A & P Lab Exam 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/214
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
215 Terms
1
New cards
anatomical position
standing erect, heels together, arms at sides with palms anterior and thumbs lateral
2
New cards
axial region
midline, core of the body
3
New cards
appendicular region
limbs, appendages
4
New cards
superior
above
5
New cards
inferior
below
6
New cards
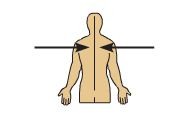
medial
towards midline
7
New cards
lateral
away from midline
8
New cards
superficial
close to surface
9
New cards
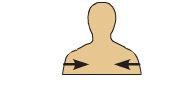
deep
away from surface
10
New cards
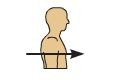
anterior (ventral)
towards front
11
New cards
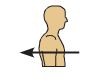
posterior (dorsal)
towards back
12
New cards
saggital plane
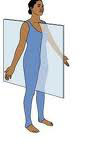
13
New cards
coronal plane
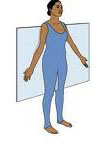
14
New cards
transverse (horizontal) plane
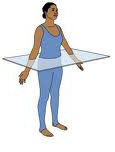
15
New cards
liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small & large intestines
major structures in RUQ
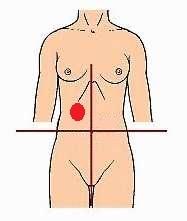
16
New cards
liver, stomach, spleen, pancreas, small & large intestines
major structures in LUQ
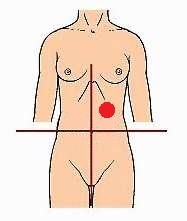
17
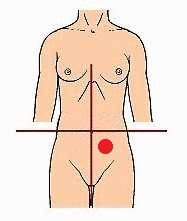
New cards
appendix, colon, right ovary & Fallopian tube
major structures in RLQ
18
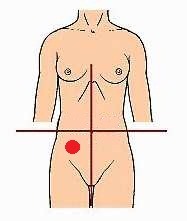
New cards
left kidney, left ureter, colon, bladder
major structures in LLQ
19
New cards
integumentary system
skin, dermis, and glands
regulation and protection, prevents water loss
regulation and protection, prevents water loss
20
New cards
skeletal system
bones, cartilages, ligaments, & tendons
protection & support, blood cell production
protection & support, blood cell production
21
New cards
muscular system
muscles attached to bones
movements, posture, and generates heat
movements, posture, and generates heat
22
New cards
nervous system
brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors
regulates and coordinates sensation and movement (and many other functions)
regulates and coordinates sensation and movement (and many other functions)
23
New cards
endocrine system
pituitary, thymus, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, ovaries, testes, and pancreas
regulation and maintenance of growth, metabolism, etc.
regulation and maintenance of growth, metabolism, etc.
24
New cards
cardiovascular system
heart, blood vessels, and blood
transport of nutrients and waste, immune function
transport of nutrients and waste, immune function
25
New cards
lymphatic system
vessels, nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, and lymph tissue
immune response, circulatory functions, fat absorption
immune response, circulatory functions, fat absorption
26
New cards
respiratory system
nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, lungs, and bronchi
O2 and CO2 exchange
O2 and CO2 exchange
27
New cards
digestive system
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
mechanical and chemical breakdown of ingested foods, and absorption
mechanical and chemical breakdown of ingested foods, and absorption
28
New cards
urinary system
kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra
waste removal, regulates pH, water balance
waste removal, regulates pH, water balance
29
New cards
reproductive systems
male: testes, prostate, scrotum, penis, and duct system
female: ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, mammary glands, and vagina
produce sex cells and sex hormones
female: ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, mammary glands, and vagina
produce sex cells and sex hormones
30
New cards
magnification
makes things look bigger
31
New cards
resolution
distinguishes 2 objects
32
New cards
ocular (10) x objective
total magnification equation (x)
33
New cards
d2 = x1 (10) x d1 (1600) / x2 (objective)
field of view equation (um)
34
New cards
cell size = diameter of field / # of cells
cell size equation (um)
35
New cards
cytoplasm
composed of fluid (cytosol) & organelles, contains cytoskeleton (provides structure & anchors organelles)
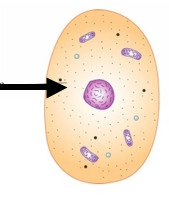
36
New cards
nucleus
surrounded by 2-layered envelope (folds to form nuclear pores), contains DNA and proteins, contains nucleolus (area of condensation inside nucleus where ribosomes are formed)
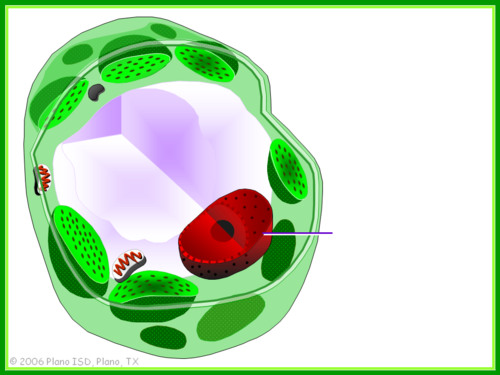
37
New cards
ribosomes
sites of protein synthesis, composed of a large and small subunit, assembled in nucleolus of cell and released into cytoplasm where they interact with mRNA
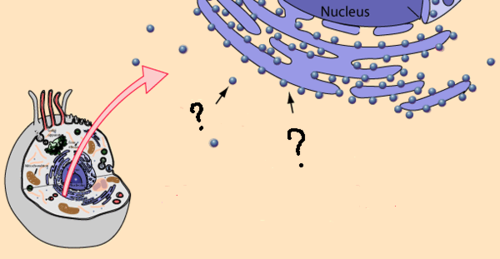
38
New cards
rough ER
has ribosomes, synthesizes phospholipids for cell membrane
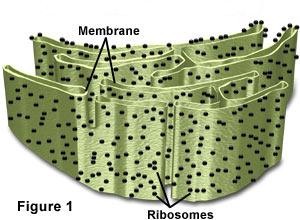
39
New cards
smooth ER
no ribosomes attached, synthesizes lipids and some steroids
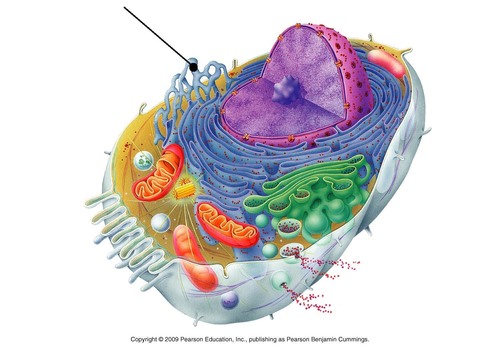
40
New cards
golgi apparatus
composed of cisternae, modifies / packages / and distributes proteins and lipids manufactured by smooth and rough ER, secretory vesicles pinch off from golgi and move to surface of cell for exocytosis
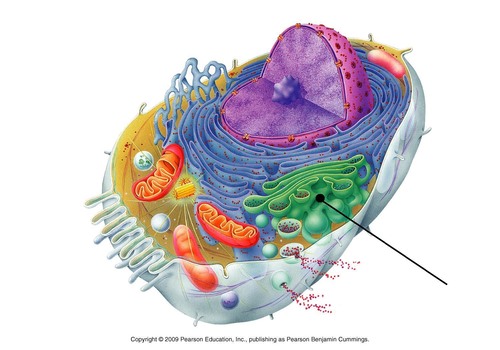
41
New cards
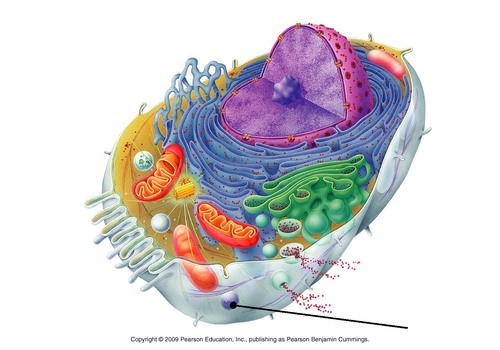
lysosomes
membrane-bound vesicles that pinch off from the golgi, contain enzymes that digest foreign material that is brought into cell by phagocytosis
42
New cards
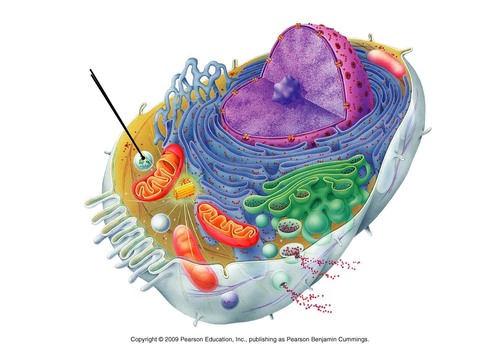
peroxisomes
lysosome-like membranous sacs that contain enzymes that detoxify alcohol, peroxides, and other chemicals
43
New cards
mitochondria
produce ATP, can be sperical / long and rod shaped, composed of inner and outer membrane (enzymes of citric acid cycle found in intermembrane space), found mainly in cells that participate in active transport of substances (gather near membrane where transport takes place)
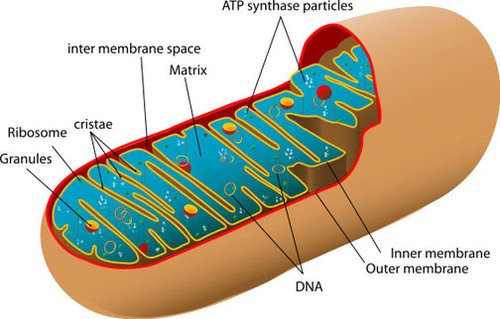
44
New cards
centrioles
paired cylindrical organelles that form an X near the nucleus, involved in cell division (normally prominent only during mitosis)
45
New cards
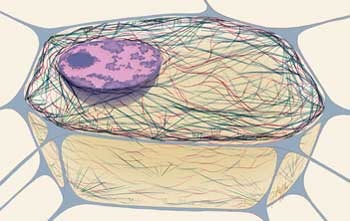
cytoskeleton
made of actin, intermediate filaments, microtubules; for mobility and increasing SA (gives structure to cilia, flagellum, microvilli
46
New cards
cell membrane
the semipermeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell
47
New cards
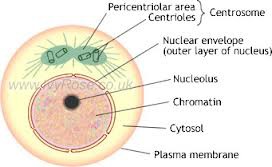
interphase
cell spends about 90% of its time in this phase, prepares itself for division by doubling its size and replicating DNA
48
New cards
prophase
chromatin coalesces to form chromosomes, centrioles migrate to poles of cell and project spindle fibers toward equator, nuclear envelope disintegrates and nucleoli disappear

49
New cards
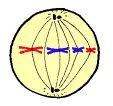
metaphase
chromosomes attach by centromeres along equator of spindle fibers
50
New cards
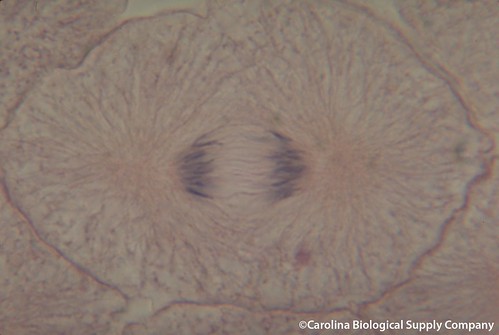
anaphase
chromatids separate into chromosomes, 2 sets of chromosomes pulled by spindle fibers to opposite poles, cytokinesis begins towards end of this phase (plasma membrane pinches together along equator and create cleavage furrow)
51
New cards
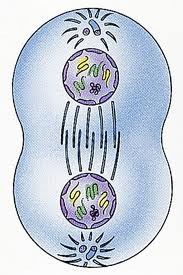
telophase
cytokinesis pinches 2 cells apart, new nuclear envelope begins to form around 2 sets of chromosomes, chromosomes again become diffuse and spread out
52
New cards
diffusion
solutes move down their concentration gradient
53
New cards
osmosis
movement of water across a membrane
54
New cards
equilibrium
no net movement of solutes within the solution
55
New cards
semi-permeable membrane
only certain substances can pass through the cell membrane
56
New cards
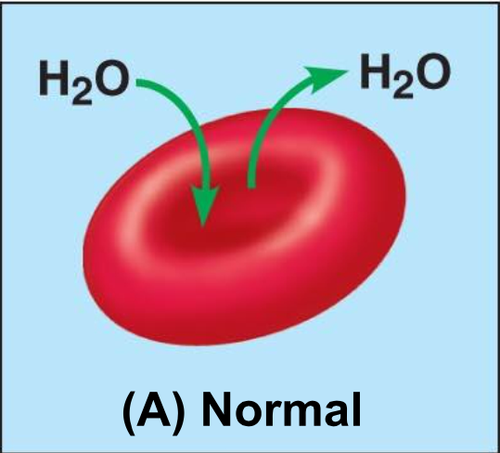
isotonic
inside the cell has the same concentration of ions as the solution, so there is no net movement of water into / out of the cell
57
New cards
hypotonic
inside the cell has more solutes than the solution, so water rushes in and causes it to swell (lyse- swell and burst)
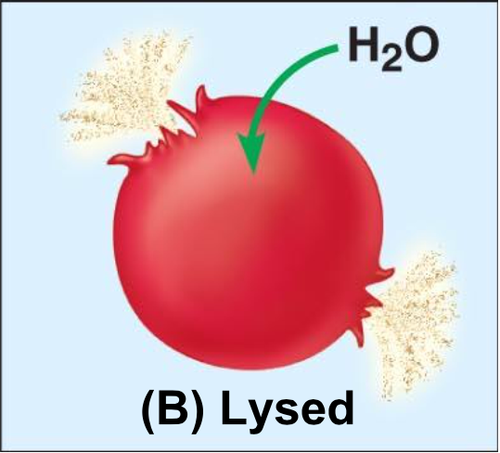
58
New cards
hypertonic
more water present in the interior of the cell than in the external solution so water leaves the cell and it becomes crenated
59
New cards
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution
60
New cards
solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves
61
New cards
concentration gradient, temperature, molecule size, SA of membrane
factors that affect diffusion / osmosis rates
62
New cards
passive
is diffusion active or passive?
63
New cards
starch, sucrose
these molecules could not pass through the dialysis tubing
64
New cards
water, glucose
these molecules were able to pass through the dialysis tubing
65
New cards
initial
which is faster: initial rate or final rate of osmosis?
66
New cards
the glucose's small size
Why was glucose able to diffuse out of the dialysis bag while starch stayed inside?
67
New cards
small hydrophobic (nonpolar) molecules and gases like oxygen and CO2
main factors that determine if a solute can pass through the dialysis bag / cell membrane
68
New cards
epithelial tissue
Tissue that covers outside of the body and lines organs and cavities
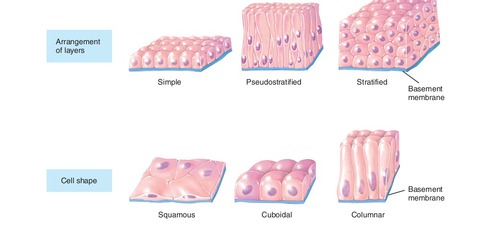
69
New cards
connective tissue
A body tissue that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts
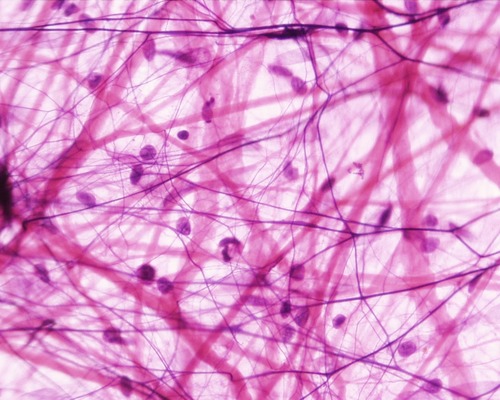
70
New cards
muscle tissue
Tissue made of cells capable of contracting
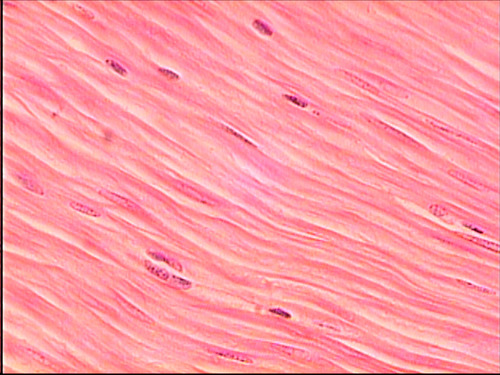
71
New cards
epithelium
type of tissue with cellularity, special cell contacts, polarity, is supported by connective tissue, avascular but innervated, regeneration by mitosis, located on the surface
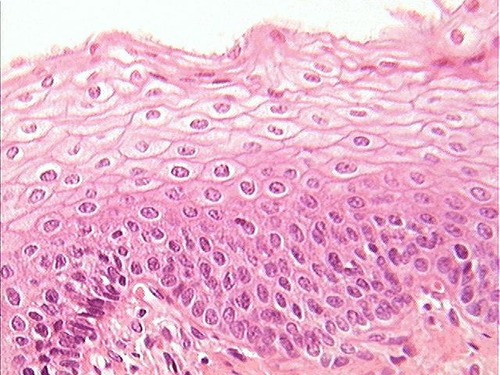
72
New cards
connective
type of tissue that develops from mesenchyme, has abundant extracellular matrix, includes collagen, reticular fibers, and elastin
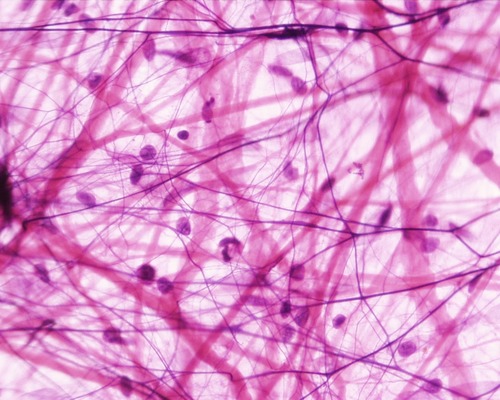
73
New cards
muscular
type of tissue that has skeletal, cardiac, and smooth types, CONTRACTILE!
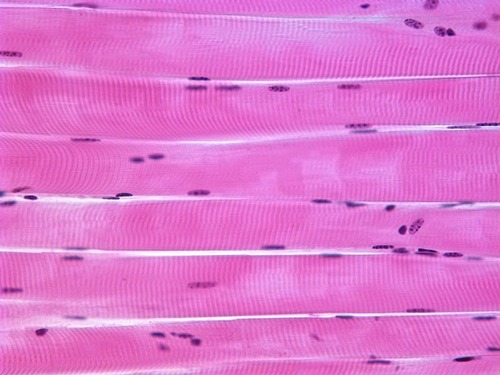
74
New cards
nervous tissue
type of tissue that carries action potentials, neurons make up the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves
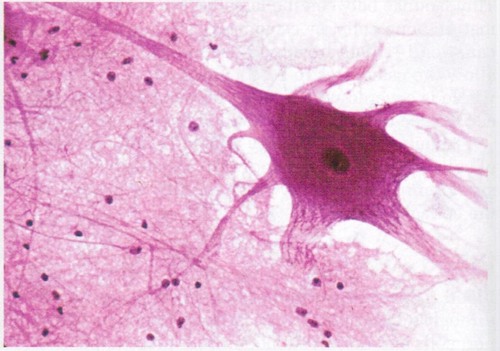
75
New cards
simple squamous
diffusion, filtration, secretion
capillaries, endothelium, alveoli (lung), glomeruli, eye lens
diffusion, filtration, secretion
capillaries, endothelium, alveoli (lung), glomeruli, eye lens
type of epithelial tissue, function, and location?
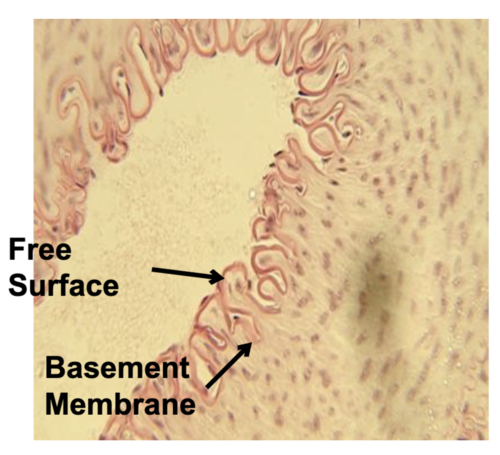
76
New cards
simple cuboidal
absorption*, active transport, secretion
kidney ducts, ovary surface
absorption*, active transport, secretion
kidney ducts, ovary surface
type of epithelial tissue, function, and location?
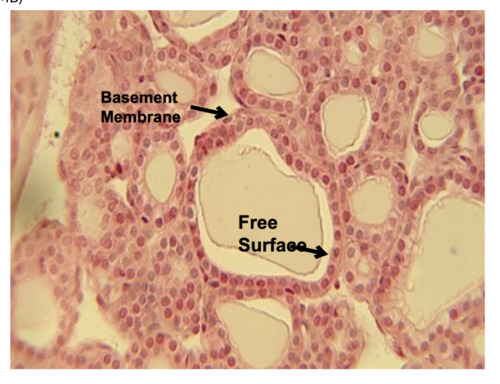
77
New cards
simple columnar
secretion of mucous, absorption
lines digestive tract, portions of uterus / uterine tubes
secretion of mucous, absorption
lines digestive tract, portions of uterus / uterine tubes
type of epithelial tissue, function, and location?
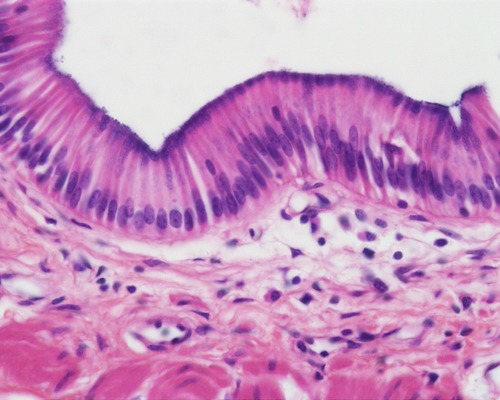
78
New cards
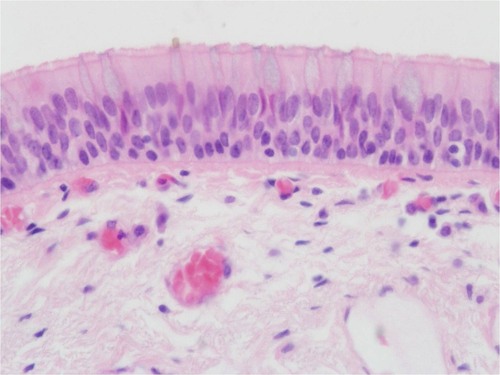
pseudostratified columnar
specialized goblet cells release mucous to coat passageways
respiratory tract, male urethra
specialized goblet cells release mucous to coat passageways
respiratory tract, male urethra
type of epithelial tissue, function, and location?
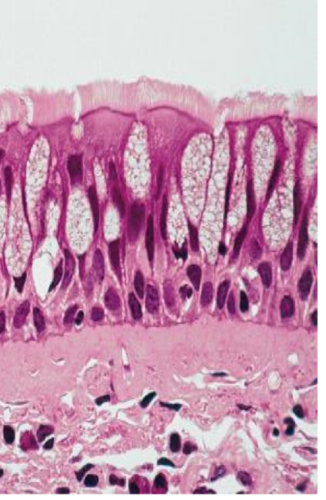
79
New cards
stratified squamous
protection against abrasion
esophagus, mouth, vagina, anus, epidermis
protection against abrasion
esophagus, mouth, vagina, anus, epidermis
type of epithelial tissue, function, and location?
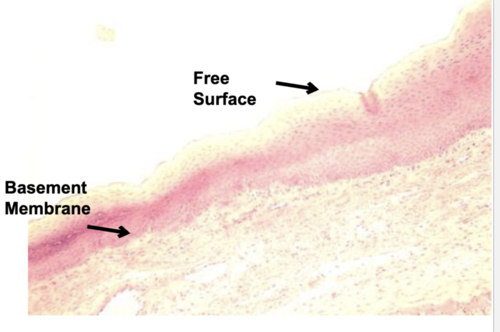
80
New cards
stratified cuboidal
protection, secretion
sweat glands, ovary follicle, mammary glands
protection, secretion
sweat glands, ovary follicle, mammary glands
type of epithelial tissue, function, and location?
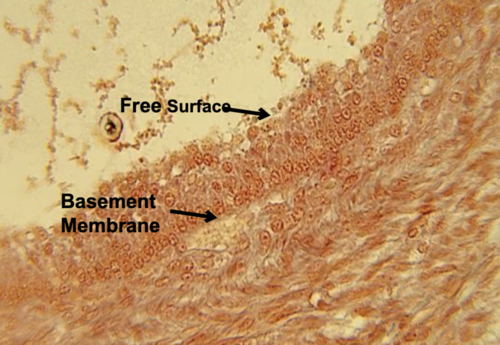
81
New cards
stratified columnar
protection, secretion
large ducts of some glands, some portions of male urethra
protection, secretion
large ducts of some glands, some portions of male urethra
type of epithelial tissue, function, and location?
82
New cards
transitional
allow stretching as it fills
bladder, urethra, ureters
allow stretching as it fills
bladder, urethra, ureters
type of epithelial tissue, function, and location?
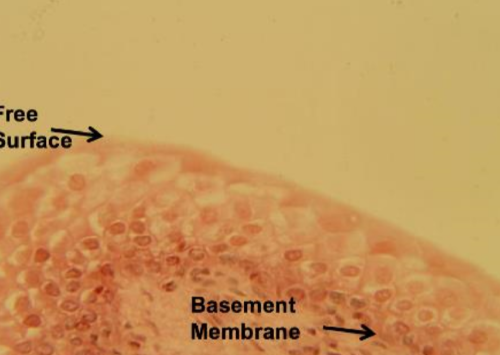
83
New cards
areolar
anchors skin to underlying tissues, anchors tissues together, around organs, surrounds capillaries, and between tissues
widespread throughout the body
thick purple = collages
light and web-like = reticular
dark and thin = elastin
anchors skin to underlying tissues, anchors tissues together, around organs, surrounds capillaries, and between tissues
widespread throughout the body
thick purple = collages
light and web-like = reticular
dark and thin = elastin
type of connective tissue, function, and location? (and what are the lines?)
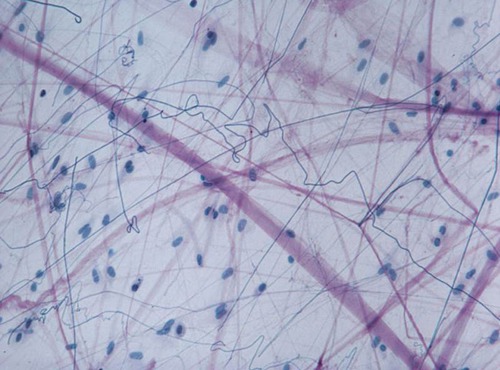
84
New cards
adipose
cushioning, insulation, energy storage
under skin, around kidney, eyeballs
cushioning, insulation, energy storage
under skin, around kidney, eyeballs
type of connective tissue, function, and location?
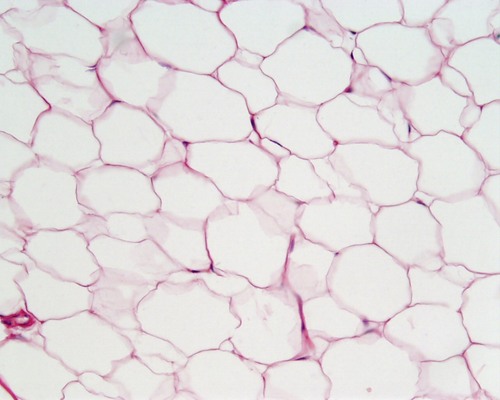
85
New cards
dense regular fibrous
tendons and ligaments
tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses
tendons and ligaments
tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses
type of connective tissue, function, and location?

86
New cards
dense irregular fibrous
strong in all directions
mostly dermis, capsules around organs and joints
strong in all directions
mostly dermis, capsules around organs and joints
type of connective tissue, function, and location?
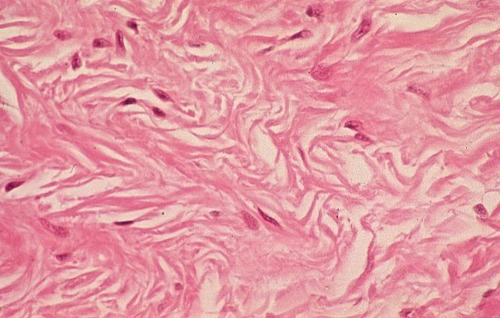
87
New cards
hyaline cartilage
helps bones move smoothly past each other in joints
lines joints and caps the ends of bones
helps bones move smoothly past each other in joints
lines joints and caps the ends of bones
type of connective tissue, function, and location?
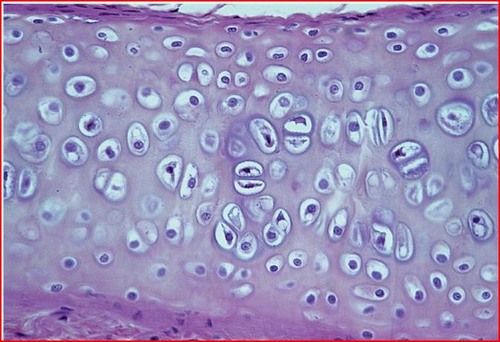
88
New cards
elastic cartilage
provides strength, elasticity, and maintains shape of certain structure
external ears
provides strength, elasticity, and maintains shape of certain structure
external ears
type of connective tissue, function, and location?
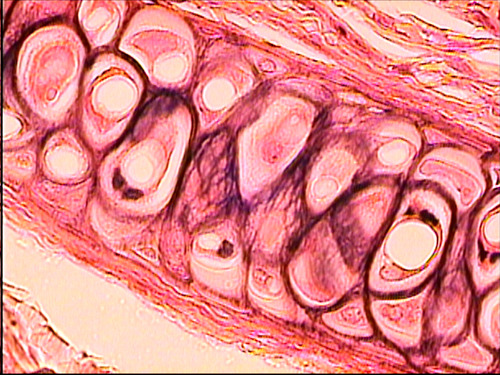
89
New cards
fibrocartilage
provides tough material of intervertebral discs
intervertebral discs
provides tough material of intervertebral discs
intervertebral discs
type of connective tissue, function, and location?
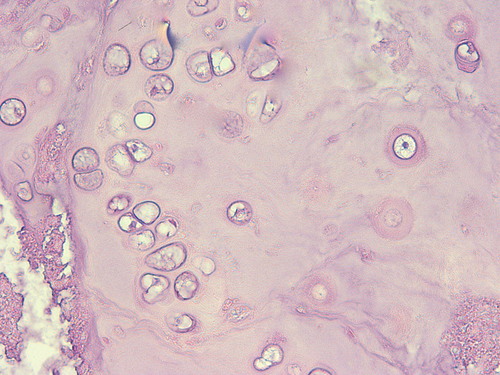
90
New cards
blood
type of connective tissue?
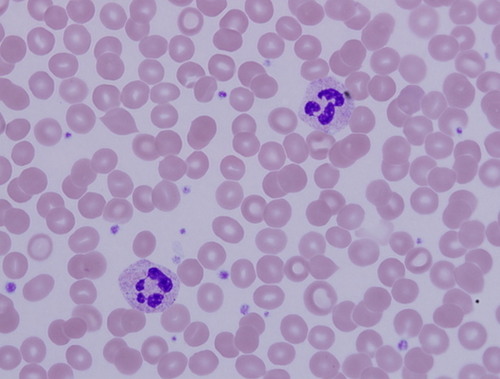
91
New cards
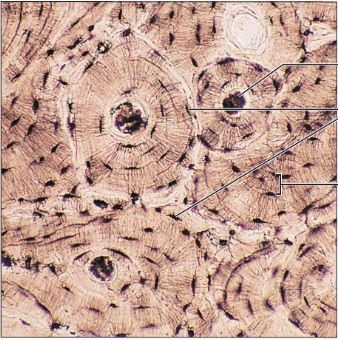
bone
type of connective tissue?
92
New cards
they are contractile!
what is unique about muscular tissue?
93
New cards
skeletal
type of muscle tissue?

94
New cards
cardiac
type of muscle tissue?
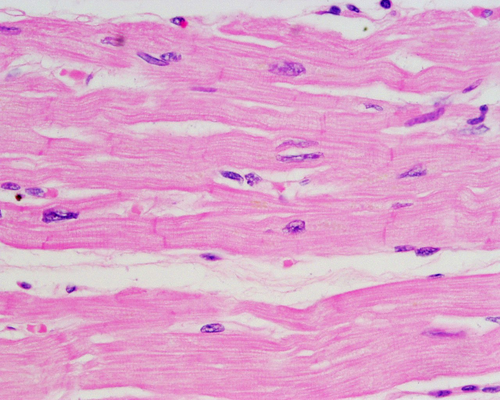
95
New cards
smooth
type of muscle tissue?
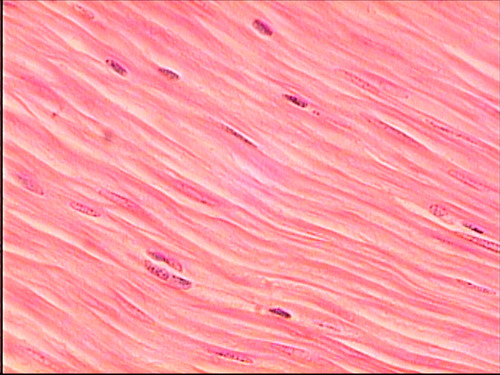
96
New cards
dendrite
part of neuron?
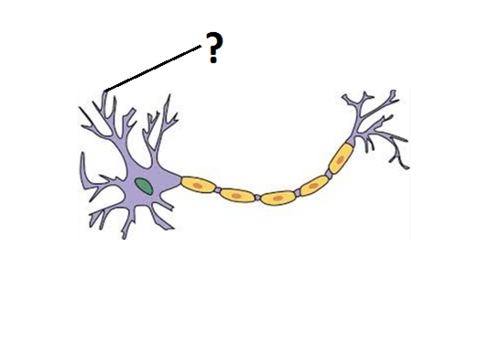
97
New cards
cell body
part of neuron?
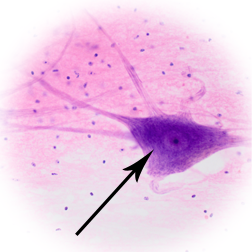
98
New cards
axon
part of neuron?
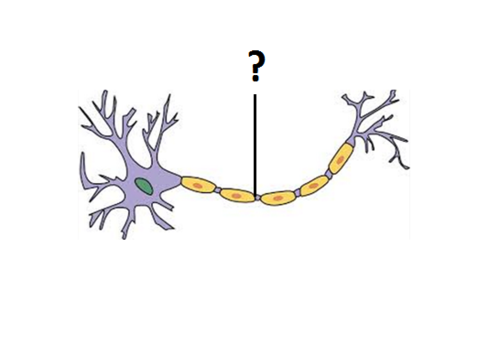
99
New cards
specialized to carry electrical signals called action potentials
what is special about nervous tissue?
100
New cards
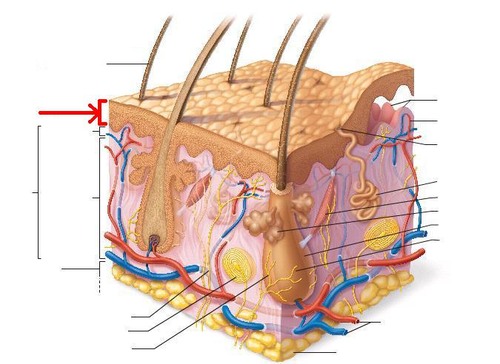
epidermis
what layer of skin?