Life Science_ Term 3 & 4 (Pt. 1)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/66
Last updated 8:30 AM on 11/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
1
New cards
Circulatory system responsible for
- transporting blood with oxygen from lungs to cells
- transporting blood with carbon dioxide from the cells back to the lungs
- distributing nutrients from digestive system to cells in the body
- removing waste products to be excreted
- transporting blood with carbon dioxide from the cells back to the lungs
- distributing nutrients from digestive system to cells in the body
- removing waste products to be excreted
2
New cards
Open blood circulatory system
When blood leaves the blood vessels and is pumped into the body cavity
3
New cards
Characteristics of an open blood circulatory system
- blood moves very slowly
- organism has low blood pressure
- restricted to smaller animals, like insects
- organism has low blood pressure
- restricted to smaller animals, like insects
4
New cards
Closed blood circulatory system
Blood remains within a system of blood vessels
5
New cards
Heart
- cone shaped organ
- strong cardiac muscle that pumps blood throughout the body
- contracts and relaxes continuously
- strong cardiac muscle that pumps blood throughout the body
- contracts and relaxes continuously
6
New cards
4 Chambers of the heart
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
7
New cards
Pericardium
Protective connective tissue membrane enclosing the heart
- protects and anchors the heart to the surrounding organs
- protects and anchors the heart to the surrounding organs
8
New cards
Location of the heart
Behind the sternum, between the lungs in the thoracic cavity
9
New cards
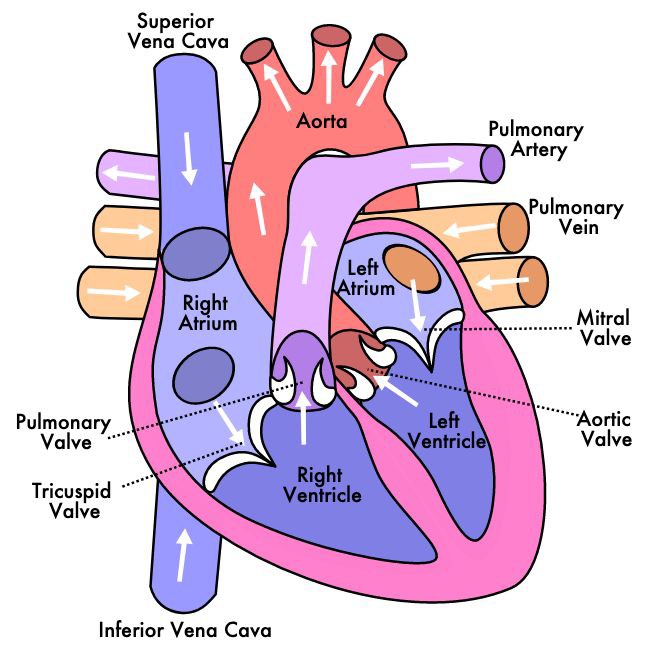
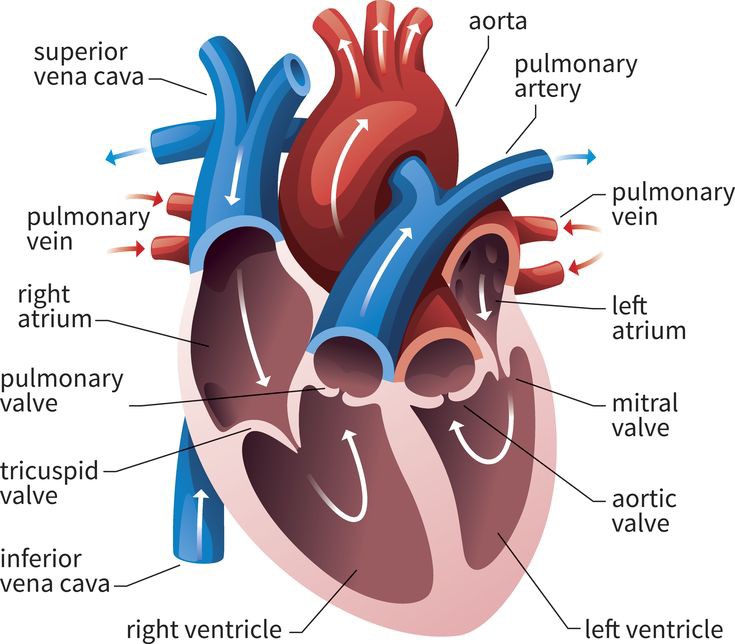
Path of deoxygenated blood
Deoxygenated blood → superior/inferior vena cava → right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary valve → pulmonary artery → lungs
10
New cards
Path oxygenated blood
Oxygenated blood → pulmonary veins → left atrium → bicuspid valve → left ventricle → aortic valve → aorta → body
11
New cards
Purpose of septum
Keeps deoxygenated blood in the right atrium and ventricle separated from the oxygenated blood in the left atrium and ventricle
12
New cards
Why is the left ventricle thicker than the right?
It is responsible for pumping blood to throughout the whole body.
13
New cards
Arteries
Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, to our body organs under high pressure
14
New cards
Veins
Carry deoxygenated blood to the heart
15
New cards
Capillaries
Lie very closely next to the cells of the body
16
New cards
Branch of blood vessels
Arteries → arterioles → capillaries → venules → veins
17
New cards
Constitution of blood
55% fluid plasma
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Blood platelets
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Blood platelets
18
New cards
Erythrocytes
- red blood cells
- biconcave discs
- average life cycle of 120 days
- biconcave discs
- average life cycle of 120 days
19
New cards
Hemoglobin
Oxygen carrying protein present in red blood cells
As red blood cells pass through the lungs, oxygen molecules attach to the hemoglobin
As red blood cells pass through the lungs, oxygen molecules attach to the hemoglobin
20
New cards
Leucocytes
- white blood cells
- microphages, T-cells, B-cells, plasma cells, memory cells
- important part of body's immune system
- microphages, T-cells, B-cells, plasma cells, memory cells
- important part of body's immune system
21
New cards
Thrombocytes
- blood platelets
- irregularly-shaped, colorless bodies present in blood
- play a role in clotting blood at the point of bleeding
- irregularly-shaped, colorless bodies present in blood
- play a role in clotting blood at the point of bleeding
22
New cards
Process of blood clotting
The platelets gather at the wound, they begin to form fibrin. The fibrin threads then begin to form a web-like mesh over the hole in the leaking blood vessel. This mesh traps the blood cells within it.
23
New cards
Pulmonary circulation
Short system that circulates blood between the lungs and heart
- part of the circulatory system
- part of the circulatory system
24
New cards
Systemic circulation
Longer system that circulates blood from the heart throughout the body and back again
- part of the circulatory system
- part of the circulatory system
25
New cards
High blood pressure
When the force with which the blood pushes against the walls of the blood vessels is too high and can cause damage to the capillaries and organs
- often results from eating too much salt
- often results from eating too much salt
26
New cards
Heart attacks
When an artery narrows or a blood clot develops in one of the blood vessels that supplies the heart muscle with blood, it can stop the blood flow to the heart muscle and can stop it from pumping (heart attack)
27
New cards
Strokes
When cells in your brain are deprived of oxygen
- often occurs as a result of a blockage in the blood vessels leading to the brain, or when once of these vessels rupture
- often occurs as a result of a blockage in the blood vessels leading to the brain, or when once of these vessels rupture
28
New cards
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
29
New cards
Respiratory system
- deals with the exchange of gases in your body
- responsible for supplying the body's cells with oxygen and removing carbon dioxide
- responsible for supplying the body's cells with oxygen and removing carbon dioxide
30
New cards
Path of oxygen in the respiratory system
mouth and nose → pharynx → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli
31
New cards
Oxygen through the mouth and nose
Oxygen rich air enters the body through the mouth and nose where it is warmed by blood vessels which close to the surface of these openings
32
New cards
Air through the larynx
Inside the larynx are vocal chords, as the air is expired the vocal chord vibrate, allowing us to make sounds
33
New cards
Trachea
- tube that enters the chests and allows air to flow form the mouth into the bronchi
- kept open by cartilage rings
- splits into two air tubes (bronchi)
- kept open by cartilage rings
- splits into two air tubes (bronchi)
34
New cards
Epiglottis
Soft flap of tissue located just above the opening of the trachea which prevents food from entering
35
New cards
What happens when dust or germs enter the trachea?
The mucus lining the trachea traps the particles and the cilia on the ciliated cells work together to flick/move them out the body
36
New cards
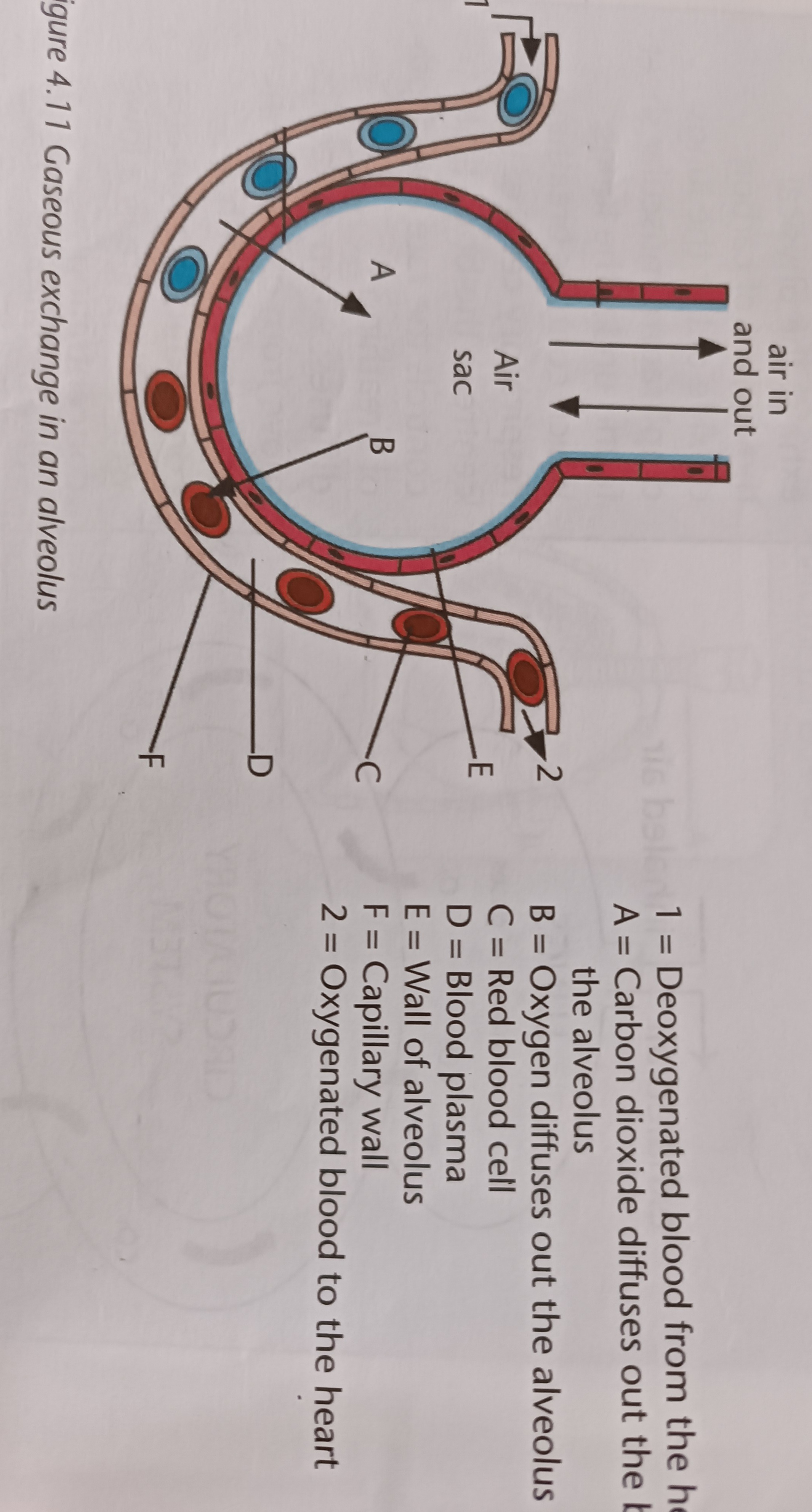
Adaptions of alveoli
Thin wall to allow rapid gaseous exchange
Large surface area for rapid exchange of gases
Rich supply of blood vessels to transport gases to and from the gaseous exchange surface
Large surface area for rapid exchange of gases
Rich supply of blood vessels to transport gases to and from the gaseous exchange surface
37
New cards
Alveoli
The surfaces through which gaseous exchange occurs
- large air sacs
- found at the ends of bronchioles
- surrounded by capillaries
- large air sacs
- found at the ends of bronchioles
- surrounded by capillaries
38
New cards
Lungs
- pink, spongy, air-filled structures
- surrounded by a protective membrane, pleura
- surrounded by a protective membrane, pleura
39
New cards
Diaphragm
Dome shaped muscle below the lungs that enables you to breath
- main muscle used for breathing
- main muscle used for breathing
40
New cards
Process of inhalation
Muscles between the ribs contract and lift it upwards
The diaphragm contracts; it flattens out
This increases the space in the chest and causes the pressure to drop
The low pressure causes air to be sucked into the lungs
The diaphragm contracts; it flattens out
This increases the space in the chest and causes the pressure to drop
The low pressure causes air to be sucked into the lungs
41
New cards
Process of exhalation
Rib cage returns to its rest position
The diaphragm relaxes; it becomes dome-shaped
This decreases the space in the chest putting increased pressure on the air in the lungs, causing it to be pushed out
The diaphragm relaxes; it becomes dome-shaped
This decreases the space in the chest putting increased pressure on the air in the lungs, causing it to be pushed out
42
New cards
Breathing
Process of taking oxygen into the lungs and forcing carbon dioxide out the body
43
New cards
Locations of gaseous exchange within the body
- in the alveoli, oxygen diffuses into the blood from the alveoli and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood back into the alveoli
- at the body tissue, oxygen diffuses from the blood into the cells and carbon dioxide from the cells diffuses into the blood
- at the body tissue, oxygen diffuses from the blood into the cells and carbon dioxide from the cells diffuses into the blood
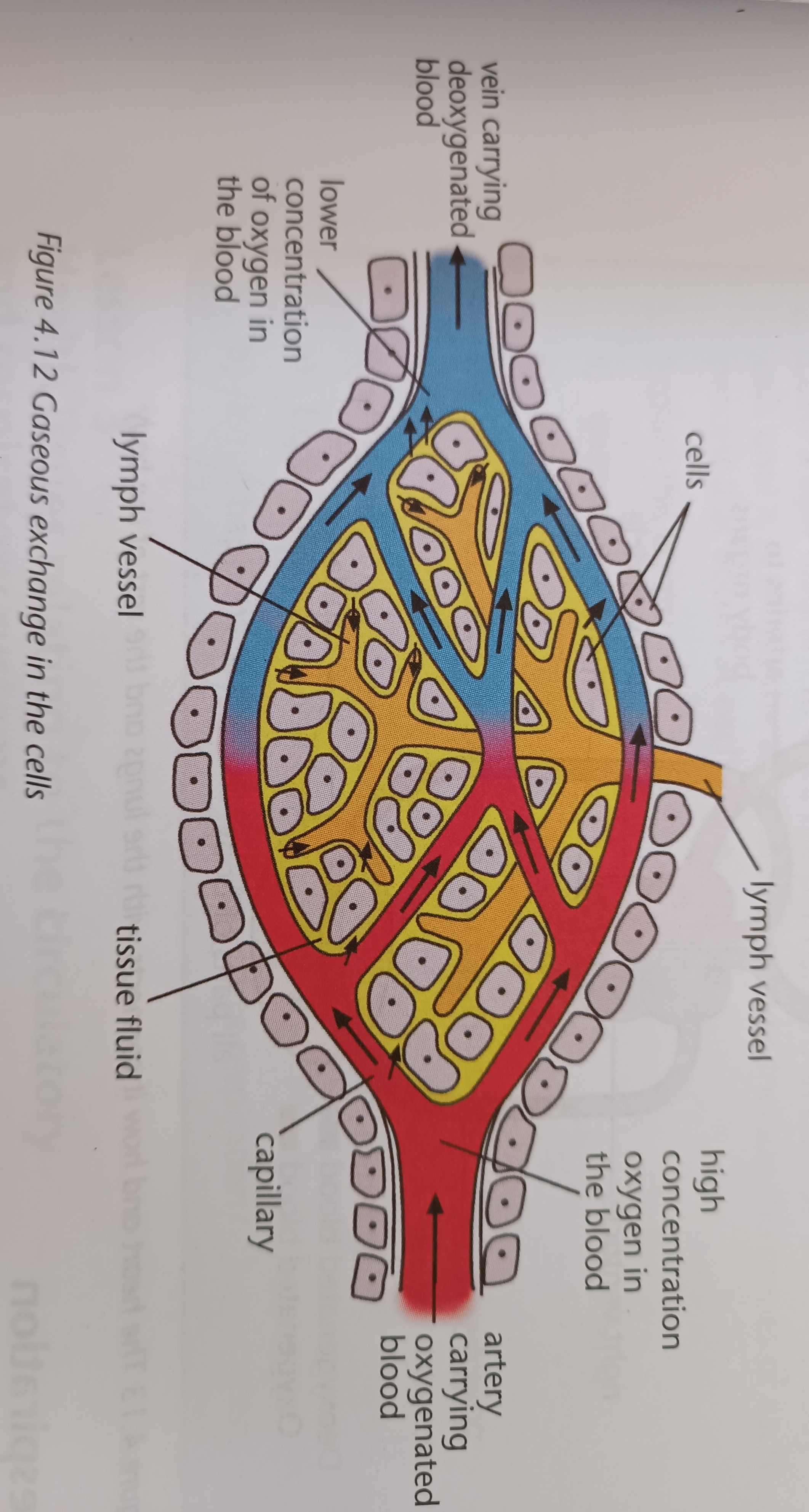
44
New cards
Cellular respiration
Metabolic reaction which occurs inside a mitochondria of a cell and results in the release of chemical energy
45
New cards
Common health issues of the respiratory system
Asthma, allergies that inflame the lung
Lung cancer, disease resulting from smoking/air pollution
Bronchitis, swelling of the lining of the bronchi due to infection
Pneumonia, alveoli fill with fluid due to infection
TB, infectious disease caused by bacteria
Lung cancer, disease resulting from smoking/air pollution
Bronchitis, swelling of the lining of the bronchi due to infection
Pneumonia, alveoli fill with fluid due to infection
TB, infectious disease caused by bacteria
46
New cards
Excretion
The removal of toxic metabolic waste from the body so the internal environment can remain stable
47
New cards
Which metabolic waste accumulates in the body?
Excess mineral salts
Excess water
Nitrogen containing waste : ammonia, urea, uric acid
Non-nitrogenous wastes : nicotine, pain-killers, tranquillizers
Excess water
Nitrogen containing waste : ammonia, urea, uric acid
Non-nitrogenous wastes : nicotine, pain-killers, tranquillizers
48
New cards
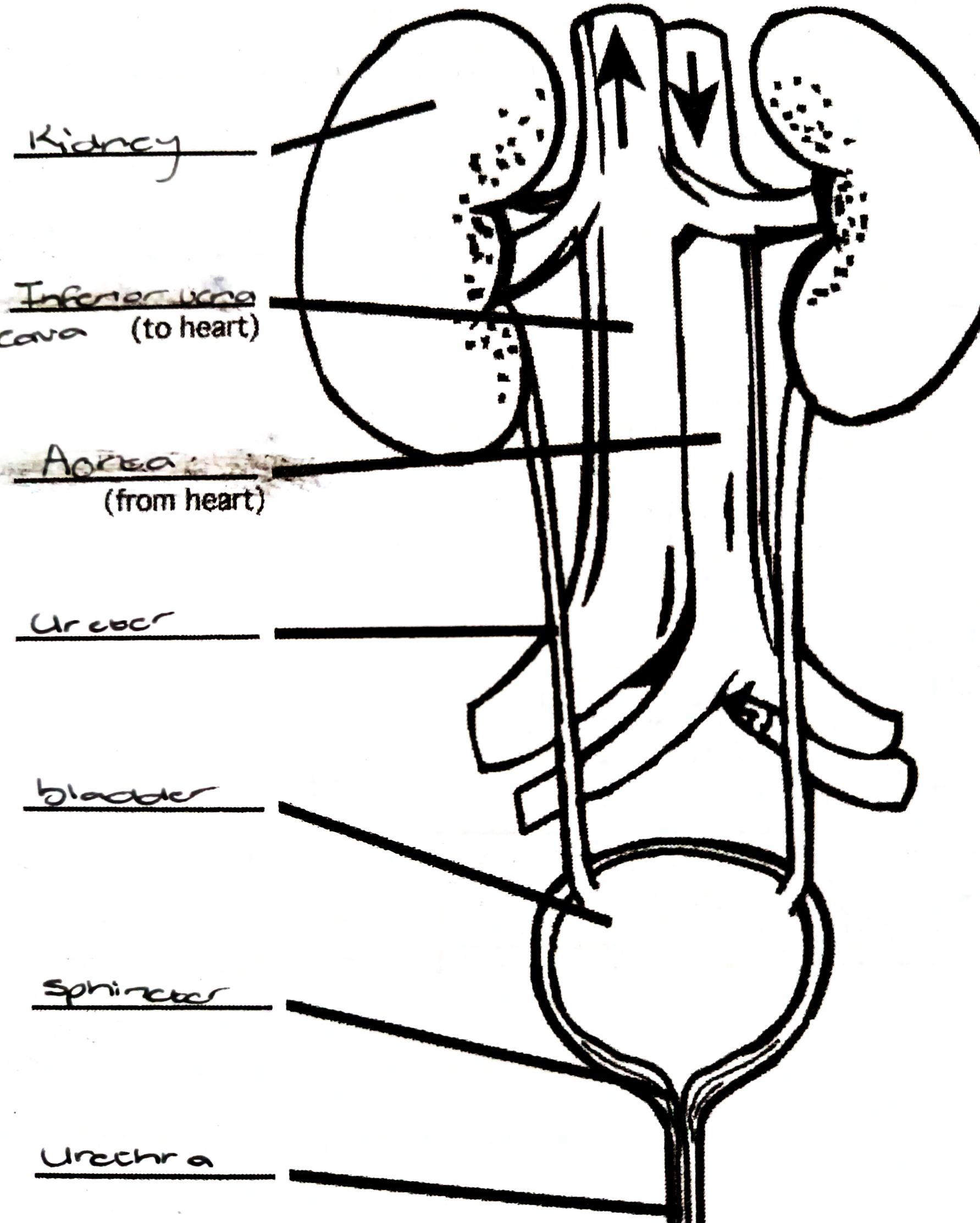
Functions of the kidney
Filtration of blood
Excretion of metabolic wastes
Reabsorption of useful substances
Control the pH of the blood
Osmoregulation
Excretion of metabolic wastes
Reabsorption of useful substances
Control the pH of the blood
Osmoregulation
49
New cards
Ureter
Tube that carries urine from kidney to bladder
50
New cards
Bladder
Stores urine
51
New cards
Sphincter/valve
Controls the release of urine from bladder
52
New cards
Urethra
Tube through which urine is released
53
New cards
Aorta (kidney)
Carries waste products, nutrients and oxygen from the heart to kidneys
54
New cards
Kidney
- acts as excretory organ
- bean shaped
- fit in between the rib cage and the pelvis, at the back of the body
- protected against heat loss and injury by masses of fatty tissue
- bean shaped
- fit in between the rib cage and the pelvis, at the back of the body
- protected against heat loss and injury by masses of fatty tissue
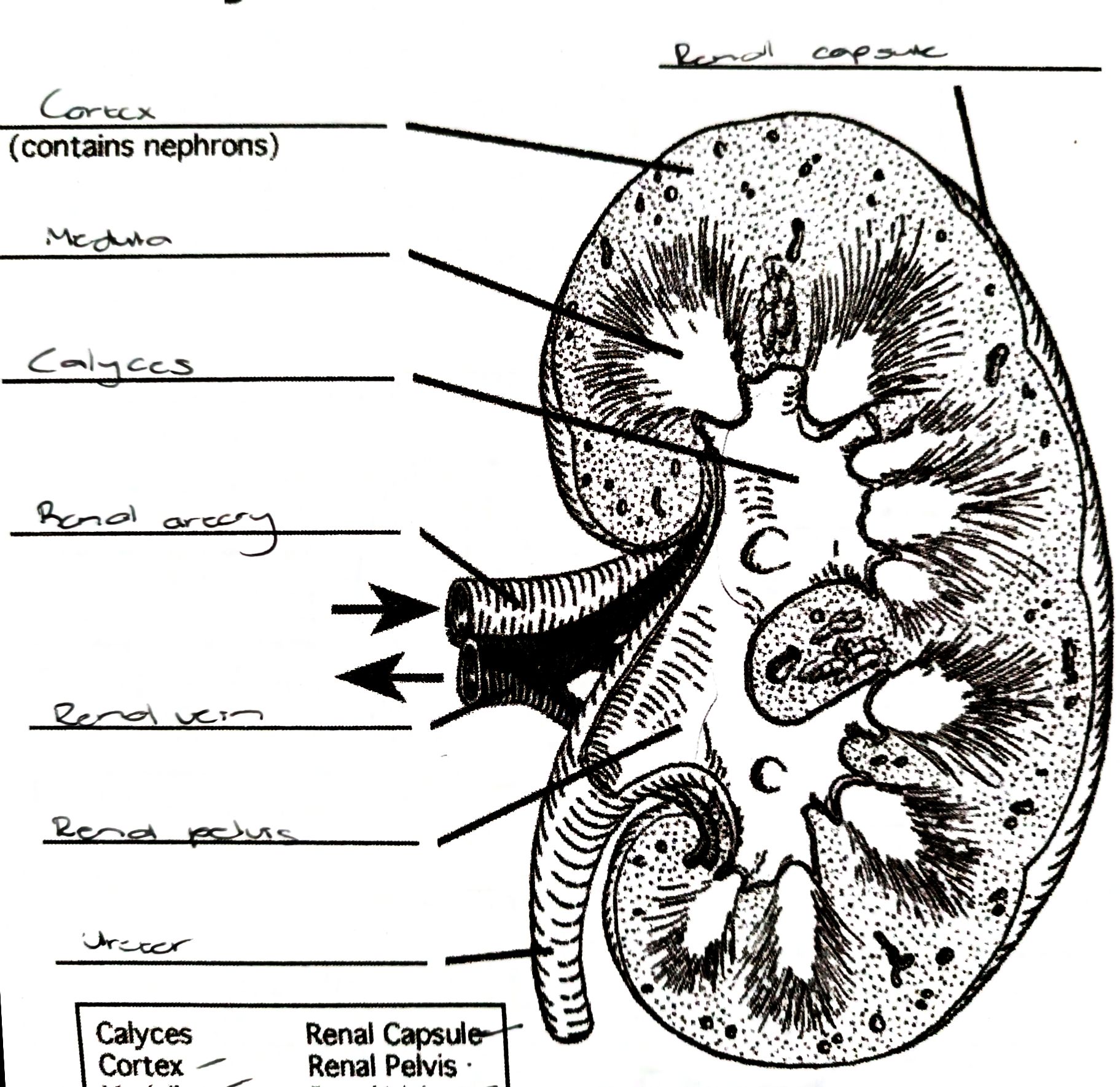
55
New cards
Renal vein
Carries purified deoxygenated blood back to the inferior vena cava
56
New cards
Renal artery
Carries impure blood containing metabolic waste from the aorta to the kidney
- branches off the aorta
- branches off the aorta
57
New cards
Nephron
Microscopic structure which carries out all the kidneys functions
58
New cards
Renal Capsule
Protects kidney
59
New cards
Cortex
Reddish outer area of kidney
60
New cards
Medulla
Light pink inner area of kidney
61
New cards
Kidney failure causes
Injury
Infection
Extensive use of certain drugs
Infection
Extensive use of certain drugs
62
New cards
Renal dialysis procedure
Blood from the artery is pumped into the dialyzer dialysis machine
The dialyzer cleans the blood by removing metabolic waste
The cleaned blood is then returned to the body
The dialyzer cleans the blood by removing metabolic waste
The cleaned blood is then returned to the body
63
New cards
Disadvantages of renal dialysis
Treatment is time consuming
Patient may feel ill during treatment
Bleeding problems, due to the anticoagulants
Kidney machines are very expensive
Patient may feel ill during treatment
Bleeding problems, due to the anticoagulants
Kidney machines are very expensive
64
New cards
Bladder infections
Bacteria and other micro-organisms get into the bladder
- most common in females; shorter urethra and closer to anus than men
- signs :
smelly, cloudy urine
burning sensation when urinating
- can be treated using antibiotics
- most common in females; shorter urethra and closer to anus than men
- signs :
smelly, cloudy urine
burning sensation when urinating
- can be treated using antibiotics
65
New cards
Kidney stones
- hard crystals of calcium and salts form inside the kidney
- can block tubules and cause terrible pain
- most pass out of the body on their own, but others may have to be removed by surgery
- symptoms:
sharp pain on the side of the body
blood in urine
- can block tubules and cause terrible pain
- most pass out of the body on their own, but others may have to be removed by surgery
- symptoms:
sharp pain on the side of the body
blood in urine
66
New cards
Disadvantages of kidney transplants
Difficult to find a suitable donor
Operation is expensive
Kidney can be rejected
Operation is expensive
Kidney can be rejected
67
New cards
Urinary systen