Exam 4 Ch. 13-15 Study Guide (A&P)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
mechanoreceptors
activated by touch, pressure, vibration, stretch
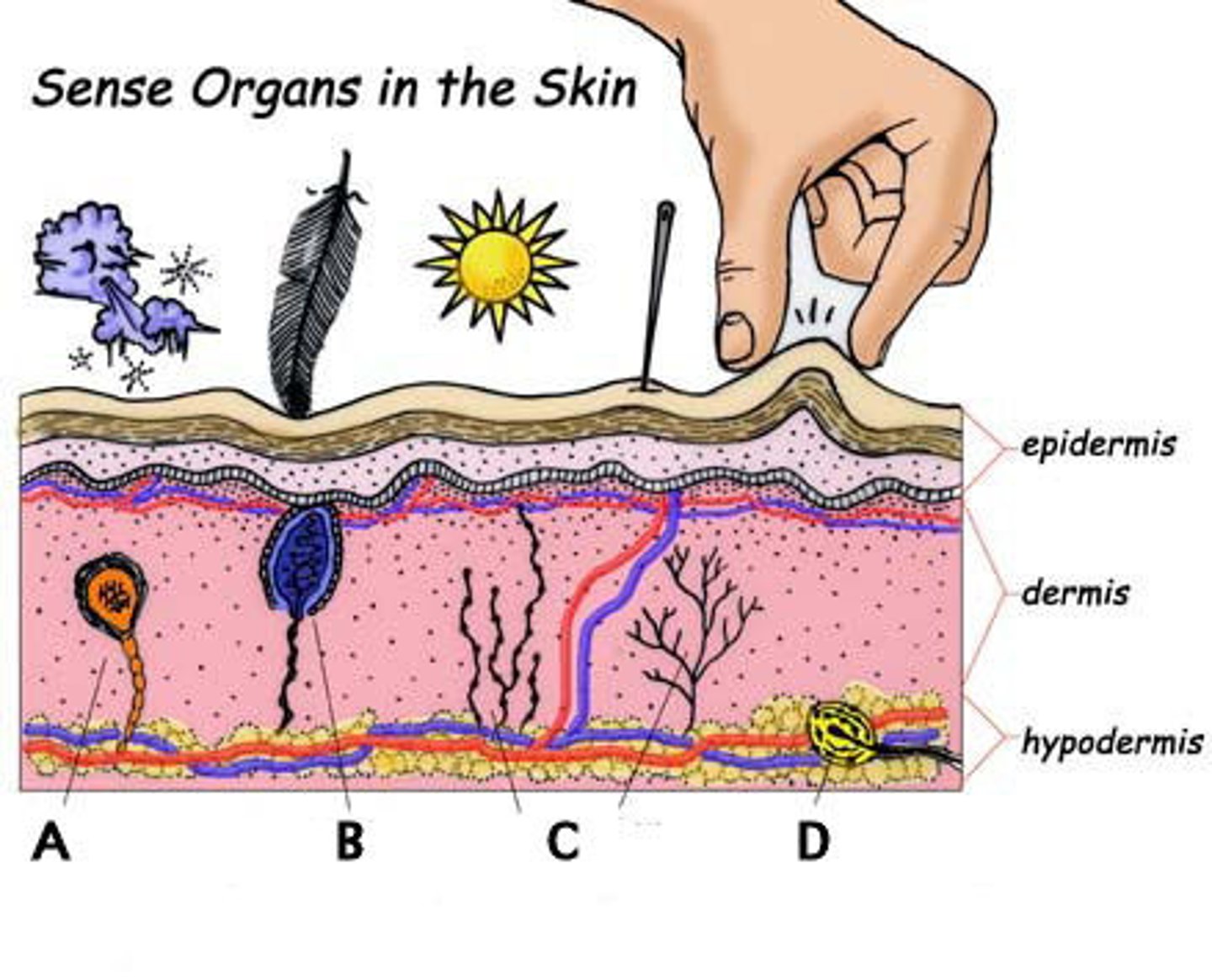
thermoreceptors
activated by changes in temperature
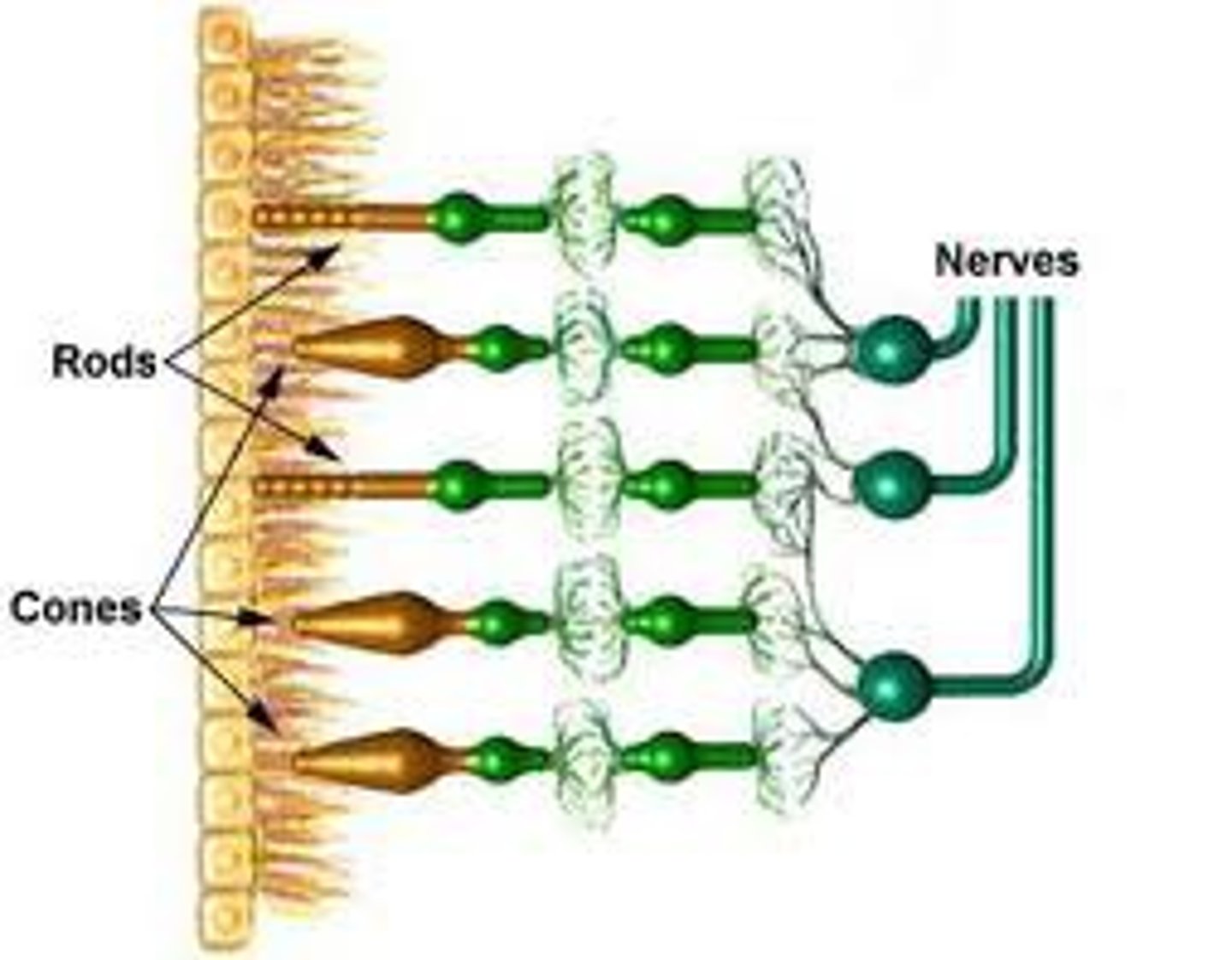
photoreceptors
-activated by light energy
-in neural layer of retina
-rods & cones
-contain photopigments (visual pigments) that change shape when they absorb light & translate it into electrical (neural) signals
rods
-more abundant
-used in dim light & peripheral vision (non-color vision)
-more sensitive
-mostly in peripheral retina
-low acuity
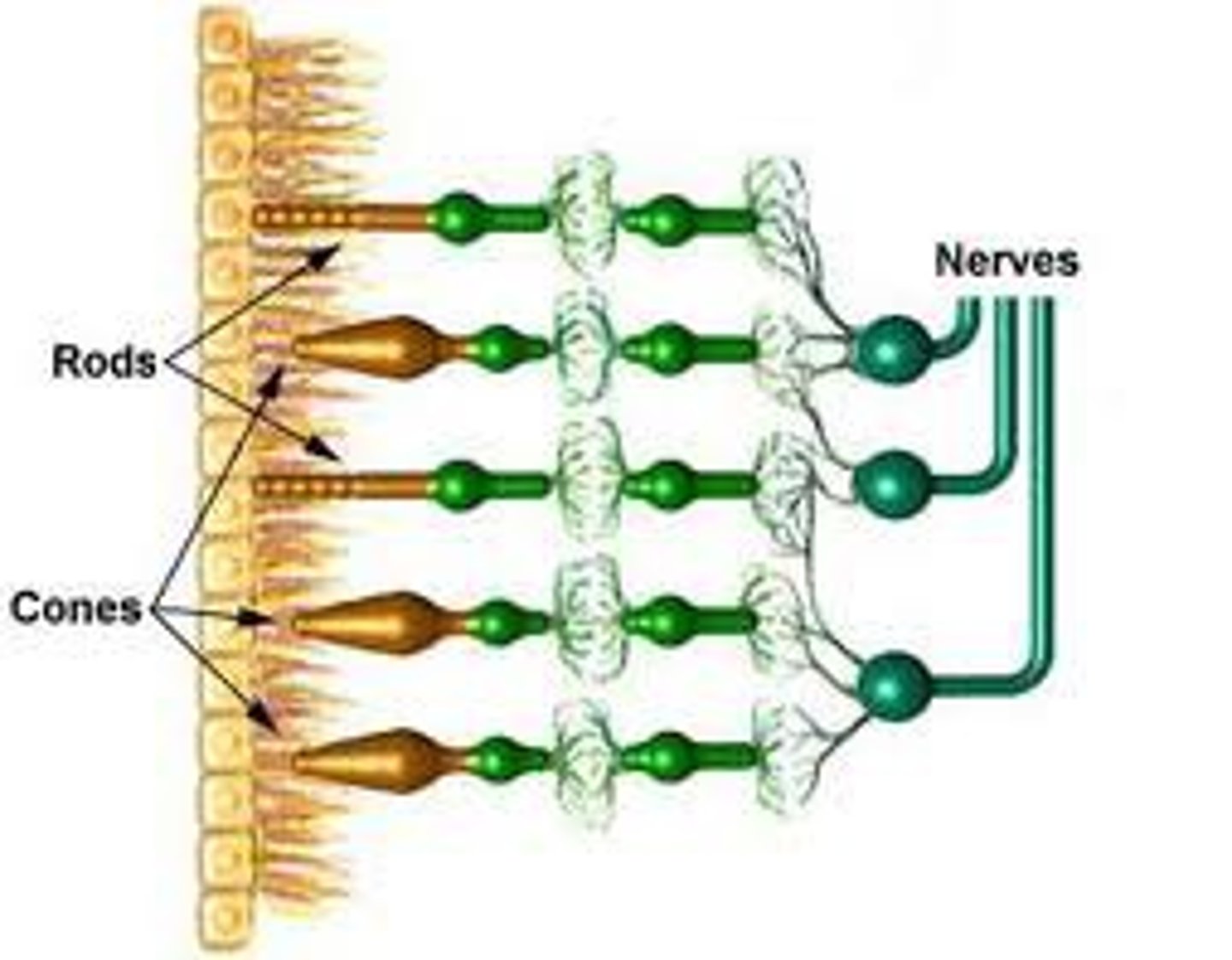
cones
-used in bright light
-provide high-resolution color vision (3 pigments)
-less abundant
-low sensitivity
-mostly in central retina
chemoreceptors
activated by chemicals
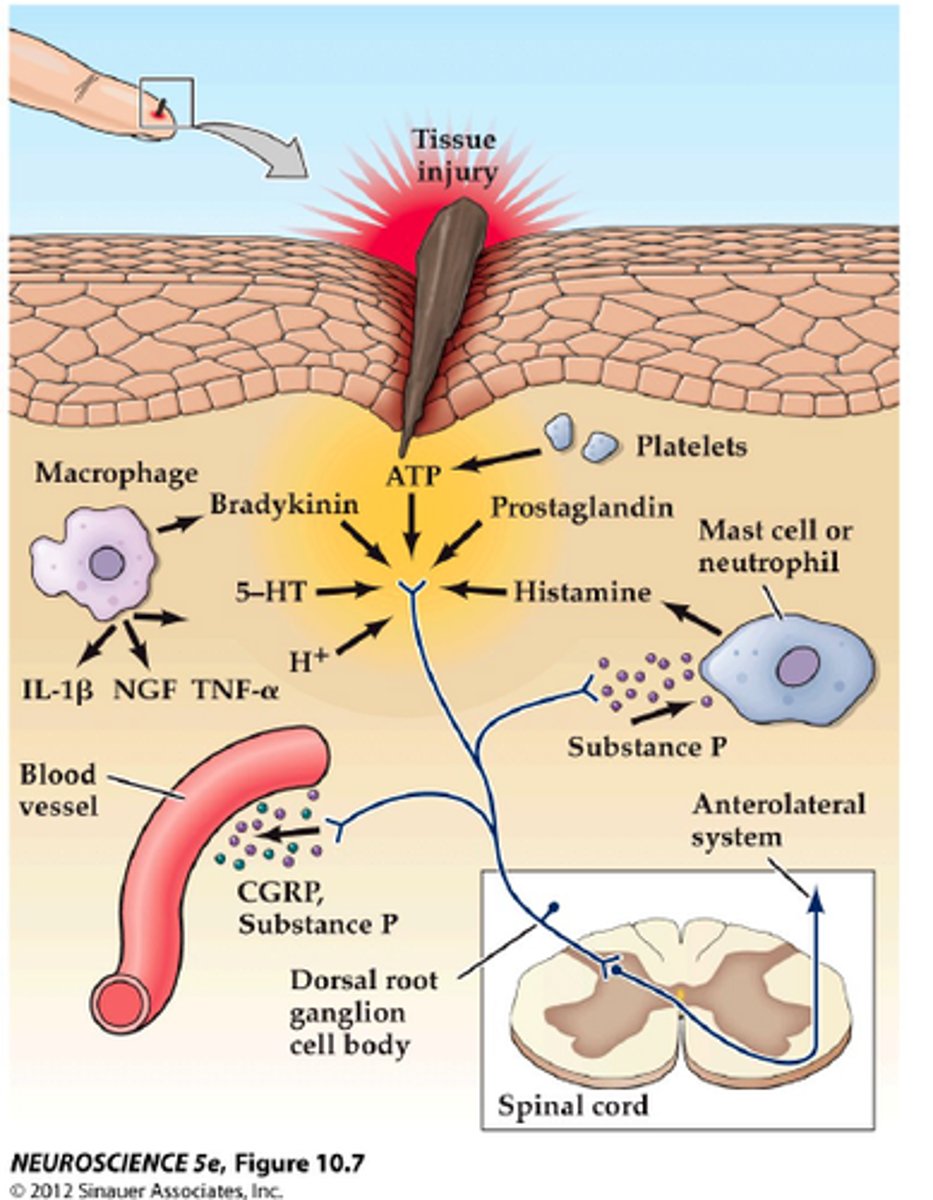
nociceptors
activated by painful stimuli
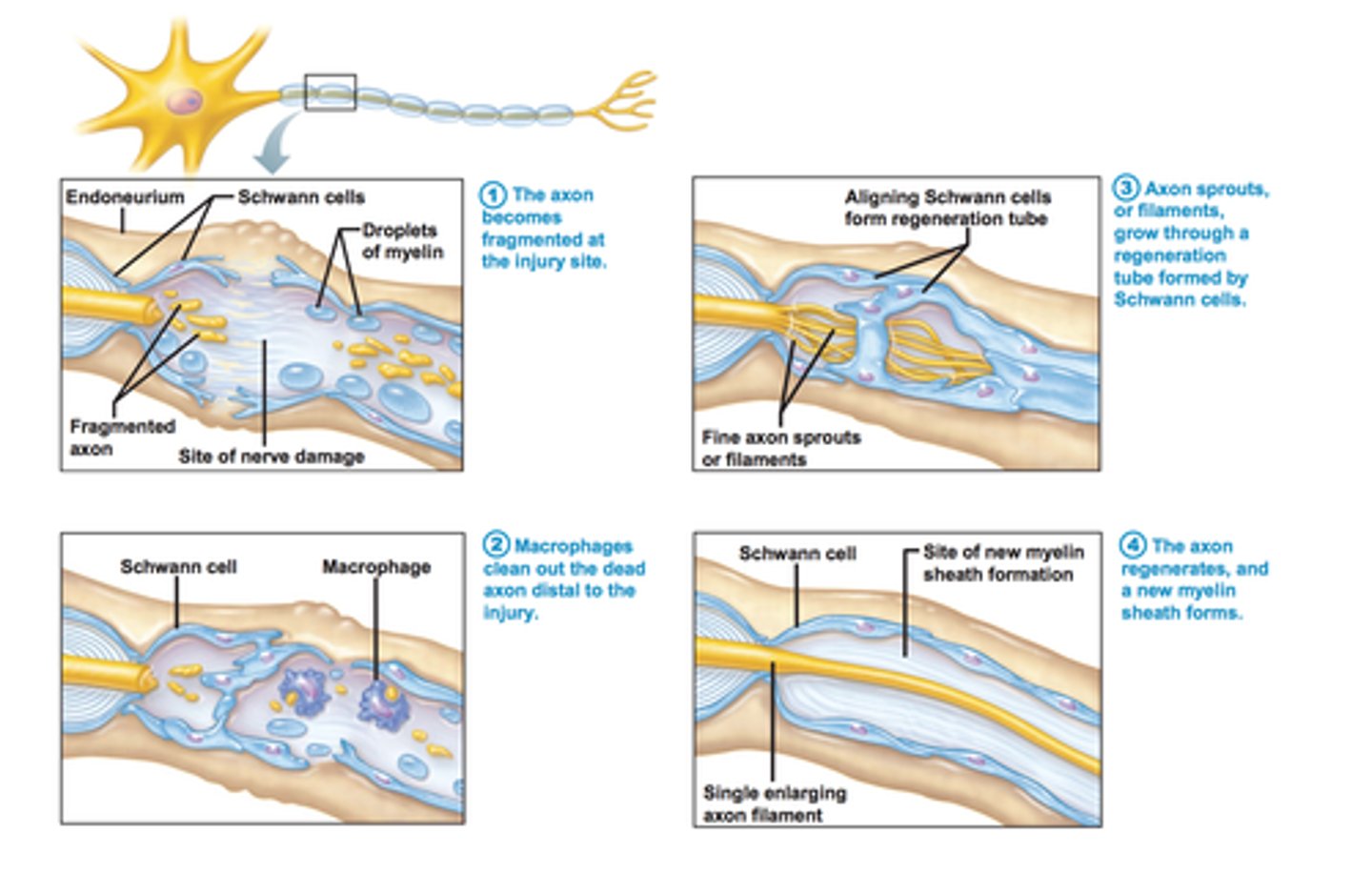
4 steps of PNS nerve fiber regeneration
1. axon fragments which causes axon & myelin sheath distal to injury to degenerate
2. schwann cells recruit macrophages to clean up debris & stimulate schwann cells to divide
3. schwann cells line up & form a regeneration tube that encourages & guides axon filament growth
4. schwann cells protect axon as it regenerates & forms new myelin sheath
cranial nerve I
-olfactory
-sensory: smell

cranial nerve II
-optic
-sensory: vision

cranial nerve III
-oculomotor
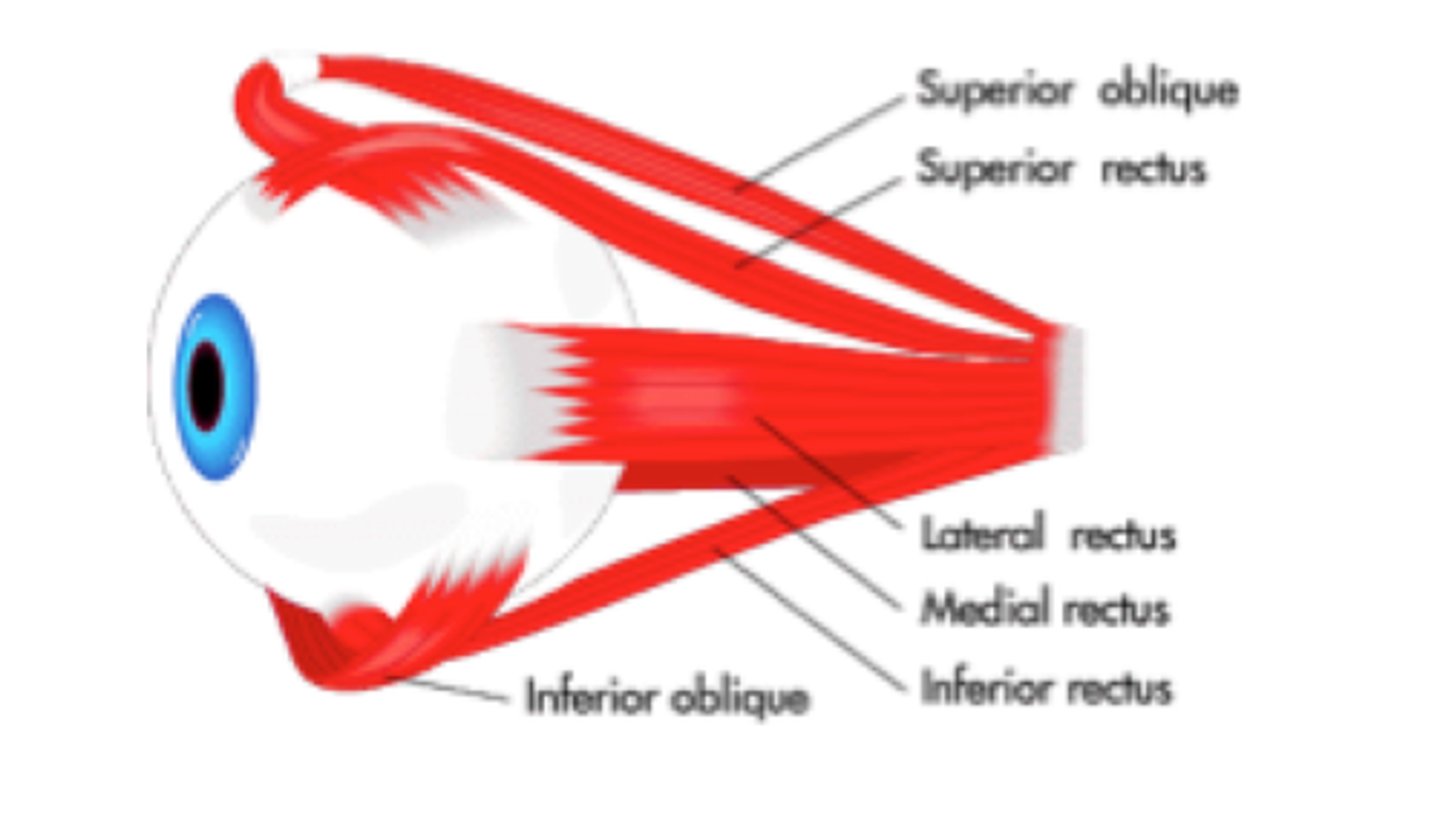
-motor: moves eye medially, upward, downward, laterally, elevates eyelid
-muscles: medial, superior, inferior rectus, inferior oblique
cranial nerve IV
-trochlear
-motor: moves eye down, laterally, medially
-muscle: superior oblique

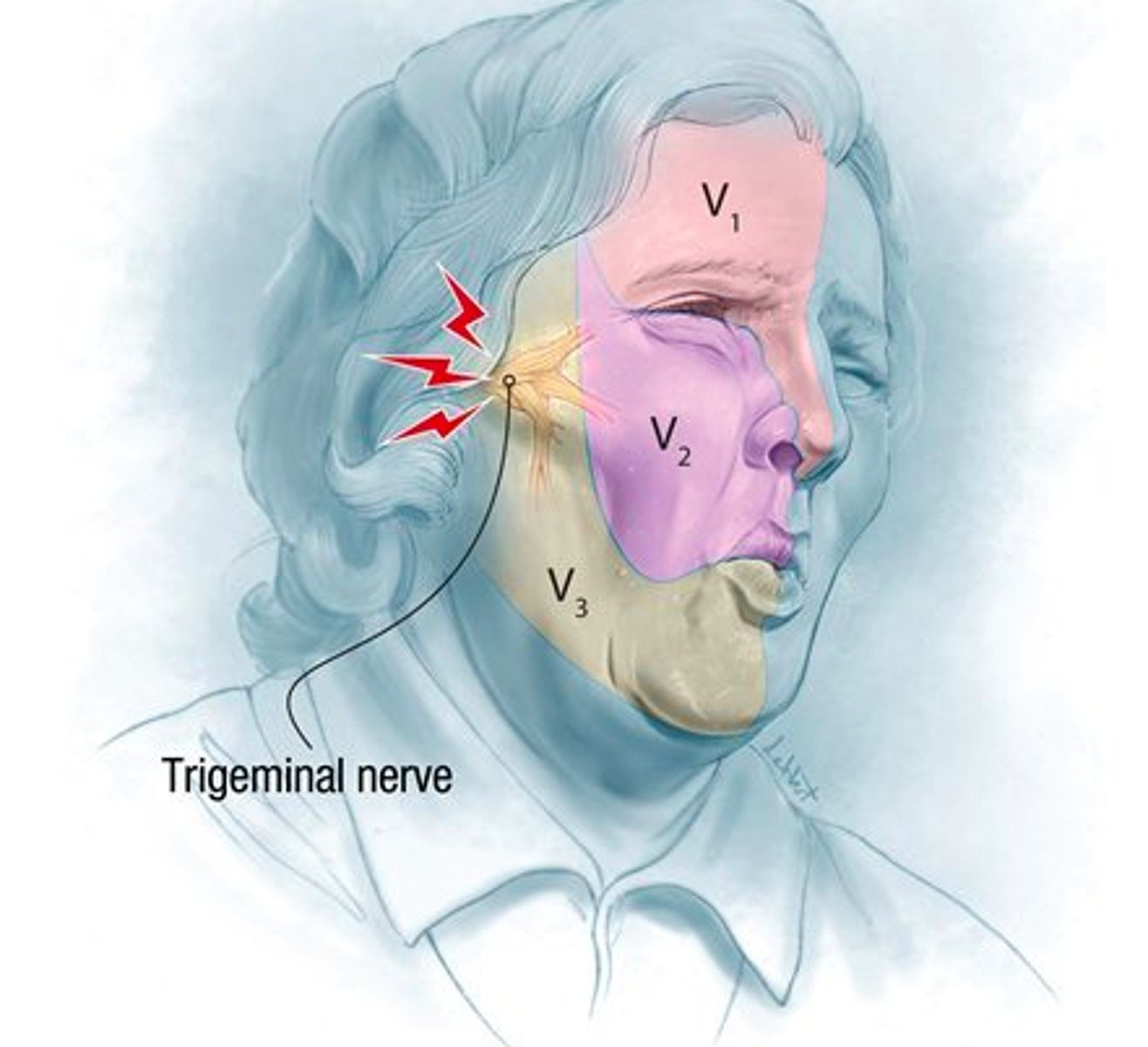
cranial nerve V
-trigeminal
-largest
-3 branches: opthalmic, maxillary, mandibular
-sensory: general sensation of the face
-motor: chewing muscles
tic douloureux
inflammation of CN V (trigeminal) due to compression near brain stem
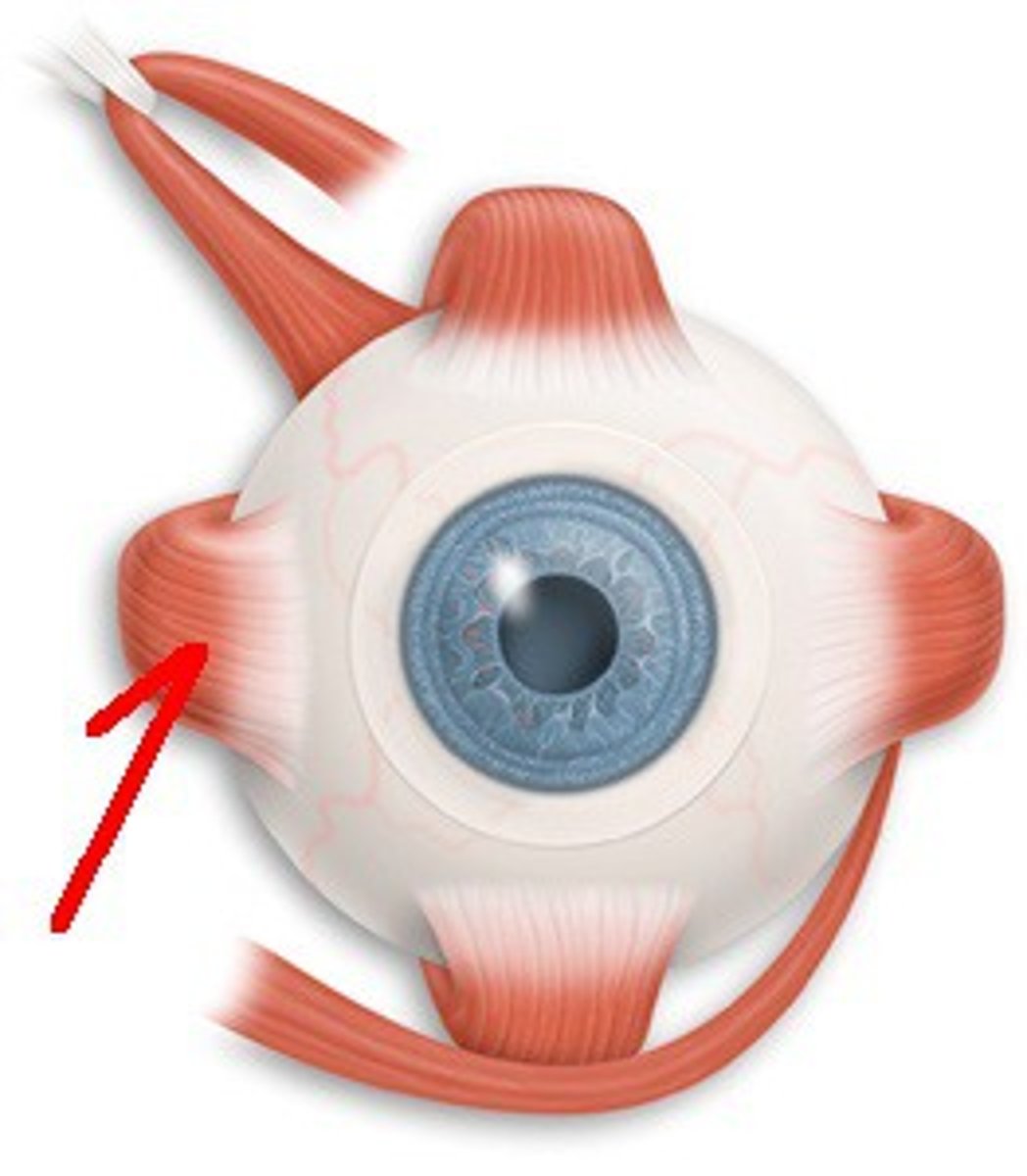
cranial nerve VI
-abducens
-motor: moves eye outward
-muscle: lateral rectus
cranial nerve VII
-facial
-5 branches: temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical
-motor: facial expression, lacrimal glands, salivary glands
-sensory: taste buds
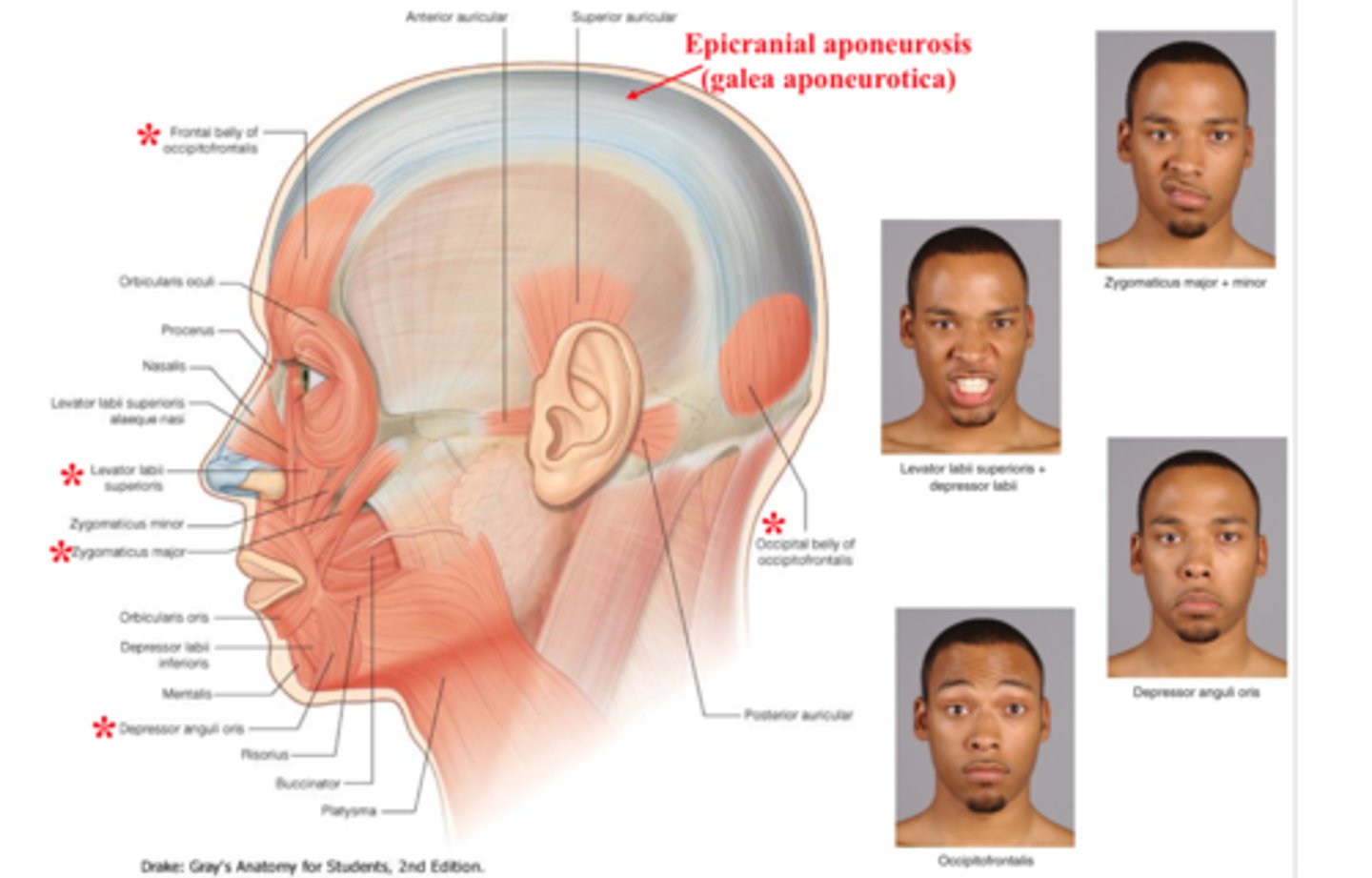
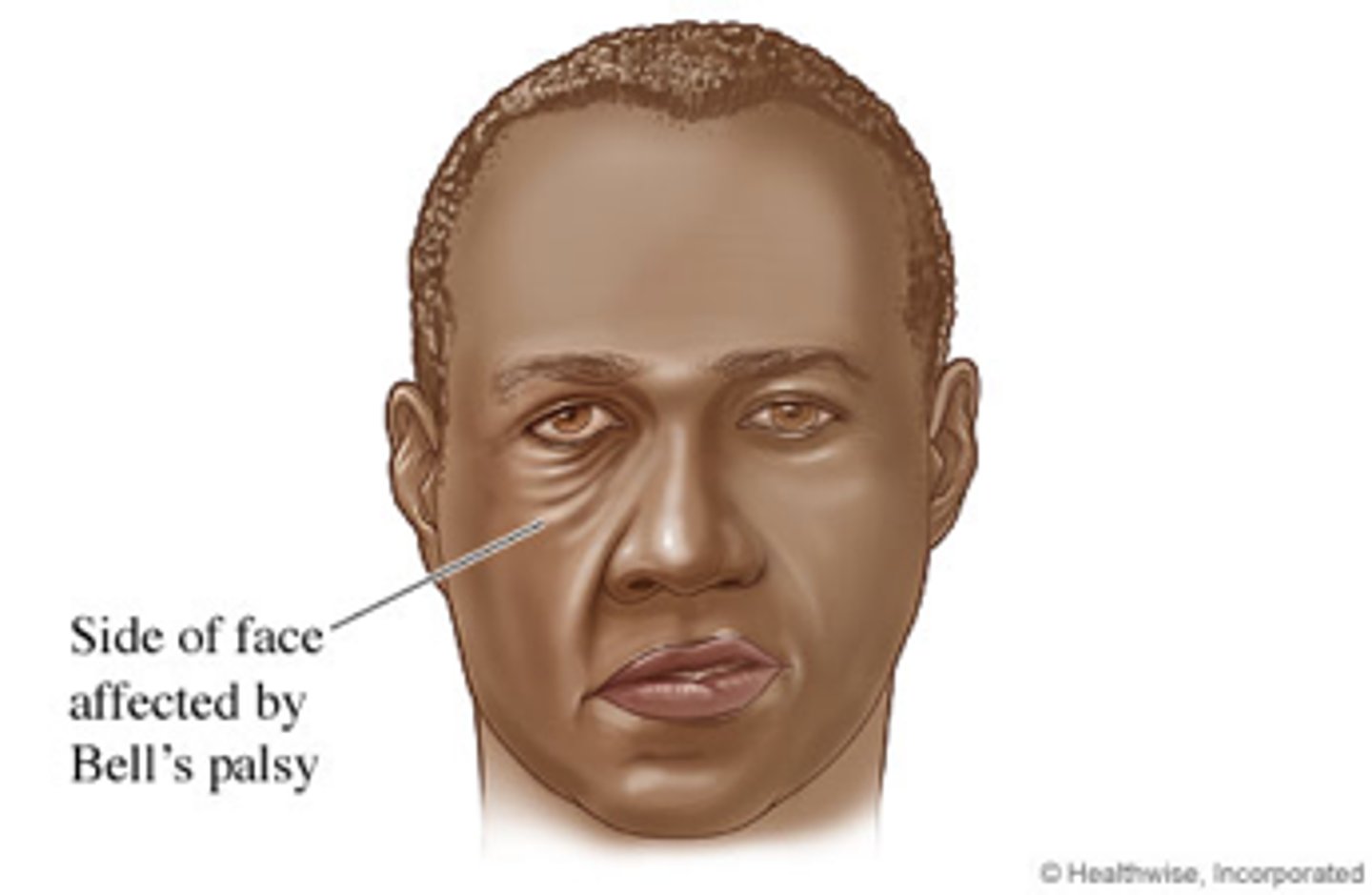
bell's palsey
-paralysis of facial muscles & taste on 1 side of afce
-caused by inflamed CN VII (facial)
cranial nerve VIII
-vestibulocochlear
-sensory: hearing, balance (cochlea & vestibule)
-motor: adjusts sensitivity of sensory receptors

cranial nerve IX
-glossopharyngeal
-sensory: taste, general sensory from pharynx & tongue, input from carotid chemoreceptors (O2/CO2) & baroreceptors (BP)
-motor: tongue & pharynx (swallowing), parotid salivary gland
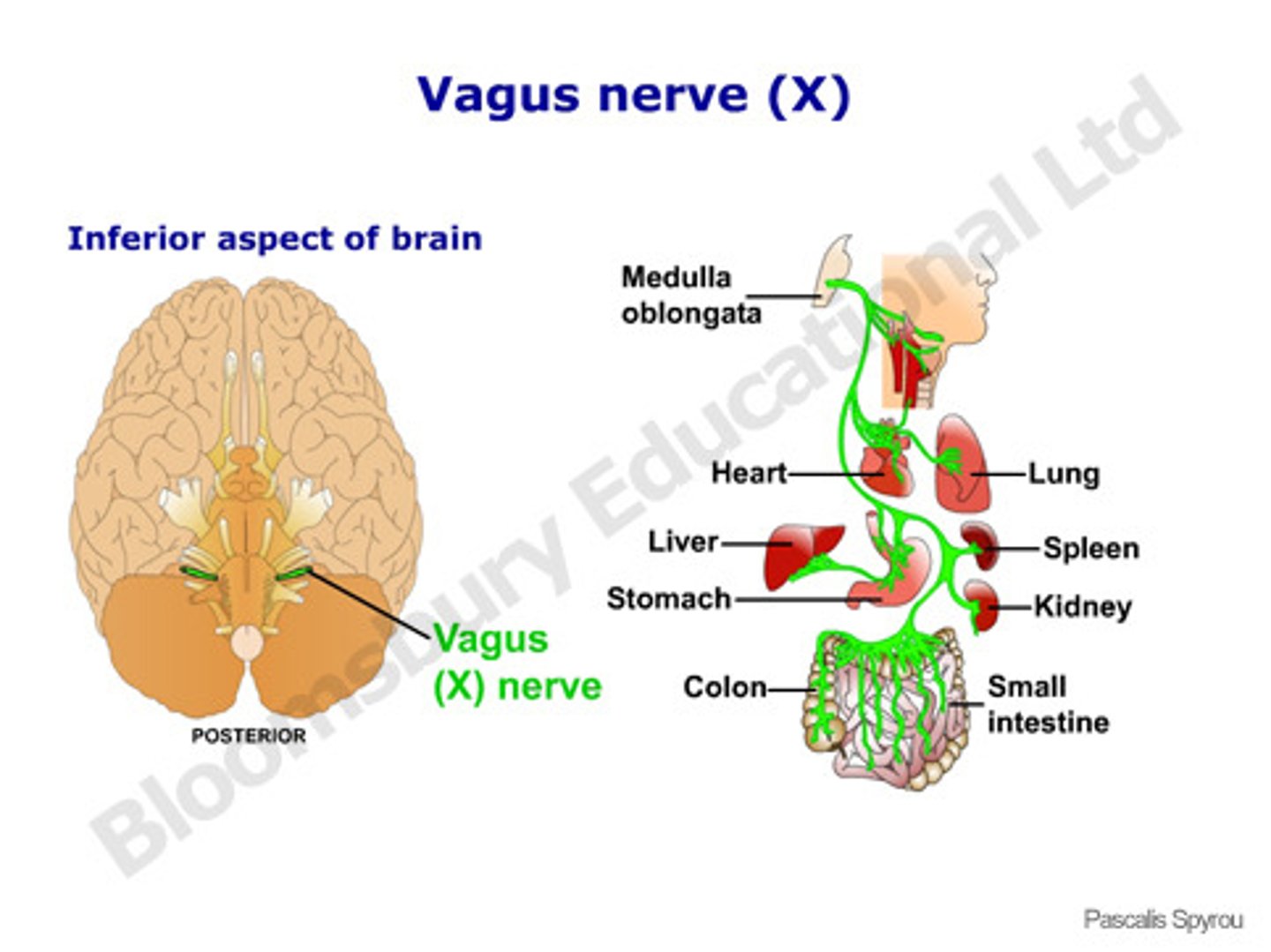
cranial nerve X
-vagus
-extends into thorax & abdomen
-sensory: thoracic & abdominal viscera, baroreceptors (BP), chemoreceptors (O2/CO2), taste buds
-motor: heart, lung, abdominal viscera, pharynx, larynx (HR, breathing, swallowing, digestion)
cranial nerve XI
-accessory
-motor: move head & neck (trapezius & sternocleidomastoid)
-sensory: proprioception of trapezius & sternocleidomastoid)

cranial nerve XII
-hypoglossal
-motor: tongue muscles (swallowing & speech)
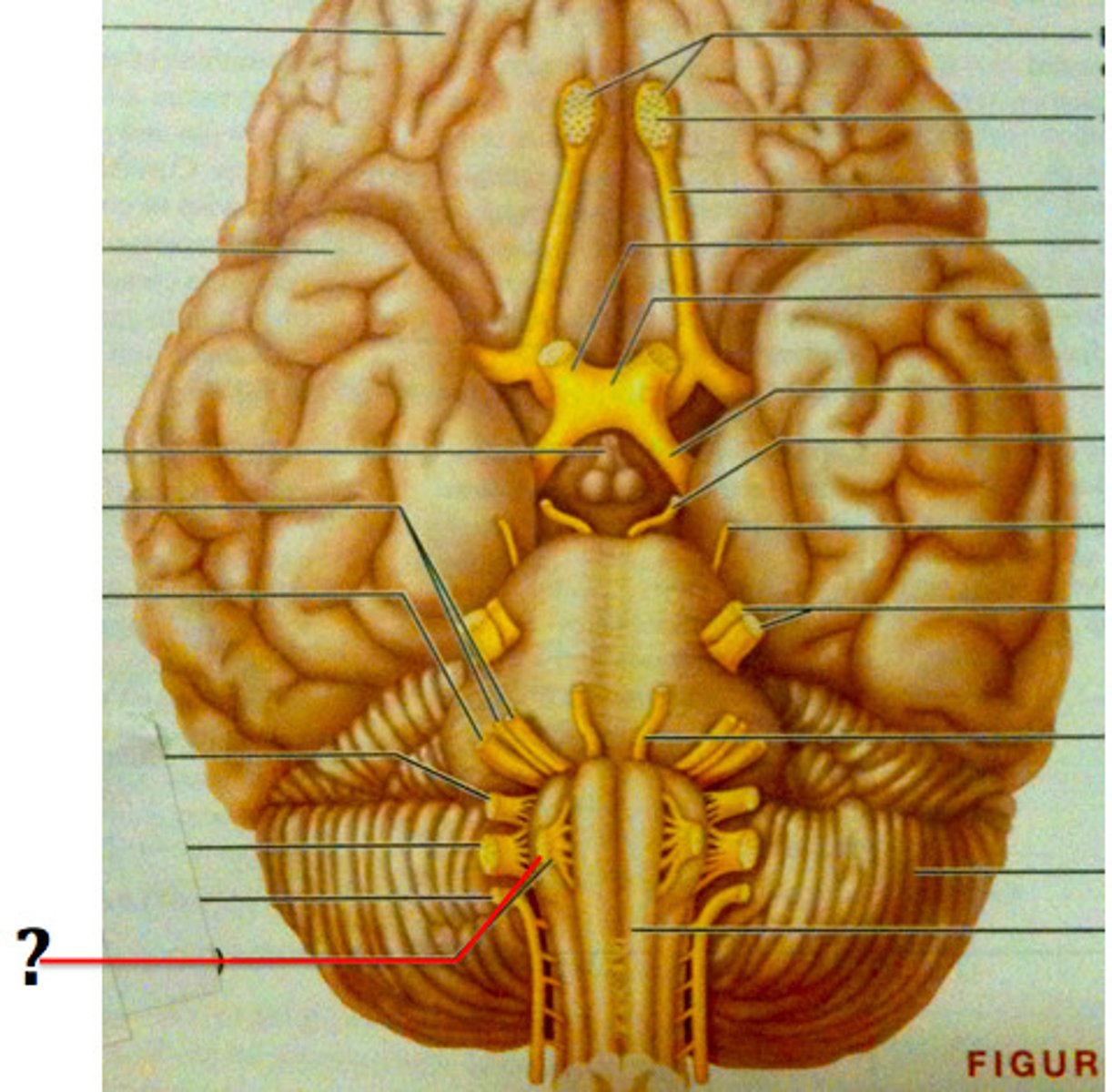
ventral rami
branches of spinal nerves that arise from ventral (anterior) root of the spinal cord
nerve plexus
-interweaving network of nerves
-damage to 1 branch doesn't cause paralysis because there are other branches involved in the plexus
cervical nerve plexus
-ventral rami of C1-C4 (sometimes C5)
-mostly cutaneous nerves
-important nerve: phrenic
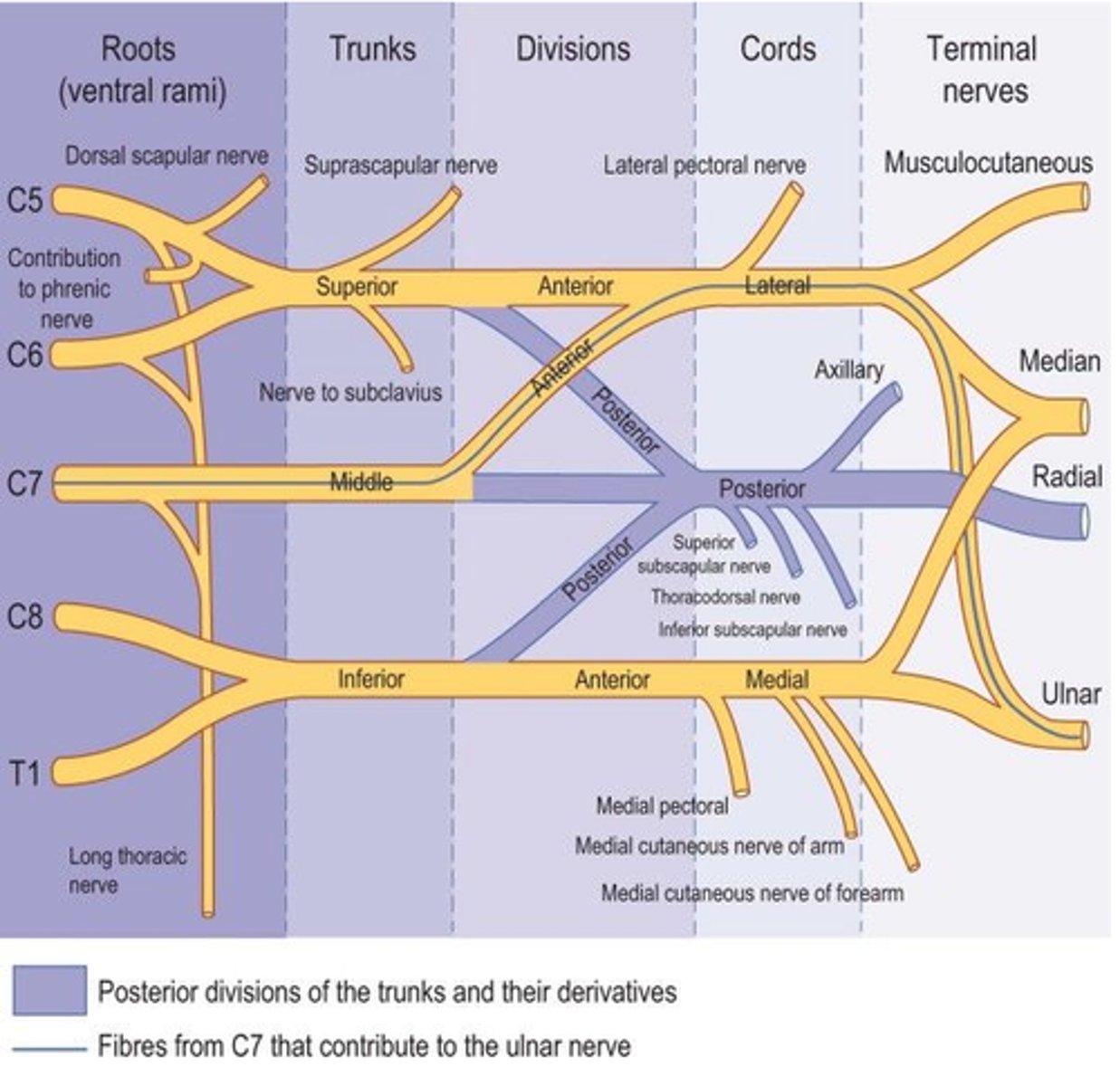
brachial nerve plexus
-ventral rami of C5-T1
-innervates upper limbs
-important nerves: axillary, musculocutaneous, median, ulnar, radial
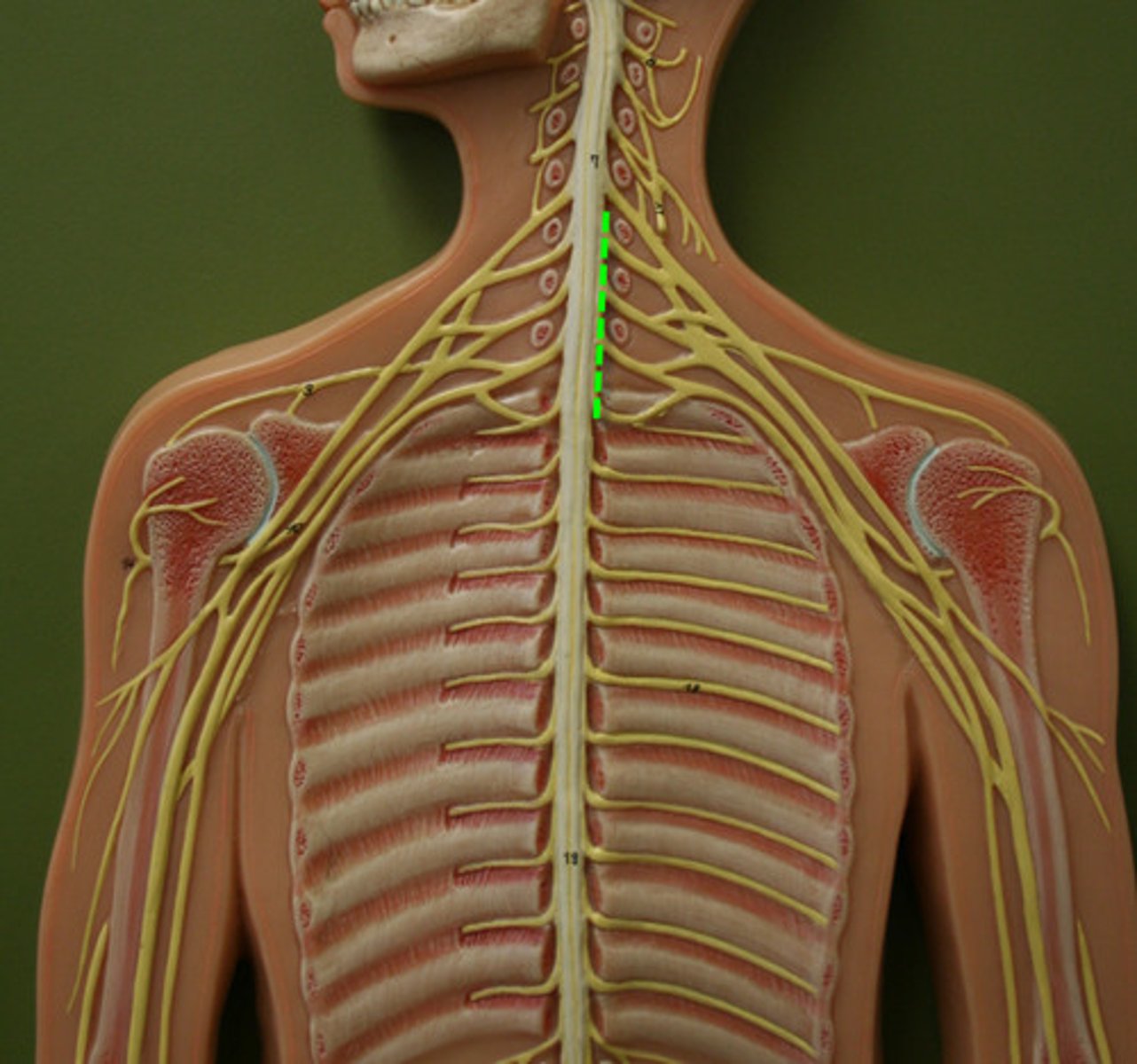
brachial nerve plexus subdivisons
-roots: 5 ventral rami (C5 to T1), medial
-trunks: united roots
-divisions: united trunks
-cords: united divisions, lateral
lumbar nerve plexus
-ventral rami of L1-L4
-innervates thigh muscles, abdomen wall, psoas major
-important nerves: femoral, obturator
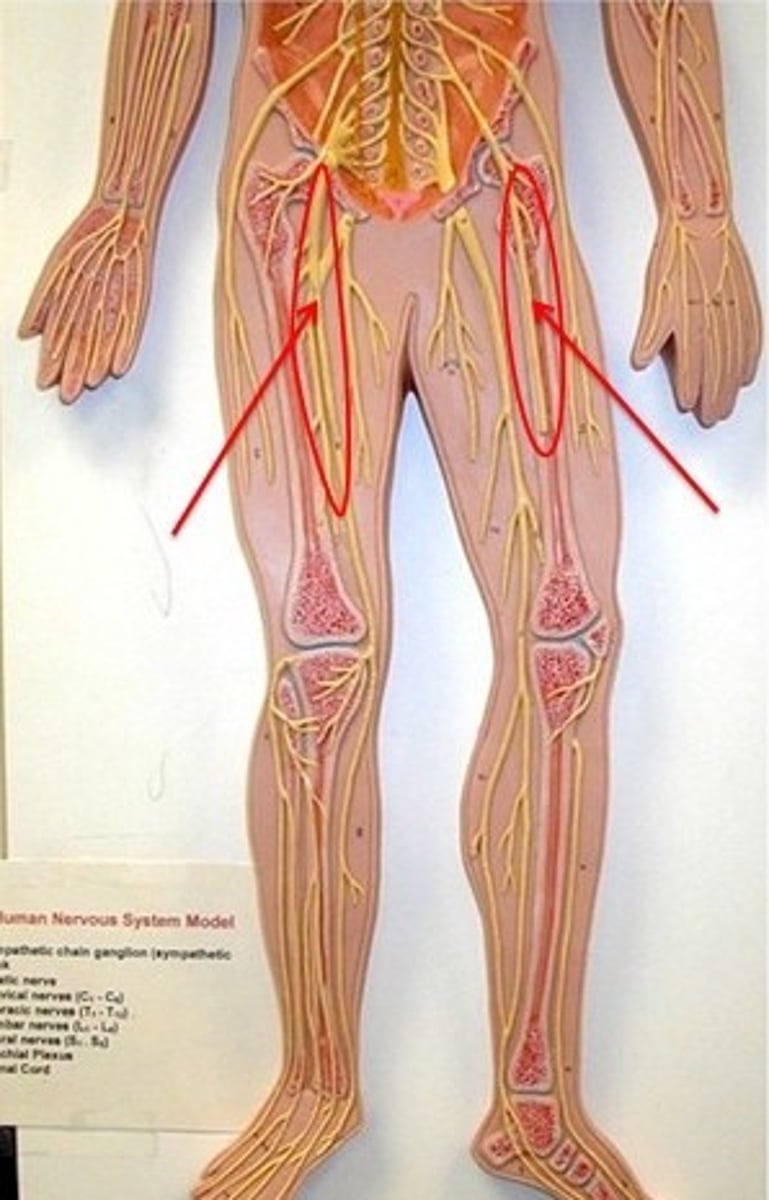
sacral plexus
-ventral rami of L4-S4
-innervates the buttock, lower limb, pelvic structures, perineum
-important nerve: sciatic nerve (longest & thickest, tibial & common fibular)
-sciatic nerve cut causes foot drop
intrinsic (inborn) reflexes
-rapid predictable movements in response to stimuli
-not learned or premeditated, subconscious, involuntary
-regulated by brain stem & spinal cord
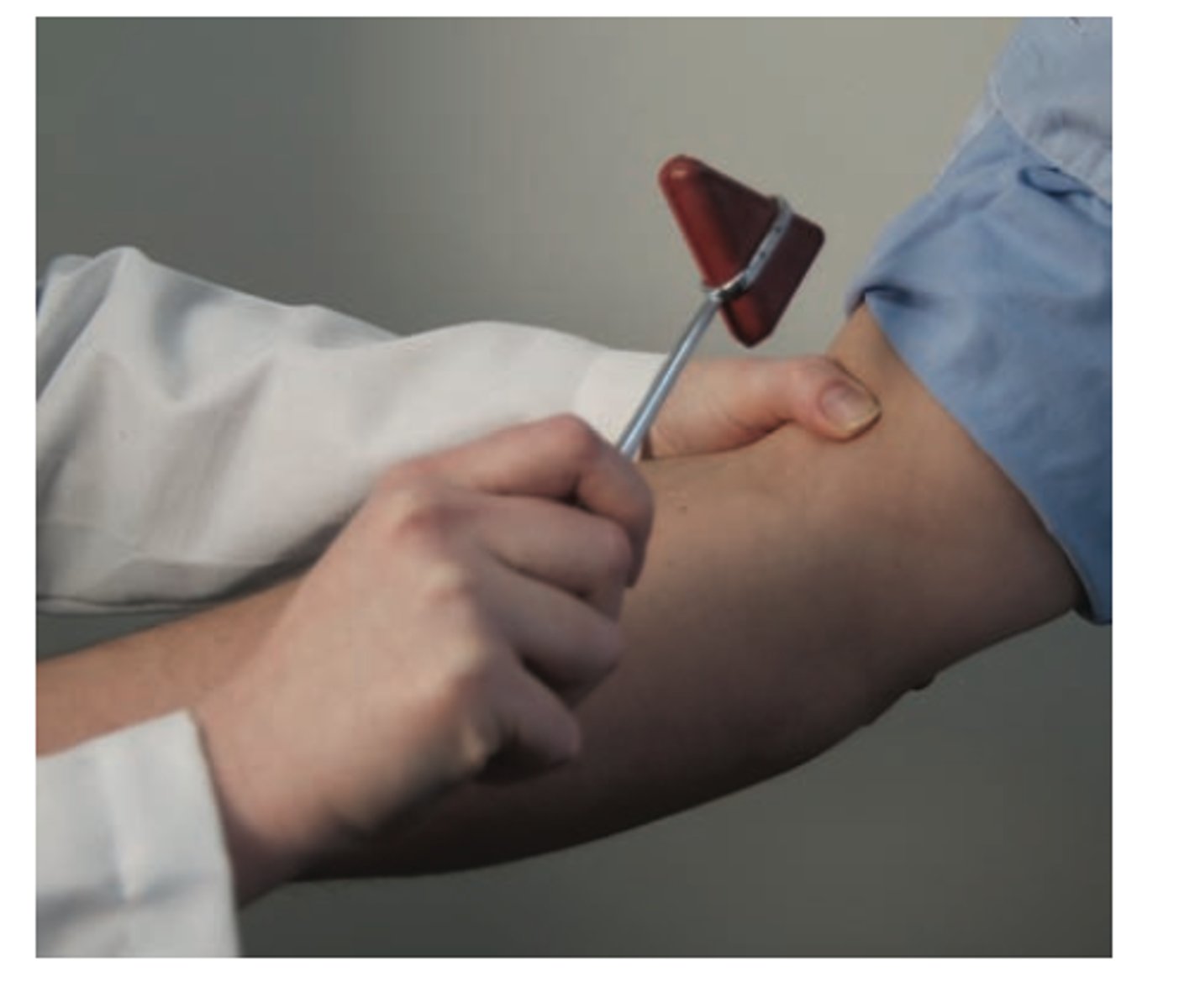
learned (acquired) reflexes
-acquired through practice or repetition
-become largely automatic over time
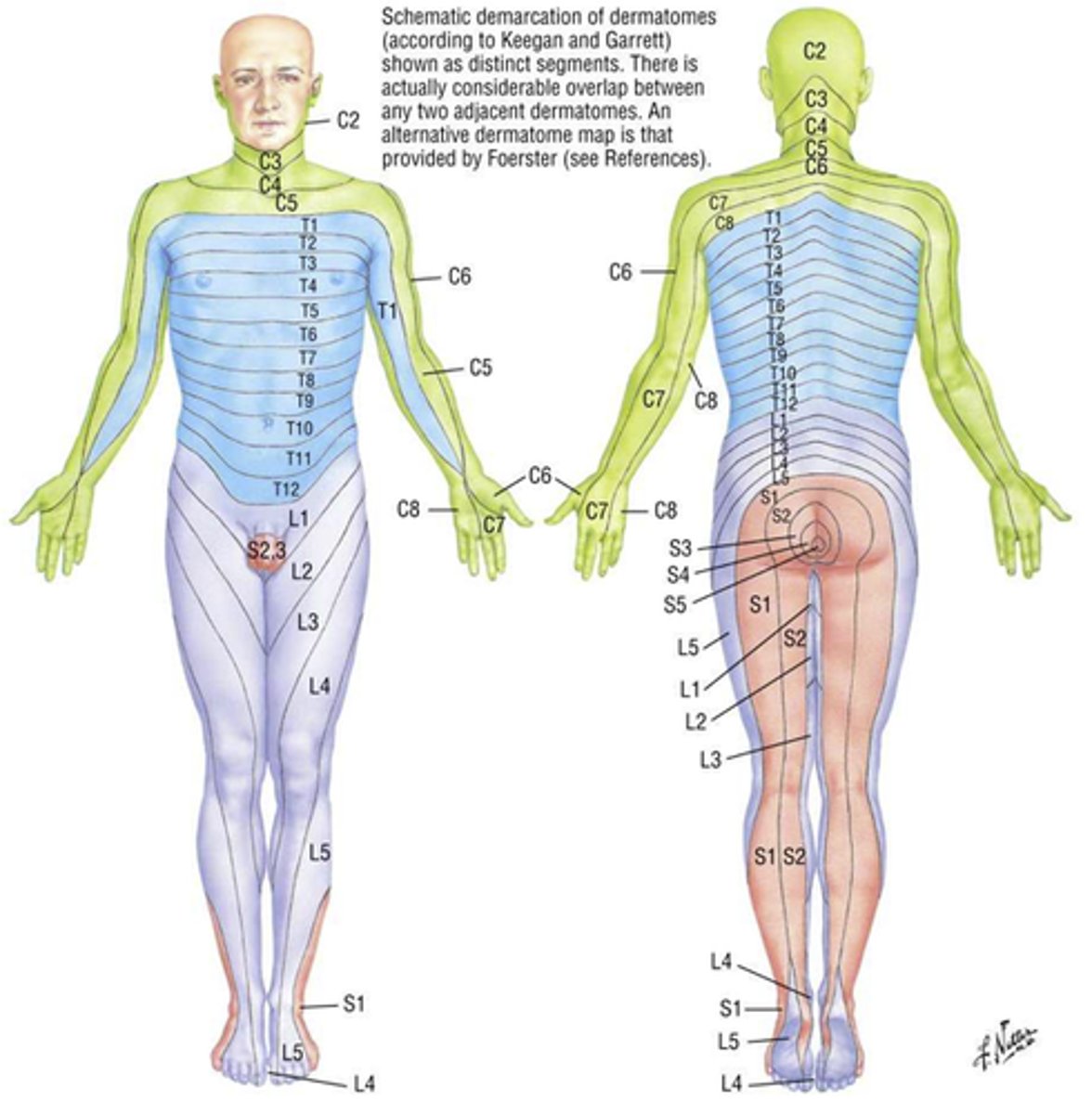
dermatomes
-area of skin innervated by cutaneous branches of a spinal nerve
-useful for clinicians because they provide a map of sensory innervation of the skin by specific spinal nerves
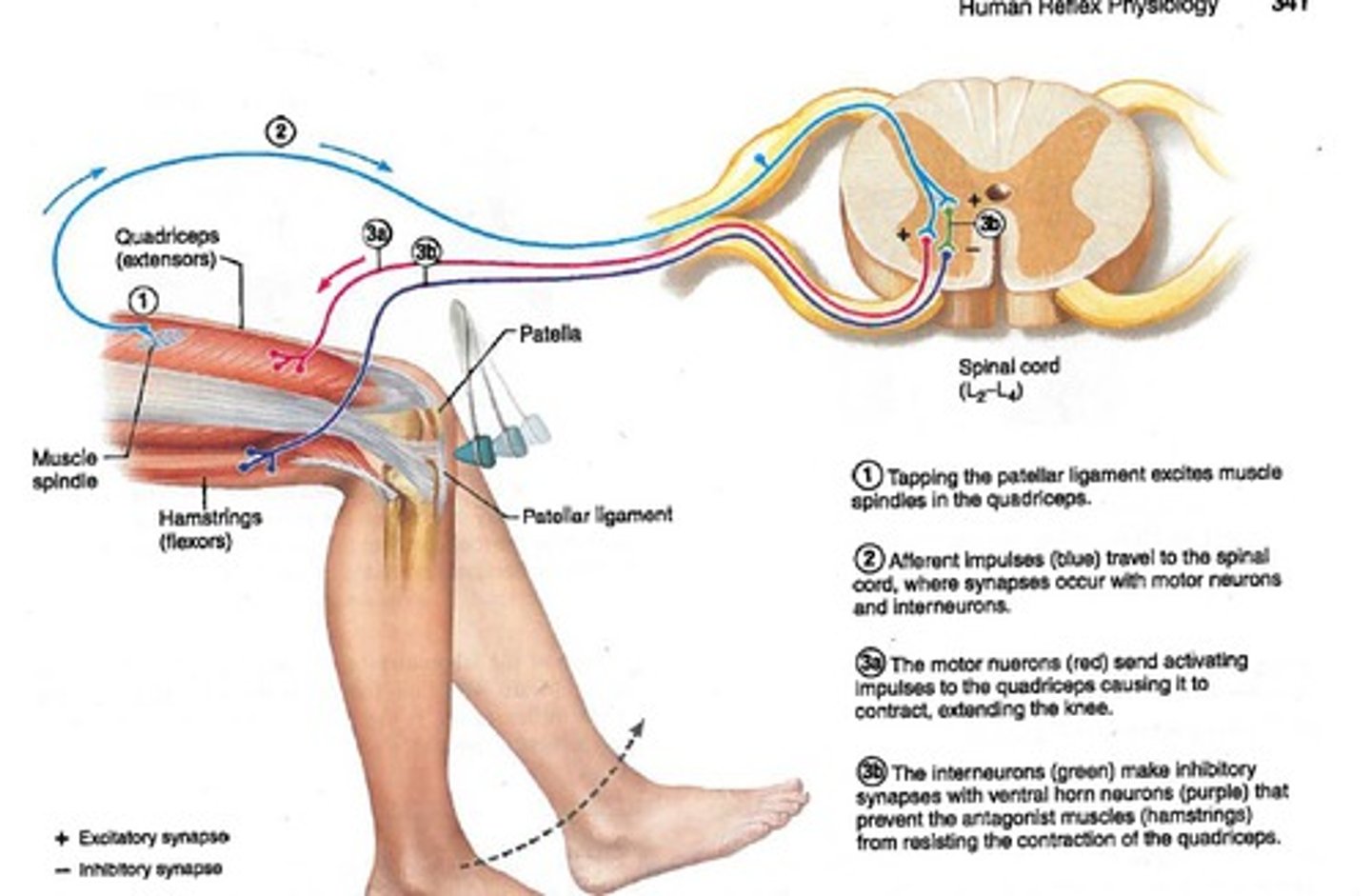
stretch reflexes
-muscle contracts if stretched too far
-maintains posture & muscle tone
-checks for intact sensory-motor connection between muscle & spinal cord
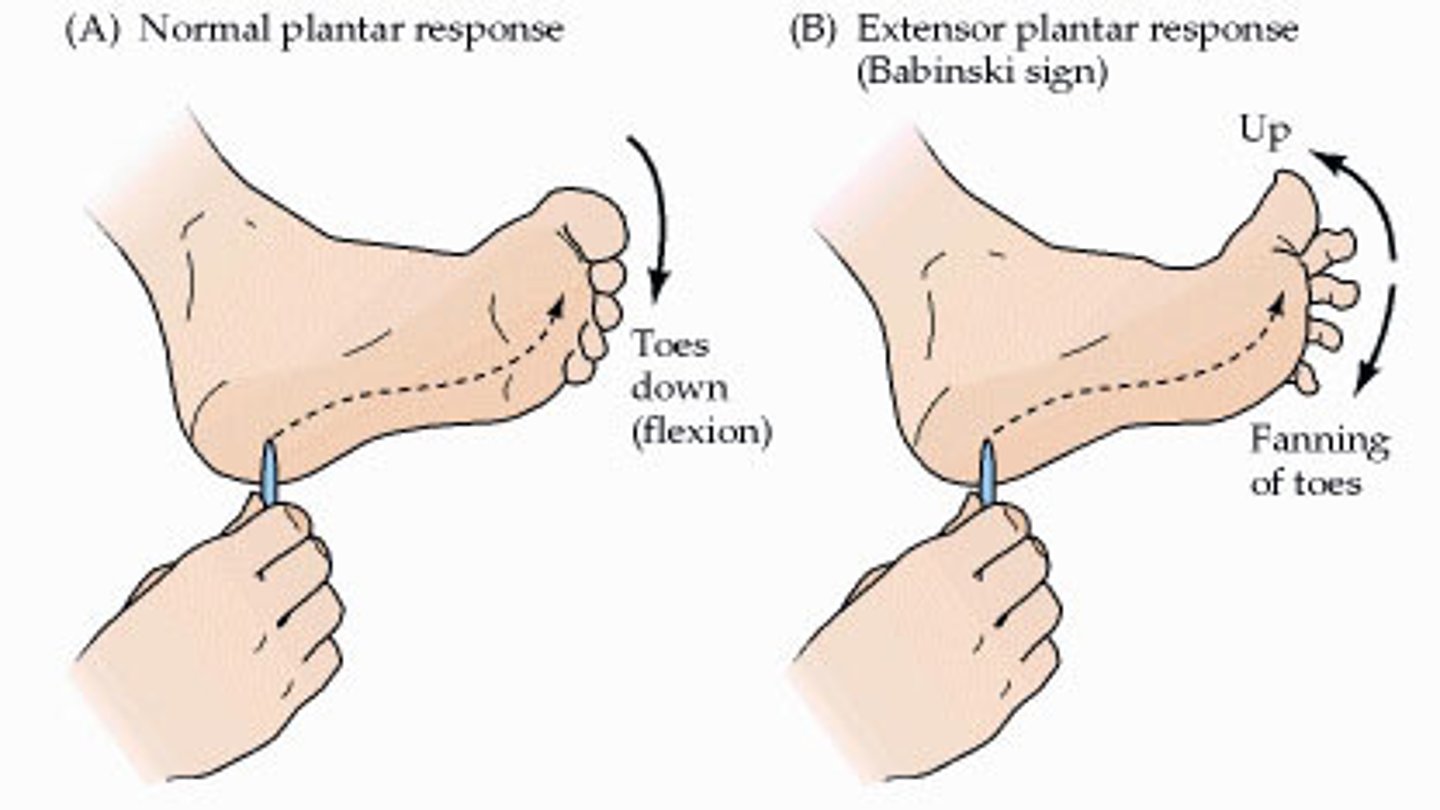
plantar (Babinski) reflex
-stimulus: stroke sole of foot
-normal response: downward curling (flexion) of toes
-tests integrity of L4-S2
-can be artificially triggered by stroking sole of foot
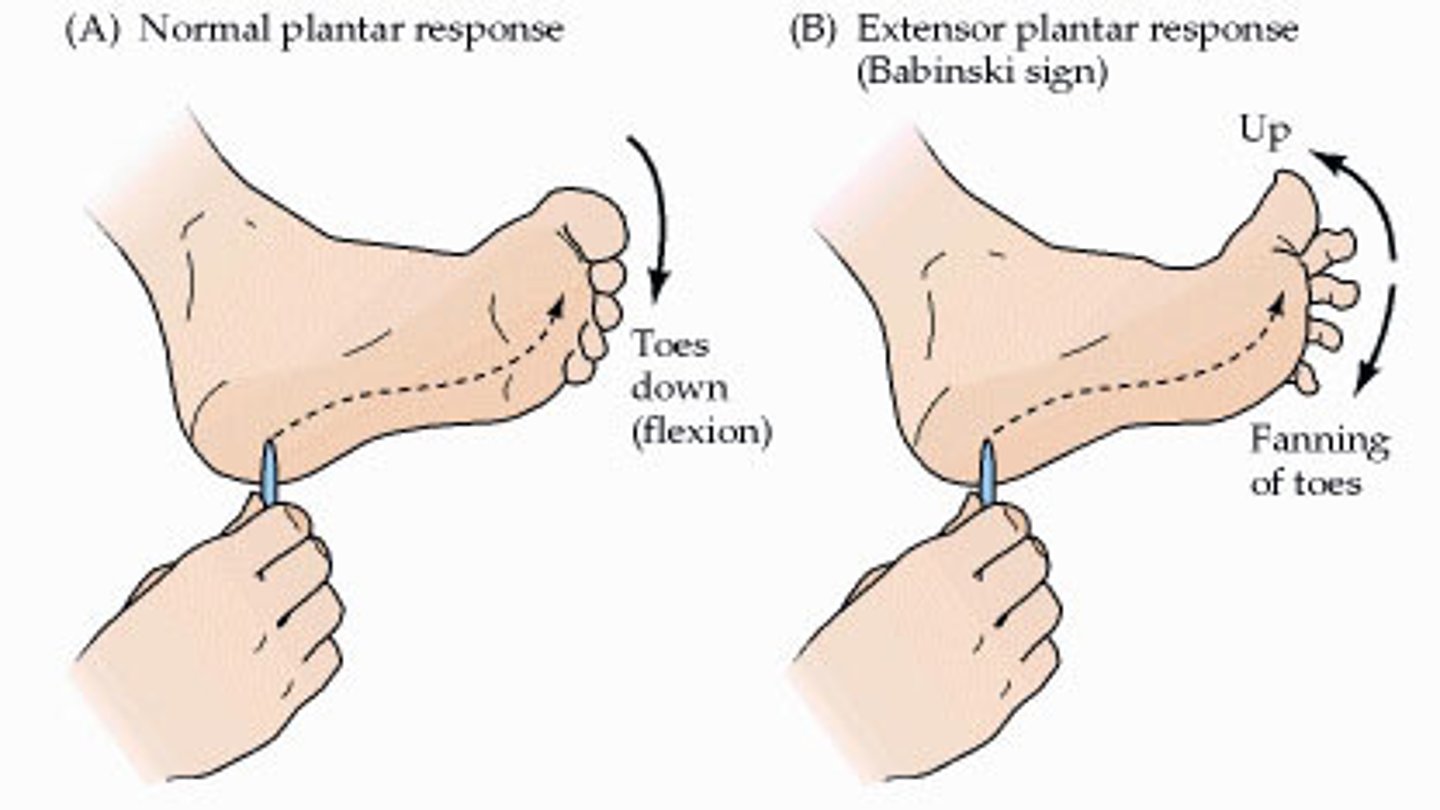
Babinski's sign
-abnormal response to Babinski reflex (big toe dorsiflexes, smaller toes fan out laterally)
-due to damage to primary motor cortex or corticospinal tracts
-normal up to 1-1.5 years
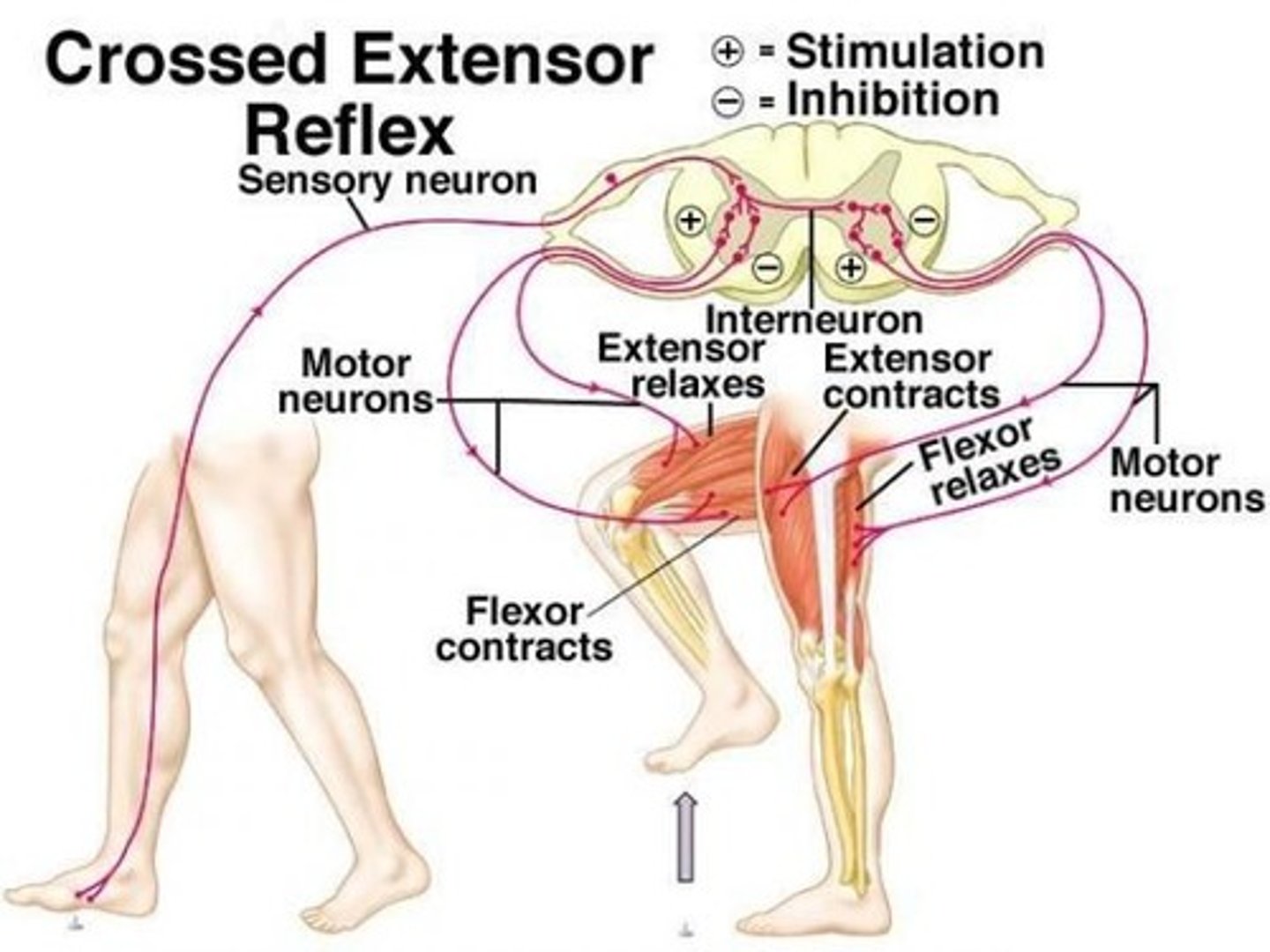
crossed extensor reflex
-flexion of the injured limb (withdrawal from painful stimulus) &
extension of the contralateral (opposite) limb to maintain balance & posture
-can be artificially triggered by applying a painful stimulus to a limb
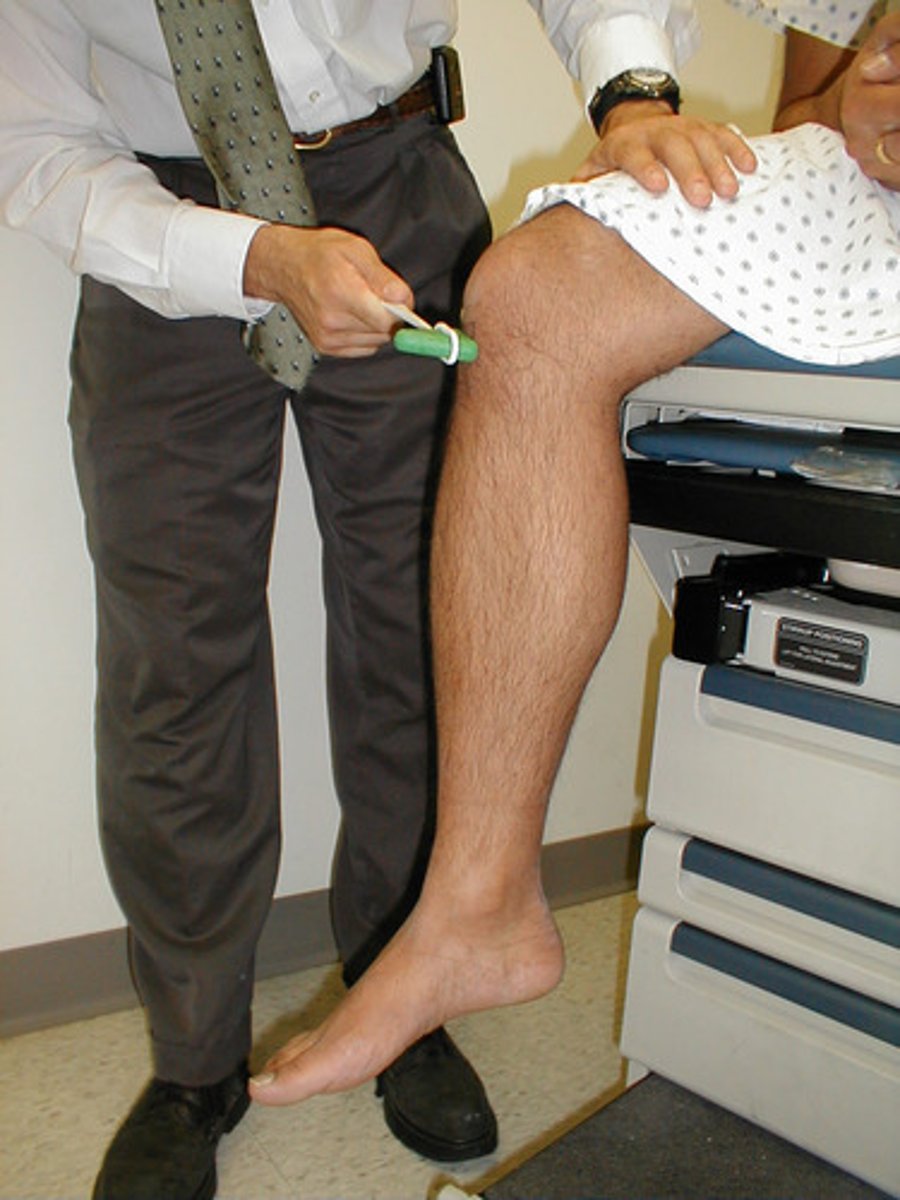
knee-jerk patellar reflex
-automatic contraction of the quadriceps in response to stretching of the patellar tendon
-artificially triggered by tapping patellar tendon
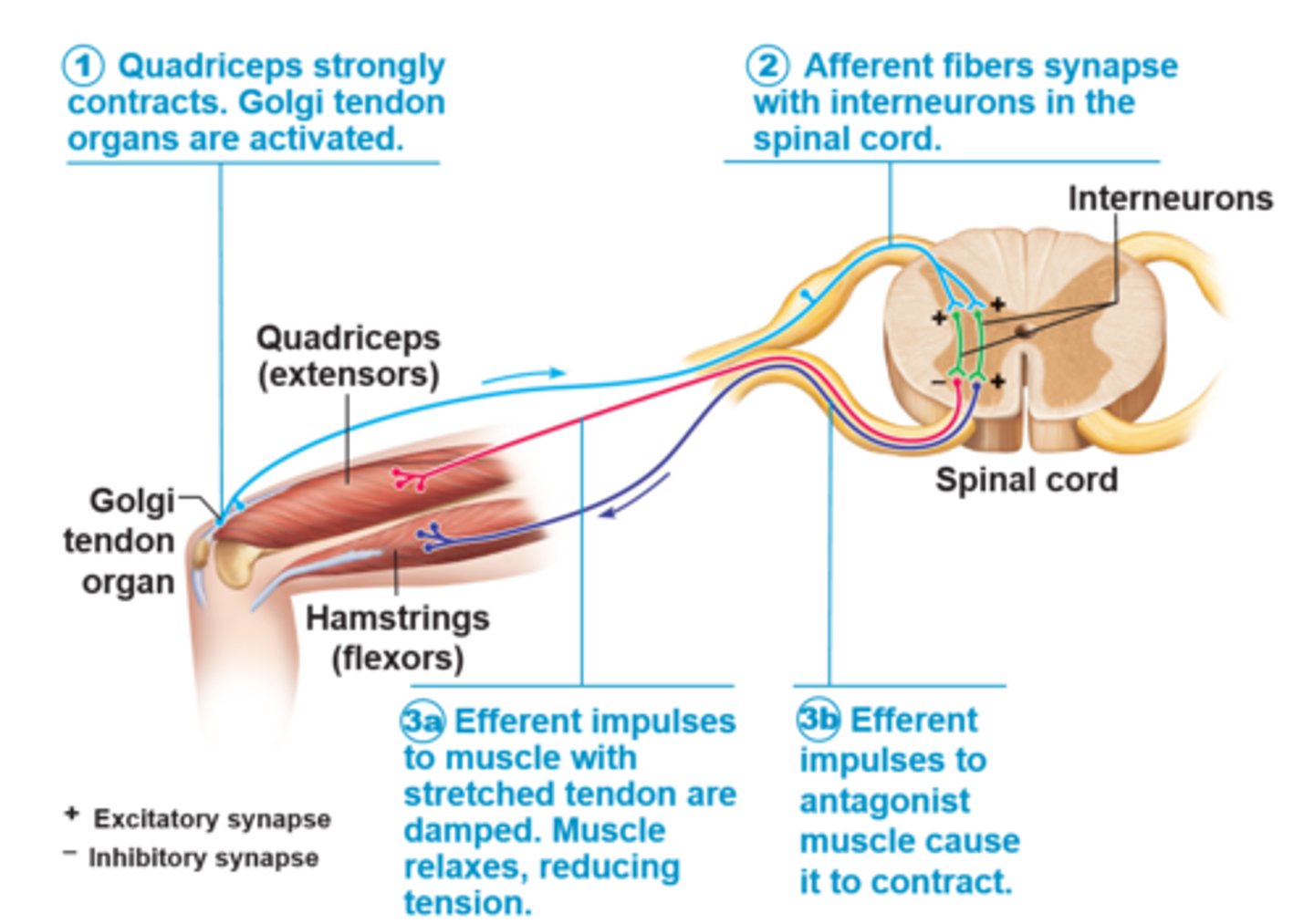
tendon reflex
-tendon organ activated in response to tension or passive stretch > muscles relax & lengthen to prevent damage
-spinal cord & cerebellum receives info & sends back impulse telling contracting muscle to relax & activating antagonist muscle & adjusts muscle tension
-can be artificially triggered by tapping on tendon
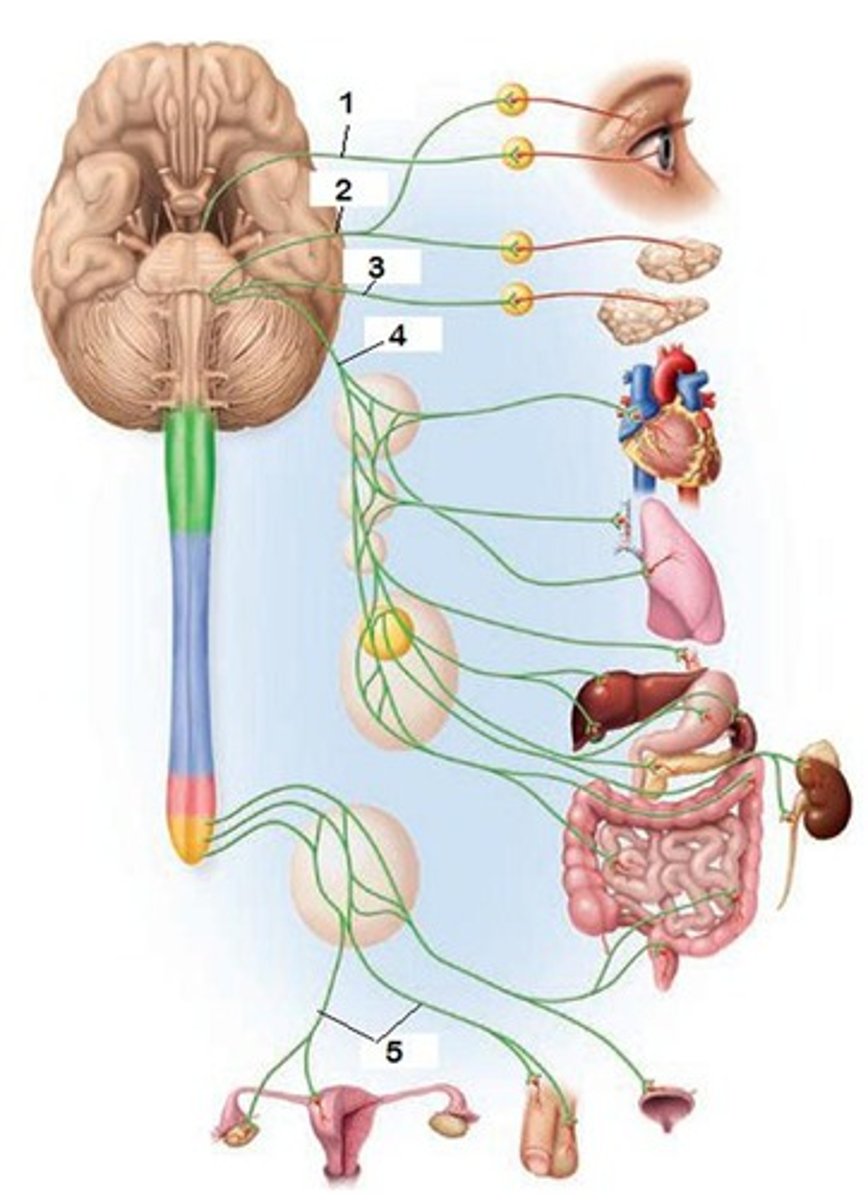
ANS vs. SNS
-ANS: involuntary functions, two-neuron pathways (pre & postganglionic), targets internal viscera, ACh & norepinephrine
-SNS: voluntary movement, single-neuron pathway (upper & lower motor neurons), targets skeletal muscles, ACh
sympathetic division of the ANS
-increases BP, HR, & breathing, bronchiole & pupil dilation, stimulates breakdown of glycogen to glucose (liver)
-more complex
-nerves originate from thoracolumbar region
-short preganglionic, long postganglionic fibers
-synapse at sympathetic trunk, prevertebral (collateral) ganglia, or adrenal medulla
-widespread effects due to longer postganglionic fibers & more distant ganglia
parasympathetic division of the ANS
-decreases BP, HR, & breathing, bronchiole & pupil constriction, stimulates metabolic processes, promotes storage of glucose as glycogen (liver)
-nerves originate from craniosacral region
-long preganglionic, short postganglionic fibers
-synapse in (terminal) ganglia located close to or w/in target organs
-localized effects due to short postganglionic fibers that synapse w/ ganglia close to target organs
most dominant cranial nerve in the parasympathetic division
-vagus nerves (CN X)
-serves all thoracic & abdominal viscera
innervation of the adrenal medulla
-not a typical two-neuron pathway (no postganglionic neuron)
-preganglionic fibers (thoracolumbar region) directly synapse in adrenal gland w/o synapsing w/ a postganglionic fiber
SNS vs. ANS motor neurons
-SNS: single motor neuron that extends from CNS directly to skeletal muscle, release ACh (excitatory)
-ANS: pregang. fibers originate in different regions of CNS & release ACh, postgang. fibers are found in sympathetic ganglia & release NE (sympathetic) or ACh (parasympathetic)
cholinergic receptors
-respond to binding of ACh
1. nicotine: excitatory; on skeletal muscle, postgang. neurons, hormone-producing cells of adrenal medulla
2. muscarinic: inhibitory or excitatory; on all parasympathetic effectors & some sympathetic
adrenergic receptors
-respond to binding of NE or epinephrine
-on all postganglionic sympathetic effectors
1. alpha receptors
2. beta receptors
beta-blocker medications
-block effects of NE & epinephrine on beta-adrenergic receptors
-treat cardiovascular conditions like hypertension & angina
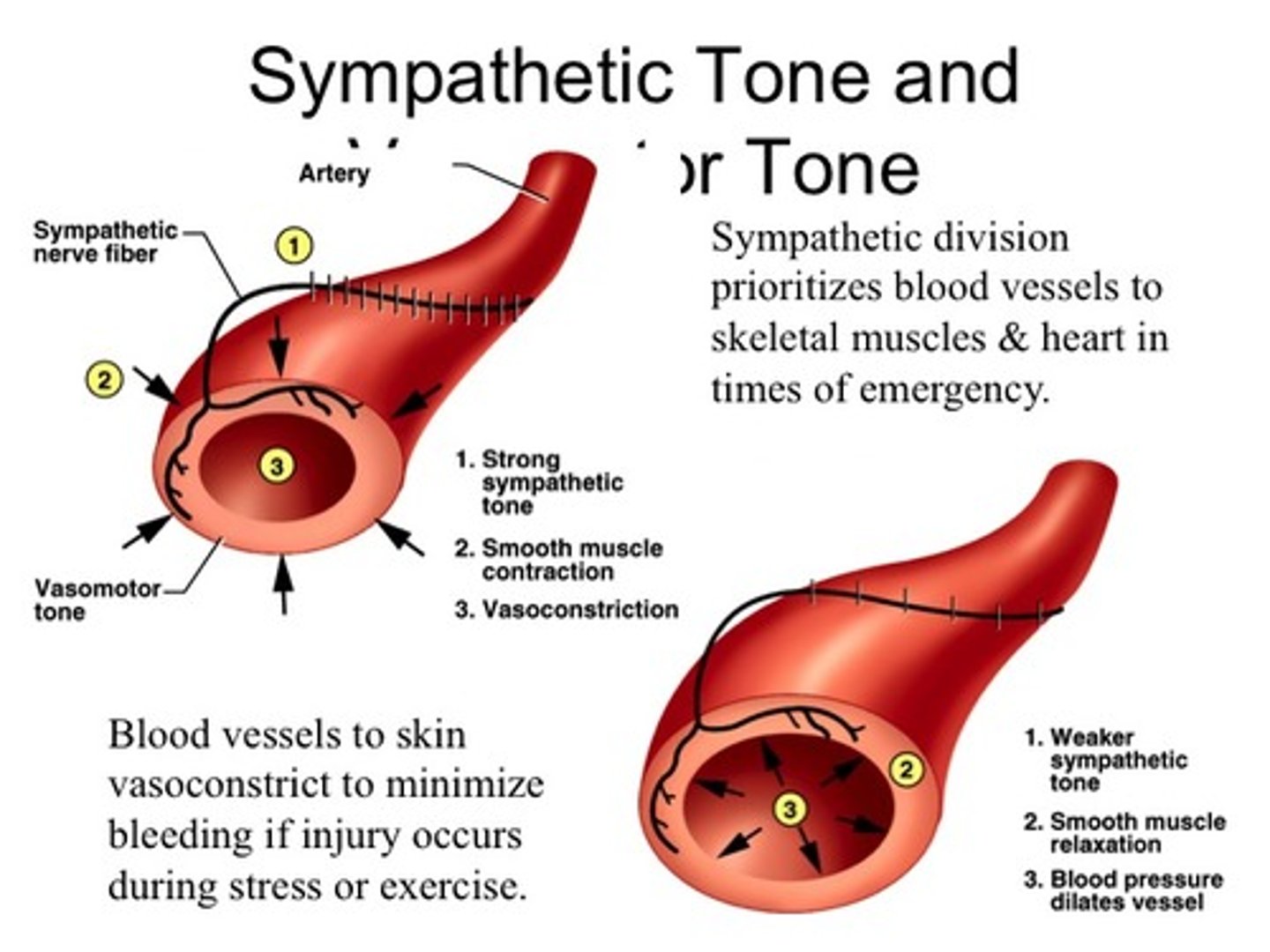
sympathetic (vasomotor) tone
-BVs in continuous state of partial contraction
-most BVs innervated by sympathetic fibers so sympathetic division controls BP
-allows shunting of blood to body areas that need it while limiting blood flow to other areas
parasympathetic tone
-constant level of parasympathetic stimulation that slows the heart & sets normal activity levels for digestion & urination
-parasympathetic division dominates heart & smooth muscle of digestive & urinary tract organs & most glands

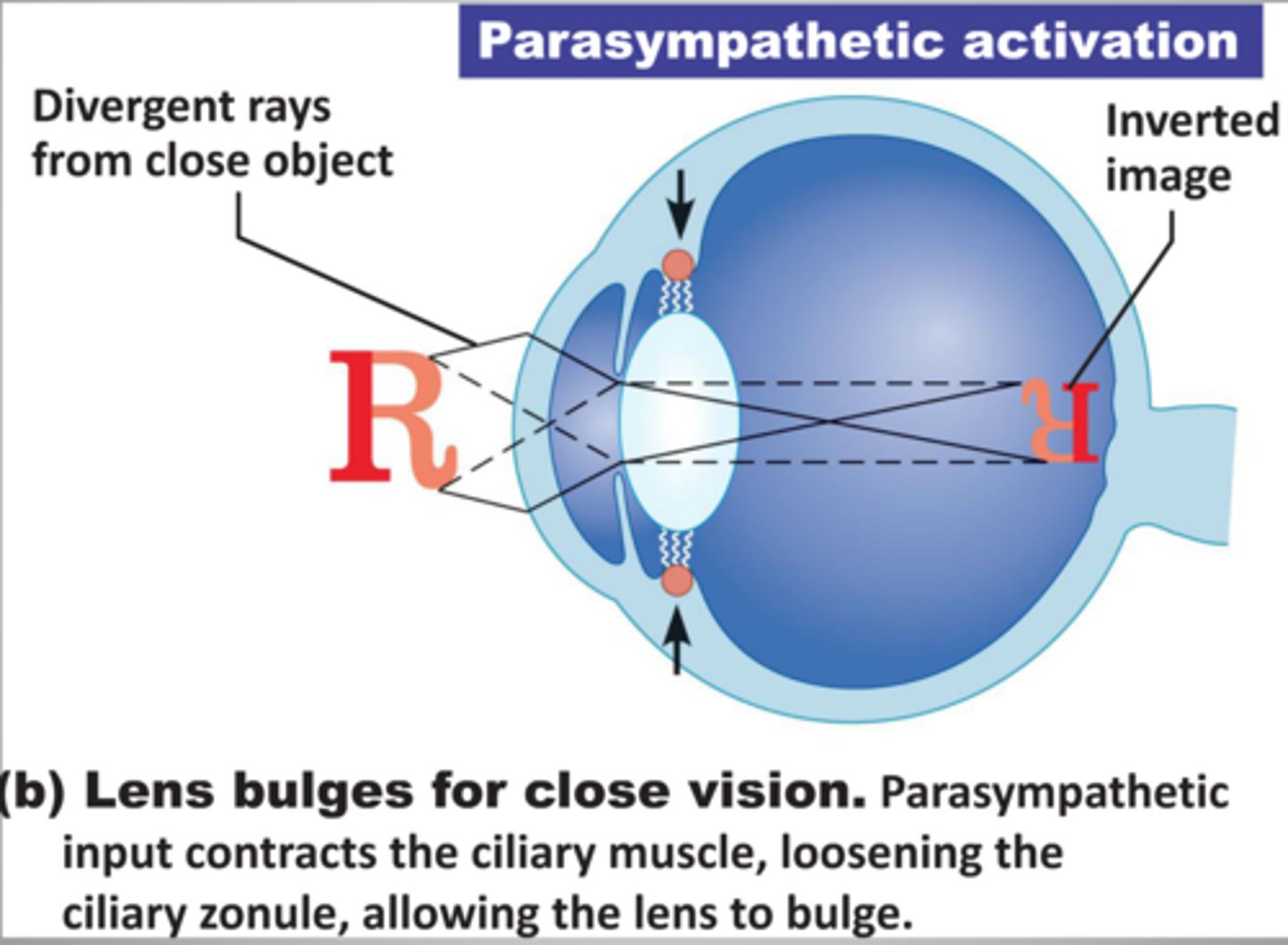
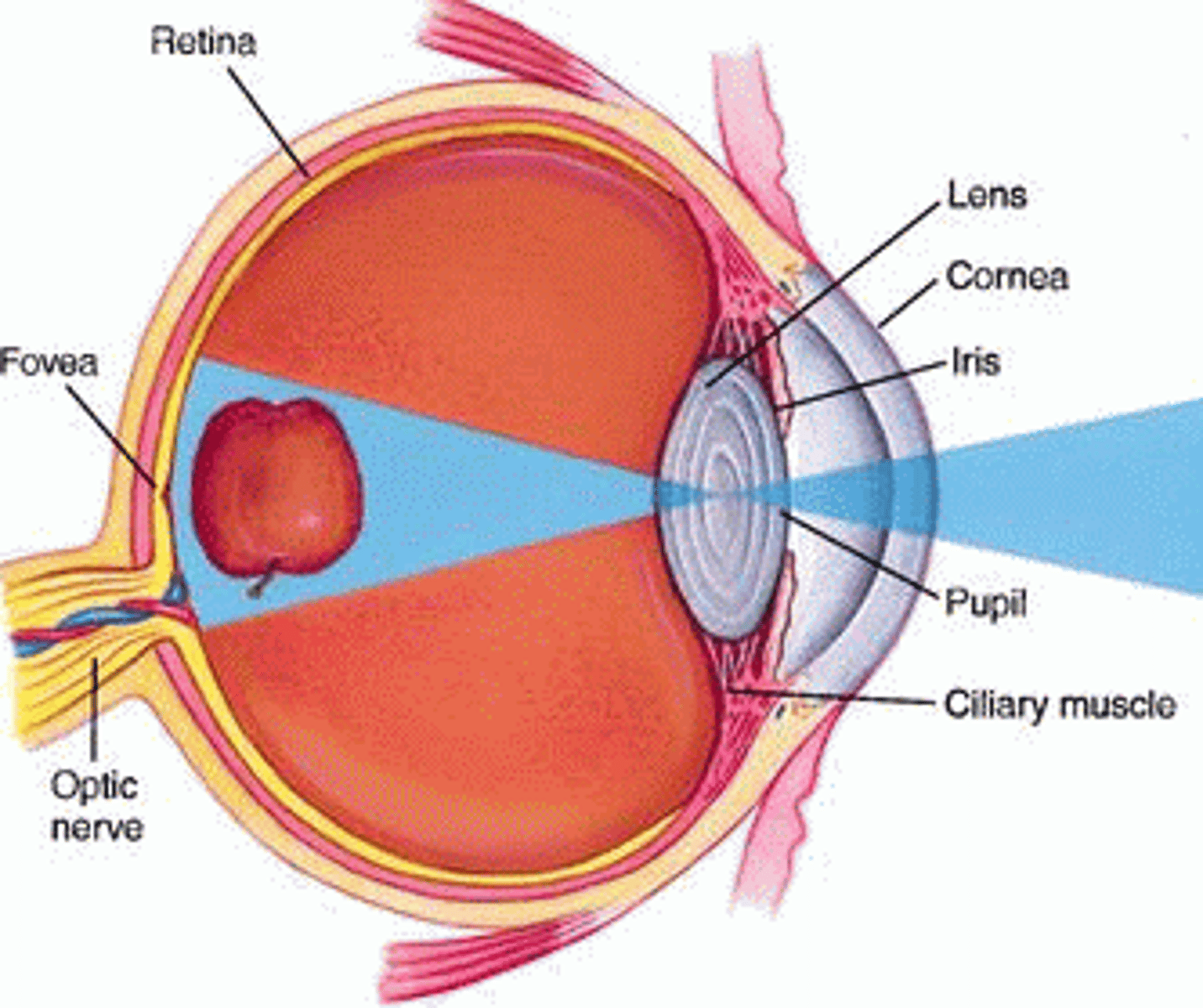
focusing for close vision
-lens accommodation: change in shape (bulges) to increase refraction
-pupil constricts to prevent entrance of most divergent light rays
-medial rotation of eyeballs to converge on close object
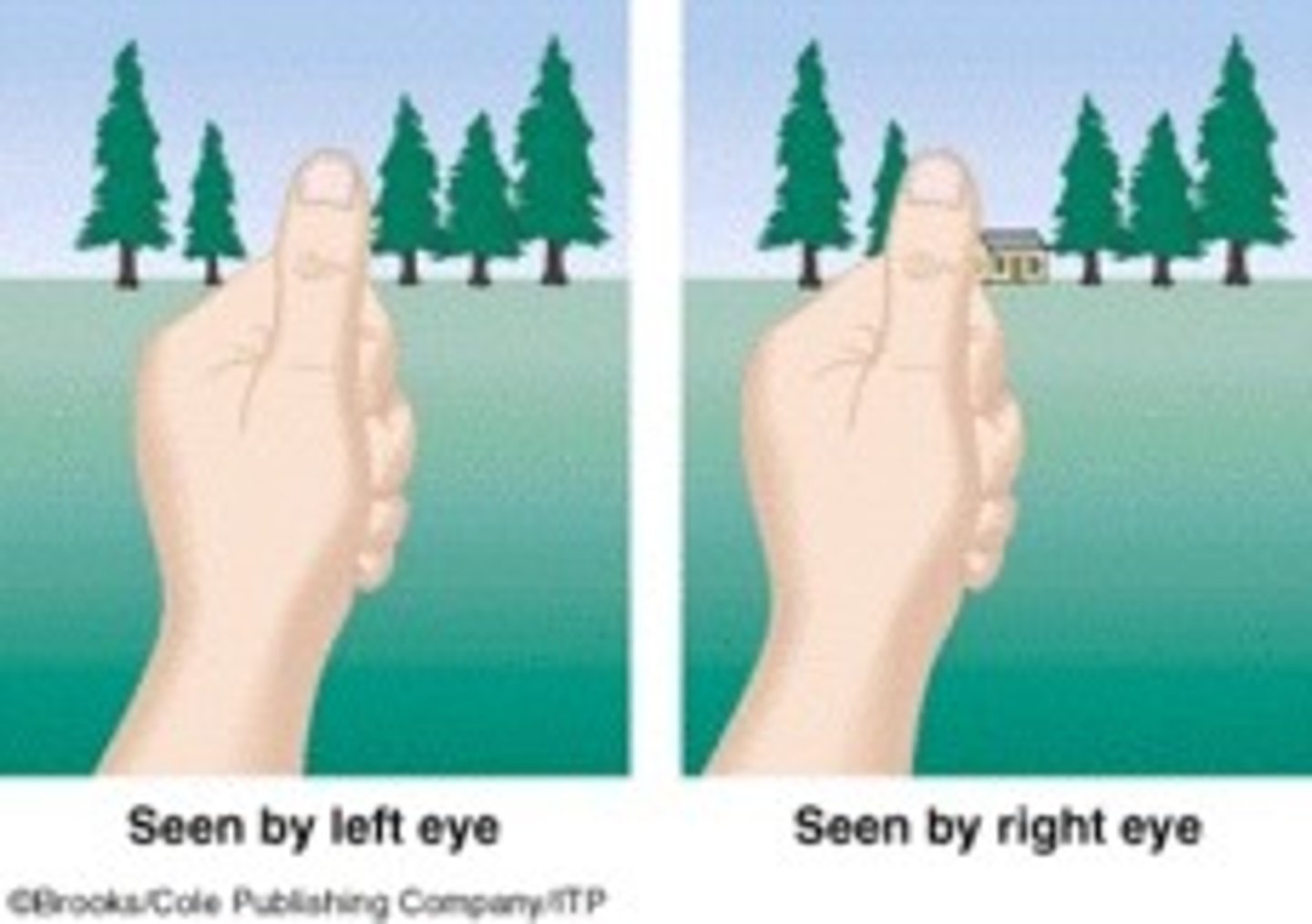
depth perception
-eyes' visual fields overlap, visual cortex processes images from both eyes & forms a 3-D image
-allows humans to accurately locate objects in space
-lost when only one eye is functioning
-thalamus
-developed by age 3
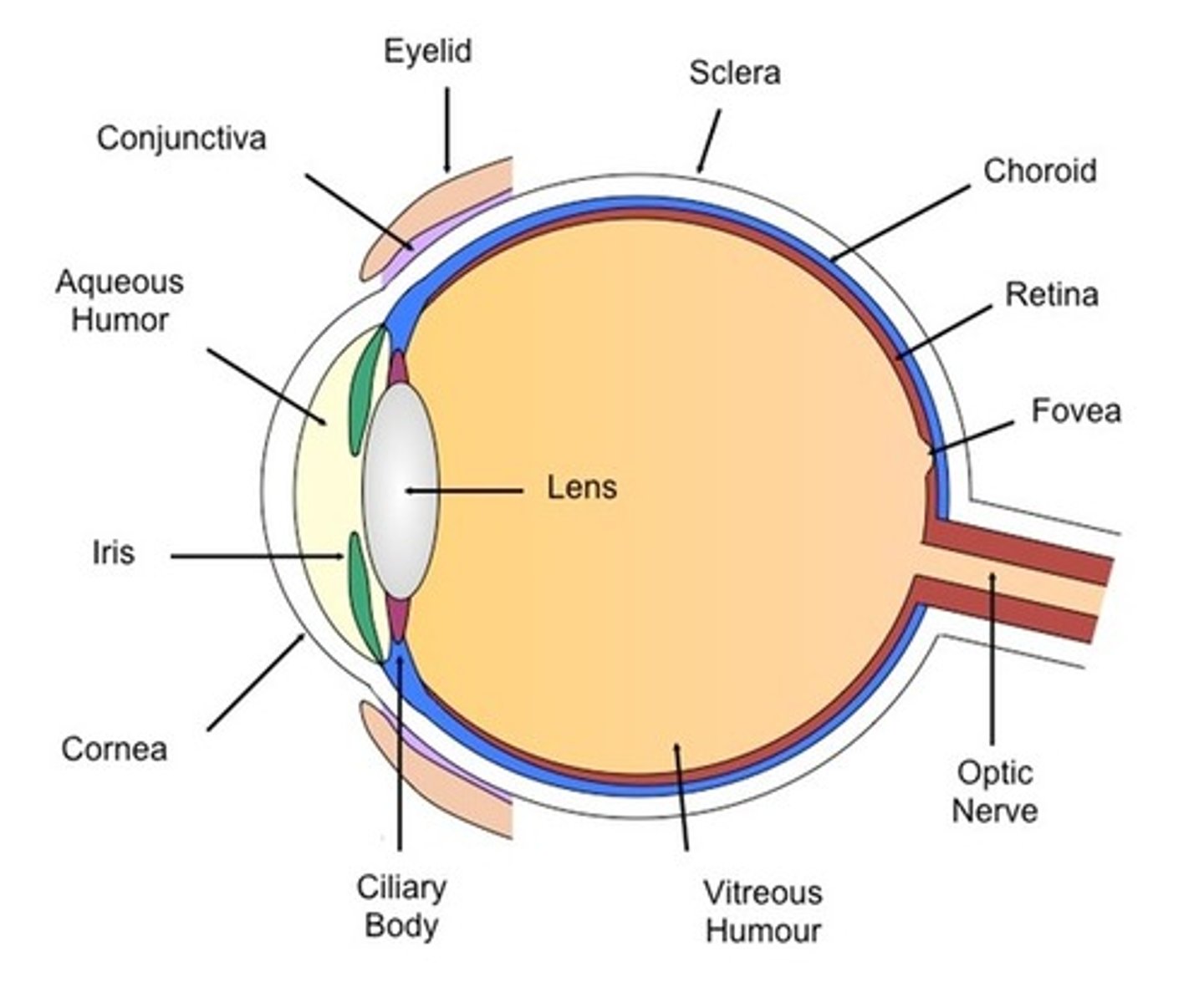
pathway of light
-cornea
-aqueous humor (anterior segment)
-lens
-vitreous humor (posterior segment)
-through neural layer of retina
-photoreceptors deep in neural layer of retina
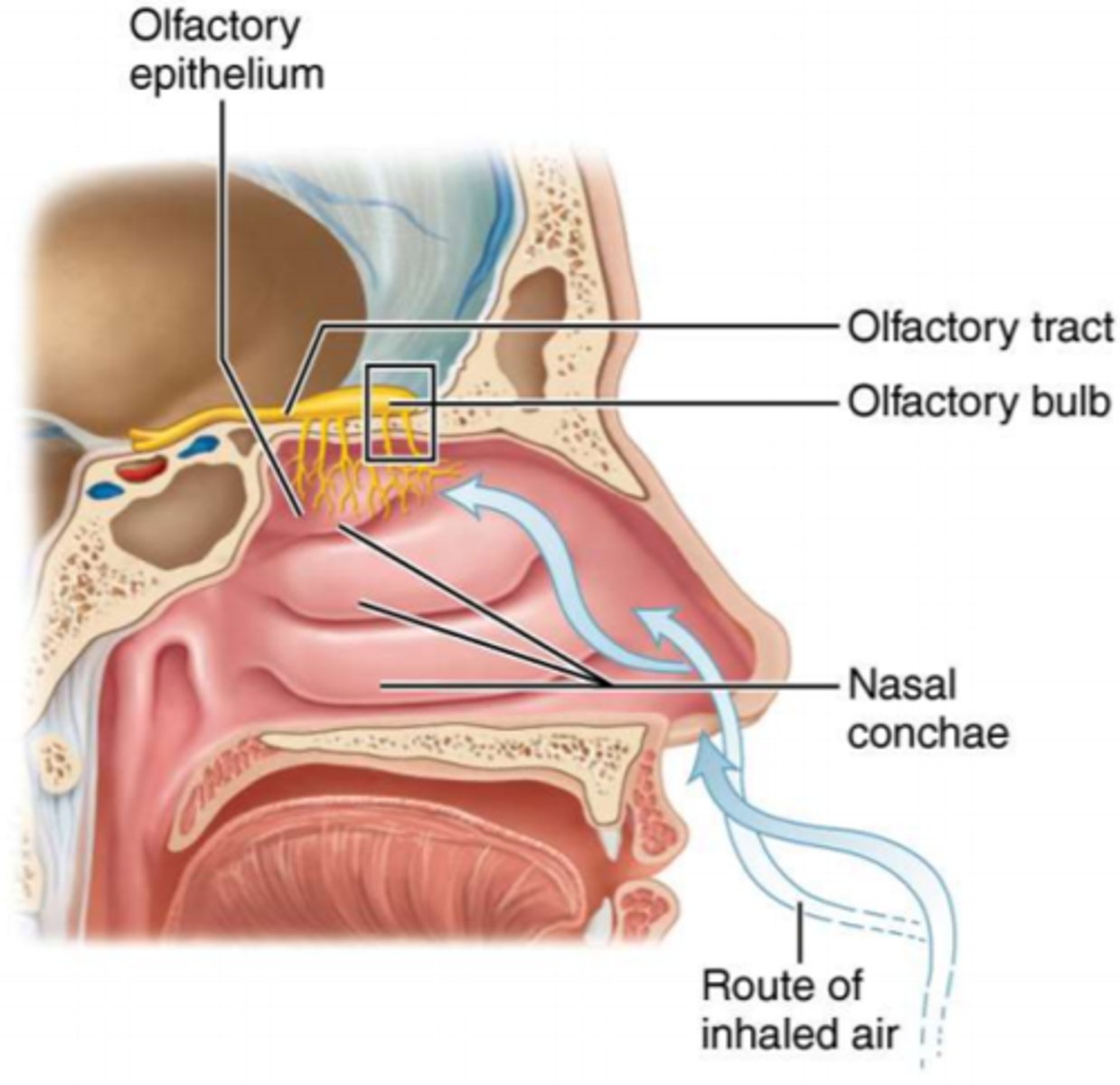
smell (olfaction)
-organ: olfactory epithelium (nasal cavity roof on top of superior nasal conchae ethmoid bone)
-neurons: olfactory sensory neurons, unique because they are replaced throughout adult lifespan
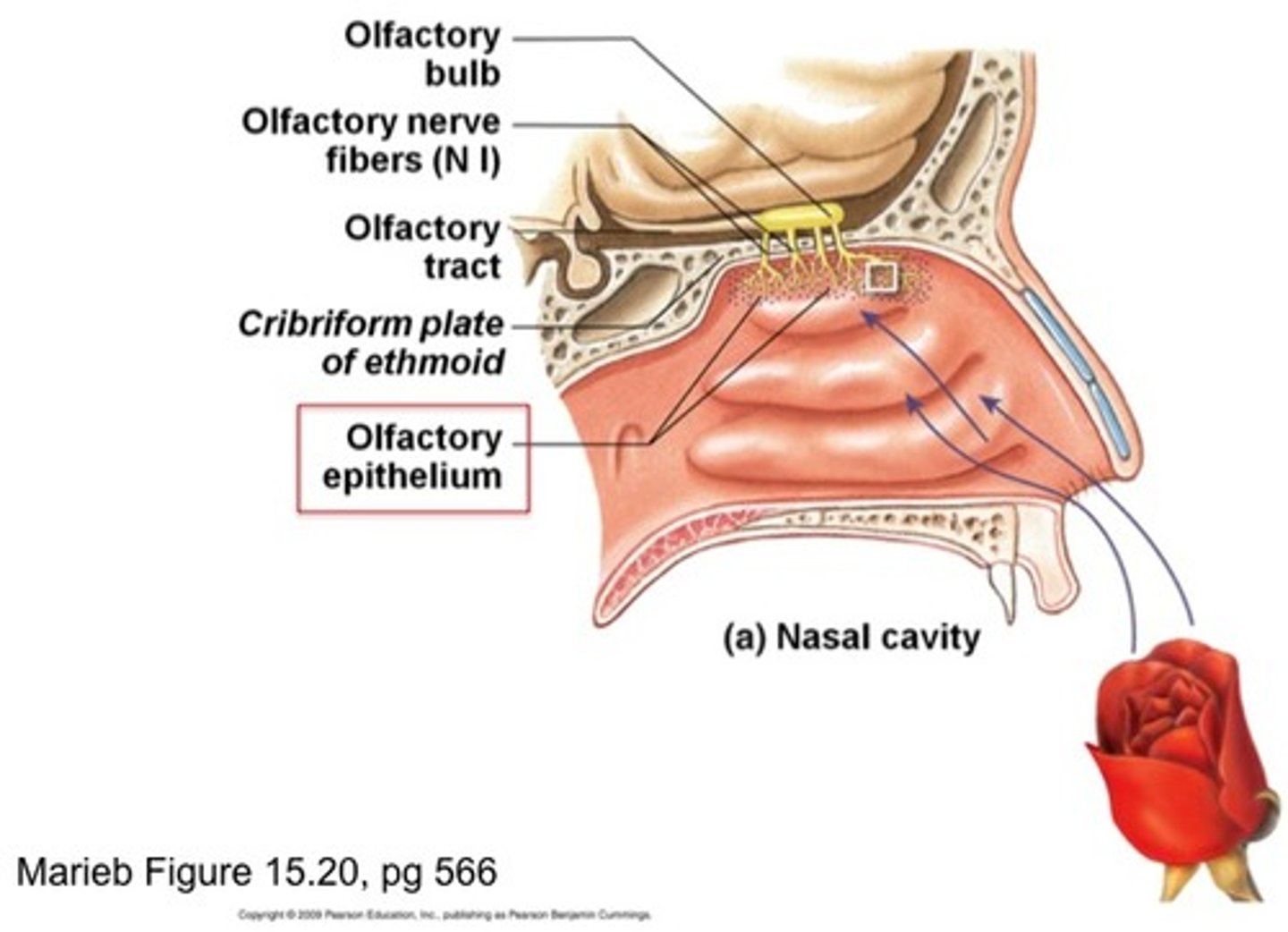
physiology of smell
each odor molecule (odorant) activates a specific combination of olfactory receptors that allows the brain to interpret the "pattern" of activated receptors as a unique smell rather than having a single receptor for each distinct odor
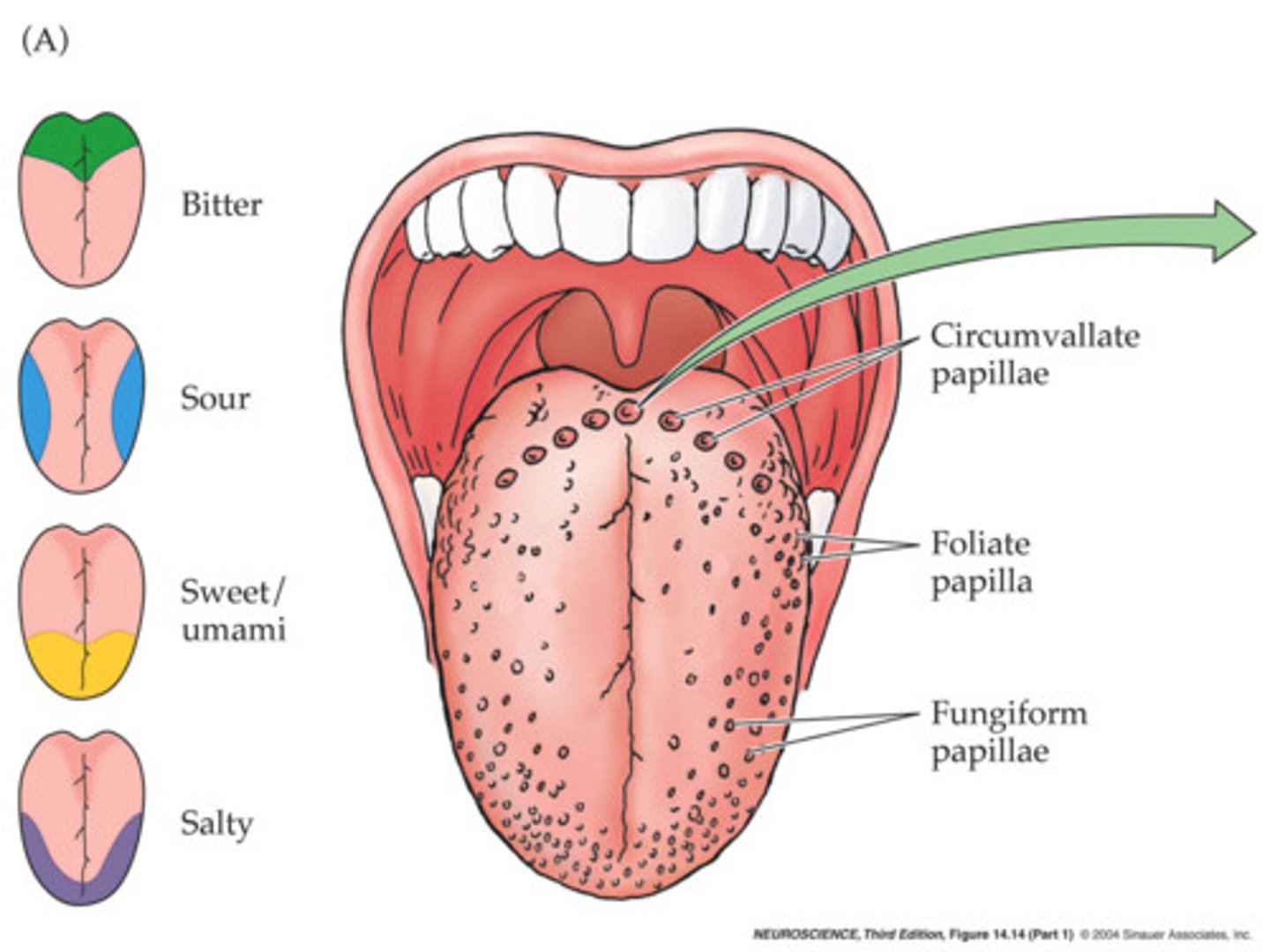
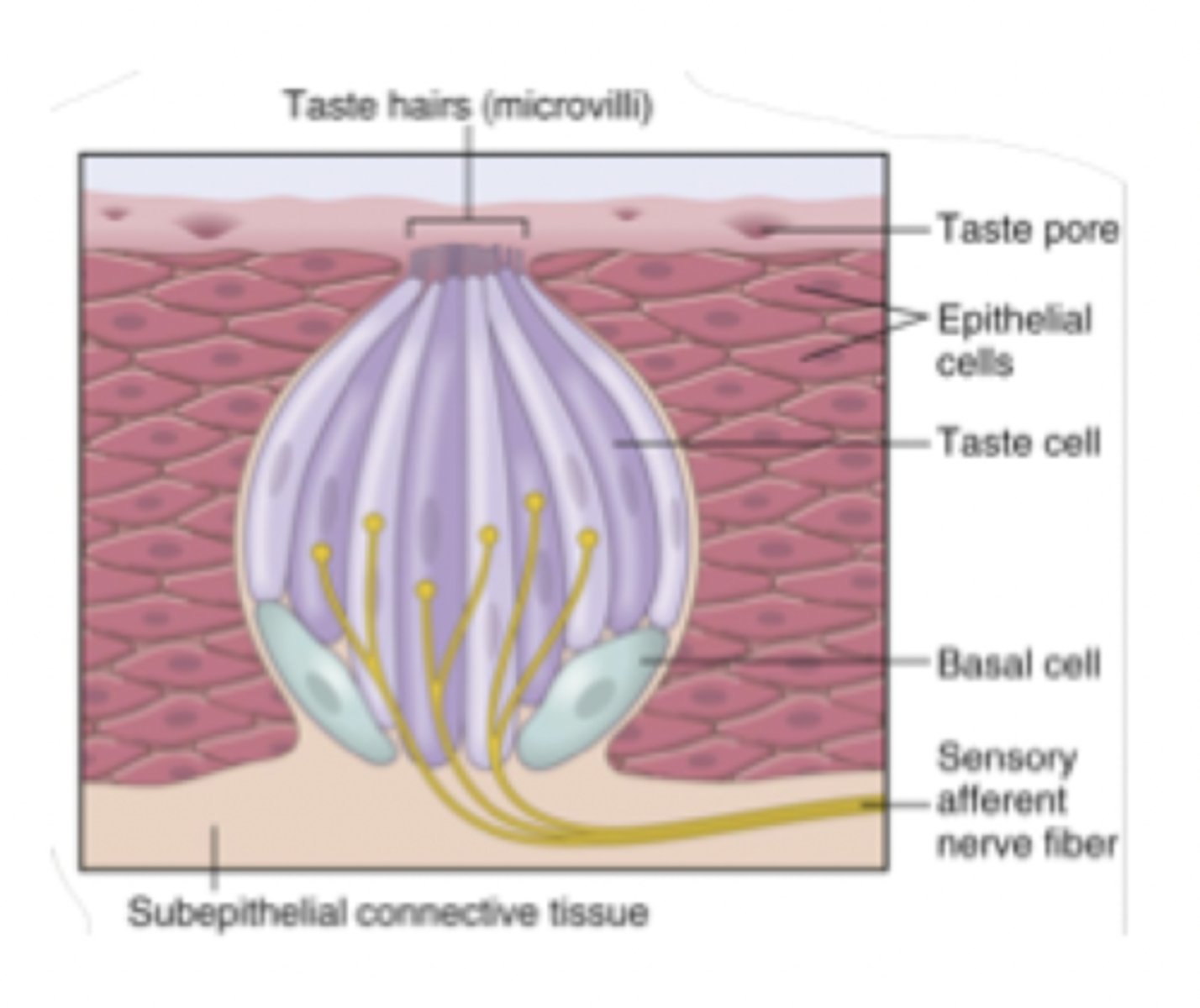
taste (gustation)
-organ: taste buds on tongue in papillae & soft palate, cheeks, pharynx, epiglottis
-gustatory hairs (receptor membrane) on taste receptor (gustatory epithelial) cells w/in taste buds
-cranial nerves: VII (facial), IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus)
activation of taste receptor (gustatory) cells
-chemical dissolves in saliva & diffuses into taste pore surrounding papillae
-chemical binds to receptor on gustatory hairs in taste pores & generates an AP
taste disorders
-less common because there are 3 nerves transmitting taste sensory input
-causes: upper resp. tract infections, head injuries, chemicals or medications, head/neck radiation therapy
other sensory receptors in the mouth
-thermoreceptors
-mechanoreceptors
-nociceptors
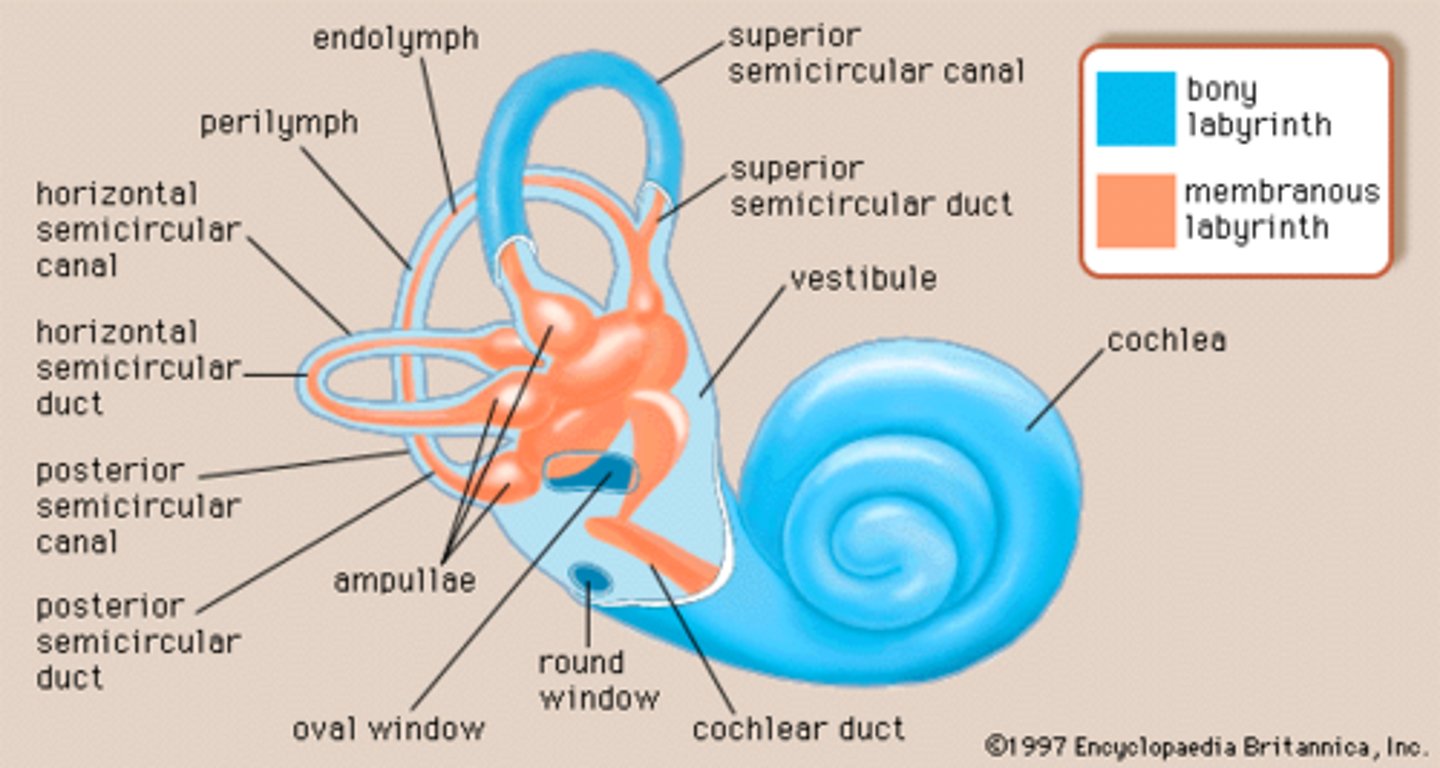
hearing & equilibrium inner ear sensory organs
-vestibule (equilibrium)
-semicircular canals (equilibrium)
-cochlea (hearing)
-in bony labyrinth (fluid filled cavities in temporal bone)
vestibule
monitors static equilibrium (proper position when head is stationary) in response to changes in linear acceleration (straight movement)
semicircular canals
monitors dynamic equilibrium (proper head position during movement) in response to rotational acceleration
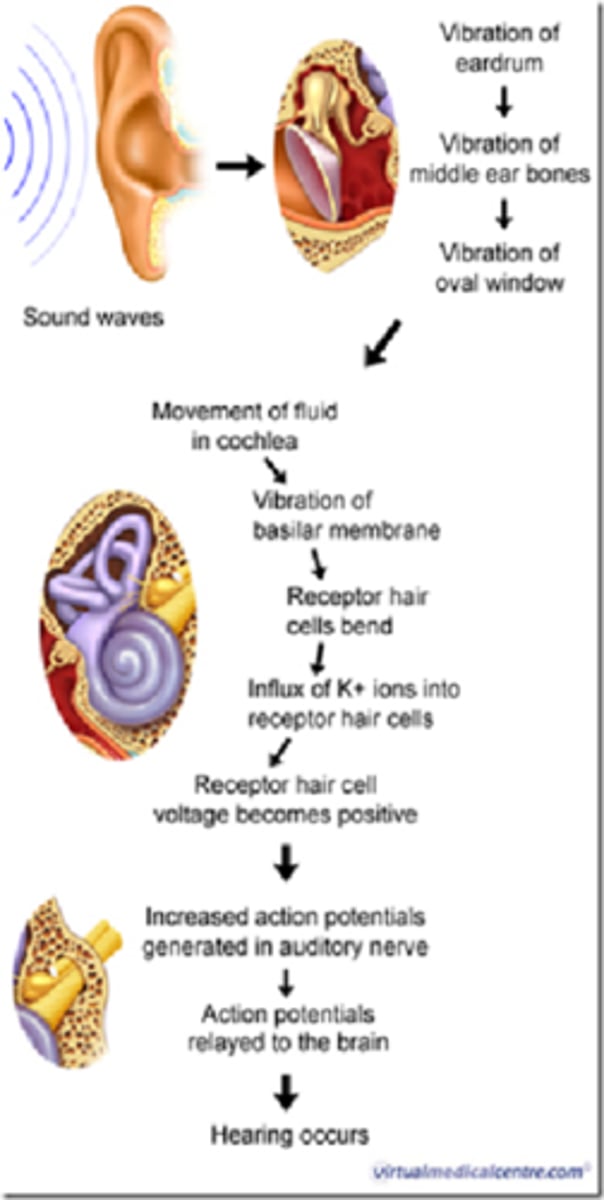
sequence of events for hearing
1. sound waves traveling through air & hit eardrum
2. force of sound hitting eardrum is transferred through bones in middle ear (ossicles: malleus, incus, stapes)
3. last bone (stapes) activates movement of fluid in inner ear
4. fluid stimulates movement of cochlear hair cells
5. hair cells activate neurons & produce an AP
6. AP travels to brain
7. brain interprets sound waves for hearing
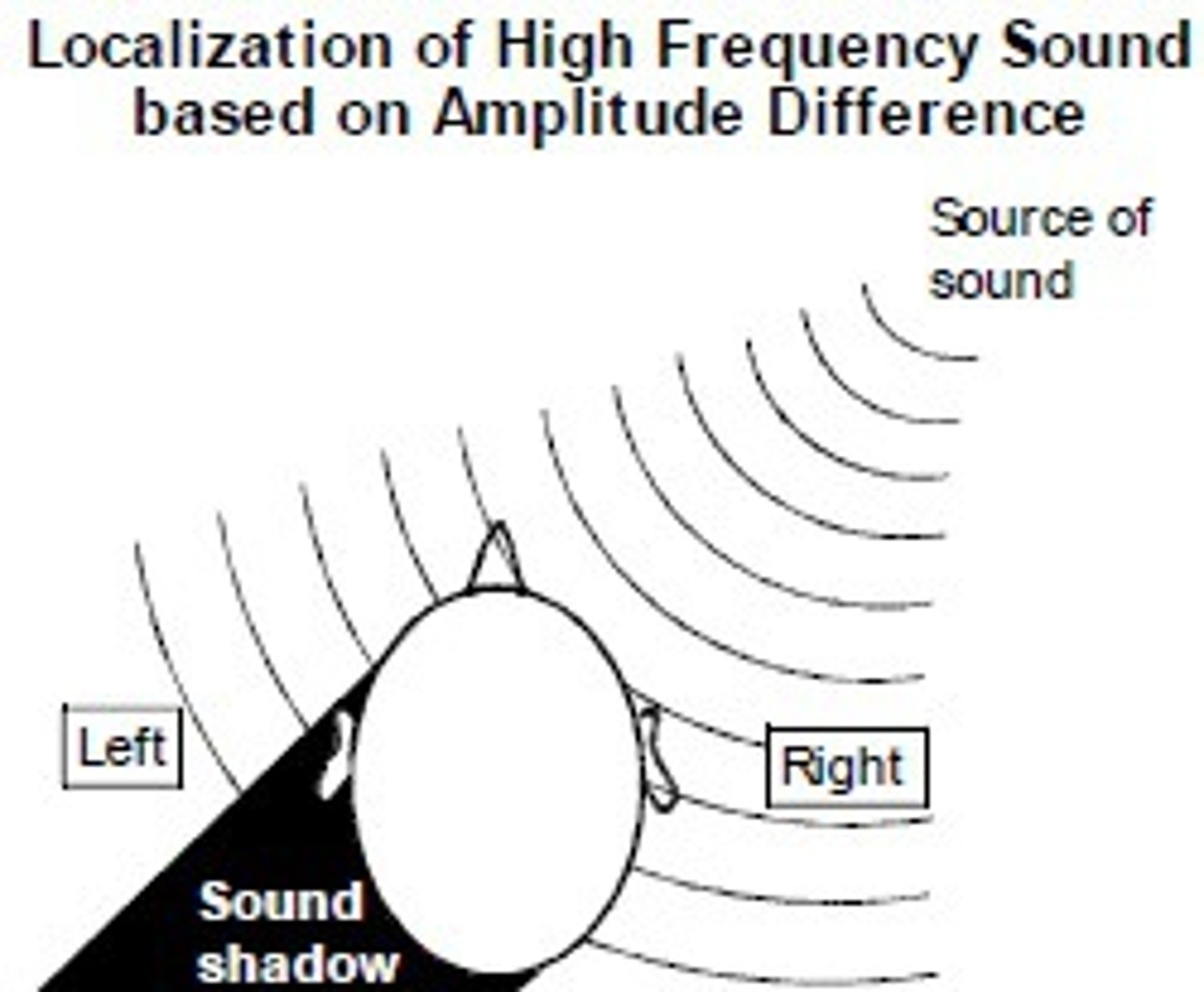
localization of sound
-dependent on relative intensity & timing of sound waves reaching both ears
-loss of hearing in one ear results in a person's inability to localize origin of sounds
motion sickness
-sensory inputs are mismatched (visual input differs from vestibular (equilibrium) input)
-treatment: antimotion drugs (depress vestibular input)