AP Bio Unit 1: Chp 3: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life (Proteins)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Proteins
Examples of uses are enzymes, defense, store, and transport
Types of proteins
Enzymatic proteins, defensive, storage (of amino acids), transport, hormonal, receptor, contractile and motor, and structural
Polypeptides
Proteins consist of 1 or more of these, they are unbranched polymers built from the same set of 20 amino acids (peptide chain)
Amino Acids
monomer unit of proteins; organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups, differ in properties due to different side chains (r groups)
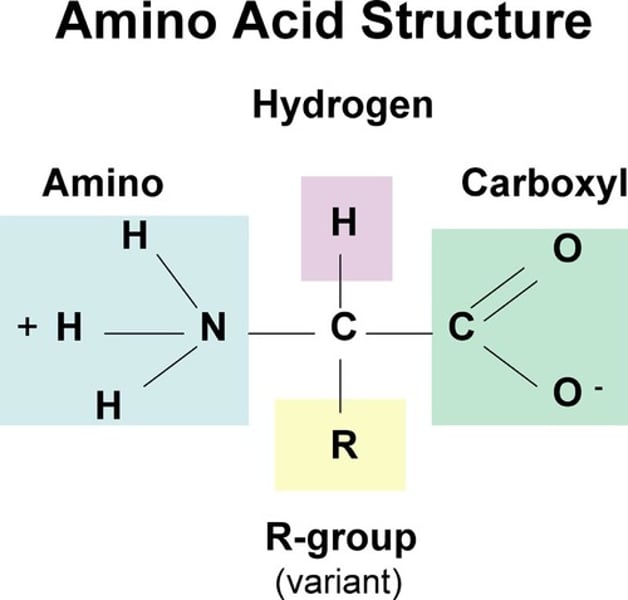
Side chains of amino acids (r groups) can be...
hydrophobic (nonpolar), hydrophilic (polar), electrically charged (acidic [-] and basic [+])
Peptide bonds
Amino acids are linked by these
Polymers of amino acids
Polypeptides, they range in length from a. few to more than a thousand monomers, each are unique linear sequence of amino acids with a carboxyl end (C-terminus) and an amino end (N-terminus)
Functional protein
Consists of one or more polypeptides precisely twisted, folded and coiled into a unique shape
Shape of Proteins
3D shape is why the protein has it's function; Structure determines function
Sequence of amino acids
are determined genetically, leads to 3D structure
4 Levels of protein stucture
1. Primary Structure, 2. Secondary structure, 3. Tertiary Structure, 4. Quaternary Structure
Primary Structure
Unique sequence of amino acids (linked peptide bonds); beaded necklace
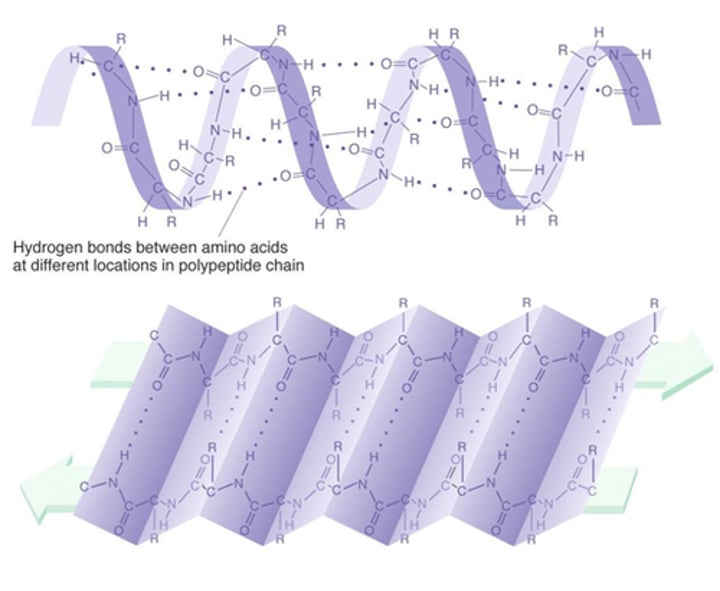
Secondary Structure
Consists of coils and folds in polypeptide chain; alpha helix or beta pleated sheet, result of hydrogen bond from polypeptide backbone
Tertiary Structure
Determined by R groups (side chains); Hydrophilic interactions, disulfide bridges -between cysteines- (covalent bonds) ionic and hydrogen bonds between polar side chains
Quaternary Structure
2 separate proteins that combine together
Slight changes in primary structure can
affect protein structure and ability to function
Sickle cell disease
results from a single amino acid substitution in the protein hemoglobin
Denaturation
Protein unravels; Caused by changes in pH, salt concentration, temperature, or other environmental factors
Renaturation
The reverse of denaturation; It involves the reconstruction of a protein into its original tertiary structure after denaturation