The Endomembrane System (2A)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Endomembrane System Components
ER
Golgi
Vesicles
Cell Membrane
Vacuoles
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
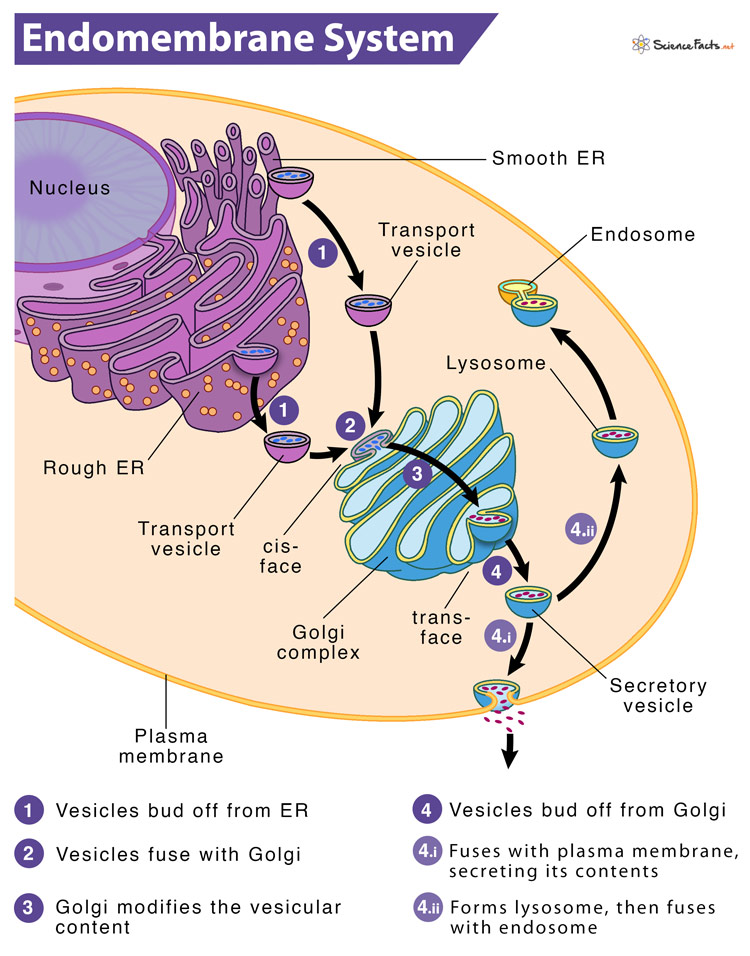
Functions (as a whole)
Synthesizes, distributes, stores, and exports molecules
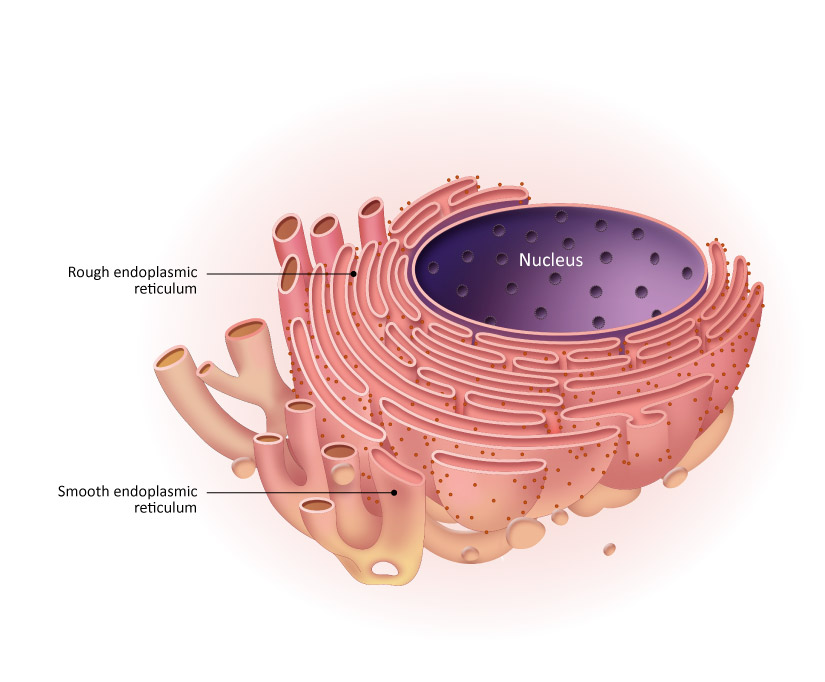
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Structure
Flattened sacs (rough) and tubes (smooth) continuous with the nuclear membrane
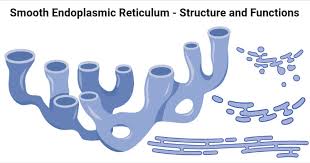
Smooth ER Functions
Produces lipids (phospholipids, cholesterol, and steroid hormones)
Detoxification of alcohol and drugs (especially in liver cells)
Stores calcium ions (especially in muscles cells)
Rough ER Functions (has attached ribosomes)
Produces proteins for secretion
a. helps proteins fold properly
b. initial protein modifications including adding carbohydrate chains and removing some excess amino acids
Produces membrane proteins + phospholipids
Produces enzymes for lysosomes
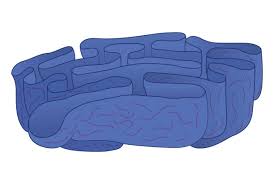
Golgi Apparatus (Golgi Body) Structure
Look like flattened pancakes, layers are not physically connected to each other

Golgi Apparatus Function
Accept proteins from the ER and make final modifications to those proteins. Then ships the proteins to their final destination (usually cell membrane or lysosomes).
Lysosomes
Membrane enclosed sacs
Contain enzymes that were produced by the ER and processed by the Golgi
Maintains an acidic pH
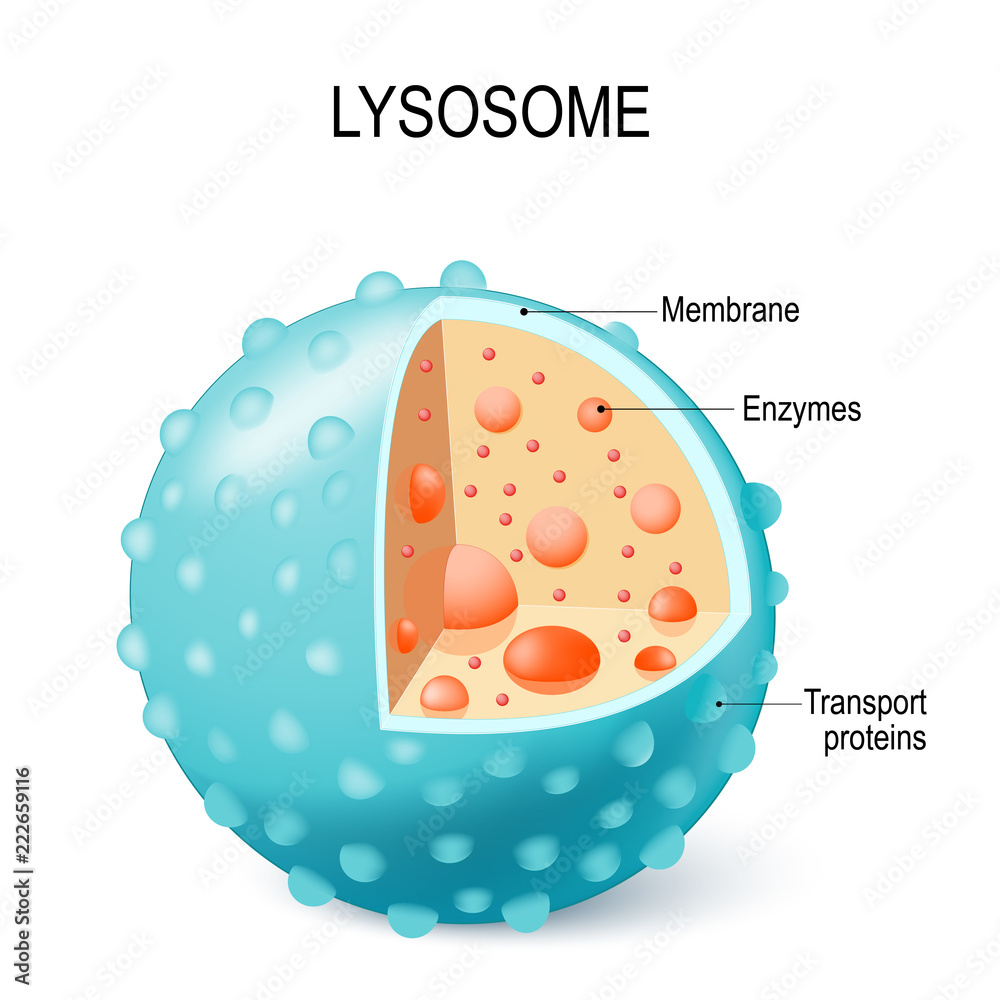
Lysosomes Function
Digestive functions
a. recycle organelles
b. combine w/ food vacuoles to digest the materials inside
Vacuoles
Membrane enclosed sacs
Vacuoles Functions
Storage of resources or cell products
Maintain cell structure
a. large permanent vacuole in plant cells (tonoplast)
b. contractile vacuole - protects some protists from exploding when they take in excess water
Peroxisomes Structure
small membrane-bound sacs (like lysosomes and vesicles)
Peroxisomes Function
metabolize hydrogen peroxide (peroxisomes have catalase)
break down triglycerides
the products of this digestion can be substrates for cellular respiration when carbohydrates are not available