Two Dimensional Imaging
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:06 PM on 5/14/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
What transducer size is used for average sized adults?
3-3.5 MHz
2
New cards
What transducer is used for large adults?
2\.25 MHz
3
New cards
What transducer is used for children?
5-7.5 MHz
4
New cards
What transducer is used for neonatals?
7\.5-10 MHz
5
New cards
What position should the patient be in for an echocardiography?
In left lateral decubitis (LLD). Patient is angled 30° to 45°. Their head may be raised 30° using a pillow.
6
New cards
If the patient can’t move, what position should you scan in?
The supine position.
7
New cards
LLD helps what?
Moves lungs out of the way and opens up the chest for the heart. You may also have to have them take a deep breath in and breathe out.
8
New cards
What are the different echocardiographic windows? (6)
* Parasternal
* Apical
* Subcostal
* Right Apical
* Right Parasternal
* Suprasternal
* Apical
* Subcostal
* Right Apical
* Right Parasternal
* Suprasternal
9
New cards
What does ultrasound gel do?
It helps to remove the air between the body and the transducer because ultrasound does not go through air.
10
New cards
Where do you go to obtain a parasternal view?
LSB (left sternal border), and in between the 3rd and 5th interscostal space.
11
New cards
What do you look for to obtain an apical view?
The apical pulse.
12
New cards
Where do you go to obtain a subcostal view?
Beneath the sternum and xiphoid area (have the patient bend their knees and breath in to relax the abdominal muscles).
13
New cards
Where do you go to obtain an suprasternal view?
Above the sternum in the suprasternal notch.
14
New cards
What view allows us to see all the chambers?
Apical 4 chamber view.
15
New cards
What view allows us to see the aorta?
The suprasternal view.
16
New cards
What view is usually used to help identify/look at diseases?
Right parasternal view.
17
New cards
What are the different planes in a parasternal view? (2)
* Parasternal Long Axis View (LAX)
* Parasternal Short Axis View (SAX)
* Parasternal Short Axis View (SAX)
18
New cards
What are the different planes of an apical view? (4)
* Apical 4 chamber
* Apical 5 chamber
* Apical 2 chamber
* Apical long axis (3 chamber)
* Apical 5 chamber
* Apical 2 chamber
* Apical long axis (3 chamber)
19
New cards
To obtain parasternal LAX, where is the transducer located?
Parallel to the long axis of the heart. The image marker should be towards the right shoulder.
20
New cards
Picture of parasternal LAX.
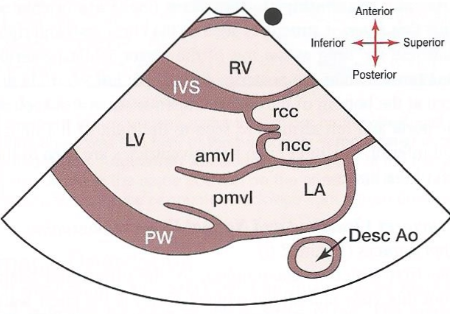
21
New cards
What is the basal part of the parasternal LAX?
The part from the tip of the papillary muscle to the AO ring and AV groove.
22
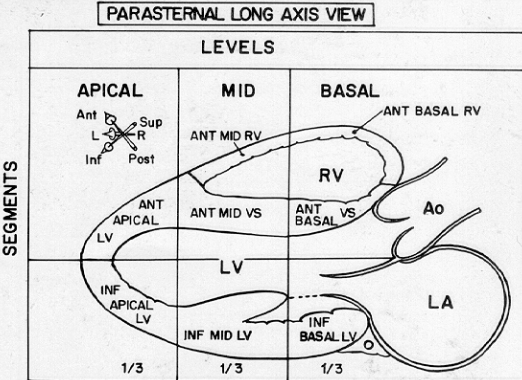
New cards
What is the mid part of the parasternal LAX?
From the base to the tip of the papillary muscle.
23
New cards
What is the apical portion of a parasternal LAX?
From the apex to the base of the papillary muscle (where it attaches to the LV inferior wall)
24
New cards
What does a parasternal long axis right ventricular inflow tract (RVIT) look like?
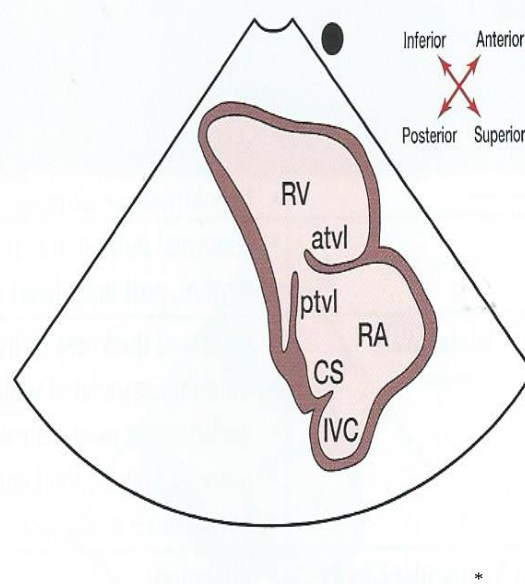
25
New cards
What does a parasternal long axis right ventricular outflow tract look like?
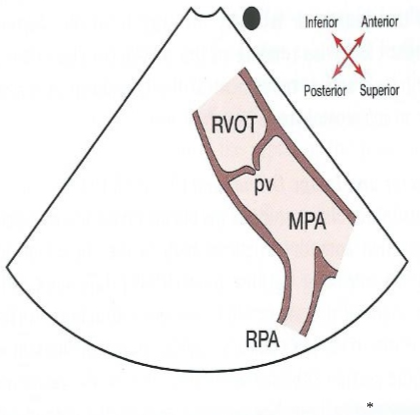
26
New cards
How do you get from a parasternal LAX to a SAX?
By rotating the transducer 90° clockwise.
27
New cards
What does a pulmonary bifurcation view look like?
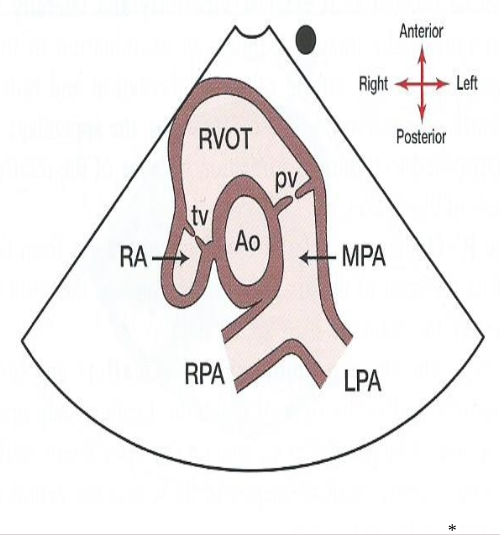
28
New cards
What does the SAX level of the aorta/aortic valve look like? What is something to look for?
The Mercedes Benz logo of the Aortic valve!
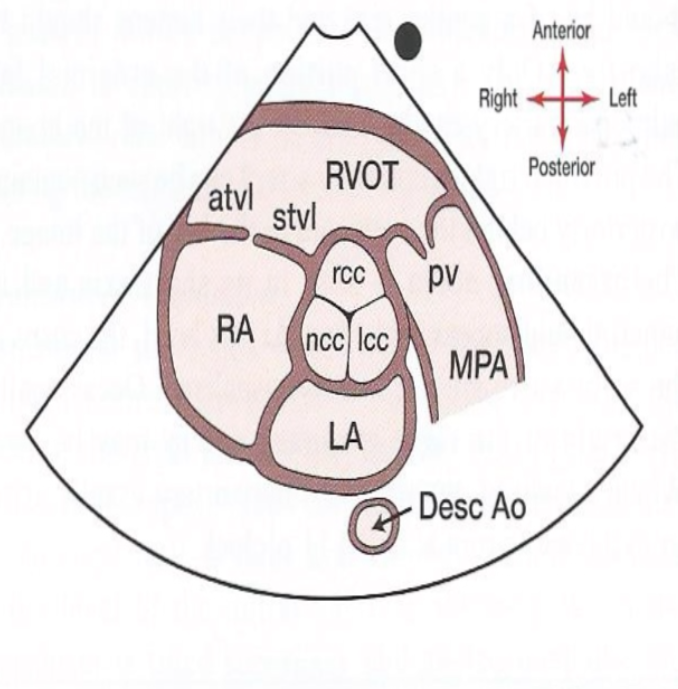
29
New cards
What does the SAX level of the LVOT look like?
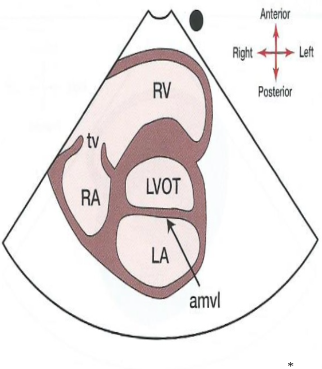
30
New cards
What does the SAX level of the mitral valve look like? What is a distinctive feature here?
The fishes mouth created by the anterior and posterior mitral valve leaflets of the mitral valve.
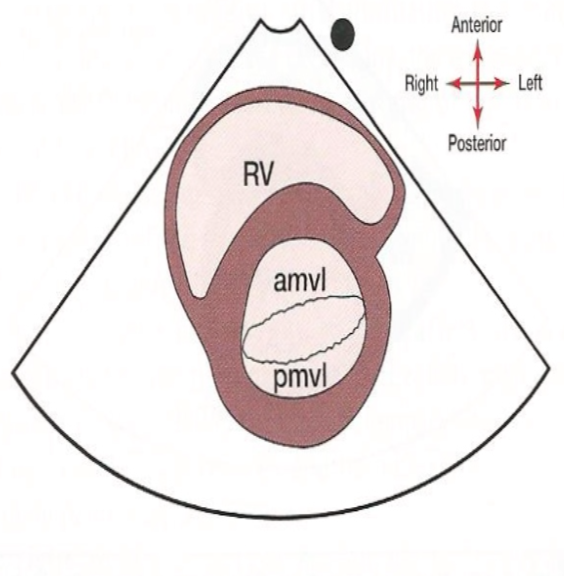
31
New cards
What does the SAX level of the papillary muscles look like?
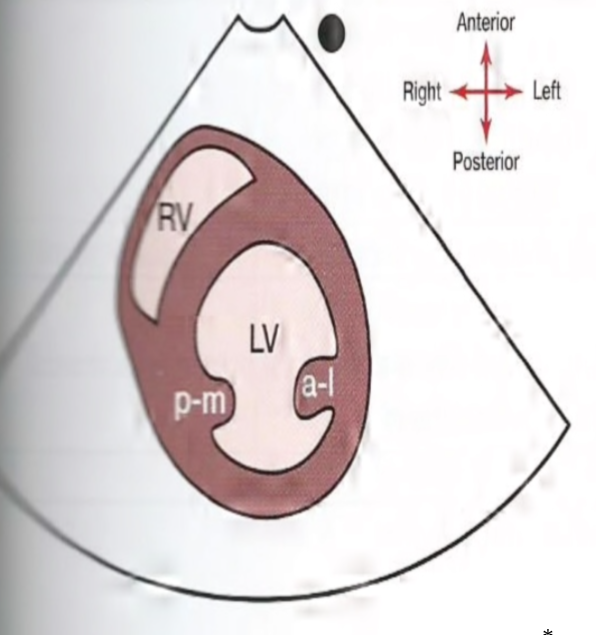
32
New cards
Where will the papillary muscles be located on a SAX level of the papillary muscles?
At the 3-5 o’clock region and the 7-9 o’clock region.
33
New cards
Is it normal to have two-headed papillary muscles?
Yes.
34
New cards
What does the SAX level of the apex look like?
(Usually only LV apex but may also see RV apex)
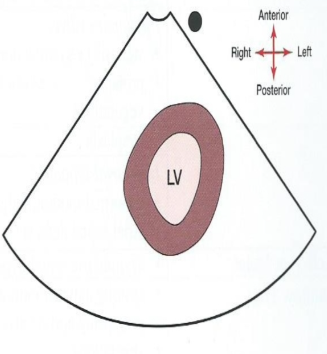
35
New cards
How do you get to the apical 4 chamber view from a SAX view?
You can move the transducer inferiorly and laterally OR you can search for the apical pulse.
36
New cards
Where is the transducer located for an apical 4 chamber view?
An interspace lower (5th intercostal) and lateral to point of maximum apical impulse. Direct the beam superiorly towards the patient’s head, with the index marker to the patient’s left.
37
New cards
In the apical 4 chamber view, what will you for sure see?
The crux (where all chambers meet). You may also see the moderator band in the RV.
38
New cards
What does an apical 4 chamber view look like?
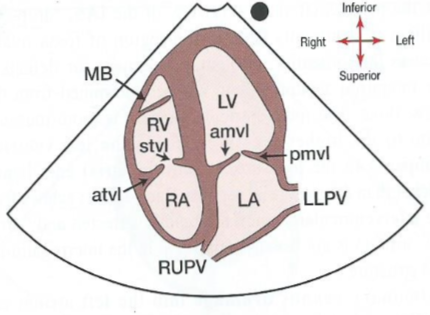
39
New cards
How do you get from an apical 4 chamber view to an apical 5 chamber view? What is the 5th “chamber”?
By angling the transducer anteriorly and superiorly from the apical 4 chamber view. The 5th chamber is actually the aorta.
40
New cards
What does an apical 5 chamber view demonstrates?
All chamber structures plus LVOT and aortic root and cusps.
41
New cards
What does an apical 5 chamber view look like?
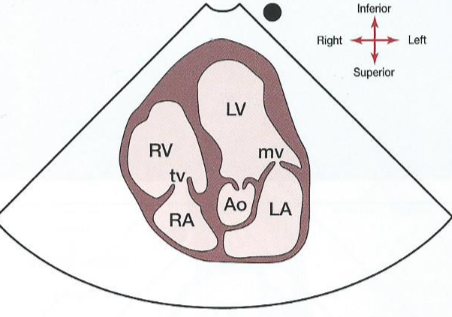
42
New cards
How do you get from an apical 4 chamber view to an apical 2 chamber view?
By rotating the transducer 90° counter-clockwise.
43
New cards
What two chambers are presented in an apical 2 chamber view?
LA and LV
44
New cards
What does an apical 2 chamber view look like?
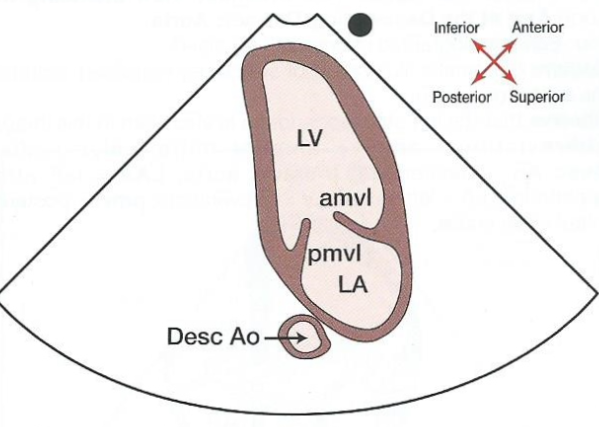
45
New cards
What is another name for the apical 3 chamber view?
The apical long axis.
46
New cards
How do you get to an apical 3 chamber view from an apical 2 chamber?
Rotate the transducer counter clockwise 20°.
47
New cards
What chambers are seen in an apical 3 chamber view?
LA, LV, and RV
48
New cards
What does an apical 3 chamber view look like?
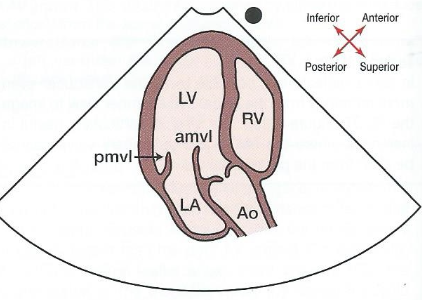
49
New cards
Where is the transducer placed for a subcostal view?
On the midline, inferior to the xiphoid process of the sternum. The image marker is located to the patient’s left.
50
New cards
What position should the patient be in for a subcostal view?
In the supine position, with their legs bent and feet flat on the bed.
51
New cards
Why do patient’s knees need to be bent when obtaining a subcostal view?
To relax the abdominal muscles to be able to make it into the heart.
52
New cards
What additional method is used to help in obtaining a clear subcostal view?
Having the patient inspire. This helps push the liver and the heart inferiorly.
53
New cards
A subcostal view is very useful for patients with what?
Lung disease.
54
New cards
What view is important when assessing Congenital Heart Disease?
The subcostal view.
55
New cards
What structures are seen in a subcostal 4 chamber view?
* Liver
* Epicardial fat (anteriorly)
* RA, LA
* RV, LV
* Interatrial Septum (IAS) - the beam is perpendicular to this!
* TV (anterior and septal leaflets)
* MV (AMVL and PMVL)
* Epicardial fat (anteriorly)
* RA, LA
* RV, LV
* Interatrial Septum (IAS) - the beam is perpendicular to this!
* TV (anterior and septal leaflets)
* MV (AMVL and PMVL)
56
New cards
What does a subcostal four chamber view look like?
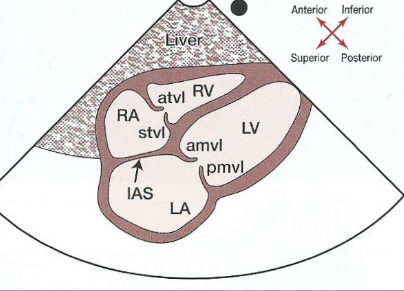
57
New cards
How long can it take to obtain a subcostal 4 chamber view?
3 mintues.
58
New cards
How do you obtain a subcostal SAX view from the subcostal 4 chamber view?
Rotate the transducer 90° counter clockwise towards the patient’s left shoulder (image marker superior)
59
New cards
The subcostal SAX view is usually used where?
In pediatric patients.
60
New cards
The subcostal view is useful for what?
Patient’s with limited parasternal and apical windows as it is able to produce comparable views to parasternal SAX.
61
New cards
Where is the transducer placed to obtain a subcostal IVC and hepatic vein view?
Transducer is below the xiphoid process, utilizing the longitudinal section of the abdomen (with the image marker superior). The transducer will be positioned slightly to the right of the midline.
62
New cards
If a eustachian valve is present, where can you see it on the subcostal IVC and hepatic vein view?
Where the IVC enters into the RA.
63
New cards
The subcostal IVC view is useful in detecting what?
Pressure changes in the RA or RV.
64
New cards
In subcostal IVC view, does the IVC collapse with inspiration or expiration?
Inspiration.
65
New cards
What does a subcostal IVC view look like?
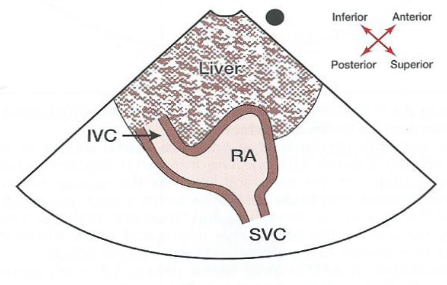
66
New cards
Where is the transducer placed to obtain a subcostal abdominal aorta view?
Below the xiphoid process, slightly left of the midline with the image marker superior.
67
New cards
What does a subcostal abdominal aorta view look like?
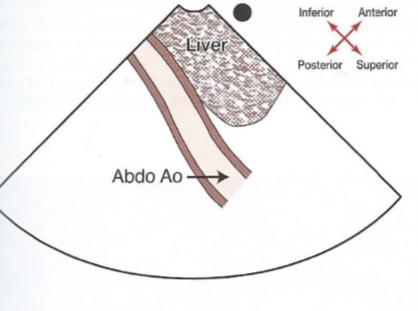
68
New cards
Where is the transducer placed to get a suprasternal notch (SSN) view?
The patient is in the supine position with the neck extened “backwards”. The transducer is placed in the suprasternal notch (near collarbone area). The image marker will point towards the left neck and angled inferiorly.
69
New cards
What is the best view to look at aortic disease?
The suprasternal notch view.
70
New cards
What does a suprasternal notch (SSN) view look like?
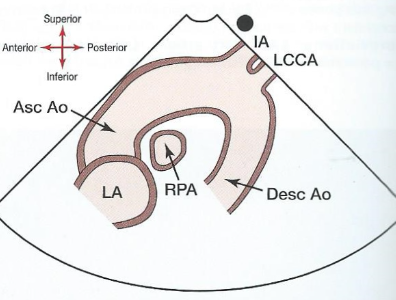
71
New cards
What is the right sternal border useful for (RSB)?
Evaluation of the proximal ascending aorta.
72
New cards
Where is the transducer placed in a right sternal border view (or right parasternal)?
2nd or 3rd intercostal space with the transducer marker rotated to the patient’s left clavicle (collar bone).
73
New cards
What position must the patient be in for a right sternal border view (AKA right parasternal)?
The right lateral decubitis position (RLD - just like LLD but to the right).
74
New cards
When is the right sternal border view performed?
When disease is present/suspected.