14 SQ: Fundamentals of Material Processes
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What is a “process“?
Series of actions that produce something or that lead to a particular result
Some steps are necessar to fulfill the primary function of the product, while others are necessary to make sure that the process runs smoothly
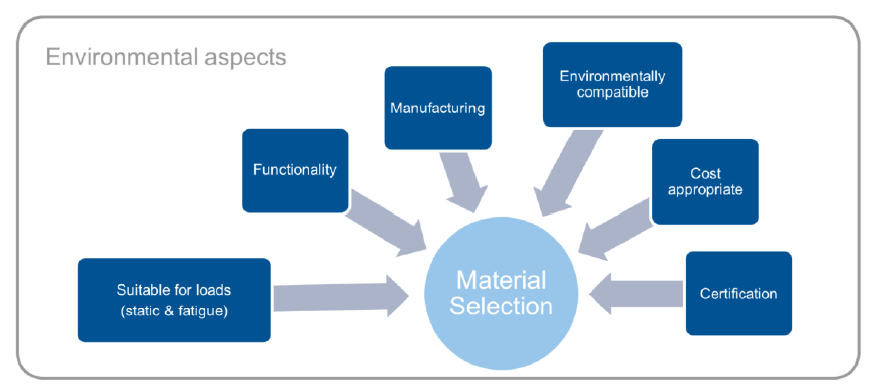
What are two factors not related to material properties that have to be considered when selecting a material for aerospace applications?
Suitable for loads (static and fatigue) (Material related)
Functionality (Material/Case related)
Manufacturing
Environmentally compatible
Cost appropriate
Certification
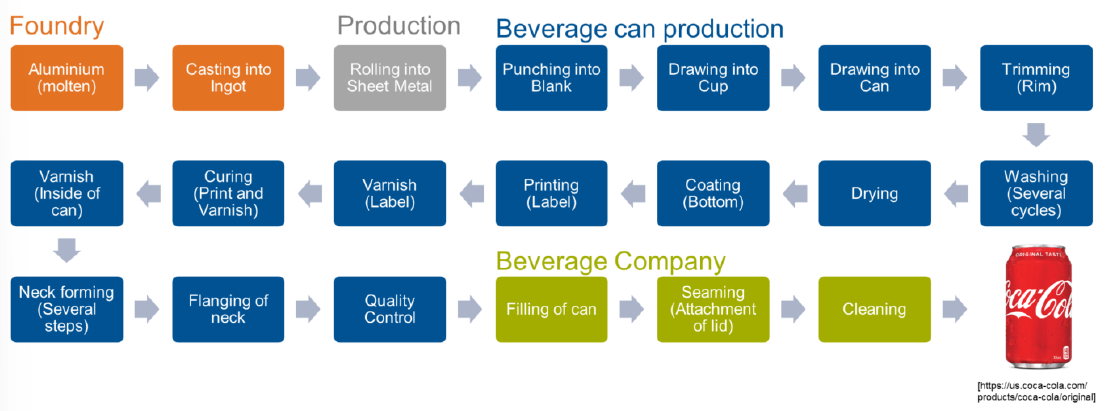
Describe a multi-step production process and how it could be used to produce a part of your choice
Process: beverage can
Melting and casting of Al → Punching → Drawing → Triming → Washing → Drying → Coating → Printing → Varnishing → Curing → Varnishing → Neck forming → Flanging → Quality control → Filling → Seaming → Cleaning
Name different types of material processes and their distinctive attributes in terms of cohesion (acc. DIN 8580)
Primary Shaping: creating cohesion from shapeless material
Forming: maintaining cohesion, plastically deforming a solid body
Separating: reducing cohesion
Joining: local increase of cohesion
Coating: local increase of cohesion
Property Modification:
In which case could a process be assigned to different DIN 8580 groups?
Depending on cohesion (¿?)
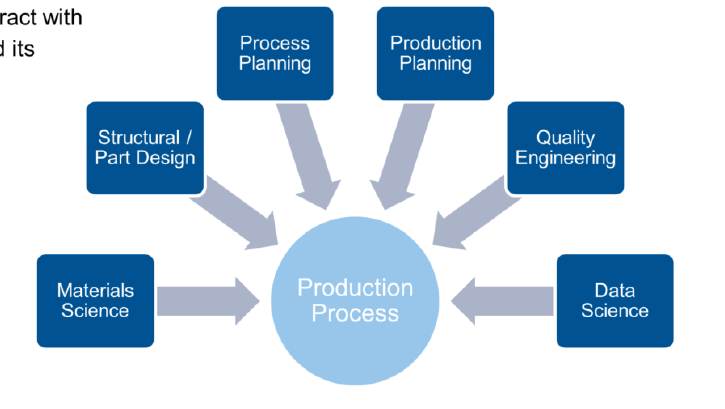
Name disciplines that interact with materials process development and briefly explain points of interaction (6)
Materials Science: at the material properties
Structural / Part Design: design for manufacturability (guidelines); utilization of new materials and processes
Process Planning: material flow and logistics; sequencing of steps; continuous/discontinuous production; cycle times; equipment requirements; material demands
Production Planning: staff; shifts; which machines; material supply; purchased/pre-produced parts; equipping plans
Quality Engineering: certification; qualification; quality assurance; process monitoring; audtis; customer complaints. FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis) and FAI (First Article Inspection); repeatability; productivity
Data Science: gathering of large amount of real-time data; complex analysis and simulation; optimization of production
What is Industry 4.0 and what tools does it provide that can help optimize production processes? (5)
Industry 4.0: implementation of big-data from sensors to analyze and optimize production
Tools:
Digital Supply Chain: digital reproduction of supple chains with e.g. sensors, trackers, thermometers, etc.
Intelligent Sensor Networks: decentralized, interconnected sensors to caputre and process relevant data from production
Data Mining/Machine learning: statistical analysis of data to find correlations and trends that can be used for Digital Twins
Digital Twin: digital representation of a part of the system to predict its behavior, ideally with AI
Cyber-Physical Systems: interaction of Digital and Physical and components using all avialable data to perform a task
What specific challenges come into play when selecting materials for Advanced Air Mobility (AAM = Air Taxis) applications?
Materials Selection:
Heavy batteries
Process selection and Production Planning:
Comparatively high-rate production
Low airframe cost for competitive market
Qualification:
Ambitious Entry into Service (EIS)
How can these challenges be met (challenges of selecting materials for AAM)?
Materials Selection:
High strength materilas such as composites
Part design
Process selection and Production Planning:
Factory and process planning
Escalable pilot facilities
Automation in all processes → Repeatability
Digital manufacturing (Industry 4.0)
Qualification:
Use pre-qualified materials and processes