Photosynthesis and respiration ( module 5)
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Where does photosynthesis occur
Chloroplast
why do plants need energy?
biological processes like photosynthesis, active transport, DNA replication and cell divison
plant would die without these processes
why do organisms need energy
DNA replication, Cell division
organism would die without processes
what are the 2 types of respiration
Anaerobic → Without Oxygen
Aerobic → With Oxygen
what properties make ATP a good energy source ?
Small, soluble molecule → easily transported around the cell
Easily broken down → energy can be released
ATP cant pass out the cell → cell always has a energy supply
where are Photosynthetic pigments located?
Thylakoid membrane
they are attached to a protein this forms a photosystem
Function of photosynthetic pigments
absorb the light energy needed for photosynthesis
Example of Photosynthetic pigments
chlorophyll a
chlorophyll b
carotene
what organism are autotrophs ?
Plants and Cyanobacteria
what type of organisms are plants
photoautotrophs
what does photoautotrophs mean?
use energy from light to form organic molecules
what does autotrophs mean
organisms that can take inorganic molecules and build them up into organic molecules
what organisms are heterotrophs ?
animals and fungi
what does heterotrophs mean
organisms that cant synthesise organic molecules
where do light dependent reactions happen?
Thylakoid membrane due to the photo pigments
where do light interdependent reactions occur?
stroma
what type of membrane is the thylakoid membrane
Phospholipid bilayer which is hydrophobic so ions cant enter
what type of ribosomes do Chloroplast contain
70s
what evidence is there that the chloroplast were once prokaryotic cells
they contain 70s ribosomes
what are the two types of photosystems
PSI
PSII
what do Photosystems have located in there centre
Photopigments
why plant leaves green?
chlorophyll reflects green light
what ions does Chlorophyll A contain
Mg and NO₃⁻ ( nitrate)
what happens if a plant lacks mg or nitrates
reduces the amount of chlorophyll → causes chlorosis → yellow colour → less photosynthesis
method to investigating the pigment in leaves
1)Grind up green leaves with anhydrous sodium sulphate then add drops of propanone
2) Transfer to test tube add petroleum ether, gently shake tube → forms two layers , top layer is the pigment
3) transfer top layer liquid into a second test tube with anhydrous sodium sulphate
4) draw a line with a pencil ( bottom of paper), add spot to the line
5) dry and repeat
what does a absorption spectrum show?
Wavelengths of light absorbed by each pigment
what does a action spectrum show
Overall rate of photosynthesis at each wavelength of light
equipment to produce a action spectrum
O₂ / time taken = rate of photosynthesis
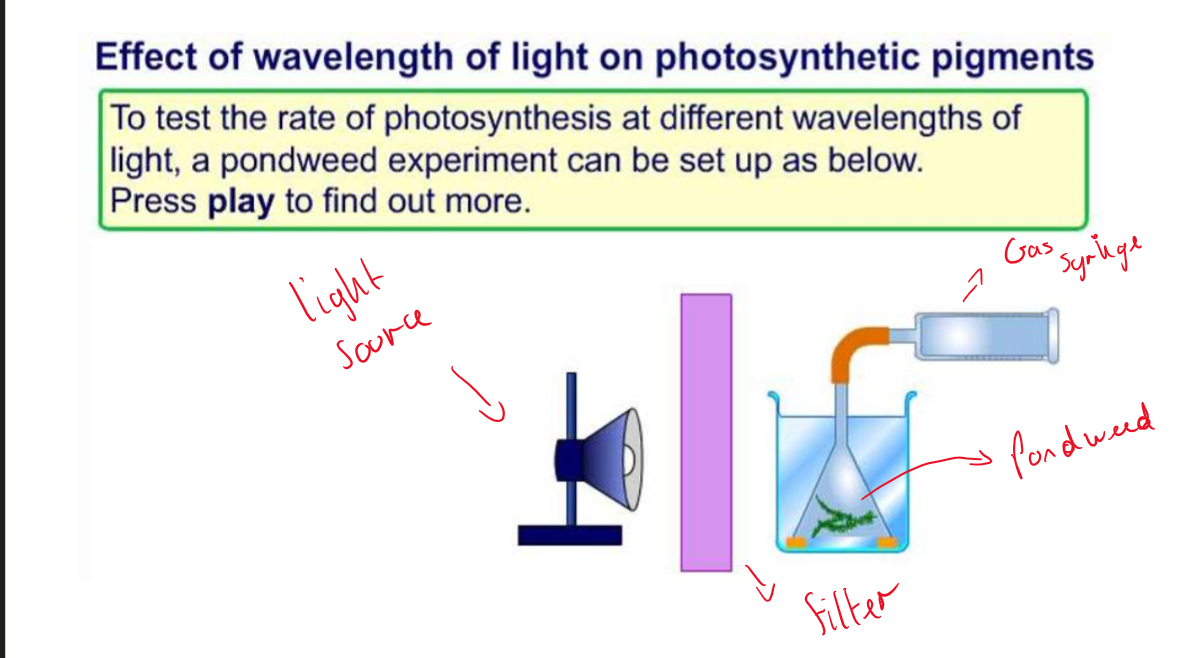
what is the method to producing a absorption spectrum
shine light through a filter
shine through a colorimeter ( set to zero absorbance with distilled water)
measure the absorption
relationship between rates of photosynthesis and absorption of pigments
strong correlation → High rates of absorption = high rates of photosynthesis
differences between PSI and PSII
PSII contains chlorophyll a which absorbs shorter wavelengths of light ( 680 nm)
PSI absorbs longer wavelengths ( 700nm)
Risk assessment for TLC experiment
Chromatography solvent are toxic and highly flammable
Wears goggles
why does the pigment separate during TLC
pigments have different solubilities
state a material that can be used as the stationary phase in TLC
Silica
why should you do step 1 and 2 of TLC quickly or in a fume cupboard
Prevents the solvent from evaporating
structure of thylakoid membrane (image)
adaptations of the Thylakoid membrane
Large Sa : Vol ratio
what are the 2 stages of photosynthesis
The light - dependent reaction
The Light- Independent reaction ( The Calvin cycle)
Oxidation definition
losing e⁻ / loses Hydrogen
Reduction definition
gain e⁻/ gains Hydrogen
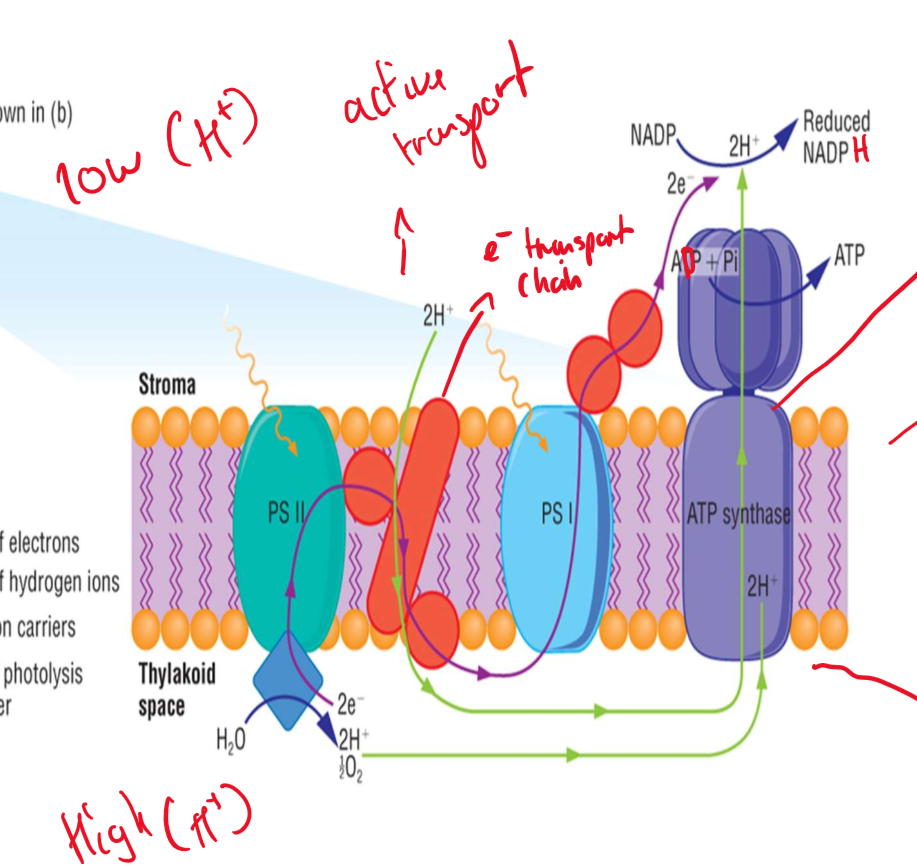
what are the 2 components of the LDP
Cyclic photo phosphorylation ( CPP)
Non cyclic photo phosphorylation ( Non CPP)
differences between CPP and Non CPP
CPP —> e⁻ are recycled, produces only ATP, Only involves PSI
Non CPP —> / involves PSI and PSII, Produces NAPH , ATP and O₂, involves Photolysis
what does the Light- Dependent reaction need?
Light
function of light in LDR
absorbed by the photosynthetic pigment and excites the e⁻
what is the Cyclic photo phosphorylation stage
Light energy excites the chloroplast and causes releases it e⁻
e⁻ flows through electron transport system ( returns to chloroplast) → releases energy
energy causes protons in the stroma to actively move into the compartment ( proton pumps)
creates a proton conc gradient, protons move back into the stroma through protein channels ( facilitated diffusion)
protons flows into ATP synthase causing it to catalyse ADP + Pi ⇌ ATP
what is photolysis
using light energy to split water into Protons , electrons and ½ O₂
In the light dependent reaction what is the light energy absorbed by the photosystems used for
Making ATP from ADP + Pi ( photophosphorylation)
making NADPH from NADP
Photolysis
Cyclic Photophosphorylation ( image)
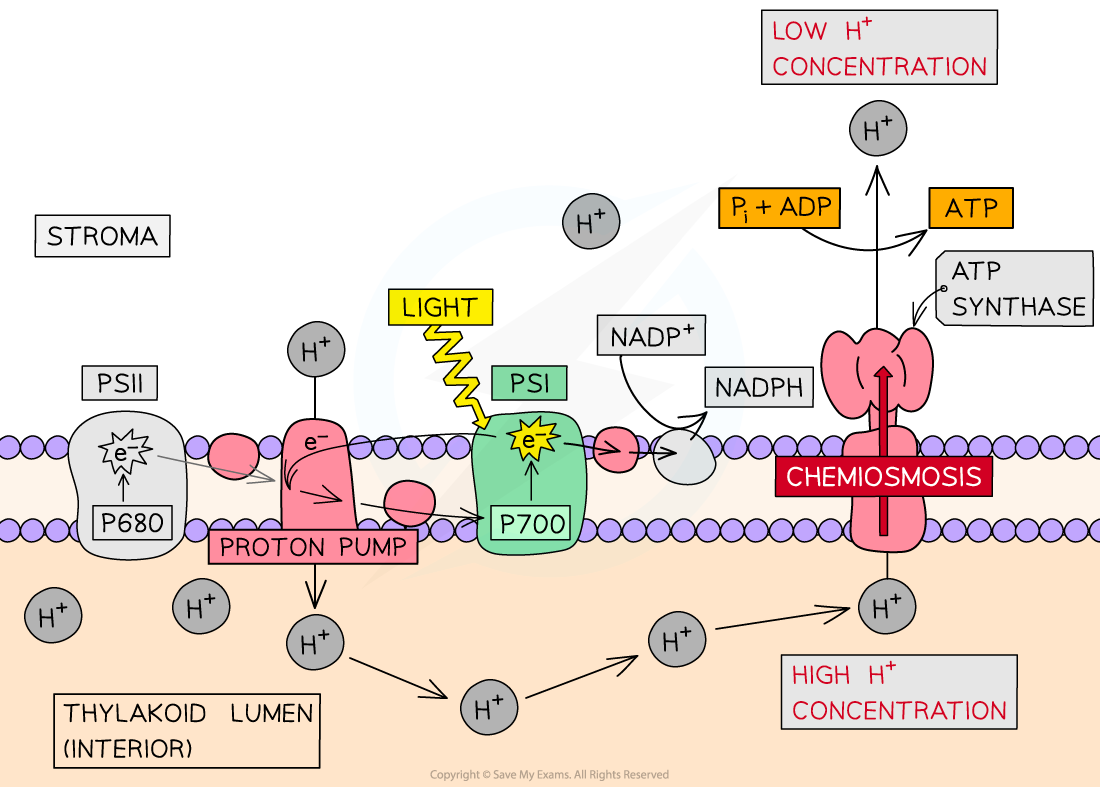
what are electron carriers
proteins that carry electrons
what are electron transport chains
Photosystems and electron carriers form electron transport chains and excited electrons flow through them
what happens during Non cyclic photophosphorylation
Light energy is absorbed by PSII, light energy excites e⁻ in chlorophyll
e⁻ move along the electron transport chain to PSI
in order to replace the e⁻ lost → Photolysis occurs
( CPP happens)
PSI absorbs light energy exciting electrons again
e⁻ react with protons forming hydrogen
NADP gets reduced forming NADPH —> to the LIR
why do electrons move after being excited
Move to a higher energy level
equation for photolysis
H₂O → 2 H⁺ + ½ O₂ + 2 e⁻
what happens to the Oxygen produced in photolysis
diffuses out of the chloroplast and plant through stomata
function of NADP
Hydrogen carrier
Non cyclic photophosphorylation (image)
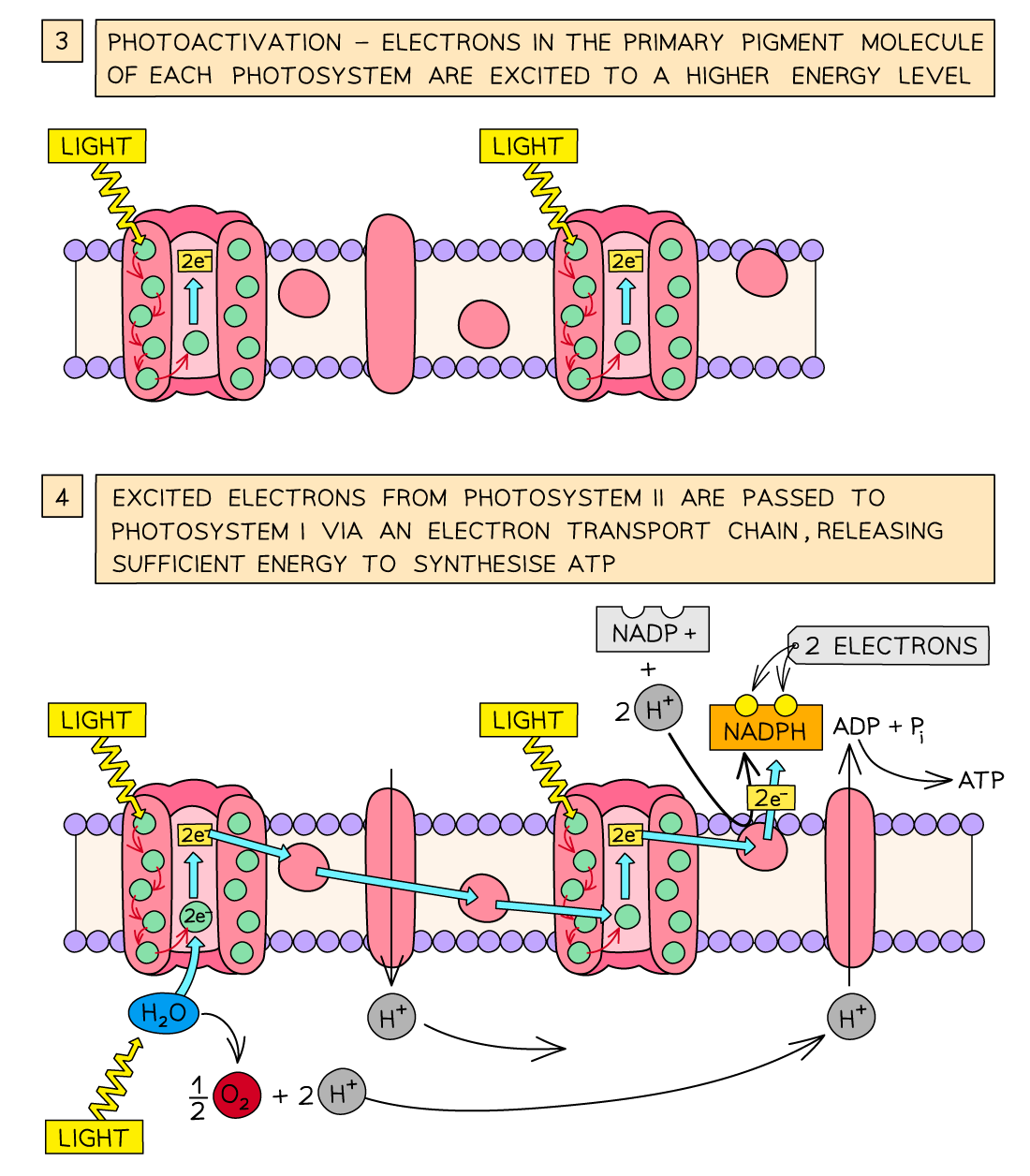
Calvin cycle ( Image)
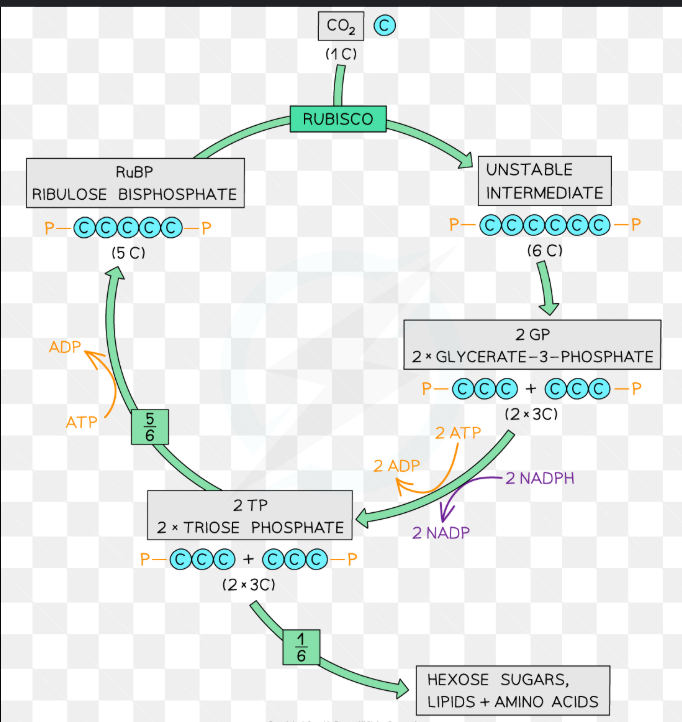
what are the 3 stages of the Calvin cycle
Carbon fixation
Reduction of GP
Regeneration of RuBP
what happens during the Carbon fixation stage ( Calvin cycle)
Rubisco enzyme catalyses CO₂ + RuBP this forms unstable hexose compound.
Hexose compound splits into 2 molecules of Glycerate -3- phosphate ( GP)
why is GP reduced ?
convert it into a carbohydrate
What happens during the Reduction of GP
Energy from ATP and Hydrogen from NADPH ( produced in LDR)
Reduces Glycerate-3- phosphate into 2 molecules triose phosphate
how many molecules of GP and TP are produced in the Calvin cycle
2 molecules
what happens during the regeneration of RuBP
Triose phosphate are actively regenerated into RuBP
what type of sugar is RuBP
pentose sugar
what type of sugar is GP
triose carbon
what type of compound is the unstable compound
Hexose compound
what are some of the TP and GP used to make
carbohydrates - Hexose sugars
amino acids ( GP)
lipids
How did Melvin Calvin discover the Calvin cycle
which stages of the Calvin cycle are Active
Reduction of GP
Regeneration of RuBP
Melvin calvins experiment method
Carbon- 14 isotope to trace carbon
algae was under light to start the light dependent stage of photosynthesis
Melvin Calvin experiment equipment
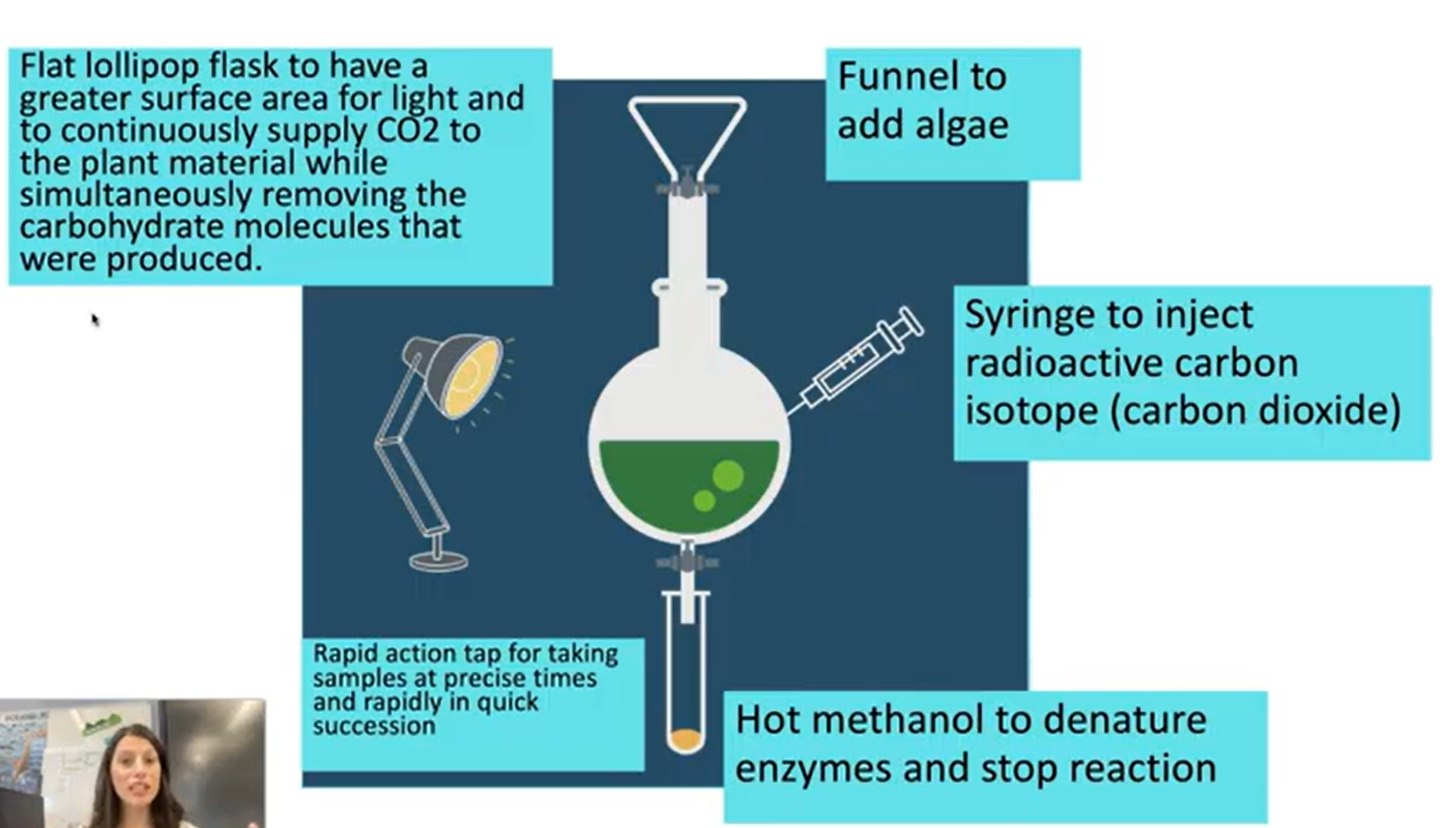
Melvin Calvin experiment why is GP more radioactive then RuBP
GP contains more radioactive carbons then RuBP
2 triose GP > pentose RuBP
why is only one TP molecule produced every 3 turns of the cycle
5 out of 6 TP molecules are used to regenerate RuBP
what are limiting factors
CO₂ concentration
Light intensity
Temperature
what wavelengths of light are used for photosynthesis
Red and blue light in sunlight
what colours are in white light?
All colours
effect of temperature on photosynthesis
High temperature —> enzymes( Rubisco, ATP synthase ) denature
Low temperature —> enzymes are inactive
Damage the thyakoid membrane → reduce number of sites available for electron transfer
effects of CO₂ on photosynthesis
Rate of photosynthesis increases until past 0.004 then stomata start to close decreasing the rate
what happens after light intensity increases past saturation point
another factor becomes the limiting factor so increasing light intensity has no effect
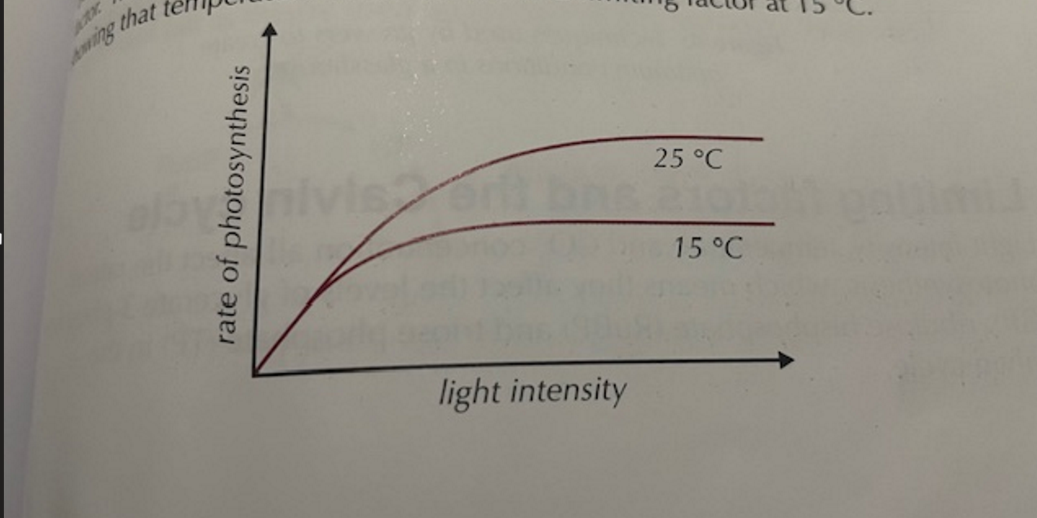
what is the limiting factor of this graph
Temperature is limiting factor as both graphs plateau at same light intensity
25°C levels off at a higher point then 15°C
effect of low light intensity on the Calvin cycle
low light intensity —> less NADPH and ATP ( from LDR)
GP levels increases but TP and RuBP levels decrease
TP and RuBP → GP
effect of High/Low temperatures on Calvin cycle
TP, GP and RuBP levels decrease
high → enzymes denature
low → slower enzyme action
effect of low CO₂
levels of GP and TP decrease
there’s less Carbon fixation
Rubp levels increase ( not being used) then decreases as it’s not being reformed
adaptations of the granum
Large SA:Vol ratio to absorb more light
contains photosystems that contain photopigments in the membrane
Why is using volume of Oxygen produced inaccurate
Oxygen is being used by the plant in respiration
what are some control variables in any experiement that involves leafs
species of leaf
age of leaf
why is the leaf dried thoroughly in TLC
so the liquid doesnt alter the rf value
What is a limiting factor
factor that stops the reaction
TLC what does pigments having same moved distance mean
pigments share a molecule
importance of photosynthetic pigments in photosynthesis
absorb light energy which excites the e⁻
Make ATP and NADPH
Accessory pigments pass energy to primary pigment → oxidises Primary pigment
In LDR