Abdominal Viscera
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
RUQ
Give the quadrant where you can find the majority of the liver (just quadrant abbreviation)
LUQ
Give the quadrant where you can find the stomach and spleen, and pancreas (just quadrant abbreviation)
RLQ
Give the quadrant where you can find the appendix
upper (quadrants)
Are the kidneys found in the upper or lower quadrants?
lower (quadrants)
Are the structures associated with the reproductive organs found in the upper or lower quadrants?
RLQ
Which quadrant can the cecum be found? (just quadrant abbrev.)
peritoneum
The covering of the abdominal cavity is known as the _______
double visceral layer
The greater omentum is special in its folds because it has what?
greater curvature of the stomach
What does the greater omentum hang off of?
pelvis
What structure is typically the lower limit of the peritoneum?
transverse colon, spleen, diaphragm
Name the 3 other structures that the greater omentum touches/attaches to other than the stomach
lesser curvature of stomach (and duodenum) to liver
The lesser omentum primarily connects what two structures?
mesentery
Name the structure that helps anchor the small intestines to the posterior abdominal wall
mesentery proper
What is the name of the more central structure than the mesentery that anchors the small intestine directly to the post. abd. wall
mesocolon
Name the structure that helps anchor the colon to the post. abd. wall
head, body, tail
The pancreas is composed of more than one segment. Name all of them in order starting with the head.
superior, descending, inferior, ascending
The duodenum is composed of more than 1 segment. Name all of them starting from the beginning.
ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid
The colon is composed of more than one segment. Name all of them.
ascending, descending
Name the segment(s) of the colon that are retroperitoneal. Give comma-separated list if >1 segment
(the) tail
Which part of the pancreas is NOT retroperitoneal?
descending, inferior
Which section(s) of the duodenum are retroperitoneal? Give the true name(s), not the numbers.
falciform (ligament)
Name the ligament responsible for connecting the liver to the ant. abd. wall and serves as a landmark separating the L/R lobes of liver
hepatogastric (ligament)
This ligament is the membranous portion of the lesser omentum
hepatoduodenal (ligament)
This ligament is responsible for the free edge of the lesser omentum and is anterior to/houses the portal triad
No (!!!!!!!)
Is the hepatic vein part of the portal triad?
Yes (!!!)
Is the portal vein part of the portal triad?
portal vein, hepatic artery, common bile duct
Name the components of the portal triad
hepatorenal (ligament)
These ligaments connect the liver to capsules surrounding the kidneys
gastrophrenic, gastrosplenic, gastrocolic
Name the three ligaments that come off the greater curve of the stomach and are part of the greater omentum (don't write the word ligament)
gastrophrenic (ligament)
This ligament comes off the stomach and attaches to the inferior diaphragm
gastrosplenic (ligament)
This ligament comes off the stomach and covers the hilum of the spleen
gastrocolic (ligament)
This ligament connects the stomach to the transverse colon
caval, portal
Name the 2 systems of venous blood
greater sac
The main subdivision of the peritoneal cavity is referred to as the _________
omental bursa, lesser sac
The smaller subdivision of the peritoneal cavity is known as the__________ (2 names)
omental foramen, epiploic foramen, foramen of winslow
The opening to the omental bursa is known by 3 names. Give all 3.
hepatoduodenal ligament
Give the anterior boundary of the epiploic foramen
IVC, right crus of diaphragm
Give the posterior boundary of the omental foramen
(the) liver
Give the superior boundary of the foramen on Winslow
superior duodenum
Give the inferior boundary of the epiploic foramen
3
How many layers of smooth muscle does the stomach have? Give number
2
How many layers of smooth muscle does the small intestine have? Give number
peristalsis
The wavelike smooth contraction of smooth muscles allowing food to pass through the digestive tract is known as ___________
duodenum
What structure comes immediately after the stomach in the digestive tract?
chewing
Mastication refers to ________
swallowing
Deglutition refers to ______
alimentary tract, gastrointestinal tract
Give all the names for the pathway extending from the mouth to anus and actually involves organs that touch the food
accessory organs
What are the organs that often assist in digestion, but do not actually touch the food called?
liver
Name the largest internal organ in the human body
skin
Name the largest organ in the human body
falciform ligament
What structure separates the L/R lobes of liver and anchors the liver to the ant. abd. wall?
quadrate lobe (4 sides)
Name the lobe located next to the gall bladder, is on the posteroinferior portion of the liver.
caudate lobe
Name the lobe on the posterior side of the liver next to the IVC and the ligamentum venosum
ligamentum teres hepatis
Identify this remnant of the umbilical vein
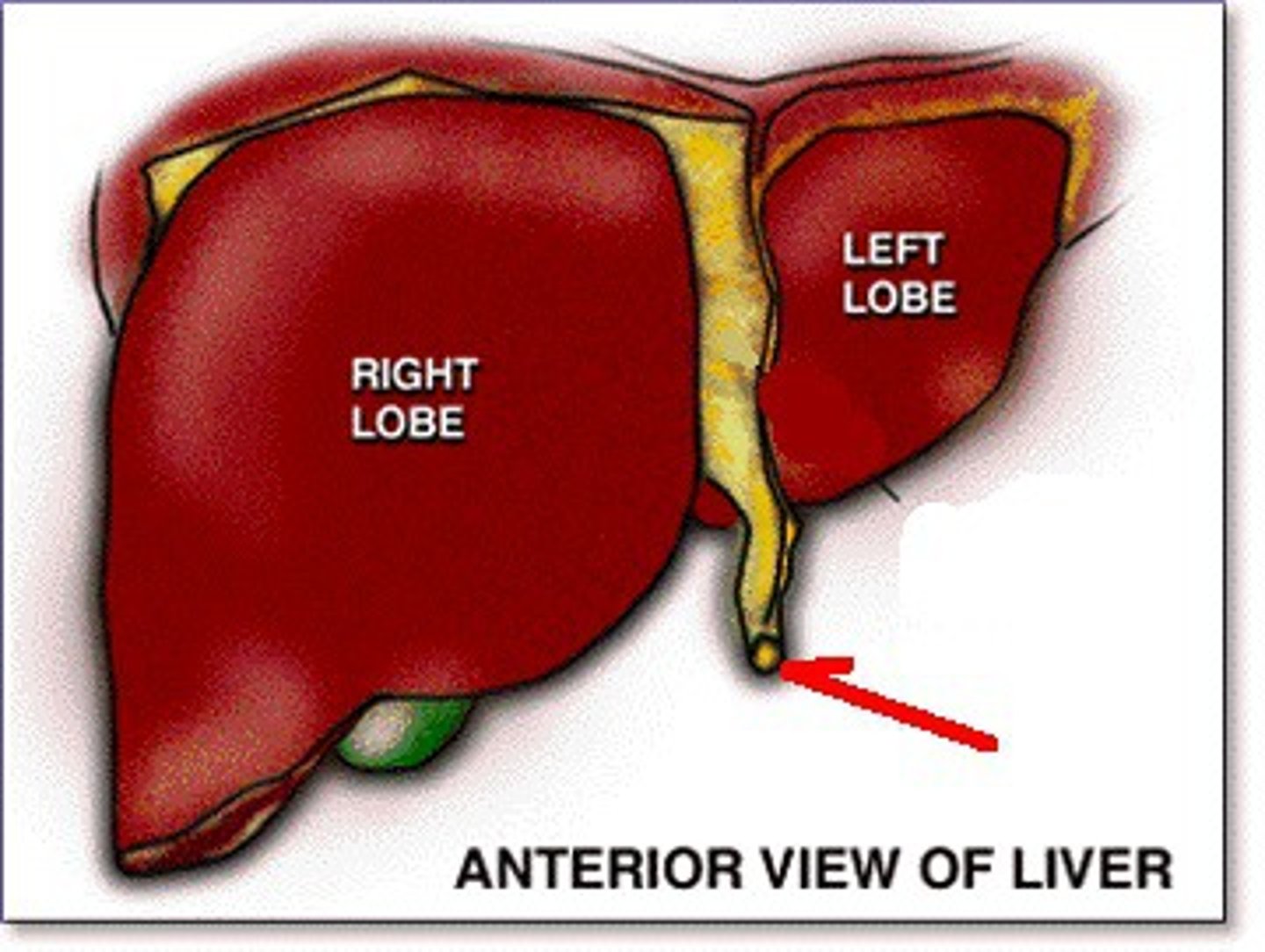
ligamentum venosum
Name the liver ligament that is a remnant of the ductus venosus
coronary ligament(s)
Identify
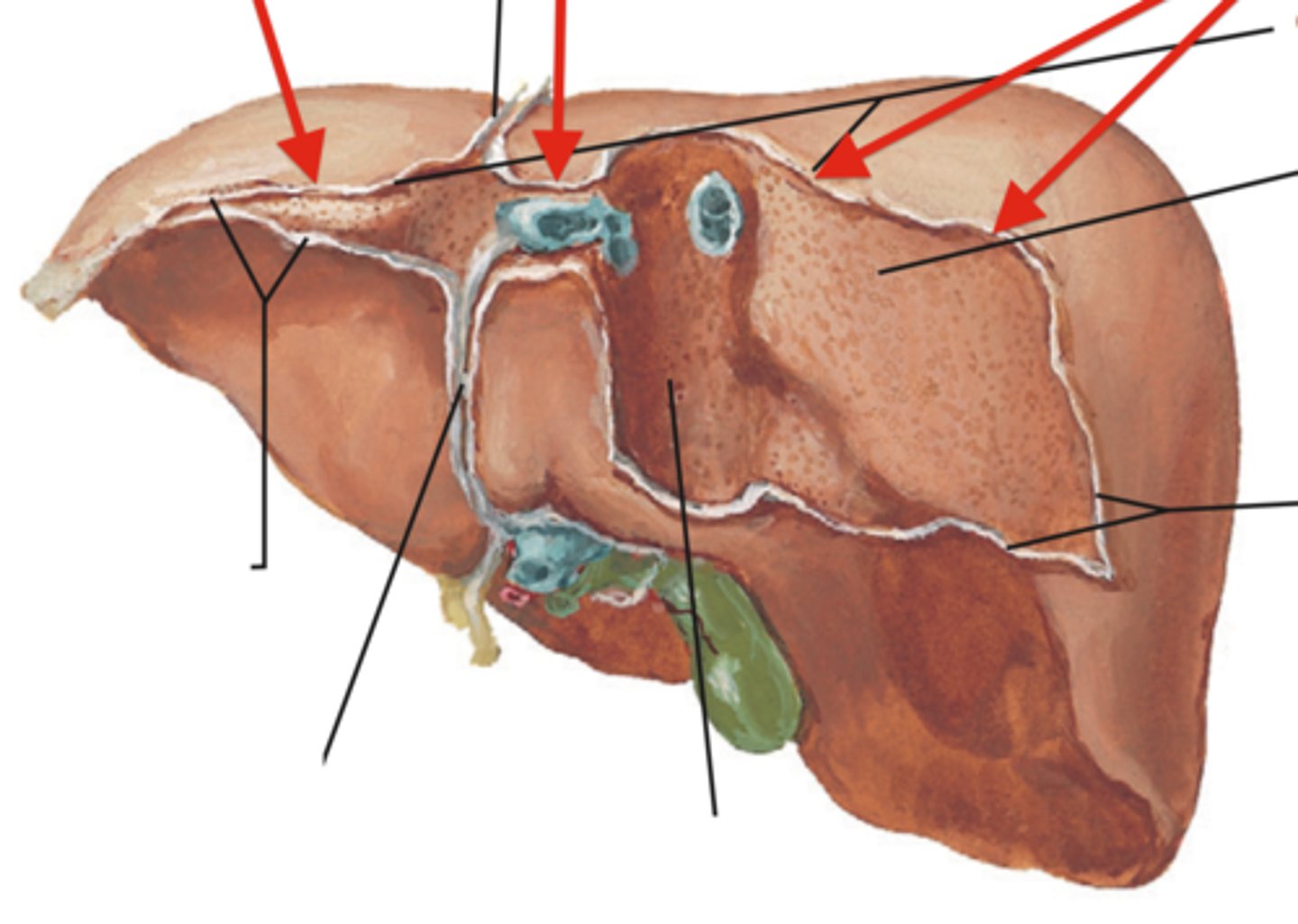
triangular ligament
Identify
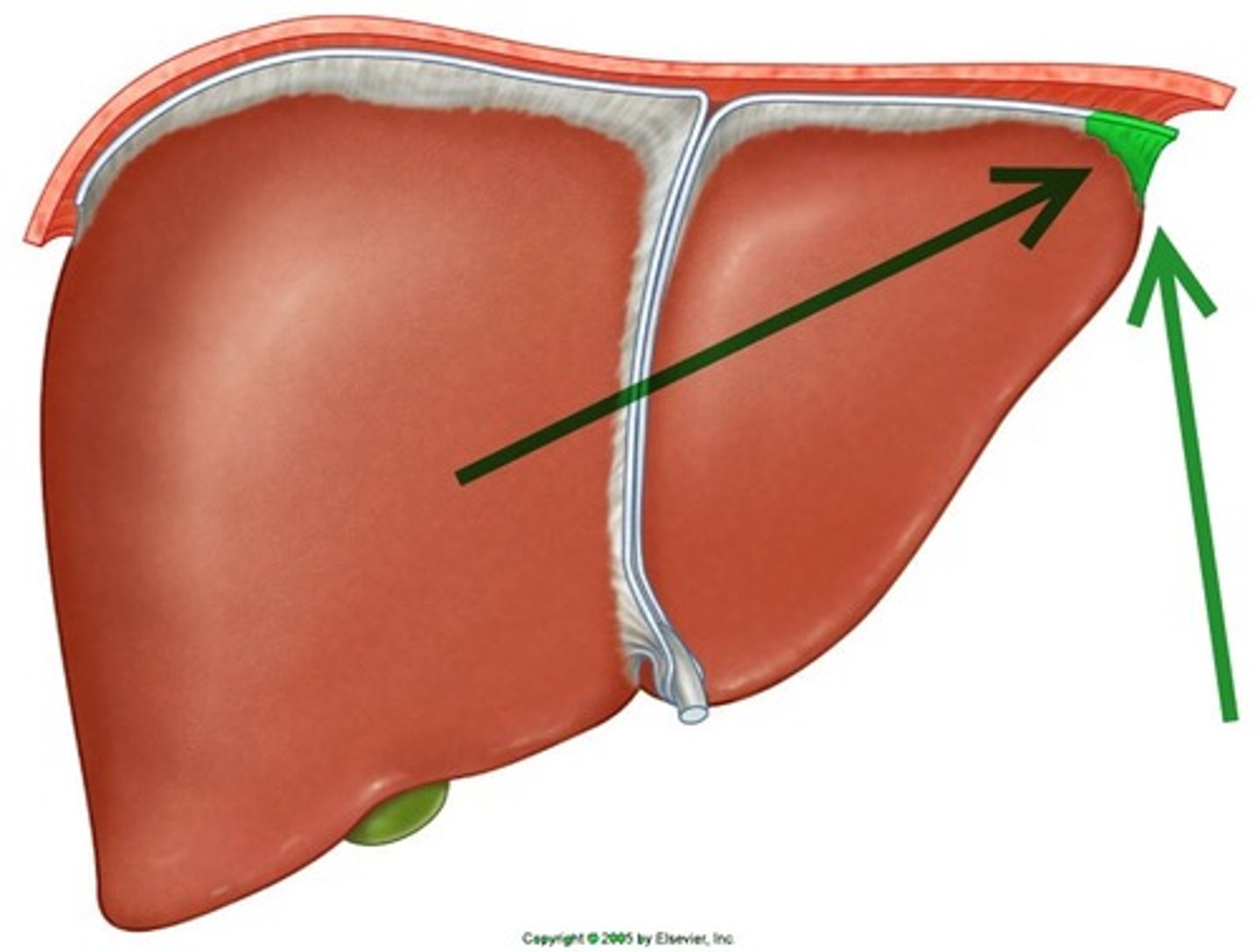
parietal peritoneum
The coronary ligaments and triangular ligaments are made up of which structure?
No (!!!!)
Does the gall bladder produce bile?
posteroinferiorly
Where is the gall bladder located in relation to the liver?
superior surface, no peritoneum
Where on the liver (superior surface, inferior surface, lateral surfaces, etc.) is the bare area of the liver? What does that mean?
(to) store bile
What is the function of the gall bladder?
99
What percentage of cells in the pancreas are dedicated to exocrine "tasks"? Just give a number
1
What percentage of cells in the pancreas are dedicated to endocrine "tasks"? Just give a number
glucagon, insulin
What hormones are secreted directly to the blood from the pancreas (exocrine) ?
main pancreatic duct, accessory pancreatic duct
Name the ducts for secretion from the pancreas.
duct of wirsung
Give the eponym for the main pancreatic duct
duct of Santorini
Give the eponym for the accessory pancreatic duct
right hepatic duct, left hepatic duct
The biliary tree starts with bile being fed into the ______
common hepatic duct
In the biliary tree, the L/R hepatic ducts combine to form the __________
No (!!)
Is the common hepatic duct part of the portal triad?
cystic duct
From the common hepatic duct, if the bile were to take an abrupt turn toward the gall bladder, then what part of the biliary tree would the bile be in?
common bile duct
From the common hepatic duct, if I were to continue straight, what part of the biliary tree would I be in?
cholecystectomy
Removal of the gall bladder is known as a __________
main pancreatic duct
What joins the common bile duct "prior to" the duodenum?
hepatopancreatic ampulla and sphincter
What are the names of the two structures where the common bile duct/main pancreatic duct meet? don't give eponyms here.
ampulla of Vater
Give the eponym for the hepatopancreatic ampulla
sphincter of Oddi
Give the eponym of the hepatopancreatic sphincter
chyme
What is a bolus turned into in the stomach?
cystic duct
Which structure in the biliary tree is known for having a spiral valve?
valve of heister
The spiral valve is known as the ________ (eponym).
(the) spleen
What organ helps recycle RBC's and helps provide immunity?
No, lymphatic (system)
Is the spleen a digestive organ? If not, what organ system?
1
How many inches thick is the spleen? Just give number.
3
What is the width of the spleen in inches? Just give number.
5
What is the length of the spleen in inches? Just give number.
7
What is the weight of the spleen in ounces? Just give number.
9-11
Which ribs is the spleen under? If you think it's five through 8, write "5-8"
No
Is the spleen something that can typically be sutured?
splenomegaly
Enlargement of the spleen is known as _________
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa
Name the layers of the alimentary canal from inside to outside
Forms the lumen
What does the mucosa do in the GI tract?
vasculature
What is the purpose of the submucosa in the GI tract?
inner circular, outer longitudinal
From deep to superficial, name the layers of muscle of the small intestine.
oblique, circular, longitudinal
From deep to superficial, name the layers of muscle of the stomach.
peritoneum
The serosa is formed from what structure?
villi
What are the finger like projections that increase the surface area of the GI tract called (particularly in sm. intestine)?
duodenal bulb
The enlargement at the top of the superior duodenum is known as the _____
cardia
The top of the region of the stomach is known as the _______
cardiac sphincter
What is the name of the sphincter in the upper stomach?