Periodicity
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Periodicity
Repeating trend of physical or chemical properties
Atomic radius increases down a group as:
There is an extra energy levels
More shielding
Attraction to the nucleus decreases
Atomic radius decreases across a period as:
Number of protons increases
Same energy level
Same shielding
Attraction to the nucleus increases
First ionisation energy
The energy required to remove 1 mol of electrons from 1 mol of gaseous atoms
X (g) → X+ (g) + e-
Ionisation energies across Group 2
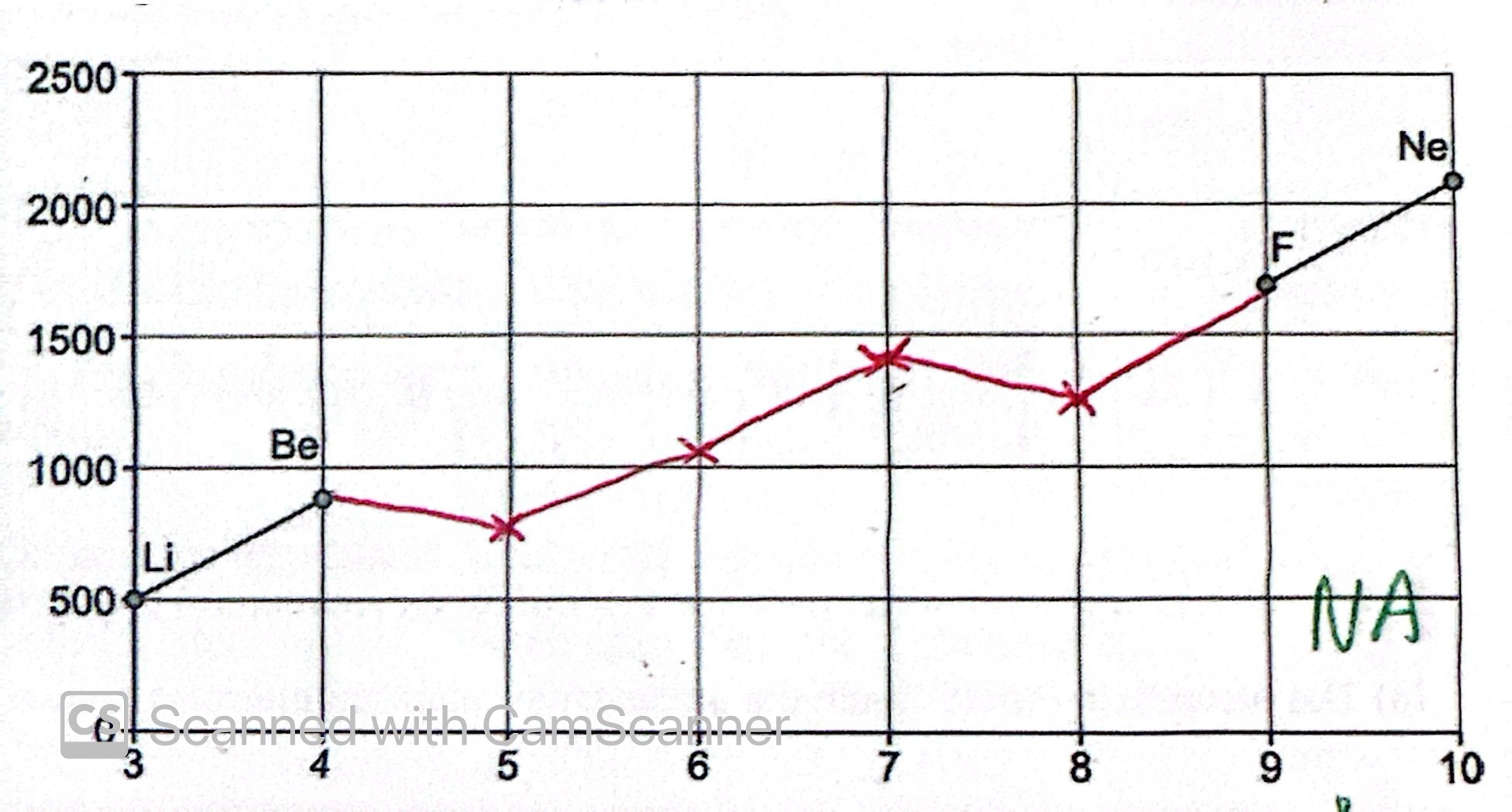
Trends in IE’s down the groups
Extra energy level
More shielding
Attraction to the nucleus decrease
Requires less energy to remove an electron
Trends in IE’s across the periods
Number of protons increase
Same energy level
Same shielding
Attraction to the nucleus increases
Requires more energy to remove electrons
Deviations across the period: Group 3 Al>Mg
Ionisation energy decreases
Electron is removed form the higher energy p sub level
Weaker attraction between the nucleus and outer electron
Deviation across the period: Group 3 S>P
Ionisation energy decreases
Mutual Repulsion
Paired P orbital
Successive ionisation energies will always increase as:
The positive charge on the ion increases
Ionic radius decreases
Nuclear attraction on the outer electron increases
Metallic Bonding
Strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions and a sea of delocalised electrons
Metallic bonding diagram
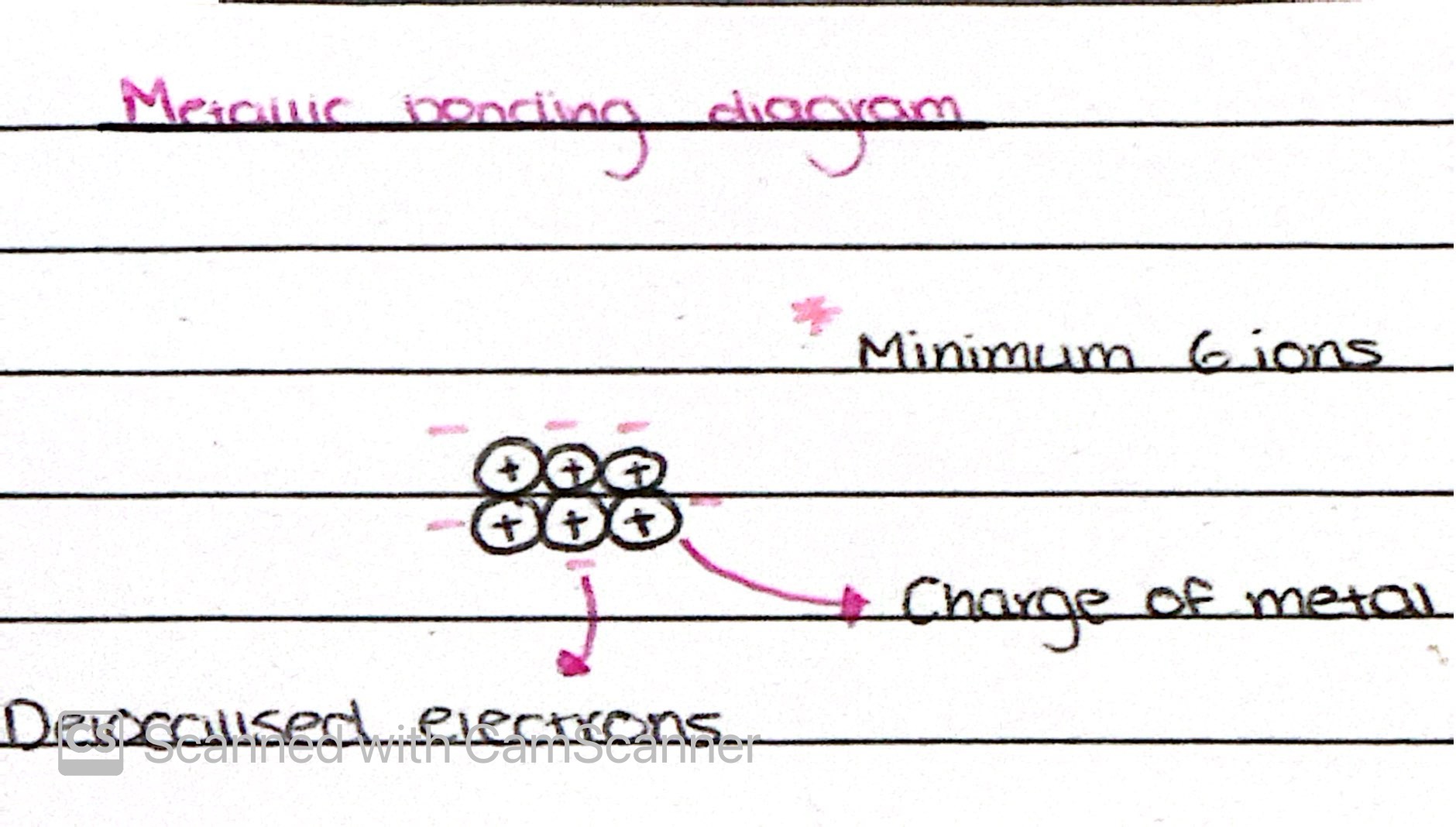
What factors affect the strength of the metallic bond?
Ionic charge of the metal
Smaller atomic radius
Number of delocalised electrons
Properties of metals: Good conductors of heat and electricity
The delocalised electrons are free to move
Properties of metals: High melting and Boiling points
They have a strong electrostatic attraction between positive ions and delocalised electrons
Properties of metals: Malleable and ductile
Layers of ions can slide over each other
Comparing melting and boiling points of substances
Name the structure of the substance
e.g. Giant ionic, Giant metallic, Giant Covalent, Simple molecular
Name the type of bonding within the molecules
e.g. Ionic, metallic, Covalent, IMF’s
Compare melting points - amount of electrons, stronger forces presen