CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 4: Biological Molecules
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
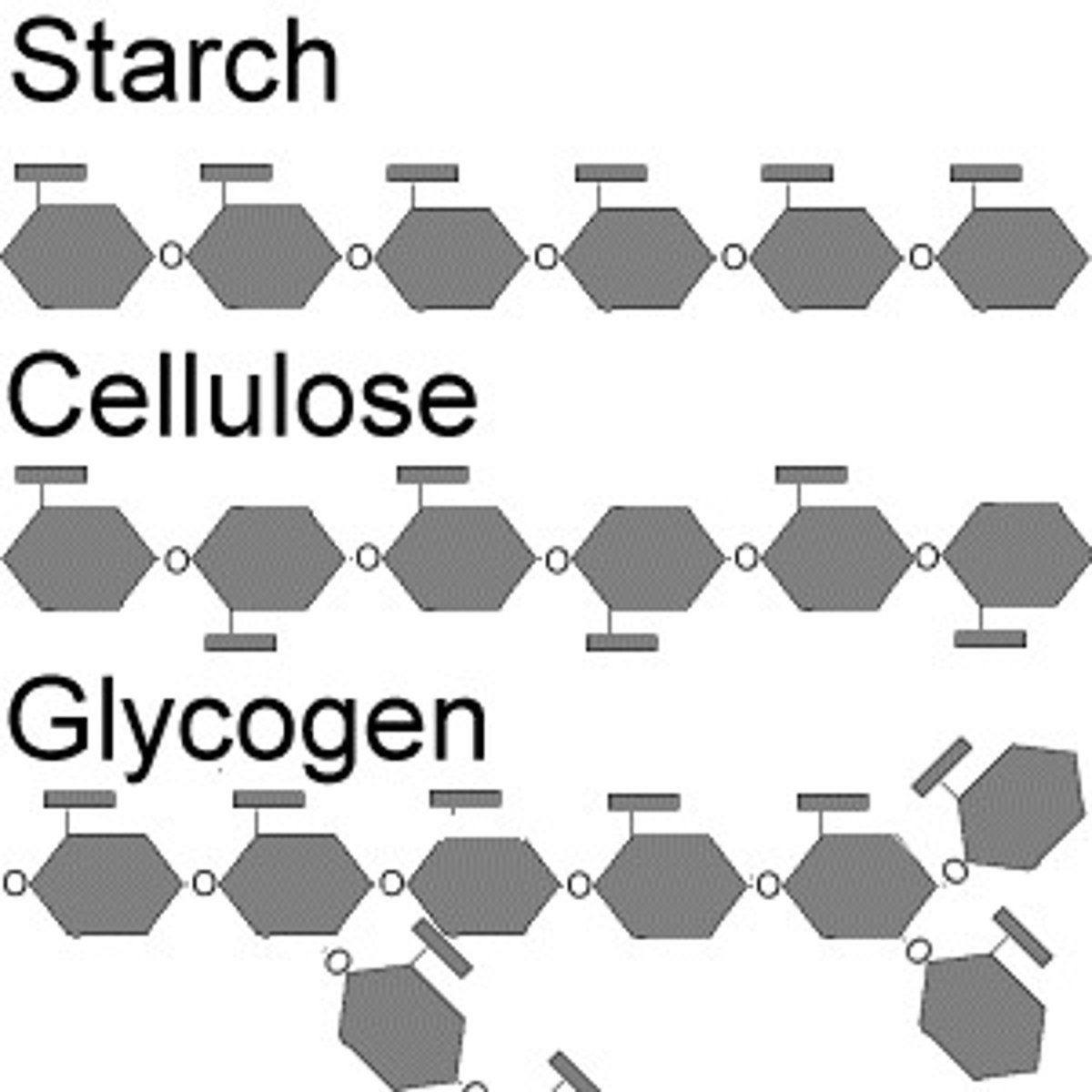
carbohydrates
- Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
- glucose, glycogen, cellulose, starch
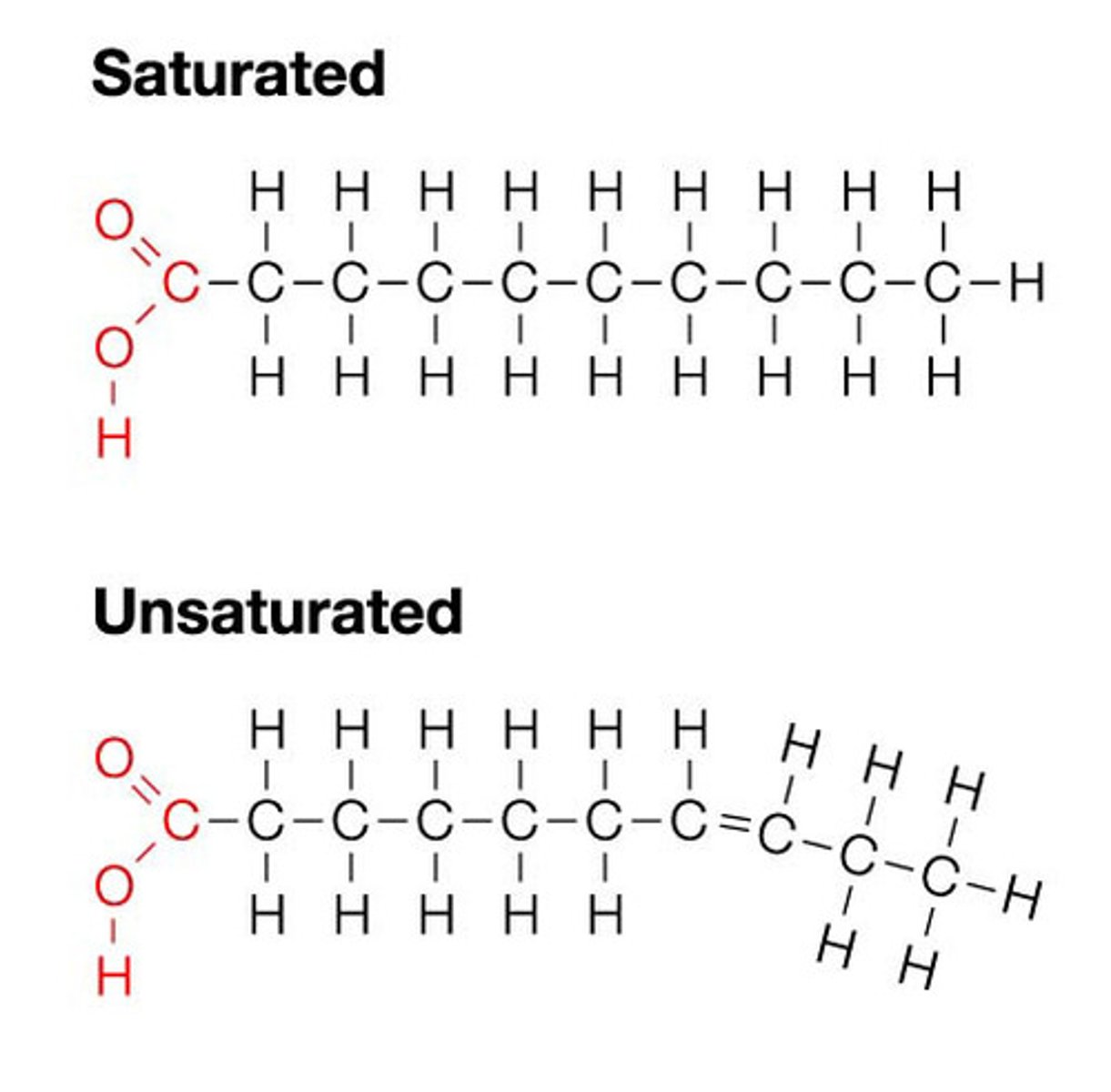
fats
- Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
- fatty acids, glycerol
proteins
- Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
- amino acids
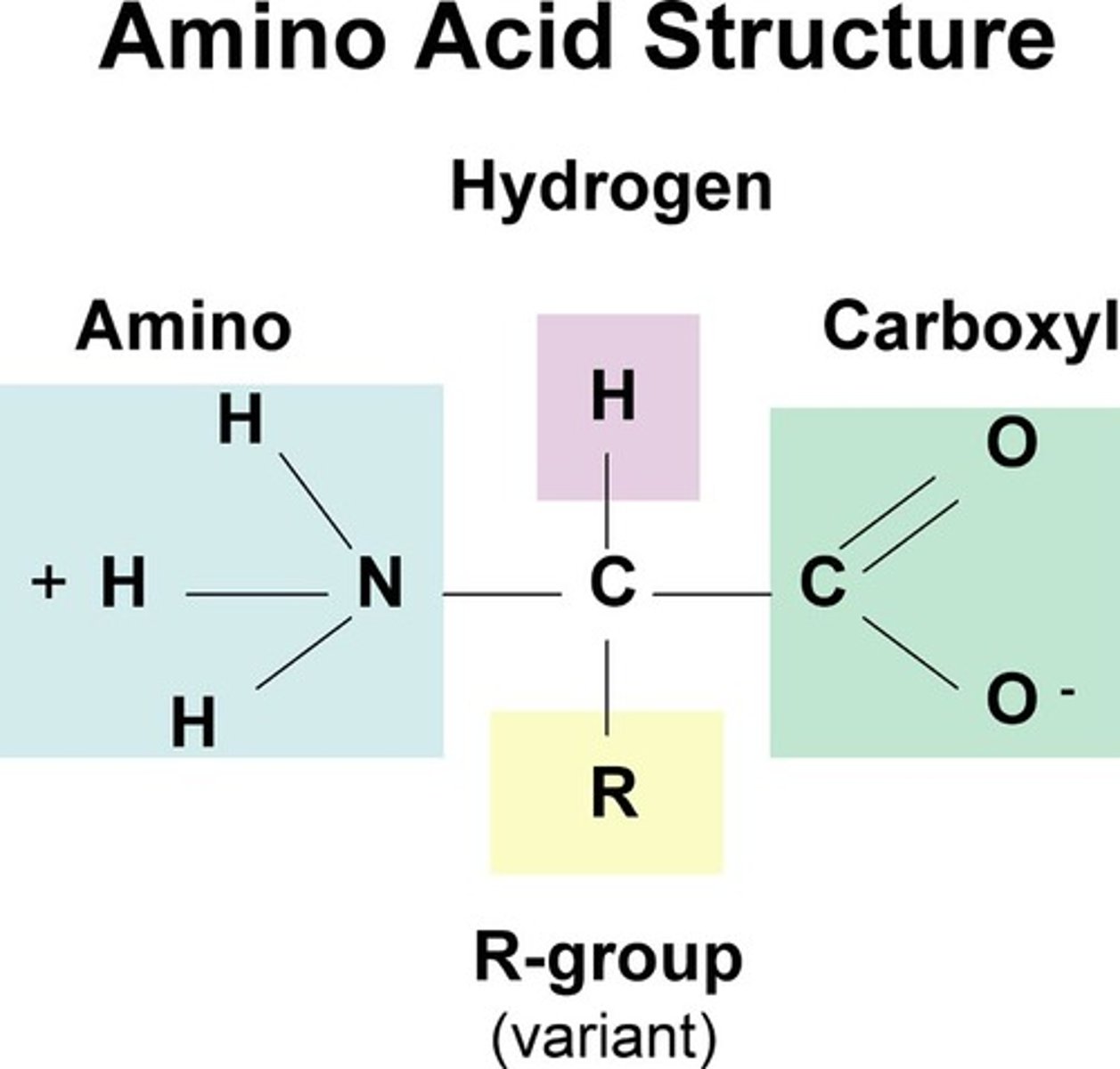
Amino acids
different sequences of amino acids
give different shapes to protein molecules
e.g. active site of enzymes and the binding site of
antibodies
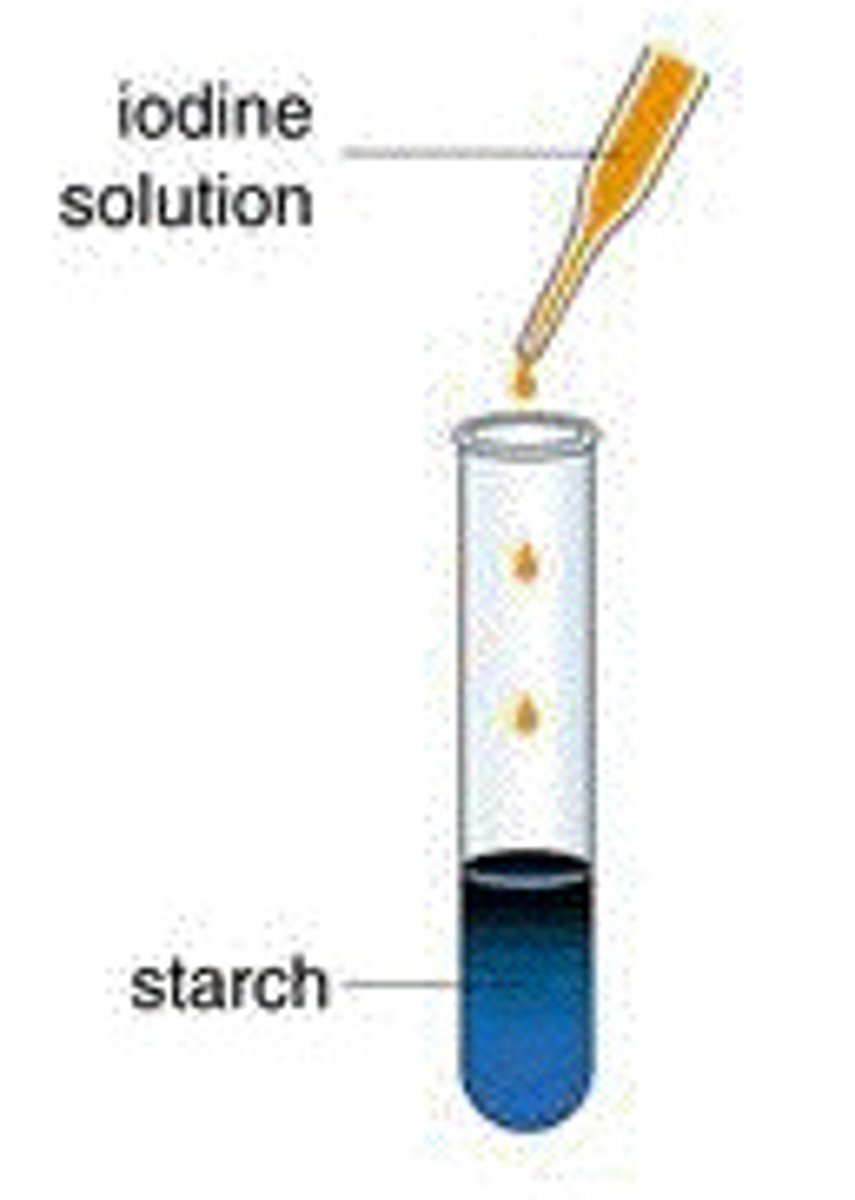
Iodine Test for Starch
Steps:
1. Obtain sample with expected trace of starch
2. Dissolve in solvent eg: ethanol or water
3. Add iodine solution to test for starch
Results: Starch causes iodine solution to turn blue-black
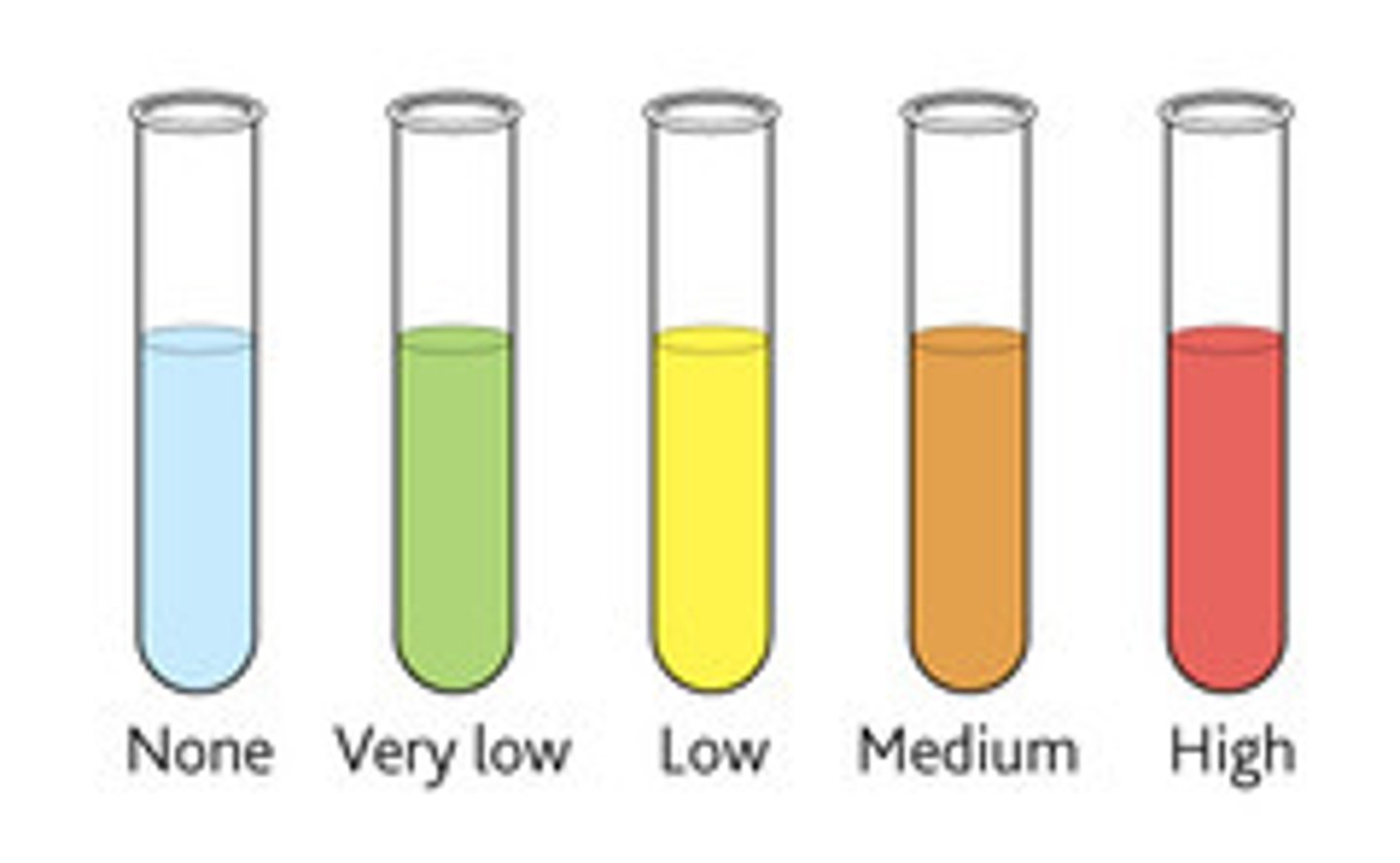
Benedicts's Test for Reducing Sugar
Steps:
1. Place substance into test tube
2. Place test tube into water bath and heat
3. Add in same volume with substance of Benedict's solution into test tube
Results:Presence of reducing sugar causes Benedict's solution to turn from blue to red
- Test for sucrose: as it is not a reducing sugar it gives a negative result, sucrose needs to be broken down into monosacchirides

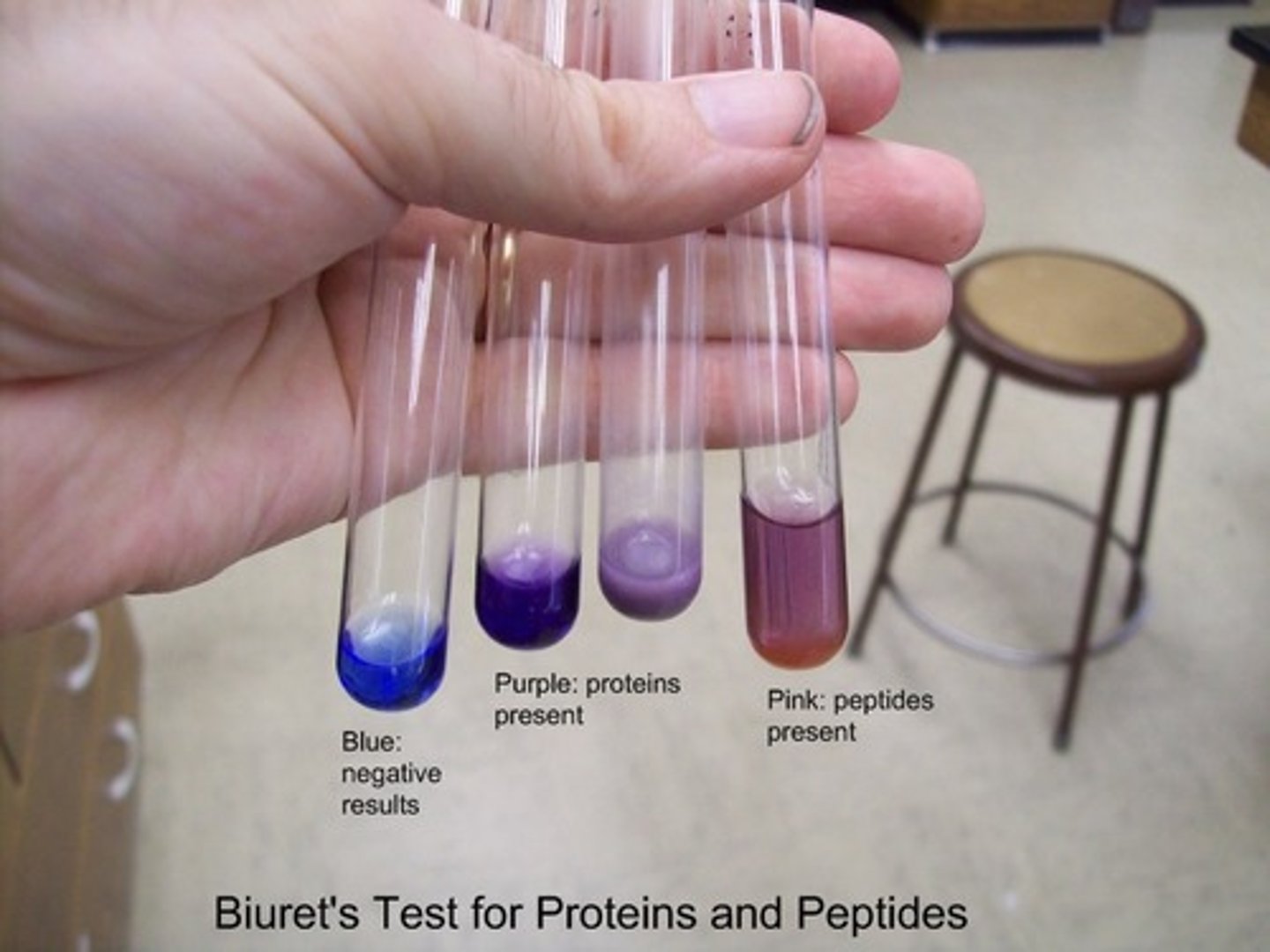
Biuret Test for Proteins
Steps:
1. Fill test tube with extracted to be tested
2. Add biuret solution into test tube
3. Gently shake test tube for faster reaction
Results: Positive results causes biuret solution to turn from blue to purple
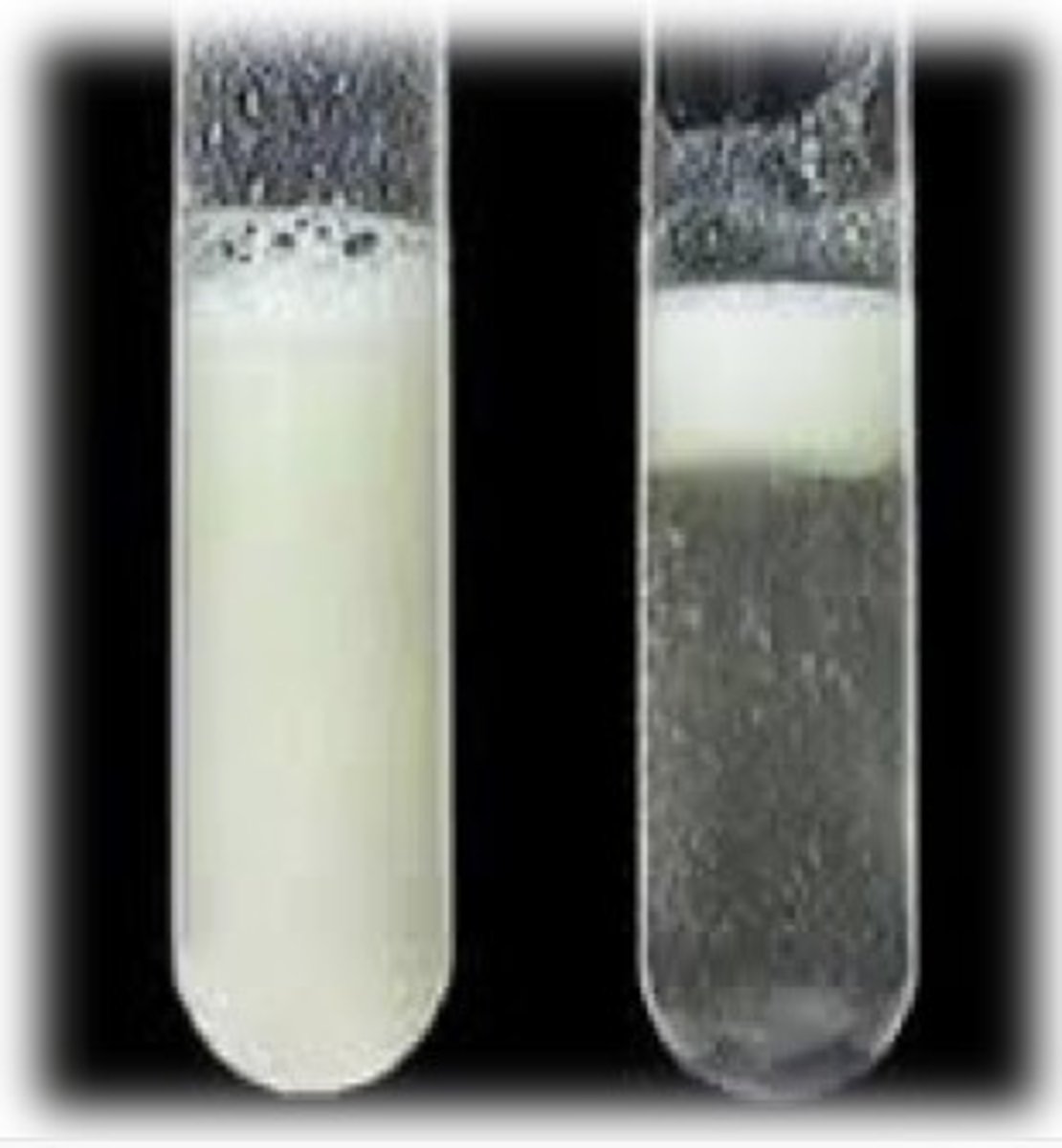
Ethanol emulsion test for fats
Steps:
1. Cut up sample to be tested
2. Add ethanol into test tube with sample
3. Put rubber stopper and shake contents
4. Add distilled water and shake contents again
Results: Positive results shows a suspension of white substance that is the presence of fats
DCPIP test for vitamin C
Steps:
1.Add solution into test tube
2.Drop DCPIP solution drop by drop and shake
3.Record number of drops required for DCPIP to turn colourless until solution doesn't dissolve
Results: presence of vitamin c causes DCPIP solution to turn colourless
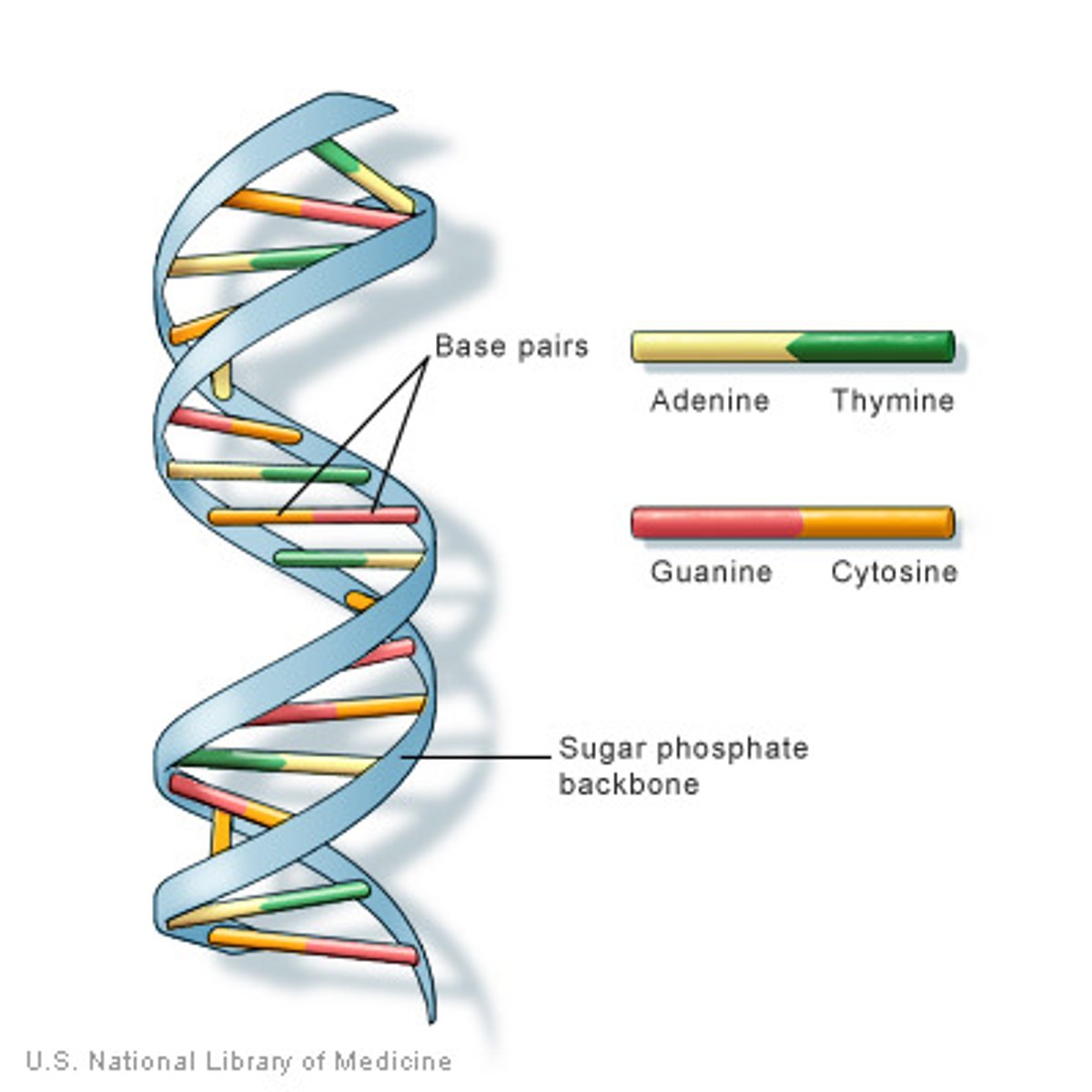
Structure of DNA
- two strands coiled together to form a
double helix
- each strand contains chemicals called
bases
- cross-links between the strands are formed by pairs of bases
- the bases always pair up in the same way:
A with T, and C with G