Food production
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
How do glasshouses and polythene tunnels increase the yield of certain crops?
Heat from the Sun is trapped so the optimum temperature of enzymes are reached
Plants are protected from pests
Carbon dioxide levels are maintained in glasshouses to optimise the rate of photosynthesis
enclosed environment protects crops from harsh weather conditions
What is the effect on crop yield when you increase carbon dioxide in glasshouses?
Paraffin lamps can be burned to increase carbon dioxide levels, which ensures that CO2 is not the limiting factor of photosynthesis
What is the effect on crop yield when you increase the temperature in glasshouses?
The heat from the Sun is trapped, raising the temperature, which allows enzymes in photosynthesis to work at the optimum temperature and so the rate of photosynthesis increases
How can fertilisers increase crop yield?
Fertilisers contain nutrients which allow plants to grow faster
Some examples are:
Nitrates - to make amino acids for proteins, for plant growth
Phosphates - for respiration and root growth
potassium - for growth of flowers and fruit, allows enzyme reactions to take place
What is pest control?
The use of pesticides or biological control to prevent insects from eating the plants.
Pesticides include fungicides, herbicides, insecticides
What are some methods of biological control?
Introducing a natural predator
Introducing a parasite
Introducing a herbivore
What are the advantages of pesticides?
Can kill the entire pest population
Quick and efficient
relatively cheap
What are the disadvantages of pesticides?
Organisms can develop resistance
Non-specific, so it kills other organisms too
Bioaccumulation can make it toxic for others in the food chain
Requires a continuous supply
Describe the role of yeast in the production of bread.
Yeast uses anaerobic respiration in order to make bread rise. A product of anaerobic respiration is carbon dioxide, which forms bubbles in the dough, causing it to rise
Describe a practical investigating the role of anaerobic respiration by yeast in different conditions.
Set up a series of closed tubes containing a solution of yeast and sugar of the same concentrations
Place each tube in a water bath of a range of temperature e.g. 10, 20, 30, 40, 50’C
Each tube should be connected to a gas syringe to measure the volume of CO2
The method above is just for temperature, but the sugar concentration can also be changed.
Describe the process to produce yoghurt.
All equipment is sterilised to kill unwanted microorganisms
Milk is heated to 70’C for 15-20 seconds to kill any natural bacteria in milk — pasteurisation
Milk is homogenised to disperse fat globules
Then, the milk is cooled to 40-45’C and inoculated with a starter culture of Lactobacillus (lactic acid bacteria)
Here, the bacteria breaks down lactose into lactic acid
During so, the lactic acid causes the pH to fall to around 4.4, causing milk proteins to coagulate and so the mixture thickens
What is the role of Lactobacillus in the production of yoghurt?
Breaks down lactose into lactic acid
lactic acid - drop in pH, prevents the growth of other microorganisms
preserves nutrients in milk
What is a fermenter?
A fermenter is any vessel that is used to grow microorganisms used for fermentation.
Describe the use of industrial fermenters.
They are large tanks that can hold up to 200,000dm3 of a liquid culture.
They enable environmental conditions (e.g. temperature, oxygen, CO2 concentrations, pH and nutrient supply) to be carefully controlled so that microorganisms will yield their products most efficiently.
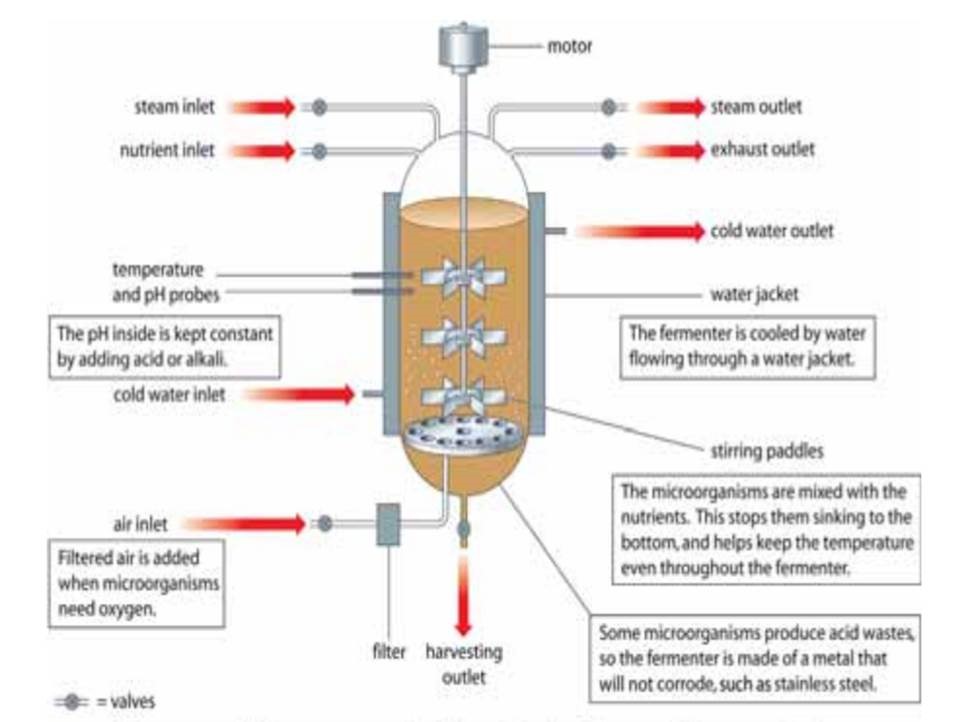
What are the components of a fermenter?
Motor
Steam inlet outlet
Nutrient inlet
Exhaust outlet
Water jacket
Stirring paddles
Temp and pH probs
air inlet
filter
harvesting outlet
Why are aseptic precautions used and how?
Aseptic precautions are used to prevent the contamination by unwanted microorganisms which could affect the growth of microorganisms in the culture.
This is done by filtering the air and sterilisng the fermenter and all solutions added to the fermenter.
What are the use of stirring paddles?
stop the nutrients from sinking to the bottom
help keep the temperature even throughout the fermenter
How is the pH kept constant in a fermenter?
By adding acid or alkali