FOM Week 15 LEC 131-137
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Each question labeled with lecture # (E.g. 131). Check out Amaya's Knowt Deck for Cranial Nerve facts: https://knowt.com/flashcards/77dd97c7-875d-42b1-84ab-8d05714e18a6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
(131) The Iliac Crest is at the level of:
L4-L5
(131) The PSIS is at the level of:
S2
(132) A positive Murphy’s Sign is suggestive of:
acute cholecysitis
(132) A positive McBurney’s Point test is suggestive of:
acute appendicitis
(132) A positive Rebound Tenderness test is suggestive of:
peritonitis or appendicitis
(132) A positive Referred Rebound Tenderness test is suggestive of:
peritonitis
(132) A positive Rovsing’s Sign is suggestive of:
appendicitis
(132) A positive Obturator Sign is suggestive of:
peritoneal inflammation and appendicitis
(132) A positive Psoas Sign is suggestive of:
appendicitis
(132) Murphy’s Sign Setup:
Hook the left thumb or fingers from right hand in the right upper quadrant. Then ask patient to breathe deeply during palpation. A sharp increase in tenderness with a sudden stop of inspiratory effort constitutes a positive test
(132) McBurney’s Point Setup:
Located 1/3 from the ASIS and 2/3 from the umbilicus in the right lower quadrant
(132) Rebound Tenderness test Setup:
Palpate the abdomen by pressing deeply with pads of fingertips. After a moment, quickly release the pressure. Notice any signs of pain. Test is positive if there is more pain with releasing the pressure
(132) Referred Rebound Tenderness test Setup:
Examiner palpates by pressing deeply any one of the quadrants and quickly releases. Patient feels pain in another quadrant with release of pressure
(132) Rovsing’s Sign Setup:
Palpation of the left lower quadrant produces pain in the right lower quadrant
(132) Obturator Sign Test Setup:
With the patient supine, flex the patient’s right thigh at the hip with the knee bent. Internally rotate at the hip (bring ankle outward). Assess for pain at the right lower quadrant.
(132) Psoas Sign Test Setup:
With the patient supine, place the hand just above right knee, and ask patient to raise the thigh against your resistance.
(133) First-generation Cephalosporins have a _____ spectrum of activity:
Narrow
(133) Second-generation Cephalosporins have a _____ spectrum of activity:
Moderate
(133) Third-generation Cephalosporins have a _____ spectrum of activity:
Extended
(133) Fourth-generation Cephalosporins have a _____ spectrum of activity:
Broad
(133) Cefazolin is a:
First-gen Cephalosporin
(133) Cephalexin is a:
First-gen Cephalosporin
(133) Cefuroxime is a:
Second-gen Cephalosporin
(133) Cefoxitin is a:
Second-gen Cephalosporin
(133) Ceftriaxone is a:
Third-gen Cephalosporin
(133) Cefotaxime is a:
Third-gen Cephalosporin
(133) Cefdinir is a:
Third-gen Cephalosporin
(133) Ceftazidime is a:
Third-gen Cephalosporin
(133) Cefepime is a:
Fourth-gen Cephalosporin
(133) Ceftaroline is a:
Advanced-gen Cephalosporin
(133) This type of Cephalosporin is the most prescribed gen:
Third-gen Cephalosporin
(133) Cefazolin is commonly used for:
surgical prophylaxis
(133) Cephalexin is commonly used for:
oral for uncomplicated infections
(133) Ceftriaxone is commonly used for:
Serious infections, including meningitis, gonorrhea, Lyme disease (disseminated)
(133) Cefotaxime is commonly used for:
Serious infections, including meningitis, gonorrhea, Lyme disease (disseminated)
(133) Cefepime is commonly used for:
the treatment of severe infections
(133) Ceftriaxone is special in that it:
is only CDC recommended treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea
(133) Amoxicillin is special in that it:
can be given during pregnancy
(133) Oral Vancomycin is special in that it:
can treat C. difficile infection in the gut
(133) Ceftriaxone excretion:
eliminated via the biliary system
(133) Cefotaxime excretion:
excreted in urine
(133) Ceftriaxone Renal Considerations:
does not need dose adjustment in patients with
renal impairment
(133) Cefotaxime Renal Considerations:
dose should be reduced in patients with severe renal impairment
(133) Ceftriaxone Half life:
longer half-life, allows 1x daily dosing
(133) Cefotaxime Half life:
short half-life requires frequent dosing (every 6
to 8 hours)
(133) Ceftriaxone and Neonates:
highly bound to plasma proteins and can displace unconjugated bilirubin, which can lead to kernicterus (encephalopathy) in the newborn
(133) Cefotaxime and Neonates:
preferred in neonates, does not cause kernicterus
(133) Ertapenem is special in that it:
is ineffective against Pseudomonas
(133) Relebactam and Vaborbactam are special in that they:
Beta-lactamase inhibitors, reversible
(133) Beta-Lactams Mechanism of Action
Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), preventing peptidoglycan cross-linking
(133) Vancomycin Mechanism of Action
Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to D-Ala-D-Ala terminus of peptidoglycan precursors, preventing cross-binding
(133) Daptomycin Mechanism of Action
Binds to bacterial cell membranes and causes depolarization, leading to potassium efflux and cell death
(133) Penicillin Antibacterial Spectrum
Gram-positive bacteria
(133) Carbapenem Antibacterial Spectrum
Very Broad Spectrum
(133) Vancomycin Antibacterial Spectrum
Gram-Positive Bacteria, especially MRSA and MRSE
(133) Daptomycin Antibacterial Spectrum
Gram-Positive Bacteria
(133) Beta-Lactams Mechanism of Resistance
Beta-Lactamase production, PBP mutations, efflux pumps
(133) Vancomycin Mechanism of Resistance
VanA/VanB genes
(133) Function of VanA/VanB genes
Modify D-Ala-D-Ala terminus to D-Ala-D-Lac to reduce Vancomycin binding
(133) Daptomycin Mechanism of Resistance
Membrane alteration, increased production of surface charge molecules
(133) Aztreonam is special in that it:
targets only gram-negative aerobic cocci and bacilli
(133) Carbapenem is special in that it:
resistant to beta-lactamase degradation
(133) Red Man Syndrome
Medical condition in which flushing on face, neck and trunk occur due to high concentration or rapid IV vancomycin infusion
(134) Aminoglycosides Mechanism of Action
Bind the bacterial polysomes at the 16S rRNA on the 30S ribosome, causing miscoding of amino acids in the emerging
peptide chain
(134) Aminoglycosides Antibacterial Spectrum
Gram-negative bacteria and some Gram-Positive bacteria
(134) Aminoglycosides Mechanism of Resistance
transferase enzymes that inactivate the drugs by phosphorylation, adenylation, or acetylation
(134) Plazomicin is special in that it:
is used for treatment of complicated urinary tract infections not responsive to other antibiotics
(134) Streptomycin is special in that it:
is used for treatment of tularemia and plague (zoonotic infections) and drug-resistant tuberculosis
(134) Gentamicin and tobramycin are special in that they:
most frequently used aminoglycosides
(134) Aminoglycosides Adverse Drug Effects
nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and neuromuscular blockade (high doses)
(134) Examples of Aminoglycosides
Gentamicin, Neomycin, Amikacin, Tobramycin, Streptomycin
(134) Concentration-dependent killing
↑ [Drug] → ↑ rate and ↑ extent of bacterial killing
(134) Post-antibiotic effect
Suppression of bacterial growth persists beyond the time during which measurable drug is present

(134) Identify the condition:
Scotomas
(134) Scotomas
Medical condition of blind spots caused by Streptomycin, due to optic nerve toxicity.
(135) Tetracyclines Mechanism of Action
prevent protein synthesis by binding reversibly to the A site of the 30S ribosomal subunit, which prevents addition of amino acids to the growing peptide chain
(135) Tetracyclines Antibacterial Spectrum
aerobic gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, some anaerobes, spirochetes, atypical bacteria, rickettsia and protozoa
(135) Tetracyclines Mechanism of Resistance
increased efflux or impaired influx, or ribosomal protection proteins
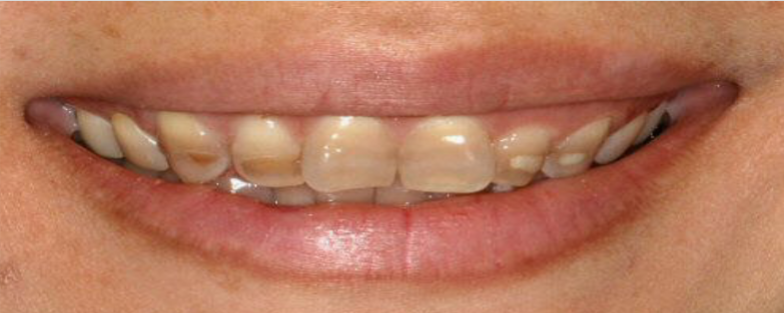
(135) Stained Teeth
Medical condition caused by binding of tetracyclines to Calcium. Doxycycline has lower affinity to Calcium
(135) Semisynthetic Tetracyclines
Tetracycline, Doxycycline, Minocycline, Demeclocycline
(135) Synthetic Tetracyclines
Tigecycline
(135) Doxycycline is special in that it:
is excreted in feces instead of urine
(135) Ribosomal protection proteins (RPPs)
Tetracycline mechanism of resistance, Production of proteins that interfere with tetracycline binding to the ribosome
(135) Tet(K) efflux pump
Tetracycline mechanism of resistance, found on Staphylococcus, confers resistance to tetracycline but not to the others
(135) Tet(AE) efflux pump:
Tetracycline mechanism of resistance, found on Gram negative bacteria
(135) Bacteriostatic
prevents the growth of bacteria
(135) Bactericidal
kills bacteria
(135) Examples of Zoonotic infections
Lyme disease, Plague, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Tularemia “rabbit fever”
(135) Lyme disease is caused by:
Borrelia spp (spirochete")
(135) Plague is caused by:
Yersinia pestis
(135) Rocky Mountain spotted fever is caused by:
Rickettsia ricketsii
(135) Tularemia is caused by:
Fransicella tularensis
(135) Examples of Respiratory pathogens
H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, C. pneumoniae
(135) Examples of mild, localized infection pathogens
MSSA, MRSA
(135) Examples of Sexually transmitted pathogens
Chlamydia trachomatis, Treponema pallidum
(135) Examples of Macrolides
Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, Erythromycin
(135) Function of CYP3A4 enzyme
Found in the liver, metabolizes drugs through Phase I reactions and reducing drug bioavailability
(135) mrsA efflux gene is found in:
staphylococci
(135) mefA efflux gene is found in:
GAS
(135) mefE efflux gene is found in:
S. pneumoniae