Periodic Properties
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
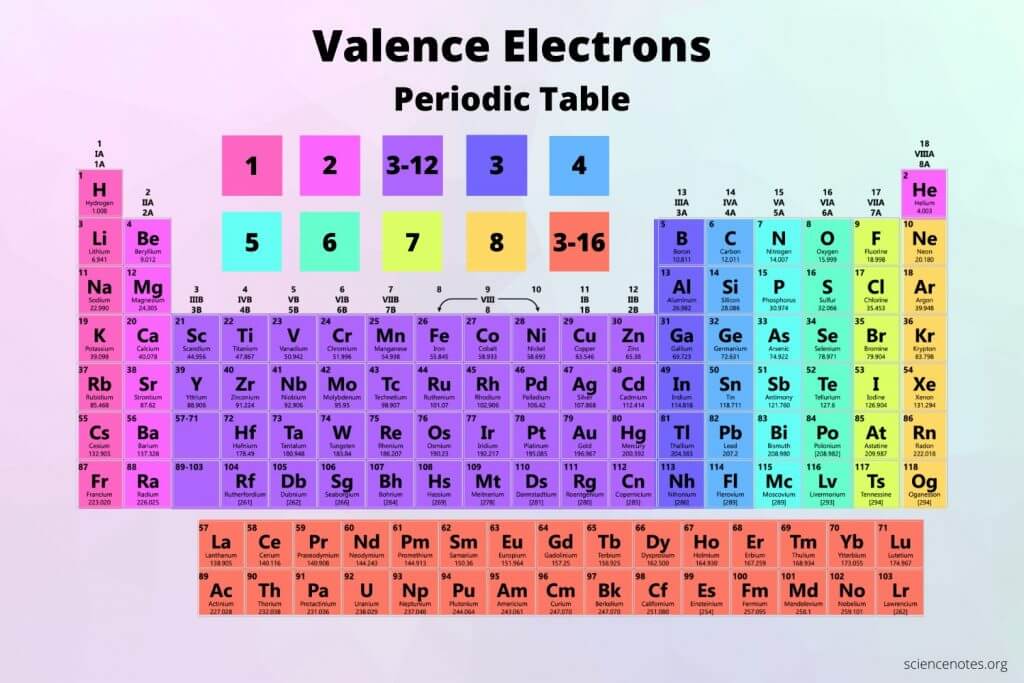
What does a group consist of on the periodic table?
Elements on the same column. They have the same number of valence electrons
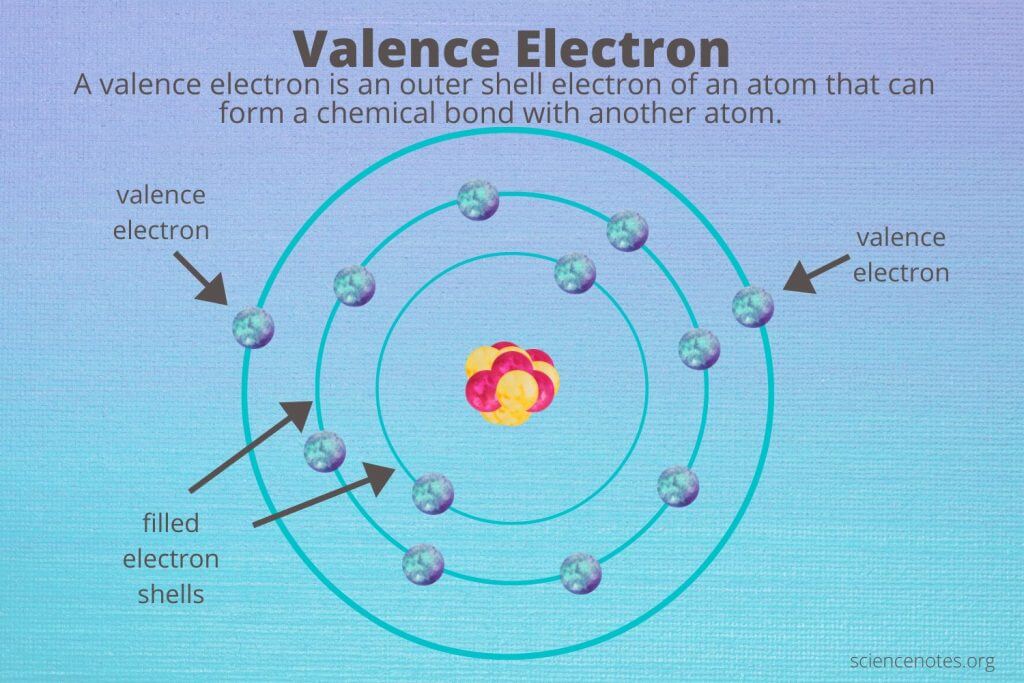
What is a valence electron?
It is the outer shell electron of an atom that can form a chemical bond with another atom
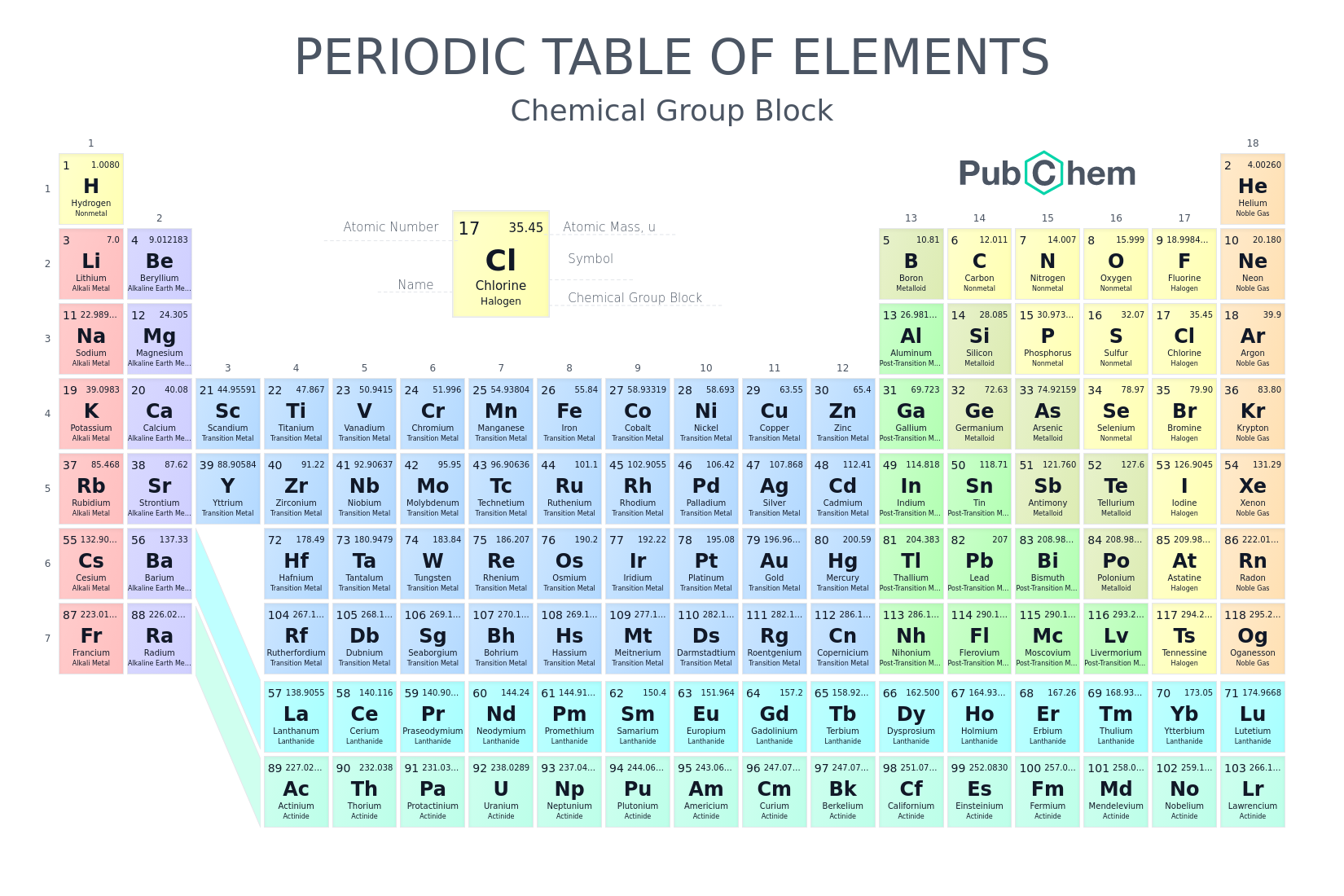
What does a period consist of on a periodic table?
It consist of elements that occupy the same row and have the same number of electron shells
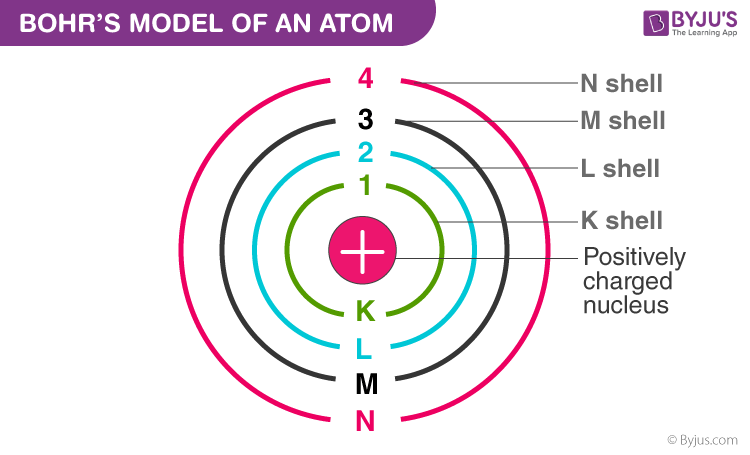
What is an electron shell?
Electron shells are regions surrounding an atom's nucleus that contain electrons. These shells are associated with specific energy levels, with the closest shell to the nucleus having the lowest energy.
The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of?
Protons
e.g → Nitrogen has an atomic number of 7 because it has 7 protons
What are group 1 elements called on the periodic table?
Alkali metals → excluding hydrogen
What are group 2 elements called on the periodic table?
Alkaline earth metals
What are group 3-12 elements called on the periodic table?
Transition metals
What are group 13-17 elements called on the periodic table?
Metallic and non-metallic → Metalloids
What are the seven metalloids?
B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po
“Bright Students Get As Studying These Problems “
What are group 17 elements called on the periodic table?
Halogens
What are group 18 elements called on the periodic table?
Noble gases
What row are the transition metals colorless?
row 4
What is oxidation state?
Oxidation state shows the total number of electrons that have been removed from an element (a positive oxidation state) or added to an element (a negative oxidation state) to get to its present state.
The last two bottom rows of the periodic table are known as?
Inner transition metals
Period 6 inner transition metals are called?
Lanthanides
Period 7 inner transition metals are called?
Actinides
What are diatomic atoms, and list the diatomic atoms that are important for the OAT
Atoms that are usually found paired due to their unstable nature
Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Fluorine, Oxygen, Iodine, Chlorine, and Bromine → Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer
What is the metallic trend on the periodic table?
Increase going from right to left across a period AND increase going down a group.
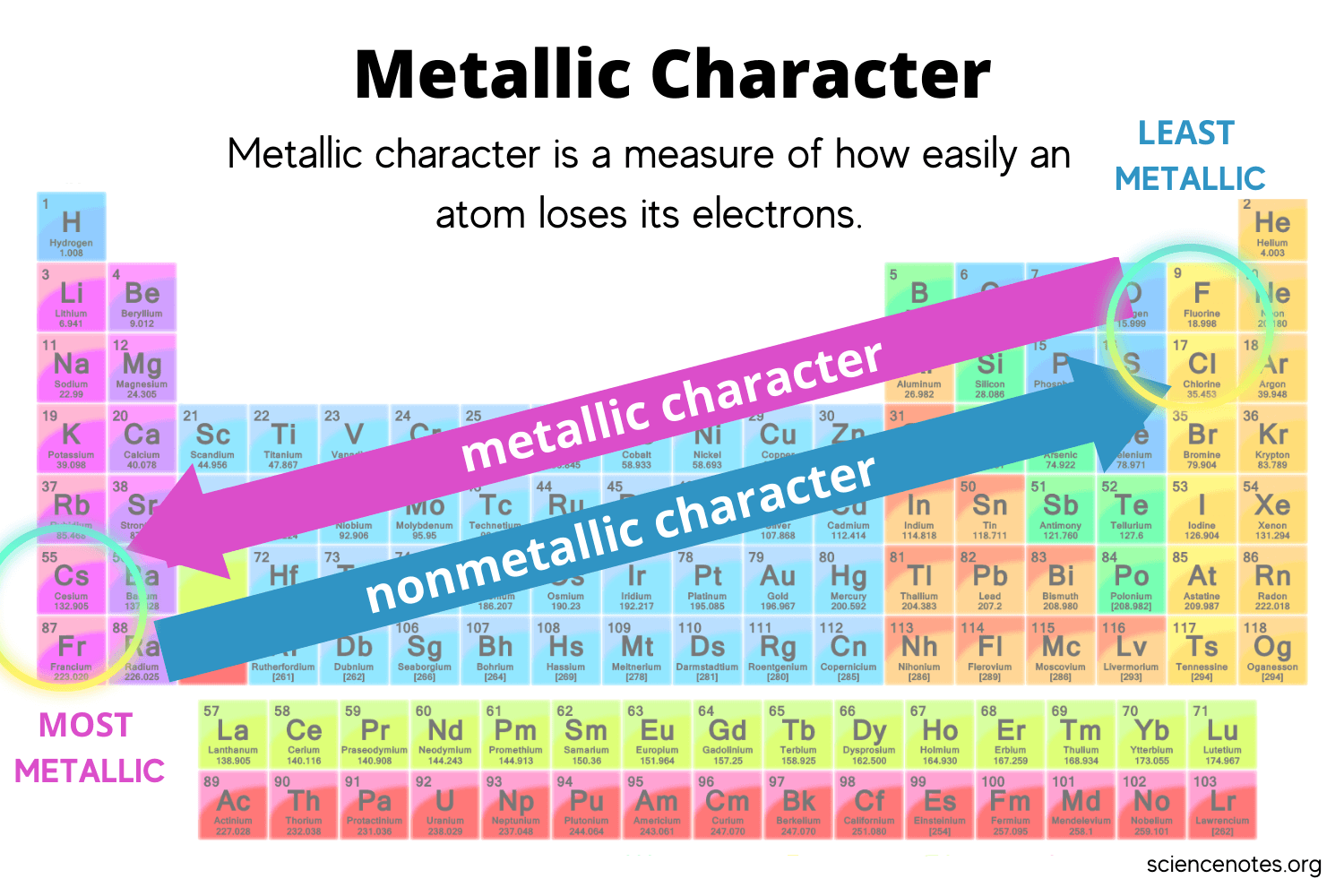
What is malleable and lustrous?
Metals
What is brittle and dull?
Non-metals
What are good conductors of electricity/ heat?
Metals
What are poor conductors of electricity/ heat
Non-metals
What forms a basic oxide?
Metals
What forms acidic oxide?
Non-metals
What lose electrons to form cations?
Metals
What gains electrons to form anions?
Non-metals
What are usually solid at room temperature, except for mercury (Hg), which is liquid?
Metals
What are gases or solids at room temperature, except bromine (Br), which is liquid?
Non-metals
What are generally high melting and boiling points?
Metals
What are generally low melting and boiling points?
Non-metals
What is the atomic radius?
Half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together
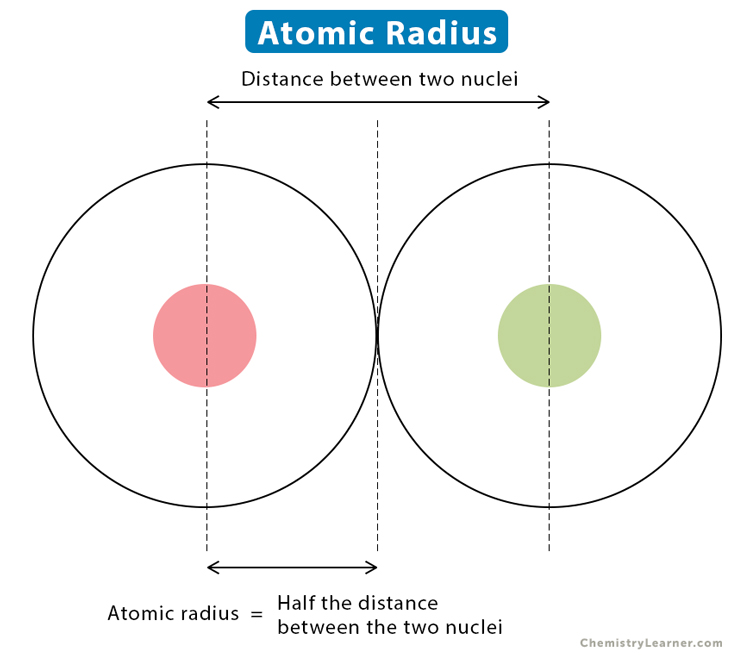
What is the atomic radius trend on the periodic table?
Atomic radius increases from right to left across a period AND increases going down a group

Why does the atomic radius increase from right to left across a period?
This is due to the decrease in proton number within the atom.
A reduction in proton results in a weaker nuclear attraction between the proton and electron, which causes the electron shells to be further apart from the nucleus, thereby increasing the radius.
Why does the atomic radius increase when going down a group?
This is due to the increasing number of electron shells as you move down a group.
As additional electron levels move further away from the nucleus, the atomic radius increases.
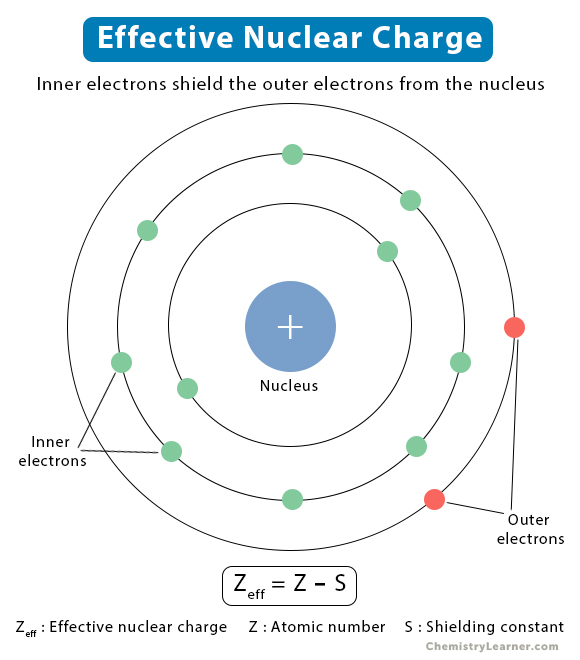
What is the effective nuclear charge?
It is the amount of positive charge experienced by an electron.
It is calculated:
Zeff= Z-s
Z= number of protons
S= number of shielding (non-valence) electrons
What is the trend for effective nuclear charge on the periodic table?
Increase left to right across a period AND increase going up a group
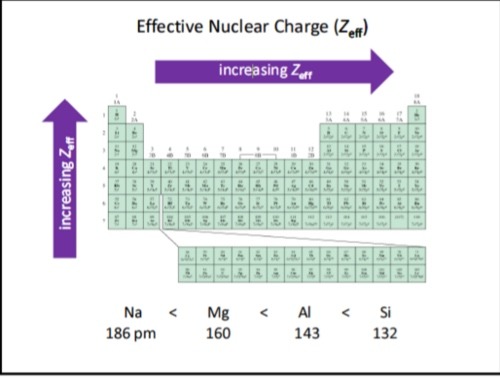
Why does the effective nuclear charge increase left to right across a period?
This is because the number of protons increases without an increase in electron shells, and thus, no increase in shielding effect.
This results in electrons being pulled closer to the nucleus due to a stronger attraction.
Why does the effective nuclear charge increase going up a group in the periodic table?
This is because the number of electron shells decreases, which brings outer shell electrons closer to the positively charged nucleus.
This increases the effective nuclear charge
What is the effective nuclear charge for a valence electron of gallium?
look at image

What is an isoelectronic series?
An atom that has an identical number of electrons but a different number of protons. Like anions and cations
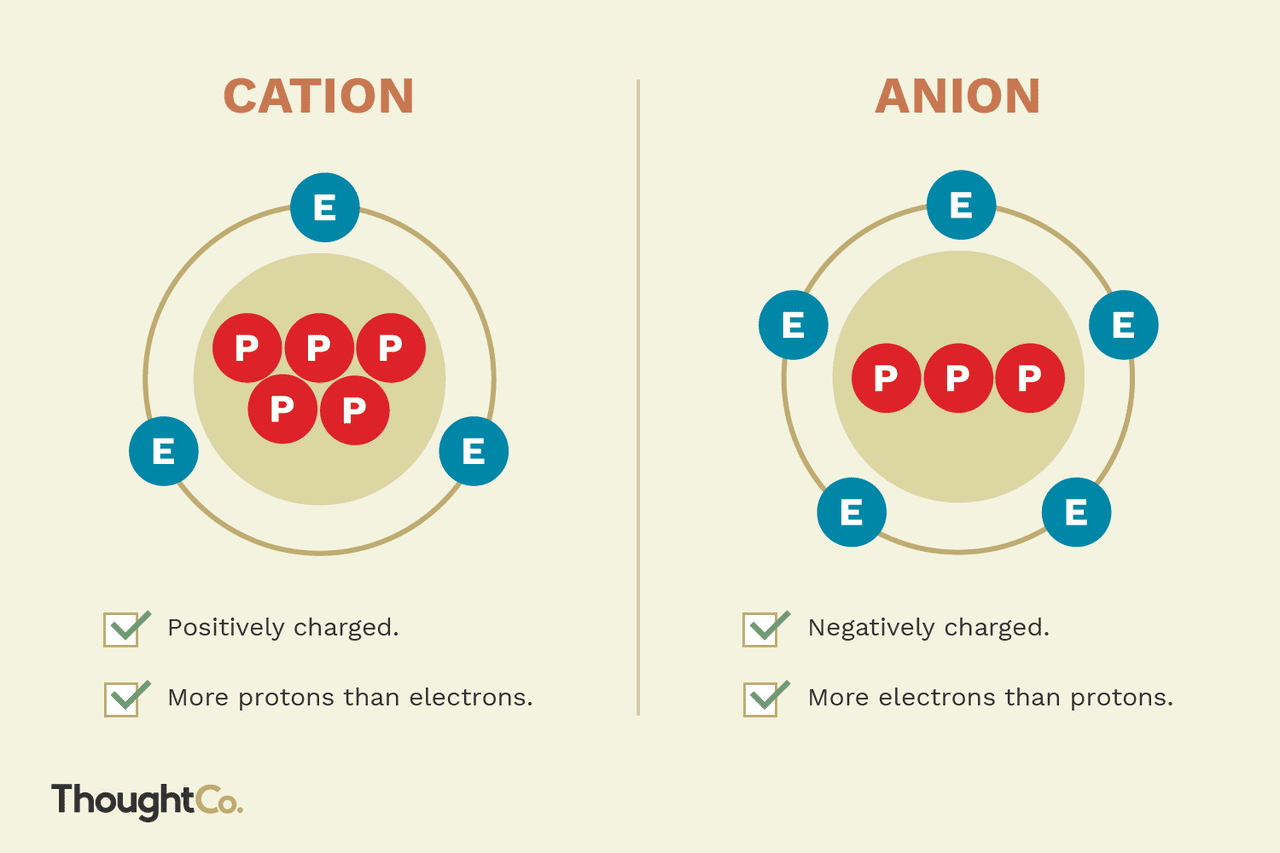
What is an anion?
They are ions that have gained electrons and have more electrons than protons, making them negatively charged.
The addition of electrons causes an electron-electron repulsion, which will result in a larger radius
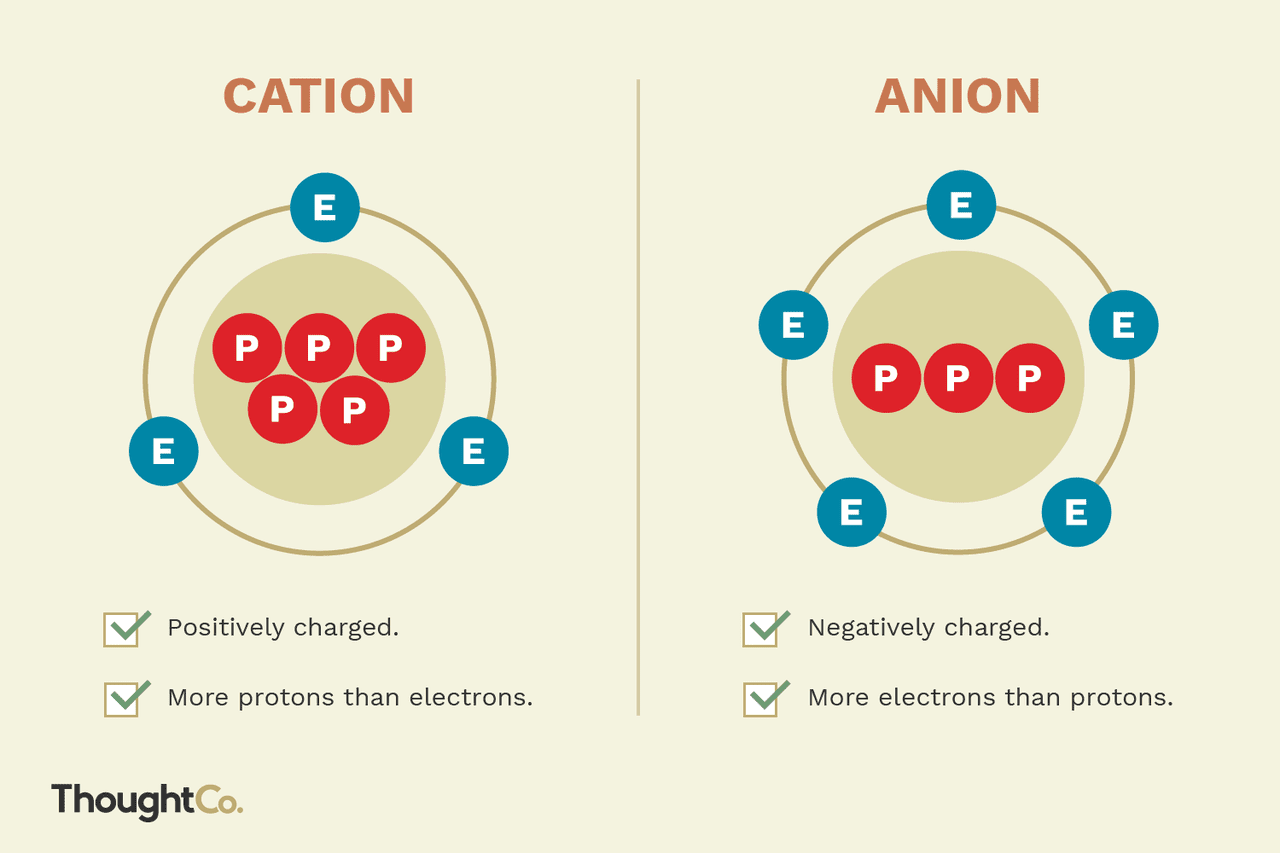
What is a cation?
They are ions that have lost electrons and have more protons than electrons, making them positively charged
The loss of electrons causes less electron-electron repulsion, resulting in a smaller radius
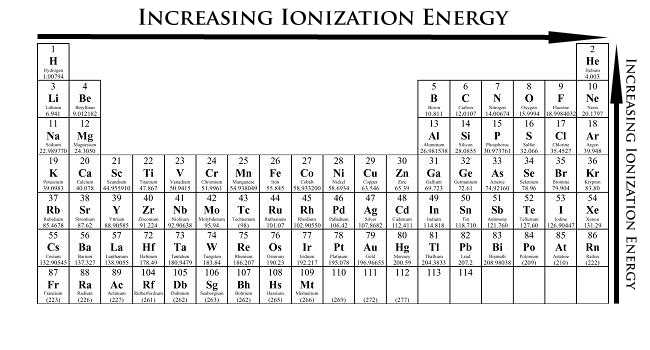
What is Ionization energy?
It is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom
What is the periodic trend for Ionization energy?
Increase going from left to right across a period and increase up a group
Noble gases have filled valence shells, making it hard to remove an electron
Why does Ionization energy increase from left to right across a period?
Across a period, the atomic number, or the number of protons, increases. Due to more stability it would take a lot of energy to remove an electron
Why does Ionization energy increase up a group?
Due to fewer electron shells and less shielding effect from the inner electrons, it creates difficulty in removing an electron
Does ionization energy increase or decrease after each removal of electrons?
Increase
It can go from 496kJxmol-1 to 4562kJxmol-1
What are the two notable exceptions to the Ionization energy rules?
Alkaline earth metals have filled orbitals (greater stability), making them have a higher ionization energy compared to elements in the same period. E.g→ Be has a higher ionization than B
Group 15 elements have half-filled orbitals (greater stability) compared to group 16 elements in the same period E.g → N has a bigger ionization energy than O
What is electron affinity?
The amount of energy released when an electron is added to an atom
What is the trend for electron affinity?
Increase going from left to right a period AND increase going up a group
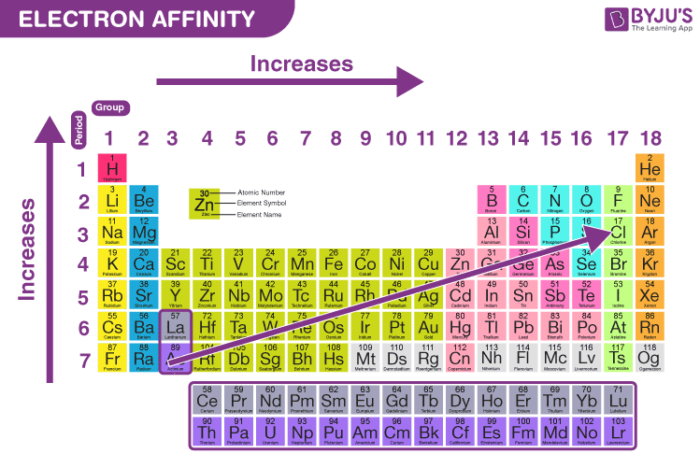
Why does electron affinity increase from left to right?
As the atom’s valence shell gets filled, there is an increased attraction between the nucleus and the electrons of the atom, causing a great affinity for electrons
Why does electron affinity increase going up a group?
There are fewer electron shells, leading to decreased electron shielding and an increased proximity between the nucleus and the valence electron, increasing the nuclear attraction and thereby increasing electron affinity
What are the three notable exceptions to the affinity rule?
Group 2 elements have filled s-orbitals, so their electron affinities are low
Group 15 elements have half-filled orbitals, so their affinity are lower than group 14 elements of the same period
Noble gases have filled electron shells, so their electron affinity are negligible
What is electronegativity?
The measurement of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a bond
What is the periodic trend for electronegativity?
Increase going from left to right across a period AND increase up a group.
Remember, Fluorine is the most electronegative element
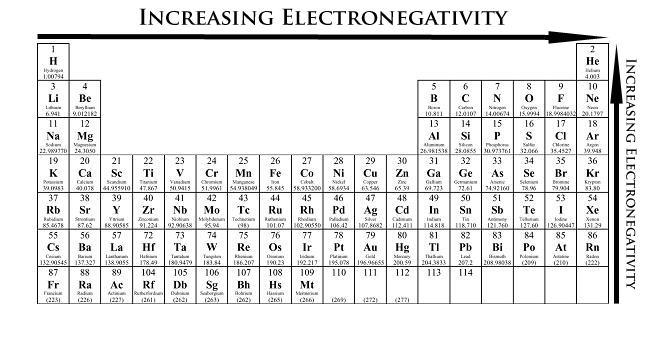
Why does electronegativity increase from left to right across a period?
Increase of protons causes an atom to attract an electron pair
Why does electronegativity increase as you move up a group?
The atomic radius decreases, and the valence electrons experience less shielding, causing the attraction of the electron pair to increase
What is the exceptions to the electronegativity rule?
Noble gases are an exception to the trend because they have filled valence shells and therefore have no electronegativity value
What is the most prominent oxidation state for transition metals?
+2
What is the most prominent oxidation state for inner transition metals?
+3
Can noble gases form acidic oxides?
No, this is due to their full valence electron shell
Magnesium (Mg) has a smaller atomic radius than barium (Ba) because of the difference in the?
Number of core electrons
Describes effective nuclear charge
The amount of positive charge experienced by an electron
Isoelectronic species have?
The same number of electrons but different number of protons
For an anion, adding electrons to the outermost shell increases?
electron-electron repulsion and will result in a larger atomic radius
For cations, removing electrons from the outermost shell increases?
The effective nuclear charge, which pulls the electron cloud closer to the nucleus, results in a smaller atomic radius
What factors directly affect periodic trends in ionization energy?
The atomic radius, number of protons, number of electron shell, and atomic number
As successive electrons are removed, the ionization energy?
Increase
What is electron affinity?
It is the energy released when an atom gains an electron
Why would fluorine exhibit a higher electron affinity than lithium?
Lithium has a lower effective nuclear charge → Moving left to right across a period, electron shielding remains constant, but effective nuclear charge increases
Do noble gases have higher electron affinity?
No
Electronegativity is the measurement of an atom’s ability to
Attract electrons in a bond
What factor does not contribute to the trends in electronegativity in the periodic table?
Ionization energy