A&P Lab Exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/139
Last updated 12:40 PM on 3/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
1
New cards
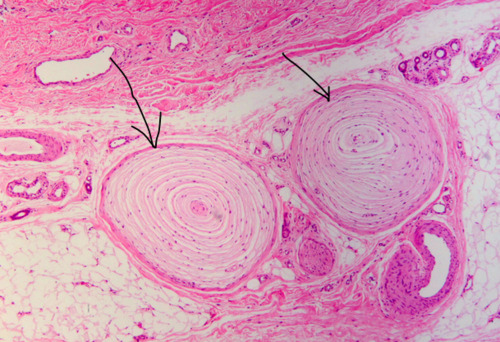
Identify this
Lamellar corpuscles
2
New cards
Identify this
Lamellar corpuscles
3
New cards
Lamellar corpuscle function
deep pressure receptors
4
New cards
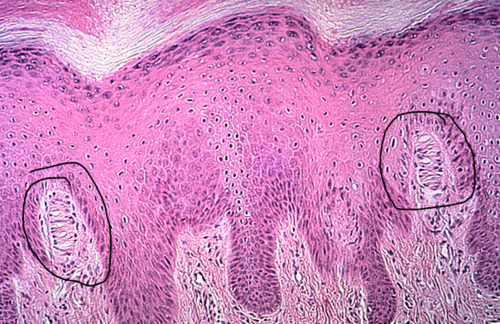
Identify this
Meissner Corpuscle
5
New cards
Identify this
Meissner Corpuscle
6
New cards
Meissner Corpuscle function
Light touch detectors
7
New cards
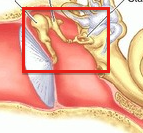
Identify this
Ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes)
8
New cards
Location of the ossicles
Middle ear
9
New cards
Malleus' function and location
Attached to tympanic membrane Articulates with incus
10
New cards
Incus' location and functions
Articulates with the stapes
11
New cards
Stapes' location and functions
Attached to the inner ear on the oval window
12
New cards
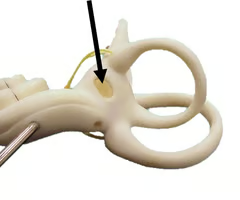
Identify this
Oval window
13
New cards
Oval window function
Where vibrations pass into cochlea into scala vestibuli
14
New cards
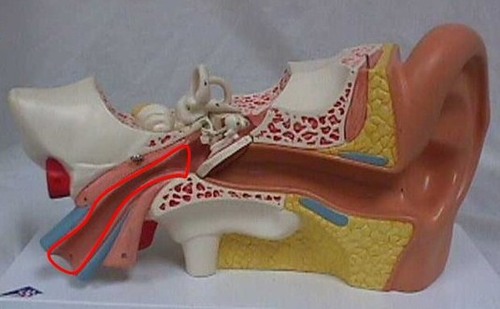
Identify this
Eustachian (pharyngotympanic) tube
15
New cards
Eustachian (pharyngotympanic) tube location
Connects middle ear to the nasopharynx
16
New cards
Eustachian (pharyngotympanic) tube function
Equalizes air pressure across tympanic membrane (eardrum)
17
New cards
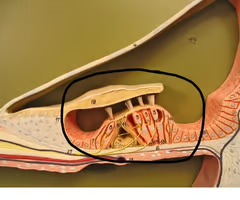
Identify this
Organ of Corti (Spiral organ)
18
New cards
Organ of Corti (Spiral organ) location
Cochlea in the inner ear
19
New cards
Organ of Corti (Spiral organ) function
Converts vibrations in cochlea fluid into an electrical signal
20
New cards
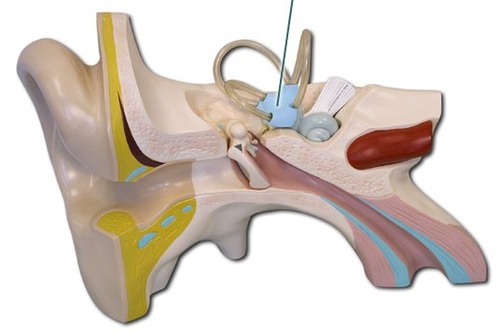
Identify this
Vestibule
21
New cards
Vestibule location
Inner ear
22
New cards
Vestibule function
Has macula that sense head position and rotation
23
New cards
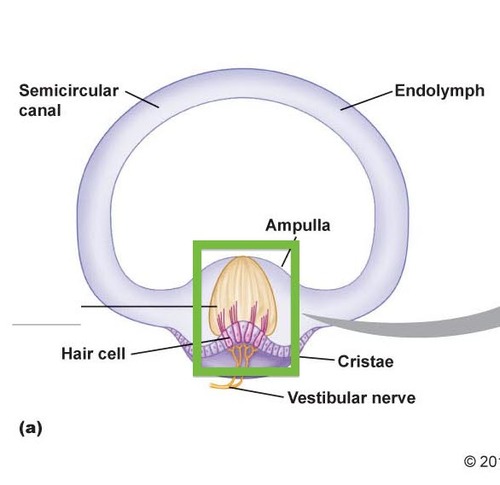
Identify this
Cristae ampullaris
24
New cards
Cristae ampullaris function
senses rotational head movement
25
New cards
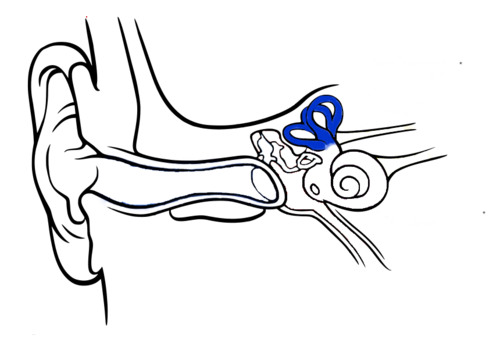
Cristae ampullaris location
base of the semicircular canals
26
New cards
Semicircular canals location
Inner ear
27
New cards
Semicircular canals function
Have equilibrium receptors to monitor dynamic equilibrium
28
New cards
How the semicircular canals work
As 1 canal moves internal fluid moves in the opposite direction causing the crista ampullaris to bend
29
New cards
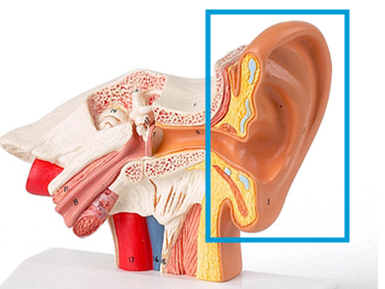
Identify this
Auricle (pinna)
30
New cards
Auricle (pinna) location and function
Outer ear that collects and directs sound waves into the auditory canal
31
New cards
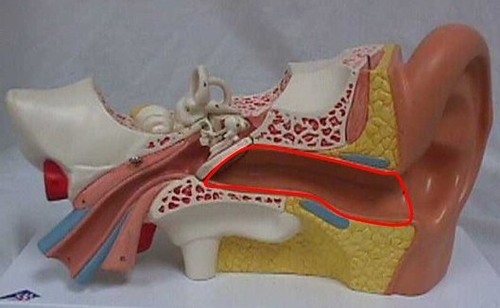
Identify this
Auditory canal (external acoustic meatus)
32
New cards
Auditory canal (external acoustic meatus) function
Transmits sound waves to eardrum (Tympanic membrane)
33
New cards
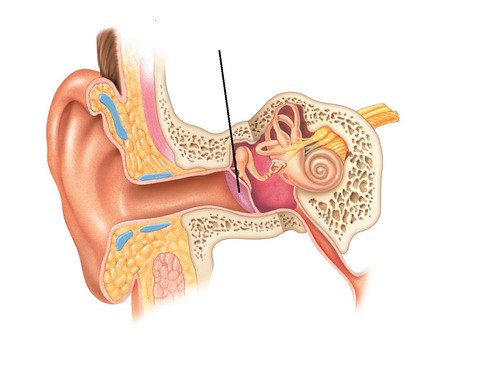
Identify this
Tympanic membrane (ear drum)
34
New cards
Tympanic membrane (ear drum) location and function
End of the auditory canal, vibrates after it is struck by sound waves
35
New cards
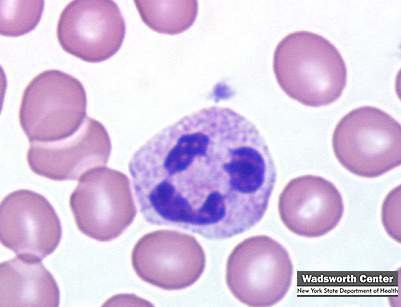
Identify this
Neutrophil
36
New cards
Neutrophil functions
WBC, rapidly responds to the site of infection
37
New cards
Abnormally high amounts of neutrophils indicates
Infection, inflammation, bacteria
38
New cards
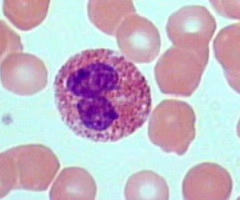
Identify this
Eosinophil
39
New cards
Eosinophil functions
Counteract histamines (inflammatory chemicals)
40
New cards
Abnormally high amounts of Eosinophil indicates
Allergies, parasitic worms, autoimmune disease
41
New cards
Abnormally low amounts of Eosinophil indicates
drug toxicity or stress
42
New cards
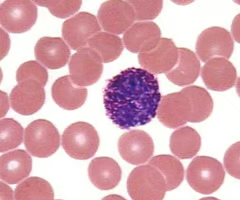
Identify this
Basophil
43
New cards
Basophil functions
Creates histamine which intensifies inflammatory response
44
New cards
Abnormally high amounts of Basophil indicates
Allergies, parasitic infections, hypothyroidism
45
New cards
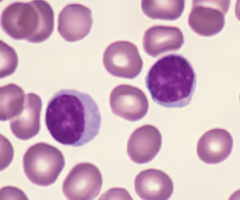
Identify this
Lymphocyte
46
New cards
Lymphocyte functions
Essential for immune response
47
New cards
Types of lymphocytes
Natural Killer cells, B cells, T cells
48
New cards
Natural killer cell functions
recognizes unknown cells and kills them
49
New cards
B cell functions and location of maturation
Make antibodies. Mature in the bone marrow
50
New cards
T cell functions and location of maturation
Defend against specific pathogens, virus, cancer. Mature in the Thymus
51
New cards
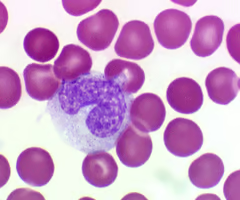
Identify this
Monocyte
52
New cards
Monocyte functions
mature into macrophages
53
New cards
Macrophage functions
* Phagocytize debris, pathogens, and worn out and damaged cells
* Release antimicrobial chemicals that attract other WBCs to site of infection
* Release antimicrobial chemicals that attract other WBCs to site of infection
54
New cards
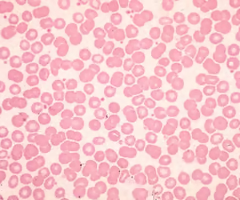
Identify this
Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
55
New cards
Erythrocytes mature in and from
Mature in red bone marrow, Mature from reticulocytes (immature RBC)
56
New cards
Erythrocyte function
Transport oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues
57
New cards
Erythrocytes lack nuclei resulting in
More interior space for hemoglobin molecules that transports oxygen
58
New cards
Erythrocytes lack mitochondria resulting in
Don't utilize the oxygen they transport, so they can deliver it all to tissues
59
New cards
Nucleus are biconcave because
Greater surface area for gas exchange, and can squeeze through capillaries
60
New cards

Identify this, state its function
Lens, allows precise focusing of light on retina
61
New cards
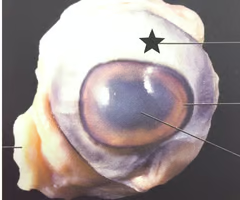
Identify this and state function
Sclera, frotects eye, anchors extrinsic muscles
62
New cards
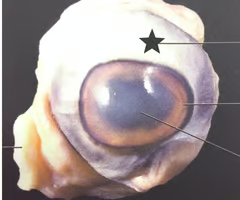
Identify this and states it function
Choroid/Vascular layer, nourishes eye
63
New cards
Identify this and state its function
Retinal and neural layer, absorbs light and prevents its scattering
64
New cards
Pigmented outer layer functions
absorbs light and prevents its scattering
65
New cards
Neural inner layer function
contains photoreceptors
66
New cards
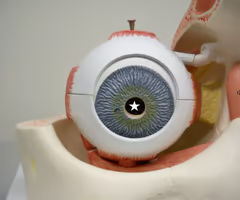
Identify this and state its function
Pupil, regulates amount of light entering the eye by contracting
67
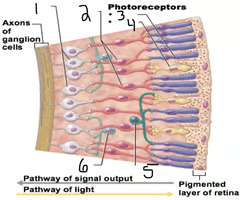
New cards
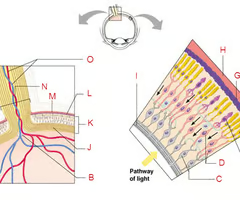
identify D and state its function
Bipolar cells, provide the main pathways from photoreceptors to ganglion cells
68
New cards
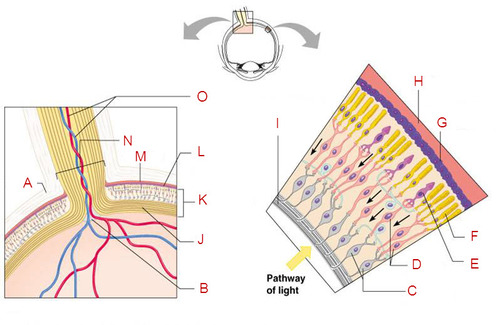
Identify E and F
Photoreceptors (rods and cones)
69
New cards
Rod functions
Respond to dim lights, see black and White
70
New cards
Cones functions
respond to bright light, sees color vision (red, green, blue)
71
New cards
Identify this and state its function
Retina, ganglion cells and the optic disc
72
New cards
Pathway of light
Photoreceptors → bipolar cells → ganglion cells (action potential generated) → the optic nerve
73
New cards
Ganglion cell axon location
Run along the inner surface of the retina, leave the eye as the optic nerve
74
New cards
Site where the optic nerve leaves the eye and lacks photoreceptors (blind spot)
Optic disc
75
New cards
Identify this
Optic nerve
76
New cards
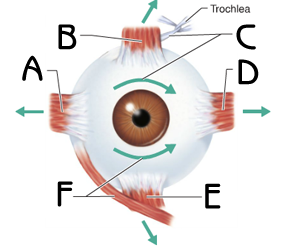
Identify A B D E state the functions
Lateral, medial, superior, inferior rectus muscle. When eye contracts it moves toward contracting muscle
77
New cards
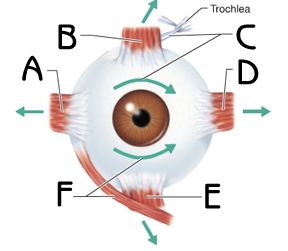
Identify C and F
Superior oblique: rotates down and laterally, \n Inferior oblique: rotates up and laterally
78
New cards
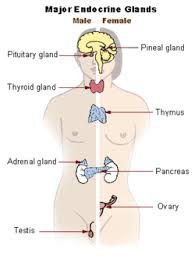
Just look at these
Endocrine organs
79
New cards
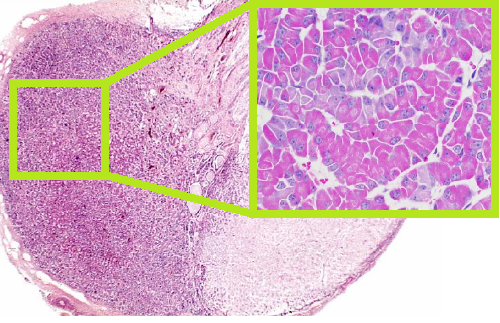
Identify this
Pituitary Gland (divided into anterior and posterior lobe)
80
New cards
Pituitary gland function
Endocrine tissue that releases stimulating hormones (-tropin)
81
New cards
Anterior pituitary gland connects and communicate to the hypothalamus through
Blood and hormones
82
New cards
Posterior pituitary gland connects and communicate to the hypothalamus through
nerves and nerve signals
83
New cards
True or False: posterior pituitary creates hormones
False: stores and releases hormones from Anterior
84
New cards
Hypothalamus releases:Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (TRH)
Pituitary releases :Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
85
New cards
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) target organ
Thyroid
86
New cards
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) effect
Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4), Calcitonin
87
New cards
Triiodothyronine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4) function
* Metabolism, development, and Catecholamine (neurotransmitter) release
88
New cards
Calcitonin function
decreases the amount of calcium in the bloodstream
89
New cards
Pituitary releases:AdrenoCorticoTropic Hormone (ACTH)
Hypothalamus releases:Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH)
90
New cards
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) target organ
Adrenal gland
91
New cards
Cortex is \____ and medulla is \___
outside, inside
92
New cards
Cortex releases
aldosterone, cortisol, androgen
93
New cards
Cortisol function
* Increases blood glucose, Suppresses immune system, Suppresses immune system, Stimulates fight or flight response
94
New cards
Aldosterone function
Increases reabsorption of salt (from kidneys), maintains hydration
95
New cards
Aldosterone chain reaction
More sodium \= more water \= higher blood volume \= higher blood pressure
96
New cards
Androgens are ?
male sex hormones
97
New cards
medulla releases
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) and adrenaline (Epinephrine)
98
New cards
epinephrine and norepinephrine
fight-or-flight responses, wakefulness, alertness
99
New cards
Pancreas releases
Insulin and glucagon
100
New cards
Insulin
lowers blood glucose when high