Nutrient Cycles
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Name the general stages in the phosphorus cycle.
1. Weathering
2. Runoff
3. Assimilation
4. Decomposition
5. Uplift
Why is the phosphorus cycle a slow process?
Phosphorus has no gas phase
- so there is no atmospheric cycle
Most phosphorus is stored as PO4 3- in rocks.
What happens during weathering and runoff?
Phosphate compounds from sedimentary rocks leach into surface water and soil
Explain the significance of phosphorus to living organisms
Plants convert inorganic phosphate into biological molecules
- e.g. DNA, ATP, NADP etc.
Phosphorus is passed to consumers via feeding.
Suggest one way in which an increase in the uptake of phosphate could increase plant growth
Used to produce phosphate compounds e.g. ATP
Suggest and explain 2 reasons why a poor supply of phosphate ions results in poor growth of plants
Phosphate required to make ATP, so less energy for growth
Phosphate required to make nucleotides, so less DNA for cell division
What happens during uplift?
Sedimentary layers from oceans (formed by the bodies of aquatic organisms) are brought up to land over many years.
How does mining affect the phosphorus cycle?
Speeds up uplift.
Name the 4 main stages of the nitrogen cycle.
1. nitrogen fixation
2. ammonification
3. nitrification
4. denitrification
describe the nitrogen cycle in soil using the remains of crop plants
proteins/DNA etc. in the soil broken down to ammonia by saprobiants during ammonification
ammonia converted to nitrite by nitrifying bacteria during nitrification
nitrite converted to nitrate by nitrifying bacteria during nitrification
nitrogen converted to ammonia by nitrogen-fixing bacteria
role of saprobiants
saprobiants break down dead materials e.g. proteins/DNA etc. into ammonia
Why can't organisms use nitrogen directly from the atmosphere?
N2 is very stable due to strong covalent triple bond
What happens during atmospheric fixation of nitrogen?
1. High energy of lightning breaks N2 into N
2. N reacts with oxygen to form NO2 -
3. NO2 - dissolves in water to form NO3 -
Explain how nitrogen-fixing bacteria could increase the growth of a plant
nitrogen fixing bacteria convert nitrogen in the air into ammonium compounds
the ammonium compounds are then converted to nitrates by nitrification
the plant uses the nitrates in the soil for protein,DNA synthesis etc.
add available nitrogen to an ecosystem
Outline the role of bacteria in denitrification
Anaerobic denitrifying bacteria convert soil nitrates back into gaseous nitrogen
Explain the significance of nitrogen to living organisms
Plant roots uptake nitrates via active transport & use them to make biological compounds e.g:
● amino acids
● NAD/ NADP
● nucleic acids
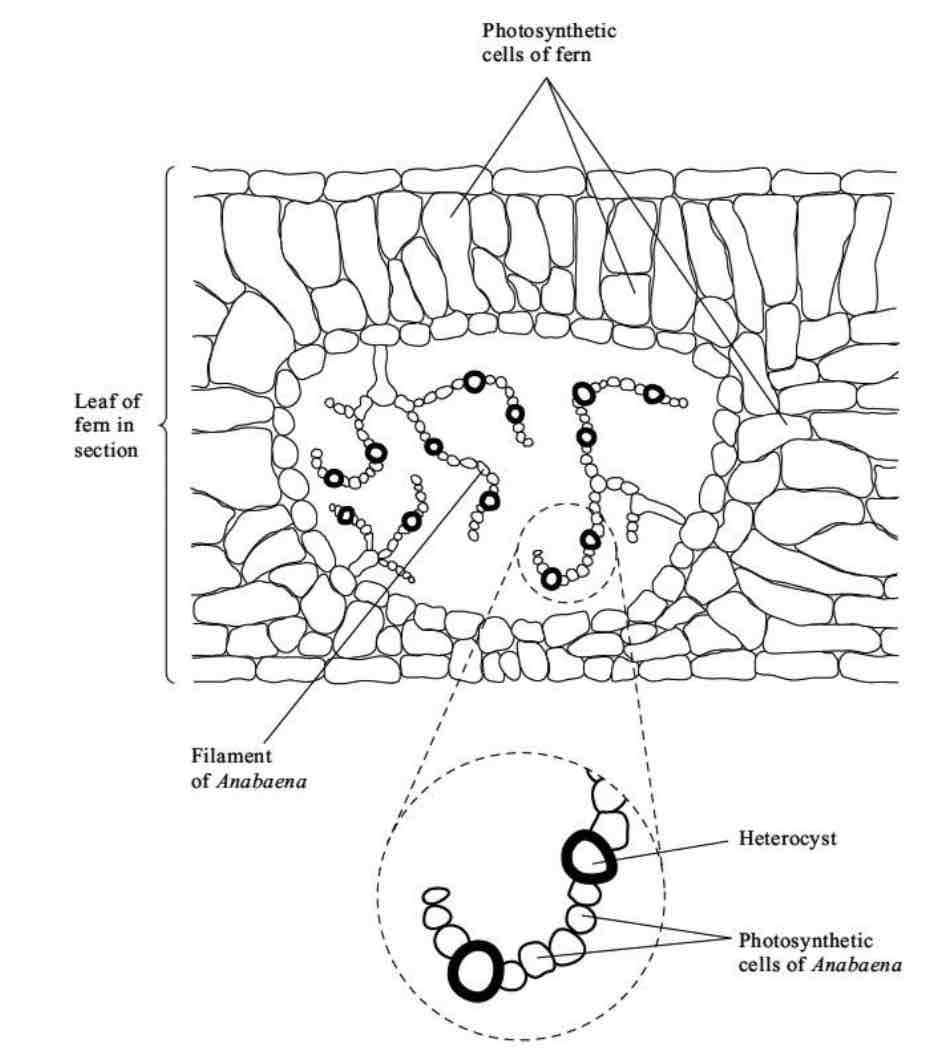
Anabaena is a prokaryote found inside the leaves of a small fern. Anabaena can produce ammonia from nitrogen (nitrogen fixation). This reaction only takes place in the anaerobic conditions found in cells called heterocysts. Heterocysts are thick-walled cells that don’t contain chlorophyll.
Suggest how the features of the heterocysts improve the efficiency of the process of nitrogen fixation.
doesn’t contain chlorophyll, so they don’t photosynthesise
Don’t produce O2 - O2 would inhibit the nitrogen fixation process
describe eutrophication
algal bloom which covers the surface and blocks out light
reduced photosynthesis so plants die
increase in saprobiants, which break down dead plant materials
saprobiants aerobically respire and use up the oxygen
so less oxygen for fish to then respire
so fish die
explain the advantage of having both algae and bacteria in a purification pond
breakdown of organic matter by enzymes from bacteria
nitrates used by algae to make proteins
algae photosynthesise
bacterial respiration produced CO2 for algae
Outline the role of mycorrhizae.
Mutualistic relationship between plant and fungus
increases surface area of root system, which increases uptake of water and mineral ions
Give 3 benefits of planting a different crop on the same field each year.
1. Nitrogen-fixing crops e.g. legumes make soil more fertile by increasing soil nitrate content
2. Different crops have different pathogens
3. Different crops use different proportions of certain ions
Name the 2 categories of fertiliser and state the purpose of using fertiliser.
1. Organic: decaying organic matter & animal waste
2. Inorganic: minerals from rocks
- usually containing nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium
● To increase gross productivity for higher yield.
give 2 advantages of using natural fertiliser rather than artificial fertiliser
aerates the soil
less leaching
At a certain point, using more fertiliser no longer increases crop yield. Why?
A factor unrelated to the concentration of mineral ions limits the rate of photosynthesis
- so rate of growth cannot increase any further
Outline 2 main environmental issues caused by the use of fertilisers.
1. Leaching: nitrates dissolve in rainwater and 'runoff' into water sources.
2. Eutrophication: water source becomes putrid as a result of algal bloom.
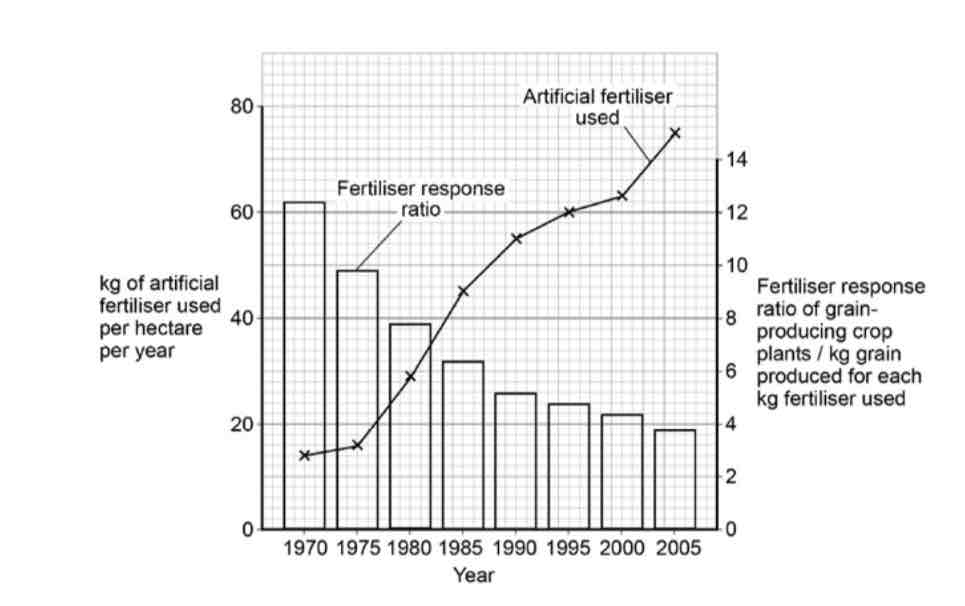
Use the data in the graph above to evaluate the use of artificial fertilisers on grain-producing crops in India
fertilisers becomes less effective over time
graph shows correlation, but there could be other factors
becomes less cost effective over time

A student who read this passage concluded that farmers should not use fertilisers to increase yields when growing tomato plants.
Evaluate his conclusion.
Shouldn’t use fertilisers:
fertilisers prevent the development of mycorrhizae
mycorrhizae helps plants defend themselves, causing an increase in crop yield
mycorrhizae help plants take up nitrates/phosphates, causing an increase in crop yield
Should use fertilisers:
fertilisers containing phosphate and nitrate cause an increase in GPP, so increase in crop yield
Most soil is poor in phosphate, so without fertilisers, the plant might not get enough phosphate
Why may bare ground be left between two crops
To prevent competition between the two crops for light, nutrients, water etc.
To prevent diseases from spreading
Explain why it is important for the farmer to reduce the leaching of nitrates.
Plants grow less well because of the lack of nitrates
Leaching causes eutrophication
It takes longer for the nitrogen-containing substances to get into the lake when an organic fertiliser is used than when an inorganic fertiliser is used.
Explain why is takes longer when an organic fertiliser is used.
The organic fertiliser is insoluble
therefore the molecules require breaking down
How can the risk of eutrophication be reduced?
● Sewage treatment marshes on farms.
● Pumping nutrient-enriched sediment out of water.
● Using phosphate-free detergent.
Denitrification requires anaerobic conditions. Ploughing aerates the soil.
Explain how ploughing would affect the fertility of the soil.
Would increase the fertility of the soil as less denitrification would occur, therefore less nitrate would be removed
Describe and explain how one farming practice results in the addition of nitrogen-containing compounds to a field
growing legumes
legumes have nitrogen-fixing bacteria in nodules
explain how using leguminous plants in a crop rotation reduces the need to use artificial fertilisers
leguminous plants contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria in nodules
so nitrogen-containing compounds are added to the soil when the plant dies
Describe and explain how one farming practice results in the removal of nitrogen-containing compounds to a field
having bare soil
results in soil erosion
3 ways in which crop rotation may lead to high crop yields
different crops use different nutrients from the soil
crop rotation means that u can grow crops with nitrogen-fixing bacteria
different crops have different pathogens
explain how farming increases the productivity of agricultural crops
fertilisers added to soil
nitrate ions used to make proteins
ploughing allows nitrification
selective breeding of crops
crop rotation for high crop yields
different crops use different nutrients from soil