Biomechanics Exam 3
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam is Wednesday, December 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
moment of inertia
Inertial resistance for an angular system is dependent on _____.
mass of object
Inertial resistance for an linear system is dependent on _____.
slope
Resistance to F(gravity) is dependent on _____.
Coefficient of friction
_____ is a variable that represents the shared resistance between two surfaces.
less
Friction resistance is ______ if the slope is 10 degrees compared to a horizontal surface.
lubrication, decreasing mass, and increasing slope
Friction resistance can be reduced by _____.
decreases
Friction resistance _____ acceleration.
moment of inertia and rolling resistance
The two types of resistance exclusively affecting wheels are _____.
v²
Air resistance is proportional to _____.
form and skin
Air resistance is affected by the shape and flow around an object. This is referred to as _____ drag.
joint friction, muscle tissue, and CNS control
Sources of internal resistance to movement include:
the force that opposes the initial movement between two surfaces that are in contact and at rest.
Static friction is ______.
the force that opposes the relative motion between two surfaces sliding past each other.
Kinetic friction is _____.
Contact force between the object and the support surface (i.e., vertical force) and the coefficient of friction (C(friction)) between the object and the support surface
Friction is dependent on _______.
parasitic drag
Typical air resistance is referred to as _____.
To calculate complex motion performance under real-life conditions
What is the main purpose of a performance equation in biomechanics?
Power
Which physical quantity is most commonly evaluated using the performance equation for biking and rowing?
Gravity
Which force acts as propulsion in downhill skiing according to the performance equation?
Efficiency of the system
What does 'eff' represent in the performance equation?
Exponential
In the performance equation, what type of relationship does aerodynamic drag have with velocity?
Biking
Which sport typically has the highest mechanical efficiency?
Performance equations use resistive forces
What is the key difference between using the performance equation versus uniformly accelerated motion (UAM) equations?
Mass
Which component contributes to rolling resistance in biking?
Watts can be positive or negative
What problem arises in skiing when solving for velocity using the performance equation?
Difficulty collecting accurate real-time data
What challenge is commonly encountered when applying performance equations to real-life activities?
Fulcrum, applied force, and load
What are the three contact points that define a lever system?
Tennis shoe sole
Which of the following is NOT an example of a lever used in sports?
Ratio of output force to input force
What does mechanical advantage (MA) of force represent in a lever?
1st class lever
Which lever class provides both force and velocity mechanical advantages?
F1 x d1 = F2 x d2
What is the formula used to express torque balance in levers?
3rd class lever
Which lever class is typically used to generate high speed at the expense of force?
Displacement
In terms of mechanical advantage, what increases when leverage force decreases?
3rd class
What class lever is the elbow?
Torque clockwise equals torque counterclockwise
What happens in a torque balance scenario?
Balancing weights on a beam
Which of the following combinations is most likely to use torque balance in biomechanics?
Force advantage (leverage)
ratio of output force to input force
Velocity advantage (speed)
ratio of distance (force) to distance (load)
Second class lever
Which lever positions the load between the fulcrum and the effort
joint compression force
When the arm is abducted into the horizontal position, contraction of the deltoid muscles causes an increase in _____.
axis of rotation
When the shoulder is externally rotated, the humerus rotates along the _____.
almost 0
Consider performing an isometric bicep curl where your humerus is vertical and your forearm is horizontal. When the elbow is flexed at 90 degrees, the compressive force on the elbow joint is _____.
line of force
In the formula for torque, F*r, r is the distance from the axis of rotation to the _____.
all
When you jump off of a curb and land on the ground, _____ muscles contract.
head of the trochanter
In older adults, increased vertical forces acting on the hip increase fracture risk of the _____.
patella
When the quadriceps contract, the _____ provides compressive force that stabilizes the knee.
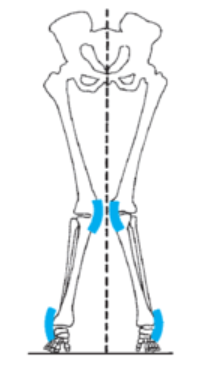
valgus, varus
In the accompanying figure, the knee alignment is considered to be excessive _____ and the ankle alignment is excessive _____.
motion segment
Two adjacent vertebrae and the associated soft tissue is called a _____.
pulposus
The part of the intervertebral disc that acts as the fulcrum for spinal bending is the _____.
Inertia
Resistive force proportional to mass
Slope
Angle of inclination
Gradient
Another term for slope or inclination
Agonist
Muscle responsible for the primary movement
Antagonist
Muscle that opposes the primary movement
Synergists
Provide secondary movement control and stability
power, locomotion, shock absorption, balance/stability
The primary functions of the lower extremities include _____.
What are the major loads acting on the hip during stance?
The weight of body segments above the hip (wt) the tension in the hip abductor muscles (Fm) and the joint reaction force (R) generated in accordance with Newton’s 3rd law
Varus
An inward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint
Valgus
Refers to an outward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint
Intervertebral Discs
fibrocartilaginous structures that cushion spinal joints
Shear forces
sliding forces perpendicular to the normal force
20
What percentage of the gait cycle is spent in the double support phase? (Remember you have two legs)
At mid-stance
In the walking gait cycle, when does the center of mass reach its highest point?
heel strike to toe-off
The double stance phase of gait is from _____ to _____.
Braking and propulsion
What does the ground reaction force in the sagittal plane primarily reflect?
Conservation of energy
Pendulum motion during the gait cycle uses which concept of biomechanics?
GAITRite
Which clinical tool is used to measure gait performance over a fixed distance?
Overground provides more natural visual feedback
What is the key difference between overground and treadmill gait assessment?
running only
The spring-pendulum model for gait applies to _____.
Decreased flexion
What would change in knee joint range of motion due to increased joint stiffness?
center of mass/center of pressure alignment
Treadmill walking alters _____.