Social Cognition (Final)
1/190
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
The Basic principle of is that the perception and memory of facial expression depend on the interpretative context
a.) Stroop effect
b.) Locke effect
c.) Libet effect
d.) Kuleshov effect
e.) Mere Exposure effect
d
Festinger’s social comparision teheory posits that:
a.) Individuals are more likely to engage in social comaprision to assess their attributes when objective standards are not present
b.) Social comparision usually creates close friendships because we assess others based on our similarities
c.) Objective standards and measures never matter for social evaluations
d.) When we want to get accurate information about an attribute, we only make downward social comparisions
e.) When we want to get accurate information about an attribute, we only make upward comparisions
a
Which of the following characterizes the independent self?
a.) Importance of harmony
b.) Importance of self-asssertion
c.) Importance of fitting in with others
d.) Prevalence in Asian societies
e.) Sensitivity to situatuinal context
b
Modern embodiement theories, like the one discussed in class, assume the following about mental processing:
a.) All mental processes use abstract, amodal, language-like symbols
b.) Cognition and emotion involve the body and its representation in the brain
c.) Perception, cognition, body responses, and action reside in separate brain modules
d.) Peripheral feedback from muscles and body has no influence on thinking and feeling
b
In the study by Bredl et al. (2001) where they asked people’s preferences regarding flowers or insects, what is one of the results?
a.) People preferred flowers over insects
b.) People preferred insects over flowers
c.) People preferred the non-word over flowers and insects
d.) People did not care about any category
c
In the study (Niedenthal & Setterlund, 1994), which examins how emotions influence perception, participants were asked to preform lexical decal decision task (word/non-word classification). What is true based on the results we learned in class?
a.) Participants who listened to sad music responded slower to the word “WEEP” and faster to unrelated words like “INJURY”
b.) Participants who listened to happy music were slower at classfying both related words (LAUGH) and unrelated words (INJURY)
c.) Participants who listened to sad music responded faster to related words like “WEEP” but not to unrelated words like “INJURY”
d.) Participants who listened to happy music preformed better on all the lexical decision tasks
c
What is FALSE about the universality of emotion expression and perception:
a.) Humans across cultures produce similar expressions for similarly valenced emotions
b.) Emotional expressions are the same across humans and animals
c.) People who cannot perceive emotional expressions can still produce emotional expressions
d.) Both facial expressions and corresponding sounds are perceived similarly across cultures
b
When studying emotions in animals, what is one method researchers do not use?
a.) Physiological responses
b.) Behavior
c.) Subjective Feelings
d.) Motivation
e.) Environmental Cues
c
In the study on rational imitation (Gergely et al, 2002), the infant watches a demonstrator turn on the light with their head. What are the main findings from this study?
a.) Infants imitate only the action itself, as shown by the fact that when the demonstrator’s hands are both free and occupied, the infants use their head to turn the light on
b.) Infants don’t just imitate the action, but also imitate the goal of the action, as shown by the fact that when the demonstrator’s hands are free, infants use their head to turn the light on
c.) Infants struggle with imitation, for instance, when the demonstrator’s hands are occupied, the infant observes the demonstrator using their head but then uses their hands to turn on the light
d.) The study did not yield conclusive results on imitation in infants
b
Timmy’s parents send Timmy to after school self-esteem classes in order to improve his grades. What would you, an expert social psychologist, say to his parents about the relationship between self-esteem and academic achievement?
a.) Self-esteem is weakly correlated with academic preformance
b.) Self-esteem is a strong predictor of academic achievement
c.) Achievement promotes self-esteem and not the other way around
d.) A and C
d
Festinger & Carlsmith (1963) conducted a study in which participants had to turn a peg 25 degrees, were paid $1 or $20, and were then asked to persuade others to do the task. How can we interpret their result?
a.) The dissonance-reducted explanation
b.) The forced-choice paradigm
c.) The self-perception interpretation
d.) A + B
e.) B +C
f.) A + C
f
Evaluative judgement
preferences
True or false
Judgements/Evaluations are based on objective and universal features
true
Objective and universal features
computer based programs
computer aesthetics
“beauty recipe”
“trust recipe”
“any judgment recipe”
Subjective route to evaluations (Subjective Experiences)
experimental
NON-analytic input
Fluency
mental effort
Physical Effort
Peripheral Cues
True or false
Subjective experiences have analytic input
false
Hedonic Fluency Theory
“why it feels good”
the ease (efficiency) we can process fluency the more it shapes our judgements
Google definition (FOR CLARITY)
“more fluently processed stimuli are rated more affectively positive than less fluently processed stimuli”
Why fluency feels good
The easier it is to do these things, the more it “feels good”
processing meets perceiver’s goals
processing is coherent
processing is inexpensive
Heuristic cue to value
Why fluency feels good (processing meets perceiver’s goals)
Cognitive goal
build better model of the world
Low prediction error
model improvement
Practical goal
recognize, understand, move on to next thing
Why fluency feels good (processing is coherent)
no internal conflict
“good structure”
Why fluency feels good (processing is inexpensive)
Efficient coding
low cost in energy, time, resources
resource rationality
Why fluency feels good (Heuristic cue to value)
Stimulus is familiar (common)
“probably safer”
Stimulus is symmetrical
“probably not diseased”
Stimulus is typical
“not a maladapted deviant”
Variables that enchance fluency, liking
Repetition
exposure, familiarity
Priming, compatibility
Readability, pronounceability, rhyme
Clarity, contrast, duration
Symmetry
Prototypicality
Beauty in averageness
“Beauty in averageness” effect
faces look better as they approach the grand average of the whole population
Phototype preference effect
people also like prototypes of a given local population
which can change via learning
True or false
Fluency does not explain attractiveness of prototypes
false
“Ugliness in averageness” effect
True or false
Beauty in averageness effect can turn into ugliness in averageness or dislike the middle effect
true
Attractiveness of prototypes Study (winkielman)
Dog fluency
Methods
measured distance from prototype
how different the dog look from “normal dog”
measured fluency
Results
CLOSER distance to prototype = MORE attractiveness
HIGHER distance to prototype = HARDER for fluency
Most typical dogs = most attractive
cause they’re EASIER to process
“beauty in averageness”
Global averageness,local protoypes Study (LaM)
fluency AND features
Methods
sequential/ simultaneous line up
some were shown more than others
Results
like global averageness
due to fluency
What explains face attractiveness
fluency (familiarity, cognitive)
objective measured features
demographics (sex, race…)
Ugly morphs, bad blends
Learning changes familarity, fluency
Categorization changes fluency
Attention changes fluency
Blends based on familiarity Study
Methods
showed participants
blends (person A and B)
person A
person B
Results
average female face blend rated HIGHEST
beauty in averageness
blends of president bush,obama rated LOWEST
ugliness in averageness
True or false
A blend is liked when it is hard (disfluent) to assign to a category
false
True or false
A blend is disliked when it is difficult (disfluent) to assign to a category
true
True or false
Fluency depends on the availability of categories in the current task
true
Androgynous face effect Study (Owen)
“Johnny Depp”
Methods
masculine/ feminine faces
two conditions
no categorization
gender categorization
rate attractiveness
Results
female OVERALL MOST attractive
no category condition
girl men attractive
categorized
mainly men more attractive
similar results with cross race individuals
from similar study
True or false
fluency is not flexible
false
What does fluency depends on
How percisely we know the object features
what categories are available for classification
what features (slectively) attended)
True or false
Fluency is determined by multiple atttentional, perceptual, and cognitive factors. Consequently, it’s effect on hedonic/evaluative judements is nuanced
true
Concept of the self (socrates)
to understand the world, we need to know ourselves first
Concept of the self (aristotle)
I count him braver who overcomes his desires than him who conqures his enemies; for the hardest victory is over self
Concept of the self (be true to your moral self)
Hamlet
Polonius
Laertes
Concept of the self (early 20th centrury views)
dignity
self respect
inner worth
meaning in life
…
Concept of the self (mid to late 20th century view)
Find yourself and actualize yourself
“create yourself”
Basic Duality of the self (self awareness)
act of thinking about ourselves
The knower
acting subject, “I”
What is this an example of:
Listen to your current stream of thoughts
self awareness
Basic Duality of the self (self concept)
our knowledge of who we are
The known
passive object, “Me”
What is this an example of:
Beliefs about your body, name, gender, age, body characteristic traits etc
self concept
Self reference paradigm
traits adjectives judges one of three ways
self
“does that trait describe you?”
private knowledge
other
“does that trait describe a famous person?”
conceptual knowledge
case
“is the trait presented in uppercase letters?”
processing of trait
linguistic knowledge
Self reference paradigm (Study)
f
Methods
self reference paraigm
Levels of processing
shallow encoding
traits judges on APPEARANCE
deep encoding
traits judged against REFERNT
Results
self adjative recalled at HIGHEST rates
self reference effect
Brain and Self
different processing effects in different brain regions
signal change as they process words
no difference between self, other in region associated with level of processing effect
Brain and Self (left interior prefrontal)
activation area
Brain and Self (Medial prefrontal cortex)
deactivation area
activity related to self knowledge often found here
HIGHER activity= no deactivation
“self referential processing is linked to a specific brain region”
Alzhimer’s study (Kein)
“I” and “Me” are still there
Method
case study
asked various questions and tests
Results
doesn’t know world but knows self
impaired world knowledge
name simple objects
lemon sour?
draw clock
intact self knowledge
described you?
intact subjectivity
Likes/dislikes, preferences, choices, opinions, will
Mark and Mirror studies (Gullup)
Emergence of self concept
Methods
place mirror in front of anima
wants to see if they understand self
Results
apes
SURPRISED by change in their own appearance in mirror
moneys and dogs
NOT surprised
Rouge Test (Lewis)
emergence of self concept
Methods
red dot on mirror
wanted to see if they would put their nose on it
Results
this tests self recognition
develops around 2 yrs old in kids
Argument for this
is it self recognition OR they just notice change
Who are you studies (Motemayour)
Development of self concept
Methods
asked quesition to both kids and young adults age
Results
younger
self concept comes from CONCRETE, focused OBSERVABLE characteristics
older
self concept comes from ABSTRACT, focused on PSYCHOLOGICAL characteristics
Ybarra Study 1 (older self as unpredictable)
competition/cooperation (moth)
Methods
Read about competition/cooperation
imagine playing
wall street
community game
draw a flight path of a moth
Results
moth trajectories are MORE complex in COMPETITIVE condition
Ybarra Study 2 (older self as unpredictable)
partner/opponent
Methods
meet potential partner/opponent
fill out unpredictability scale
Results
GREATER unpredictability in COMPETITIVE condition
Social Comparision Theory (Leon Festinger)
we compare ourselves with other people as a source of info when judging attributes about the self
more likely to happen when there is NO objective info
if similar = more compassion
upward comparison
BETTER than me
downward comparison
WORSE than me
Morse & Gergen study
Mr. Clean vs Mr. Dirty
Methods
males fill applied for job
fill out self esteem scale
meet
Mr Clean
smart suit
science books)
Mr. Dirty
cheap clothes
cheap sex novel
fill out self esteem scale
Results
Mr clean condition
self esteem DECREASES
Mr dirty condition
self esteem INCREASES
Social comparision and Loneliness
Arnold et al (2021) Study
momentary feeling of loneliness, more enduring trait judgements
depend on TEMPORAL(my past vs present), SOCAIL(other people) comparisons
Internal States
preferences
beliefs
moods
emotions
Claim to internal states
we DONT know internal states
infer from own behavior, situational cues
True or false
Psychology should rely on introspecton
false
True or false
We know our own internal states
false
Festinger & Carlsmith
insufficient justification paradigm
Methods
do boring task
paid $1/$20
asked to persuade others to do it as well
Results
paid MORE
find task MORE AVERSIVE
LESS likely
to do it again
to persuade other
paid LESS
finds task MORE pleasant
MORE likely
do it again
persuade others
Dissonance reduction explanation (interpretation of insufficient justification paradigm)
discrepancy between attitude, behavior induces unpleasant internal tension
change preference to reduce internal tension
Self perception (interpretation of insufficient justification paradigm)
“Why did I do this”
“it couldnt have been that bad since it was $1 and I still did it. I must have liked it”
Example
“Do I like brown bread? Well I buy it so I must like it”
Nisbett & Wilson (1977) Study
Telling more than we know
Methods
watch a movie
conditions
loud noise outside
no loud noise outside
rate the movie
“How intresting was it?”
“How much did you like the main character?”
acess the impact of the noise (casually)
“did noise level increase/decrease your ratings?”
Results
almost half claimed noise DECREASED their ratings
NO actual effect from the noise
“people are horrible at juding what causes their own behavior
True or false
People do no have access to the causes of their own behaviors
true
Self introspection
The process of looking inward and examining one’s own thoughts, feeling, motives
self awareness theory
benefits of self focus
Self Awareness Theory
Situational, individual differences in the extent to which people pay attention to their own self
True or false
Self focused cannot be increased with mirrors
false
Benefits of self focus
improves acess to some internal states
attitudes
level of arousal
sensations
behave more in line with their attitudes
candy jar study
more likely to JUST take 1 candy as told
Winkielman (2002)
Self focus improve casual reports?
Methods
listen to audio taped short story
no noise
static
respond to story
rate aspects
recall details
rate influence of noise
self focus manipulation
just respond to story and noise questions
respond after they made self aware with mirror
Results
noise had NO actual negative effect on ratings, recall
subjects INNACURATE reporting negative effect of noise
self aware people (with mirror)
JUST AS INACCURATE
Two positions on self awareness
Introspective access
Encapsulation
Introspective access
bodily reactions
“the force”
Encapsulation
no acess to many bodily reactions
Bornemann et al (2011)
bodily response to detect emotion of subliminal face
Methods
baseline (white dot)
prime
shows face QUICK
match subliminal face
was it angry/netural?
facial EMG measured throughout trial
strategies
look (wgere face was presented)
feel (“use the force”)
none
Results
bodily response PRESENT
feel strategy
NO significant improvement
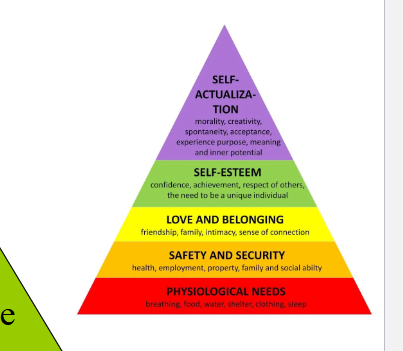
Maslows hierarchy of needs
self actualization
esteem
belongingness, love
safety
physiological
Self in 21st century
actualize
embrace
reshape self
orgins of modern view of self esteem
selfishness, egotism
Ayn Rand
Self enhancing bias (weinstein)
most people show unrealistic optimism
GOOD things are MORE likely to happen to THEM then similar average person
BAD things are LESS likely to happen to THEM than similar average person
Popular beliefs about self esteem
low self esteem is associated with…
low academic achievement
aggression
so the solution MUST be build up self esteem
Baumeister et al Study
self esteem, achivement
Methods
teachers boosed a child’s self esteem
SE interventions (in CA)
measured
self esteem (SE)
educational achievement
Results
relationship betwen SE and achievement is WEAK
OPPOSITE direction
achivement PROMOTES SE
May hurt learning
kids werent told what to do
“concentrate on self control instead”
Cost of self esteem
HIGH SE asoociated with NEGATIVE behavior
agression
bullyng
sense of entitlement
self centeredness
True or false
Most people rate themselves as better than average
true
Rosenberg self esteem scale
most POPULAR self esteem scale
LARGE increase in SE over time
goes AGAINST generational sterotype
boomers confident and gen X down on them selves
Changes in self esteem over time
everyone went up
high school, middle school, college
expecially middle school
Alternative explanation why people believe in themselves so much
learned to be MORE positive when talking about themselves
mental health seems to be getting WORSE
Markus & Kitayama (cultural definition of the self)
Individualissm vs Collectivism
Individualist
many WESTERN cultures
INDEpendent
context free view of self
Collectivist
NON western cultures
INTERdependent
contextual view of self
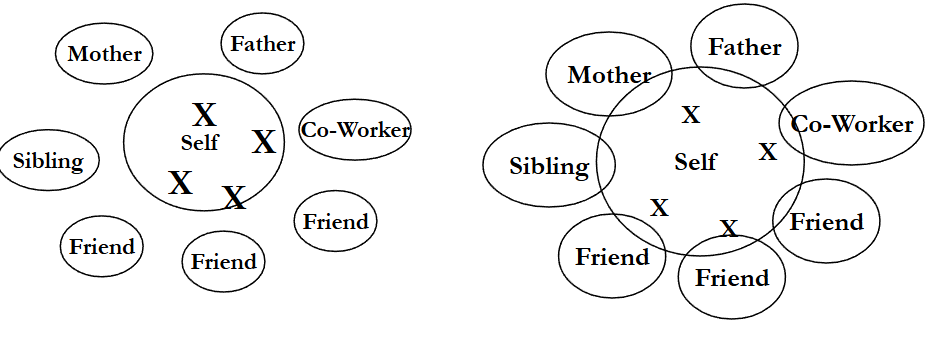
Twenty Statements test
answer the question of “Who am I”
psychological attributes
“im outgoing, honest, silly”
physical attributes
“tim tall”
preferences/intrests
“ i like to cook”
goals
“I want to get an A”
attitudes
“I am not racist”
activities
“I have a part time job”
social roles
“I am a student”
Cousins Study
Who are you in different cultures test
Methods
US, Japanese
do the 20 question response
choose 5 most self defining attributes
Two types of “who am I”
Global
“Who am I”
Contextualized
“Who am I in school, work…”
Results
americas had MORE GLOBAL
Japanese had MORE CONTEXTUALIZED
Western cultures emphasize importance of
stable
cross situational
internal
psychological traits
Non western cultures emphasise importance of
flexibility in context
True or false
Culture and violence happens when self respect and honor goes wrong
true
Nisbett & Cohen Study (culture of honor)
reason for high homicide rate
South characteristics
culture of HONOR
respect, reputation = KEY
RECIPROCITY
pay back both good, bad
HONOR CAN be taken away
susceptible to attack
expecially by insults
insults must be DIRECTLY paid back
SHAME
North characteristics
culture of dignity
intrinsic value equal of every other person
INTERNAL standards, conscience, norms
DIGNITY CANT be taken away
GUILT
IMPERVIOUS to insults
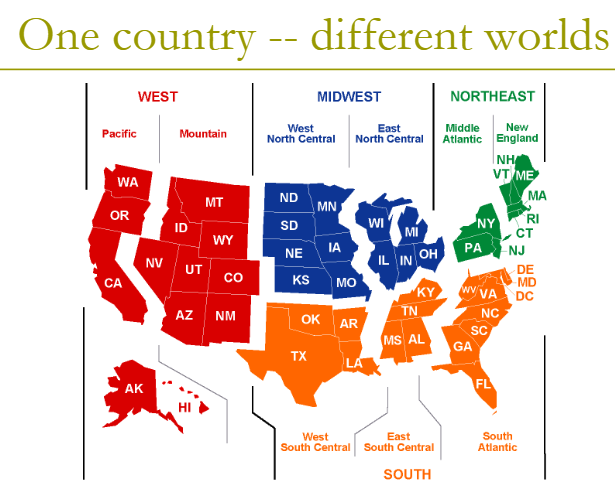
Cohen et al Study
experiment on culture of honor
Methods
fill out questionnaires
spit
insult
questionaire
spit
measured
cortisol
testosterone
self reports
Results
North
LOW cortisol
South
HIGH cortisol
HIGH testerone
Embodied cognition
mental process are supported by bodily, modality based mechanisms
Mind-body Connection
processing using embodied modality based mechanisms
input
sensory
motor state
stimulation (old)
simulation (new)
thought
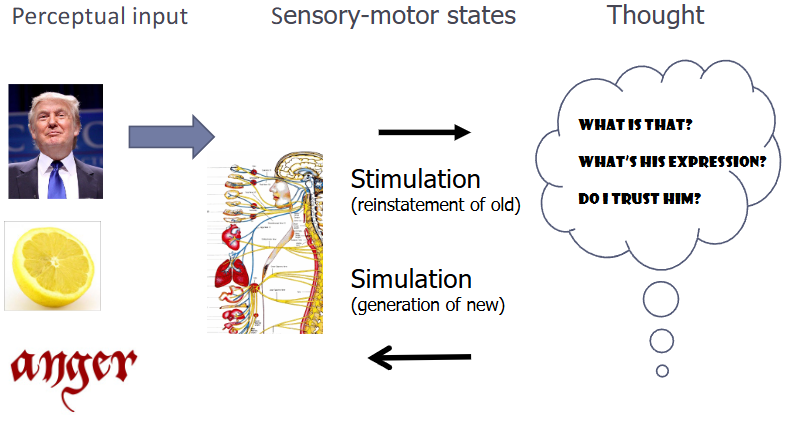
Dumb and Cleaver Embodiment
Dumb
REFLEXIVE
automatic, encapsulate, unconscious
inflexible “perception action” links
Learned via REPEATED association
Clever
RATIONAL
meaning dependent
flexible, conditional
social situated