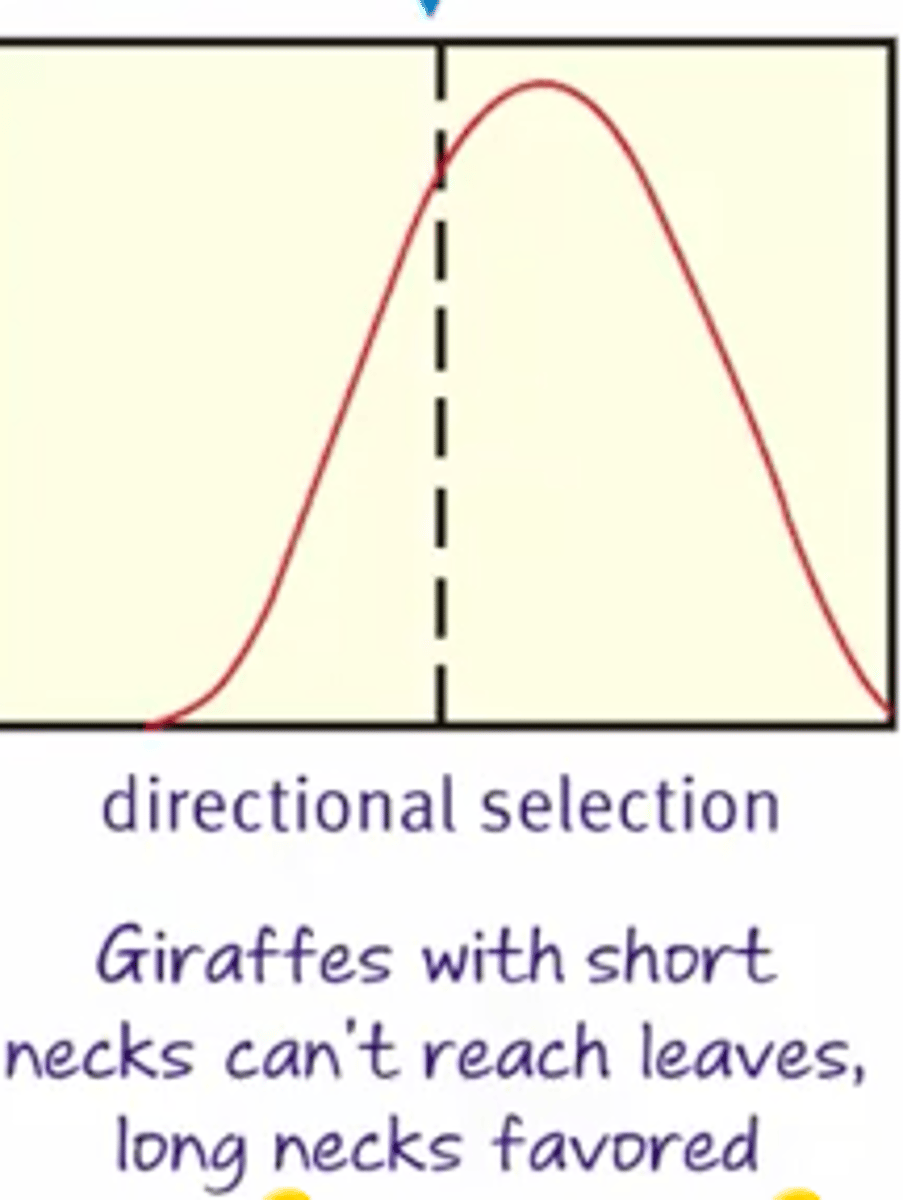
Directional selection
Moves the average phenotype toward one extreme.
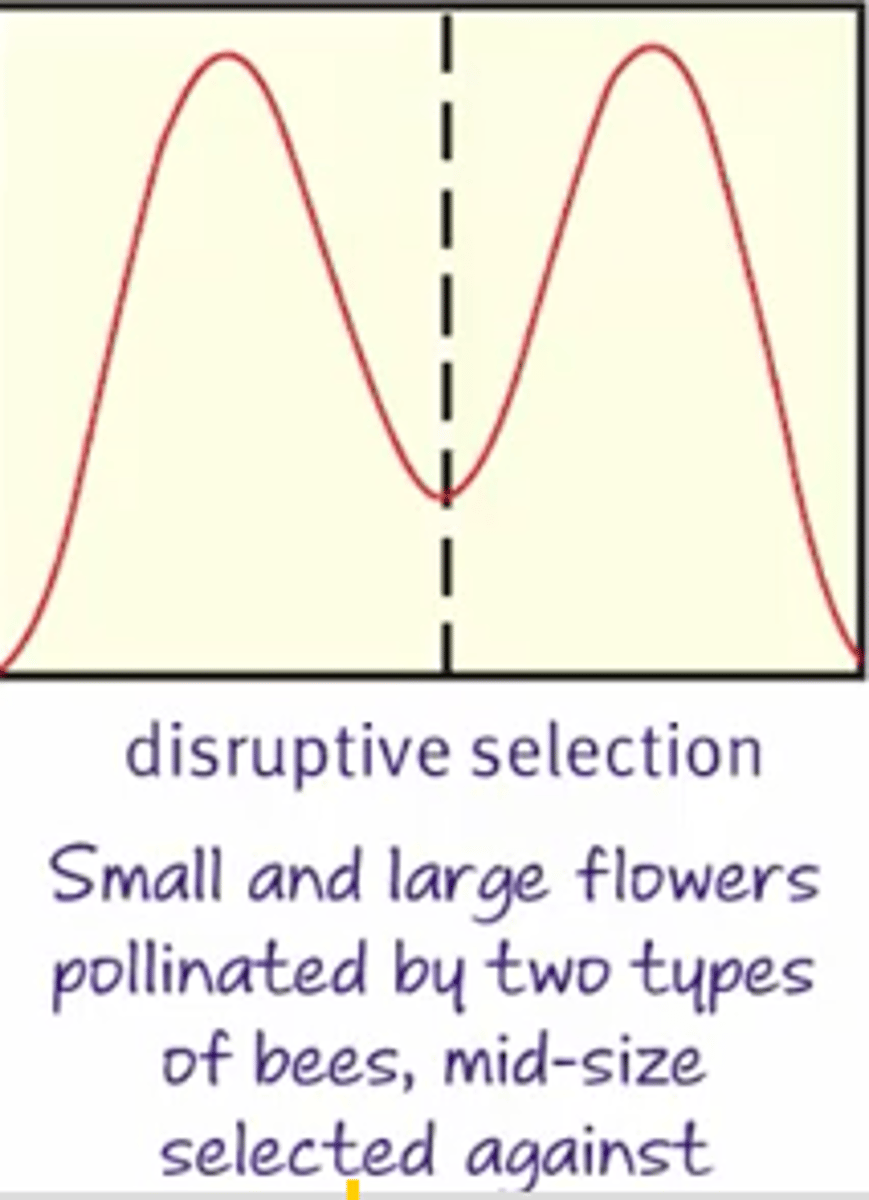
Disruptive selection
Moves toward two different phenotypes at the extremes and can lead to speciation.
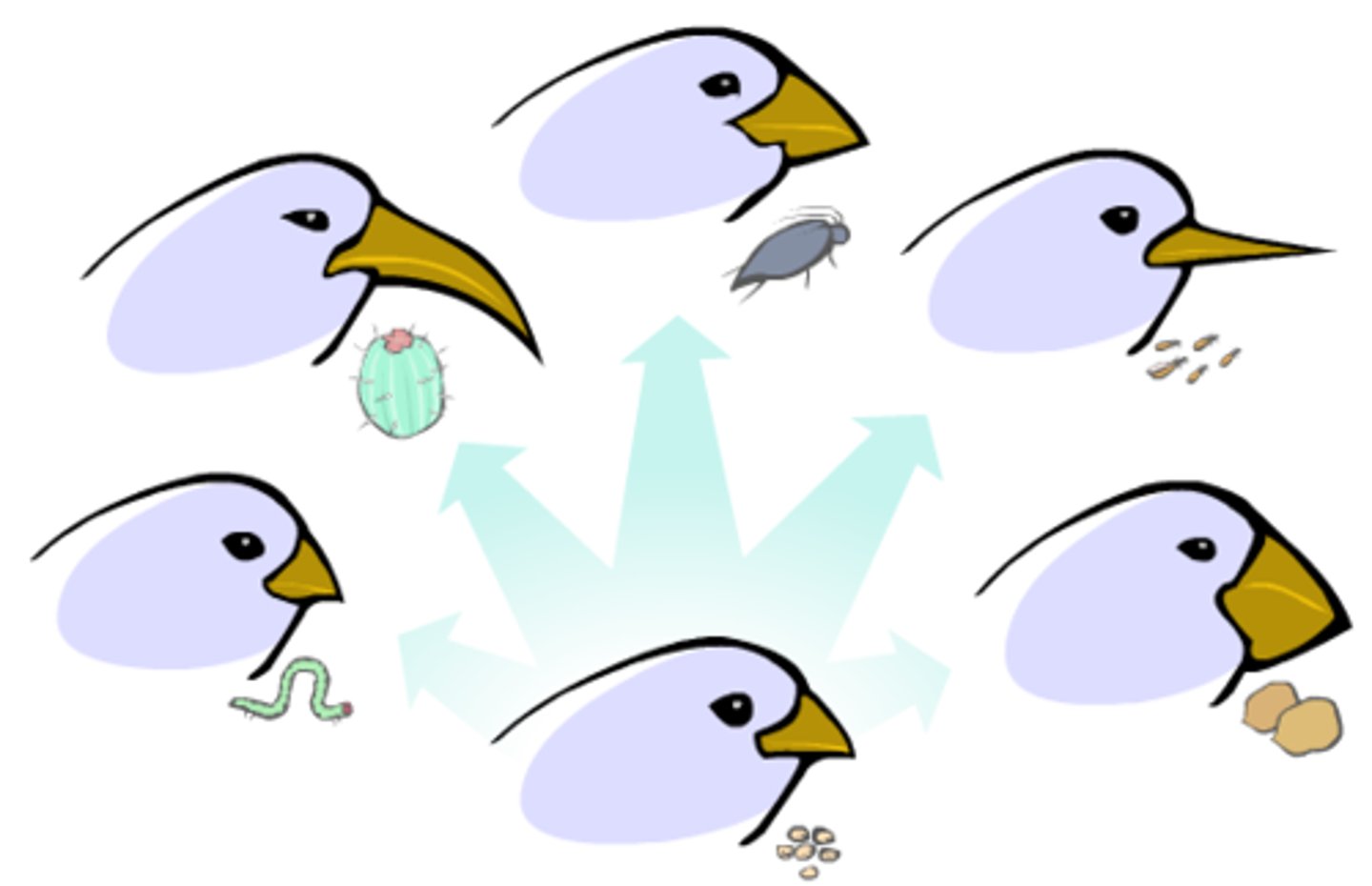
Adaptive radiation
The rapid emergence of multiple species from a common ancestor, each which occupies its own ecological niche.
Species
The largest group of organisms capable of breeding to form a fertile offspring.
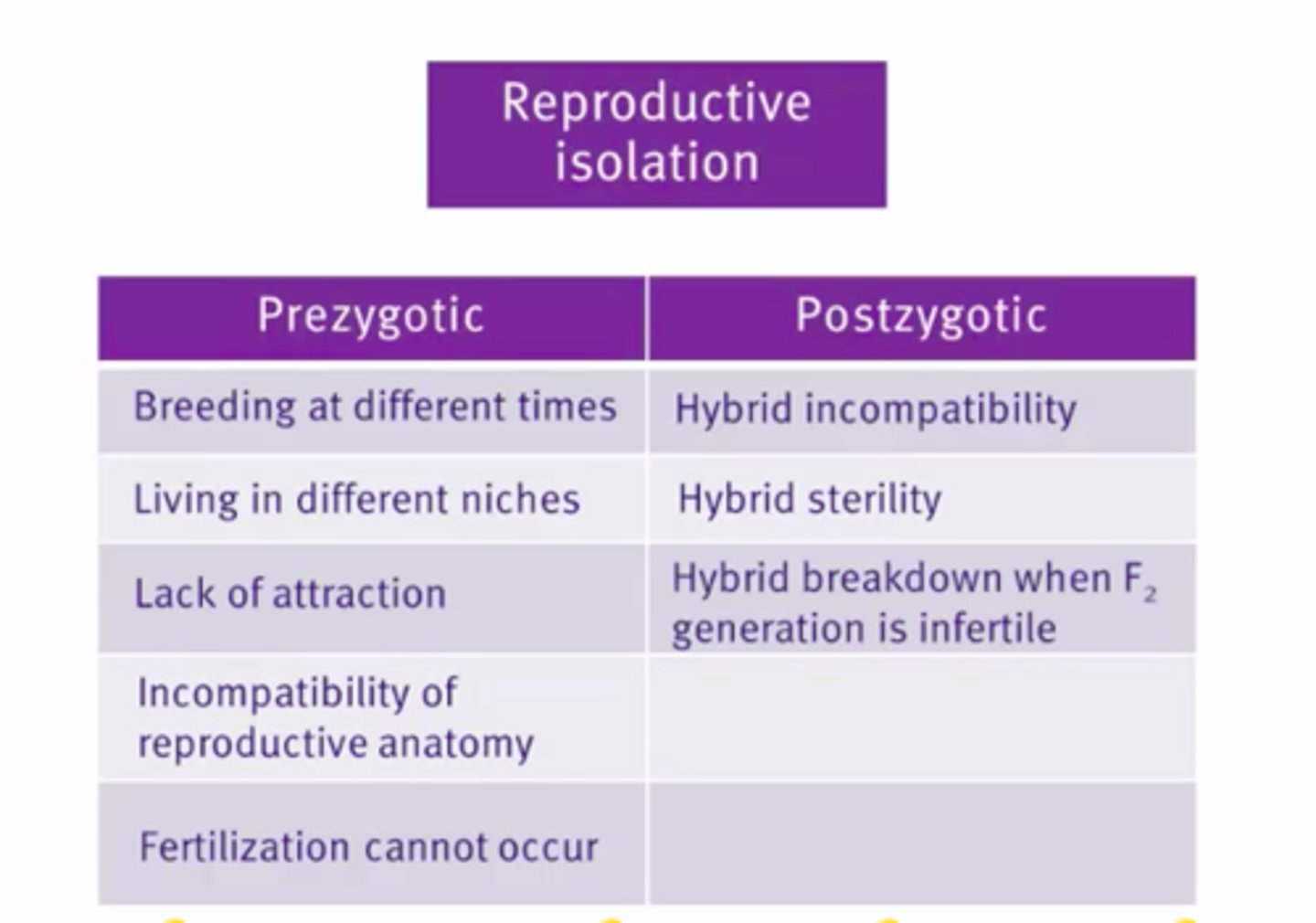
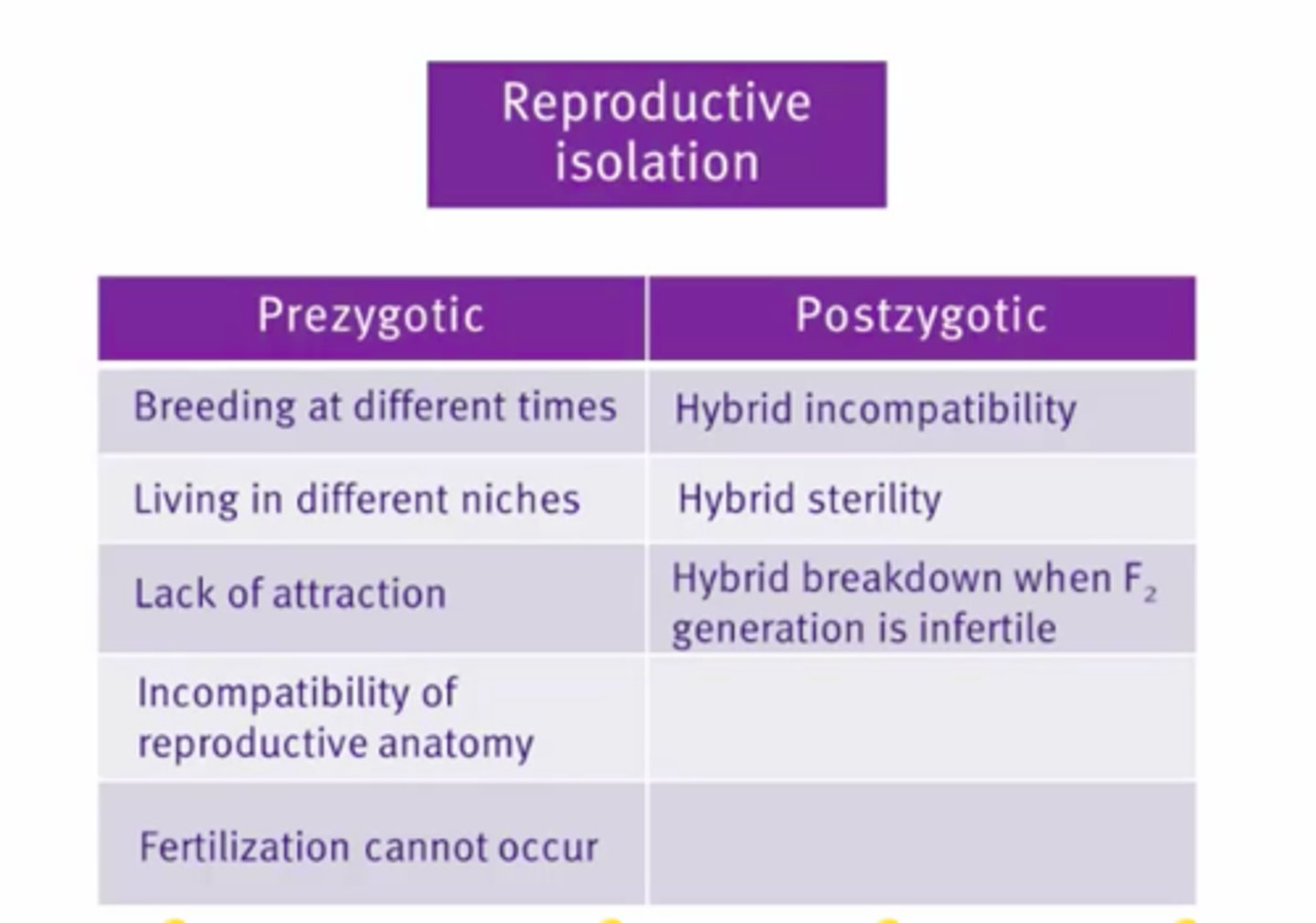
1) Reproductively isolated from each other by pre- and post zygotic mechanisms.
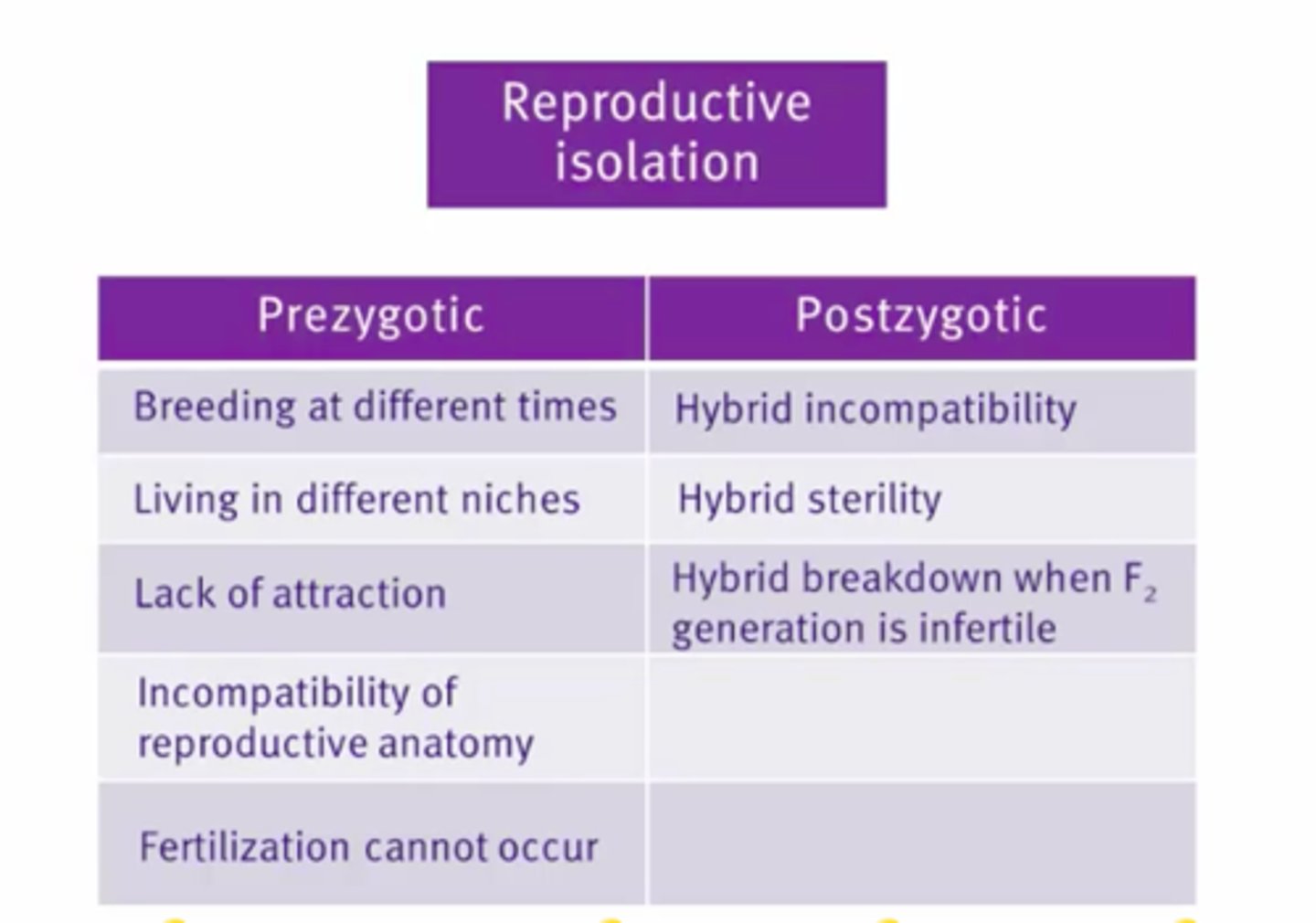
Pre zygotic mechanisms
Prezygotic reproductive isolation
Ecological, Temporal, Behavioral, Mechanical, Gametic
Isolation
when 1 species is separated, different evolutionary pressures leads to isolation, in which the progeny of these populations can no longer interbreed
Post zygotic mechanisms
Postzygotic reproductive isolation
Hybrid inviability, sterility
Evolution (types)
1) Divergent evolution
2) Convergent evolution
3) Parallel evolution
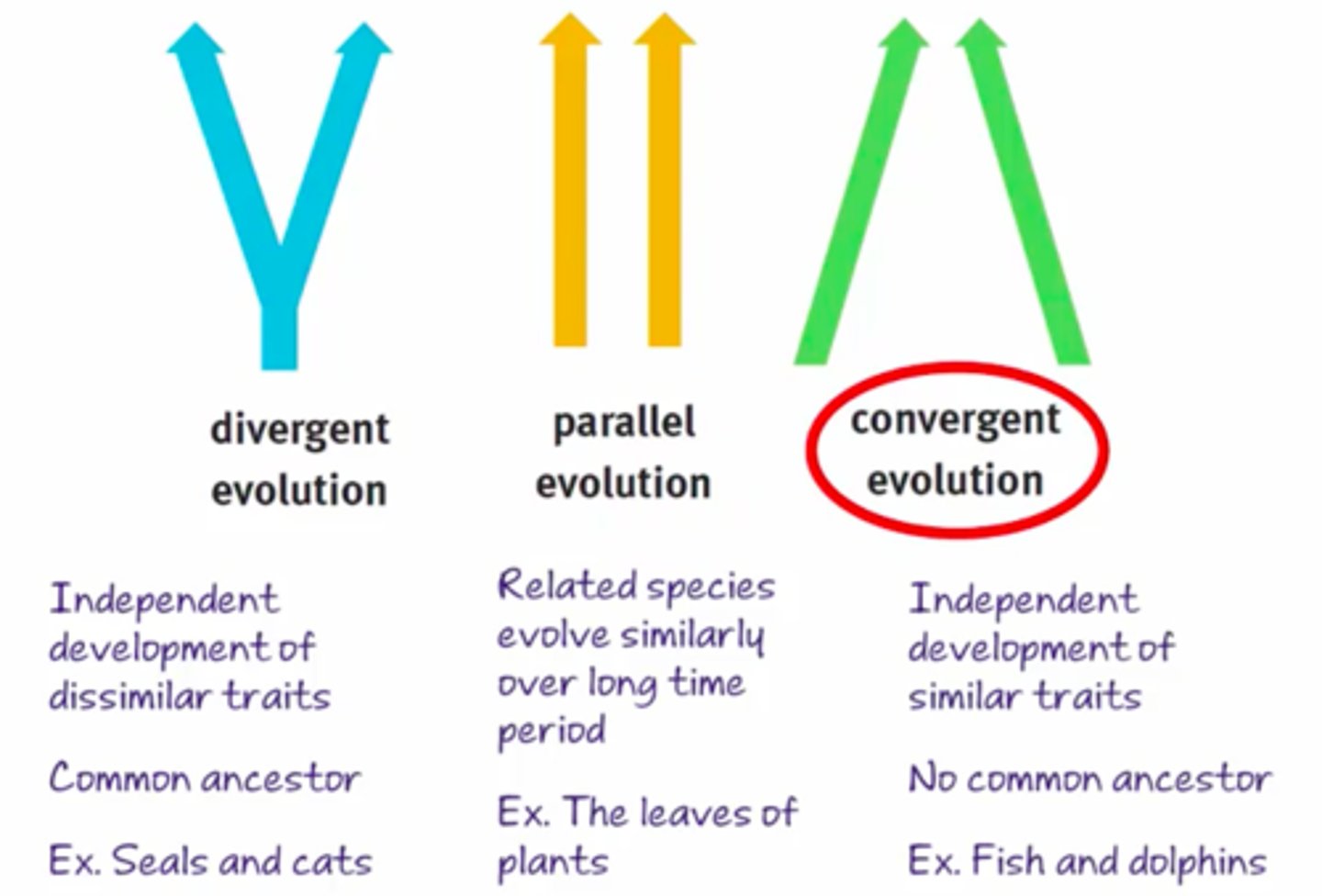
Divergent evolution
Occurs when two species sharing a common ancestor become more different.
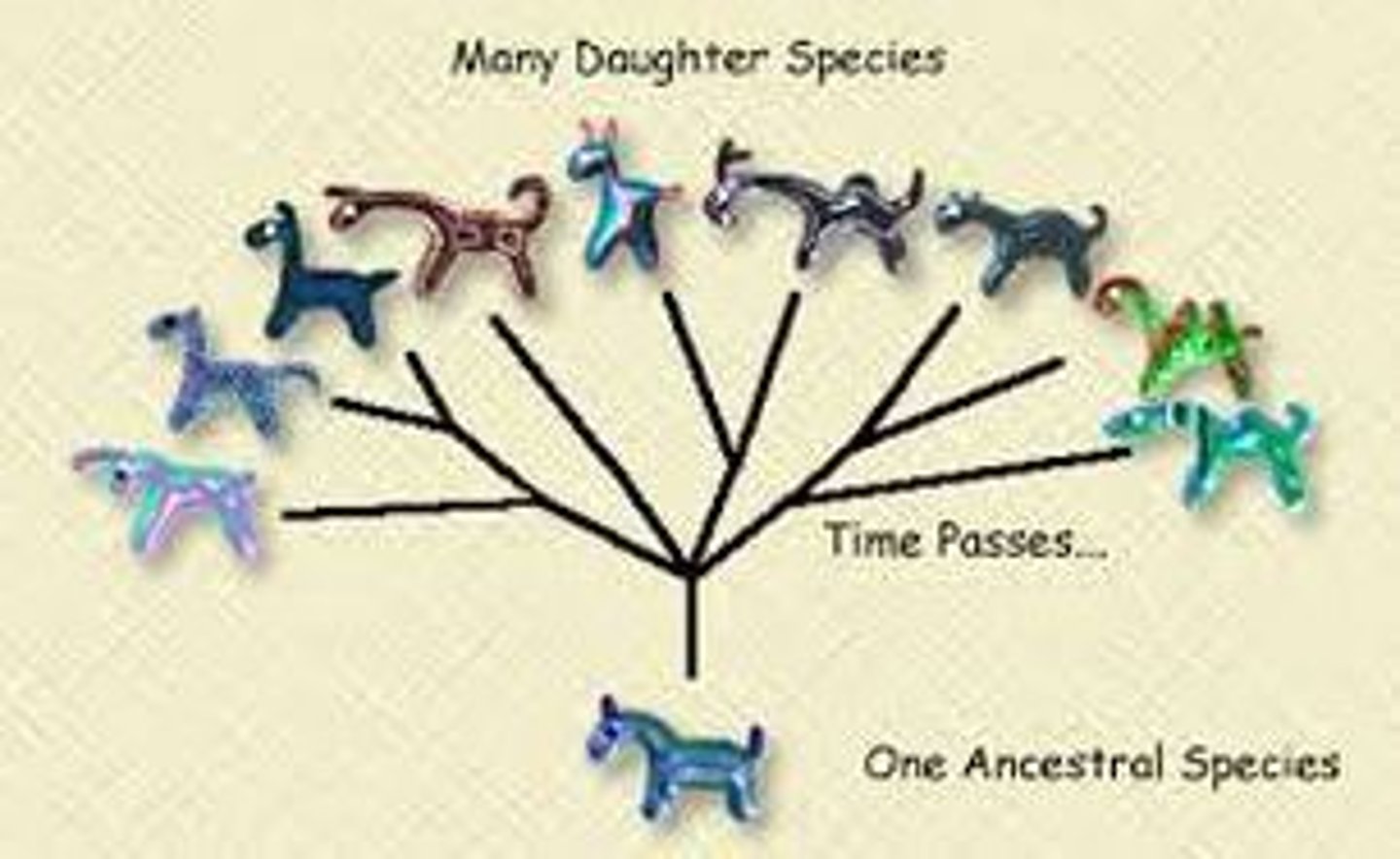
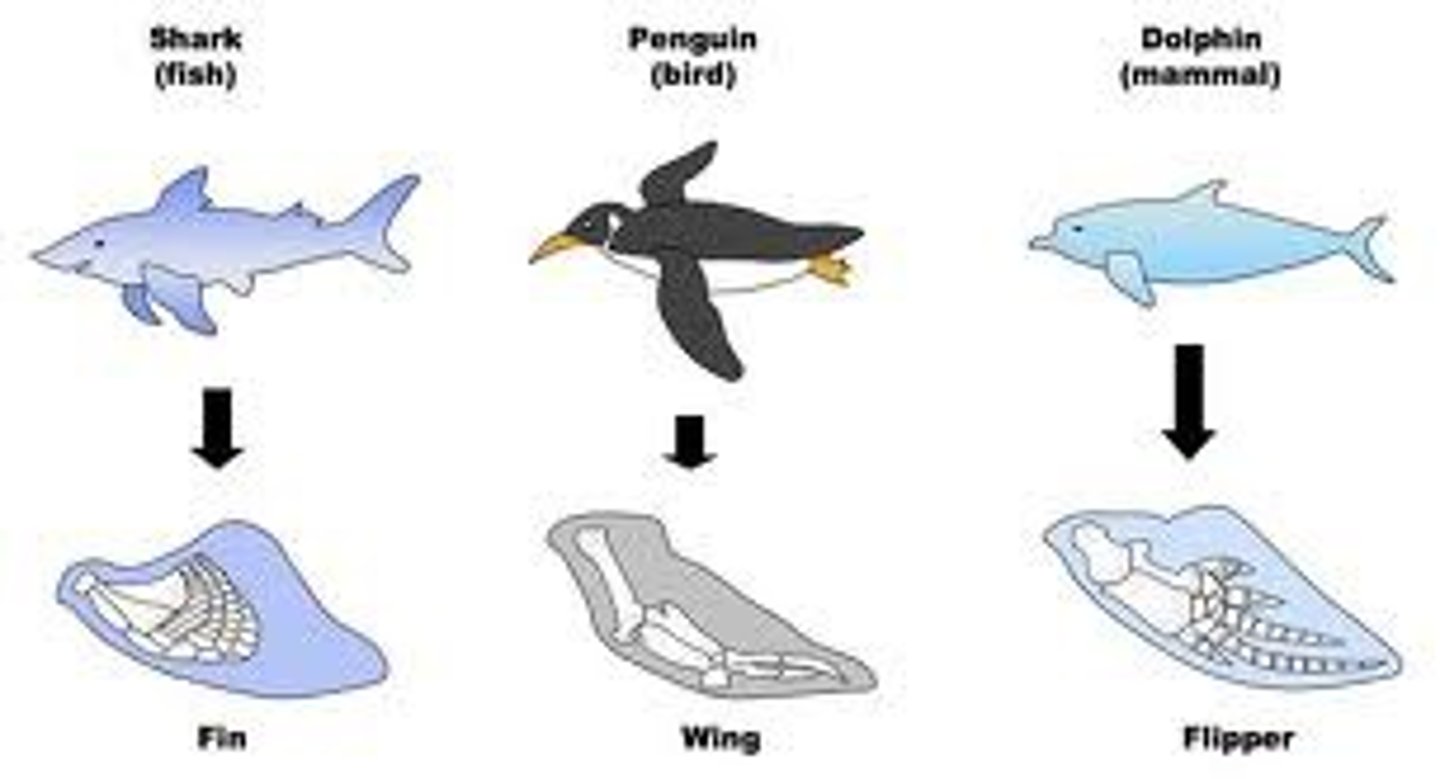
Convergent evolution
Occurs when two species not sharing a recent ancestor evolve to become more similar due to analogous selection pressures.
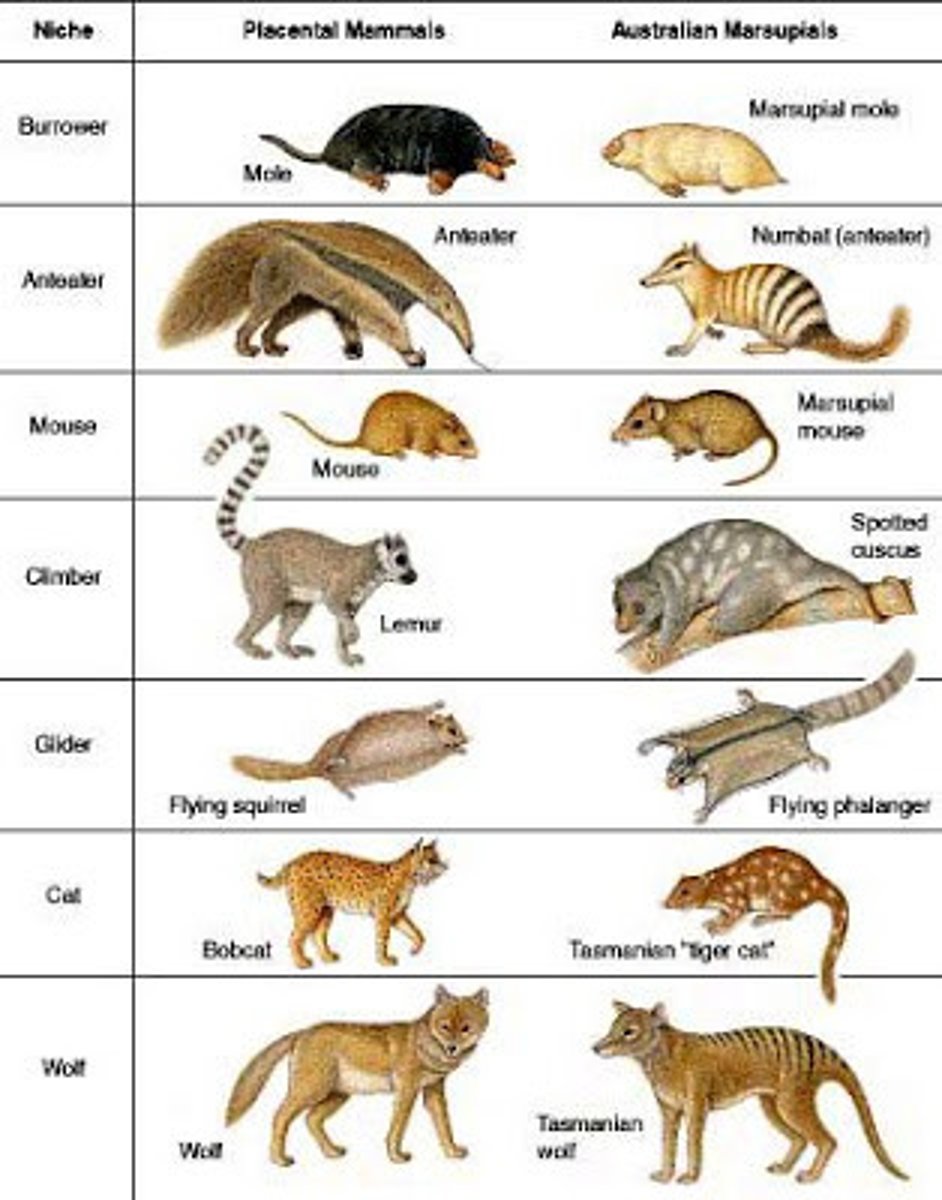
Parallel evolution
Occurs when two species sharing a common ancestor evolve in similar ways due to analogous selection pressures.
Molecular clock model
States that the degree of difference in the genome between two species is related to the amount of time since the two species broke from a common ancestor.