Chapter 2 smartwork
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Which statement is true of hydrophilic molecules?
They mix well with water.
What distinguishes the chemistry of life from other types of chemistry?
it takes place almost exclusively in water
it is dominated by collections of polymers
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a crucially important energy carrier in cells.
true
is the term used to describe fatty acids that have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic components within the same molecule, like in this example.is the term used to describe fatty acids that have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic components within the same molecule, like in this example.
Amphipathic
water is expelled in
condensation
water is consumed in
hydrolysis
What chemical group is found in a nucleotide but not in a nucleoside?
phosphate
What is the covalent linkage between two adjacent amino acids in a protein called?
peptide bond
Which chemical group is found on all amino acids
carboxylic acid group
Amino acids are subunits of which of the following macromolecules?
proteins
Why do phospholipids aggregate to form cell membranes?
They are amphipathic.
Lipids can include all except which of the following?
amino acids
Which term describes a hydrocarbon tail of a fatty acid that has no double bonds between its carbon atoms?
saturated
Which term best describes a fatty acid?
amphipathic
What type of reaction is the reverse of a condensation reaction?
hydrolysis
Sugars are linked together when a covalent bond forms between an –OH group on one molecule and an –OH group on another. When this bond forms, what molecule is released?
H2O
Is the following statement true, false, or impossible to determine?
Most of the organic matter in a living organism consists of macromolecules, with a much smaller contribution from the small molecules that serve as potential subunits for macromolecules.
true
How are covalent bonds in the cell rapidly broken?
by enzyme catalysis that is specific between protein and substrate
Which type of bond makes it possible for a macromolecule to interact with great specificity with just one out of the many thousands of different molecules present inside a cell?
noncovalent bond
How do protein, nucleic acid, and polysaccharide molecules polymerize (grow in length)?
by condensation reactions
Long polymers are made from single subunits in cells using a ___________ reaction, which ___________ water.
condensation; releases
What is the name used for a molecule in which two carbons of glycerol are attached to fatty acid chains, and the third carbon is attached to a phosphate group?
phospholipid
Which way do the fatty acid tails of a phospholipid face in a cell membrane?
both directions
If these fatty acids were in a phospholipid molecule, which of the two would form the most fluid membrane?
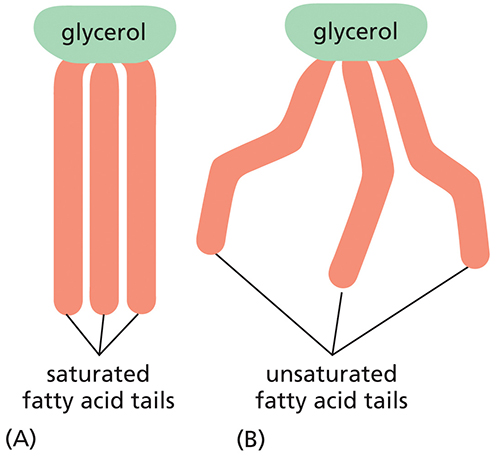
unsaturated
All amino acids have which of the following chemical groups in common?
carboxyl group
Amino acids with side chains that contain -COOH groups, like those shown, would be ___________ in the aqueous environment of a cell.
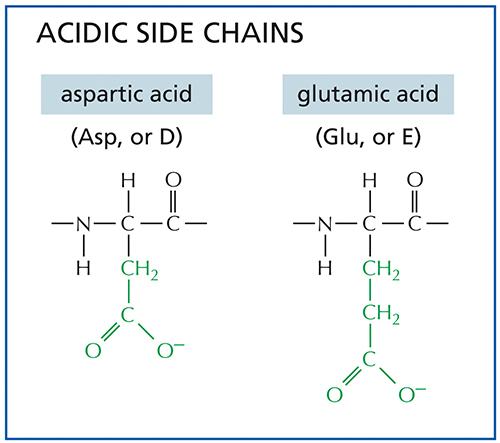
acidic