Brain, Nervous System, Endocrine, Neuron
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
Dopamine (DA)
Chemical messenger mainly associated with pleasure/reward
Lack: Parkinson's Disease, Excess: Schizophrenia
Reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
Lateralization
The idea that each hemisphere of the brain has specialized functions
Corpus Collosum
connects the brains left and right hemispheres
Axon terminals
Branches at the end of the axon that transmit sigals to other neurons
Aphasia
Broca's Aphasia: Affects a persons ability to produce speech and write
Wernicke's Aphasia: makes it difficult to understand spoken and written language
Oxytocin
A hormone excreted through the endocrine system that helps physical functions such as child brith.
SSRI
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, one of the most commonly used drugs to treat depression
Limbic System
refers to multiple parts controling learning, memory, and basic drives
Antagonist
Molecule that inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitters action.
EEG (Electroencephalography)
Amplified recording of waves of electrical activity sweeping across brain's surface; waves are measured by electrodes placed on scalp
Glutamate
excitatory neurotransmitter involved in long-term memory and learning. Excess glutamate can cause migraines, seizures, insomnia
autonomic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system; controls the involuntary activity of muscles of the internal organs and glands
Endorphins
inhibits pain signals and regulates pleasure
lack of: lowers pain threshold (no established disorder)
excess: higher pain threshold
afferent neurons
Nerve cells that carry impulses towards the central nervous system
motor nuerons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands
Agonist
Molecule that increases a neuron and neurotransmitters action.
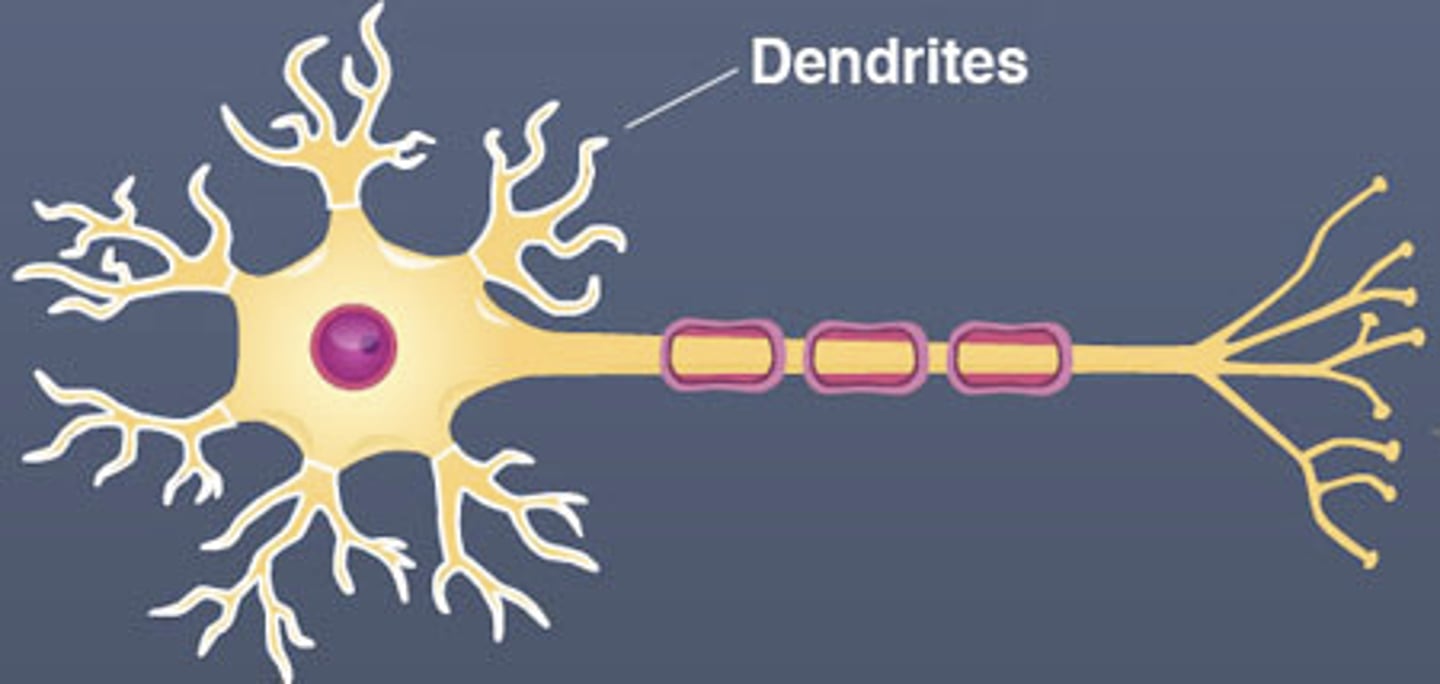
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
GABA
a neurotransmitter that controls sleep, slowing down body
Heritability
the ability of a trait to be passed down from one generation to the next
MRI
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain
Melatonin
A hormone manufactured by the pineal gland that produces sleepiness.
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Serotonin
a neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal. Undersupply linked to depression.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
In the autonomic nervous system of PNS, controls rest, conserve energy, and digestion
Lesion
Tissue destruction. Either naturally or experimentally caused
Nature vs. Nurture
The controversy over the contributions of experience and genes in influencing a persons traits and behaviors.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
a neurotransmitter involved in memory, movement, and learning
axon
a neuron that passes messages through its branches to other neurons.
myelin sheath
a fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons of some neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed as neural impulses hop from one node to the next
Stimulants
drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions
Neuroplasticity
the ability within the brain to constantly change both the structure and function of many cells in response to experience or trauma
Hallucinogens
psychedelic drugs, such as LSD, that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
Sensory Neurons
Sends signals from your senses to the CNS. Found in the PNS
Occipital Lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields
Somatic
voluntary
fMRI
A technique for revealing blood flow to show brain function and structure
Amygdala
two lima bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion.
Parietal Lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position
Sympathetic Nervous System
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
Gaba
Sleep, and movement. lack of gaba can result in Huntingtons disease, and anxiety. Excess Gaba can result in being over relaxed/ sedated.
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands just above the kidneys. the adrenals secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress.
PET Scan
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
Depressant
A drug that slows brain and body reactions
Central nervous system (CNS)
- Consists of the brain and spinal cord
Function:
- Interprets sensory info
- Issues instructions (based on past experiences)
- Considered as the processing and command center
Reticular Formation
Part of the brainstem, filters important information and controls arousal
CT scan
series of X-ray images (radiation) from different angles for a 3D picture
Frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
Resting state
The state in which a neuron is not being stimulated nor conducting an impulse
hypothalumus
control center for recognition and analysis of hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and body temperature
Thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills such as balance and coordination.
Still learning (9)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!