Selective Attention 3
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are ERPS influenced by?
attention even when the probe stimuli were irrelevant, brain activity was modulated depending on whether the pp was paying attention to the colour
When is the early visual processing stage enhanced?
when attention is directed toward a certain colour
When does attention affect perception?
early - this modulation happens very quickly within the 1st 100ms after the stimulus appears and it applies across the entire visual field
What can selective attention to a feature like colour do?
enhance early visual processing even when stimuli themselves are irrelevant
What is the emotional superiority effect?
the tendency for emotional stimuli, particularly negative emotions such as anger to be detected faster and more accurately than neutral stimuli
How are threat related stimuli detected?
with the highest accuracy across all lags demonstrating the emotional superiority effects
How are faces detected in the ESE?
neutral faces detected with lowest accuracy sugg they are less attention grabbing
positive faces fall in bt threat and neutral faces in terms of detection accuracy
What is prioritised in visual processing?
emotional info, esp threats, likely due to its survivial importance
What is an attentional blink?
where the brain temporarily blinks and misses the 2nd target in a rapid stream - threat faces resist this which sugg an evolutionary advantage where detecting threats quickly cld improves chances of survival
What is supporting ESE?
threatening stimuli are more easily and accurately detected compared to neutral and positive stimuli which supports the ESE where negative emotions demand more attention and are processed more efficiently
What does attention act as?
a filter selecting what gets transferred from perception to STM
What factors affect recall accuracy?
capacity/load x decay
decay function which is exponential, info fades from memory quickly at first then more slowly
selective attention and visual working memory - by focusing on certain items, attention reduces cognitive load and improves recall
What is attention necessary for?
encoding visual info into memory
What do lower thresholds indicate?
better spatial acuity - smaller gap sizes can be detected
What do peripheral cues in exogenous attention do?
enhance spatial acuity at the cued location but performance drops when cue is at an unattended location
What does voluntary attention do?
improves spatial acuity but effect is smaller than for exogenous cues
When is attention and spatial acuity significantly enhanced?
when condition/stimulus is valid
How can attention enhance signal detection?
by reducing impact of external noise or improving contrast sensitivity
What can an exogenous cue do?
demonstrates how external attention can direct focus, making targets easier to identify even under noisy conditions or with low contrast
How does attention enhance perceptual processing?
by increasing contrast and visibility of relevant/attended stimuli while suppressing irrelevant ones (unattended)
What is endogenous spatial orienting?
voluntary attention where pps actively focus on a specific location based on a cue
What is exogenous spatial orienting?
reflexive attention where attention is automatically drawn to a location by a sudden stimulus
What benefits reaction time?
endogenous attention but it takes time to engage
What is exogenous attention like?
fast acting but short lived
What is endogenous attention?
voluntary, deliberate top down process where indvs consciously direct focus based on internal goals or expectations
requires cognitive effort to maintain focus on a certain stimulus ans can be maintained over extended periods, taking longer to initiate
Can you name an example of endogenous attention?
listening intently to a certain instrument in an orchestra based on prior knowledge of its entry
What ie endogenous attention?
involuntary bottom up process where attention is captured by sudden/salient stimuli in env
triggered reflexively without conscious effort and effects are short lived
Can you name an example of endogenous attention?
turning your head in response to loud unexpected noise
What is feature search?
based on a single distinct feature and the RT remains constant regardless of the set size - target pops out instantly which sugg parallel processing where brain processes multiple items at once
What is conjunction search?
req combining multiple features to find the target and RT increases as set size increases - search becomes harder with more items which sugg serial processing where the brain examines each item one by one
What is a difference between feature and conjunction search?
FS - fast and automatic, unaffected by no distracts whereas CS is slower and effortful,
What does this graph support?
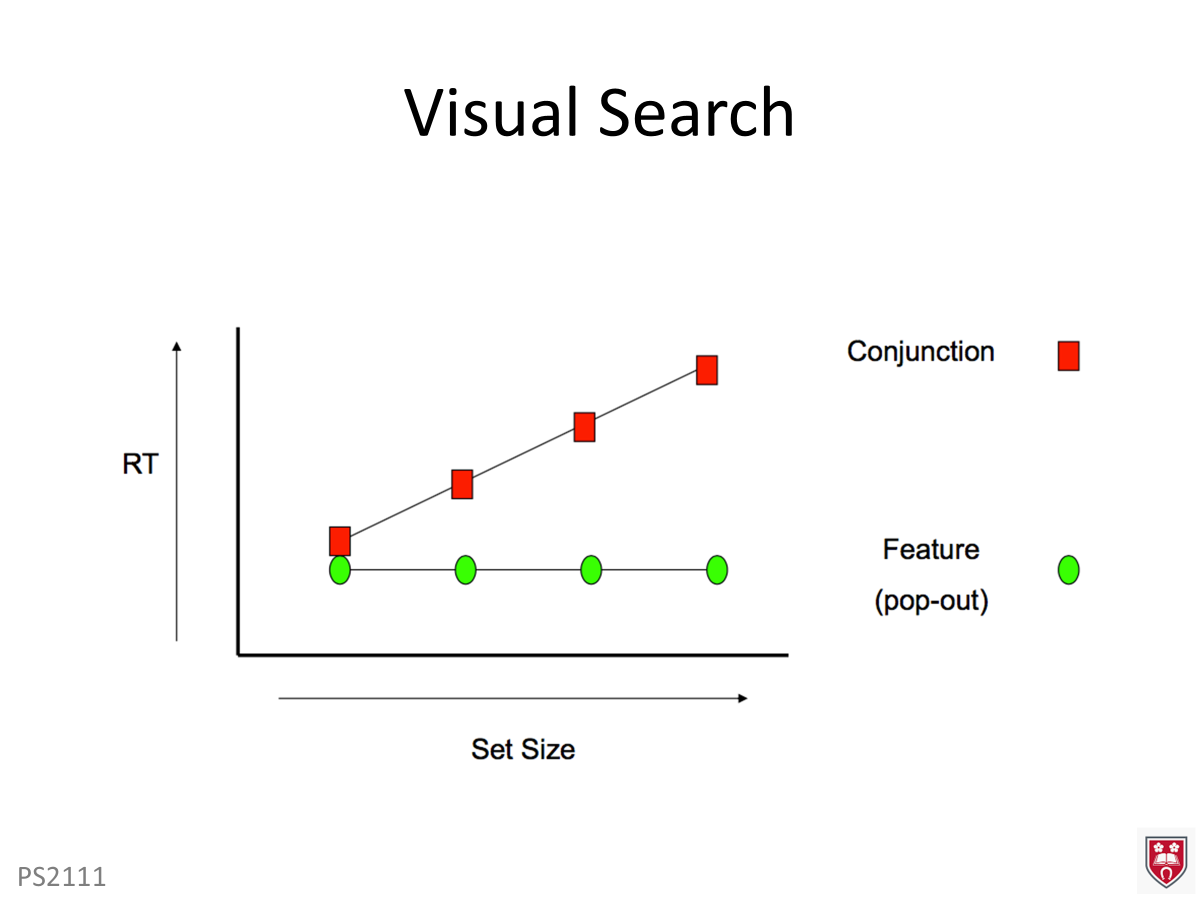
Treisman’s Feature Integration theory which explains how attention is required for conjunction searches but not FS
What is the pre-attentive stage in the FIT?
fts like colour and shape are processed automatically and in parallel - each feature is registered in a separate feature map and the stage does not require focused attention
What is a master map of locations in the FIT?
a combined map of where all features are located in space but at this stage features are not yet bound together to form whole object
What is the focused attention stage in the FIT?
when multiple features need to be combined sa identifying an object with a specific colour, attention is required
serial process making it slower than detecting a single unique feature
What happens when pps must divide attention bt RSVP task and spatial task?
accuracy suffers at short lags but improves over time - supports idea that engaging temporal attention interferes with spatial attention but this interference lessens as lag increases
What happens in a single task condition?
performance remains stable - suggesting that spatial and temporal attention operate differently
What is temporal attention?
tracking events over time
What is spatial attention?
focusing on locations are distinct but interact
What happens in dual task scenarios?
shifting attention takes time - leading to performance deficits when events occur too closely together
What do salient features do?
attract attention automatically
When do pop out effects do?
occur when an item differs
What happens when multiple elements share?
varying features , attention is distributed rather than focused on one item which relates visual search theories - some searches are easy (feature search) while others are harder (conjunction search)