Neural Development and Disorders: Embryogenesis, Synaptogenesis, and FAS
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is neurodevelopment?
The development of the nervous system, specifically the central nervous system, including how axons find their end targets.
What is the initial structure of the central nervous system during embryonic development?
The CNS begins as a hollow tube that elongates and forms pockets and folds to become the brain.
What percentage of live births involve CNS functional impairments?
0.1%-0.2%.
What are congenital problems?
Problems that occur at birth, which can be genetically or environmentally caused.
What is gastrulation in early development?
The process where a fertilized egg divides and rearranges to form a hollow ball of cells called the blastula, which differentiates into three layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
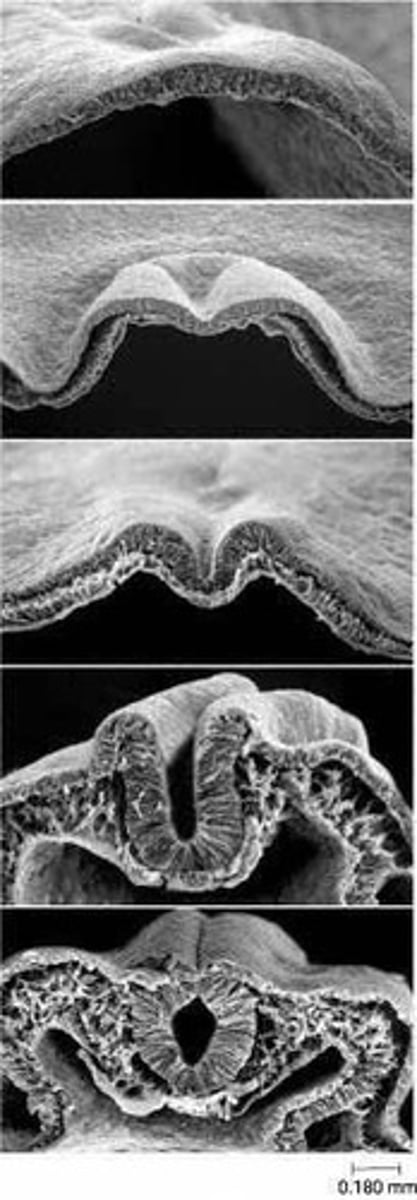
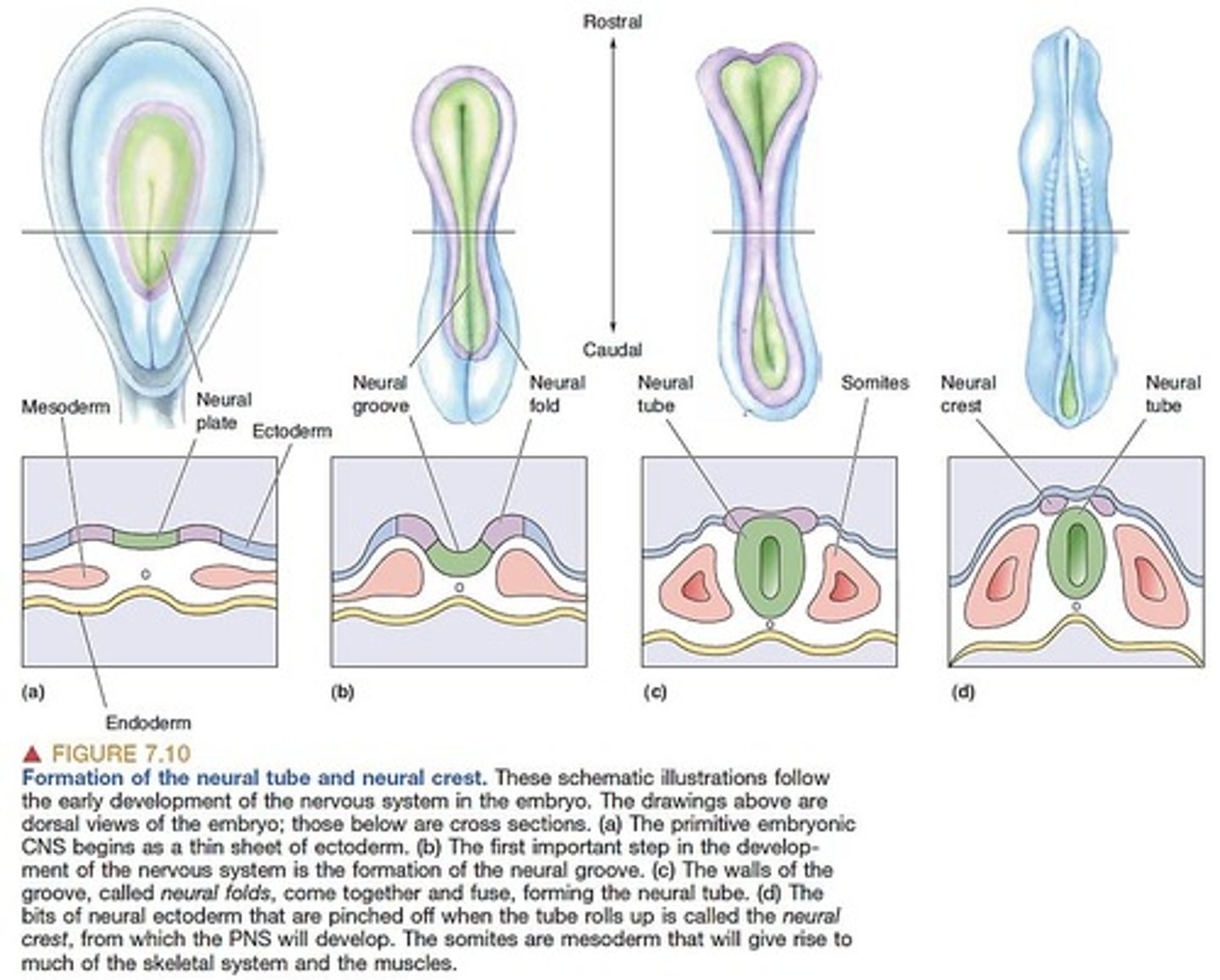
What occurs during neurulation?
The nervous system arises from a subset of ectodermal cells approximately 24 days after conception, forming a neural plate.
What are pluripotent cells?
Early-stage cells that can become any cell type in the body, often referred to as embryonic stem cells.
What is the role of neural crest cells?
They are formed during neural tube closure and give rise to various cell types in the nervous system.
What type of division do progenitor cells undergo initially?
Symmetrical division, producing two new progenitor cells.
What happens to progenitor cells after 7 weeks of development?
They begin asymmetrical division, producing one progenitor cell and one brain cell.
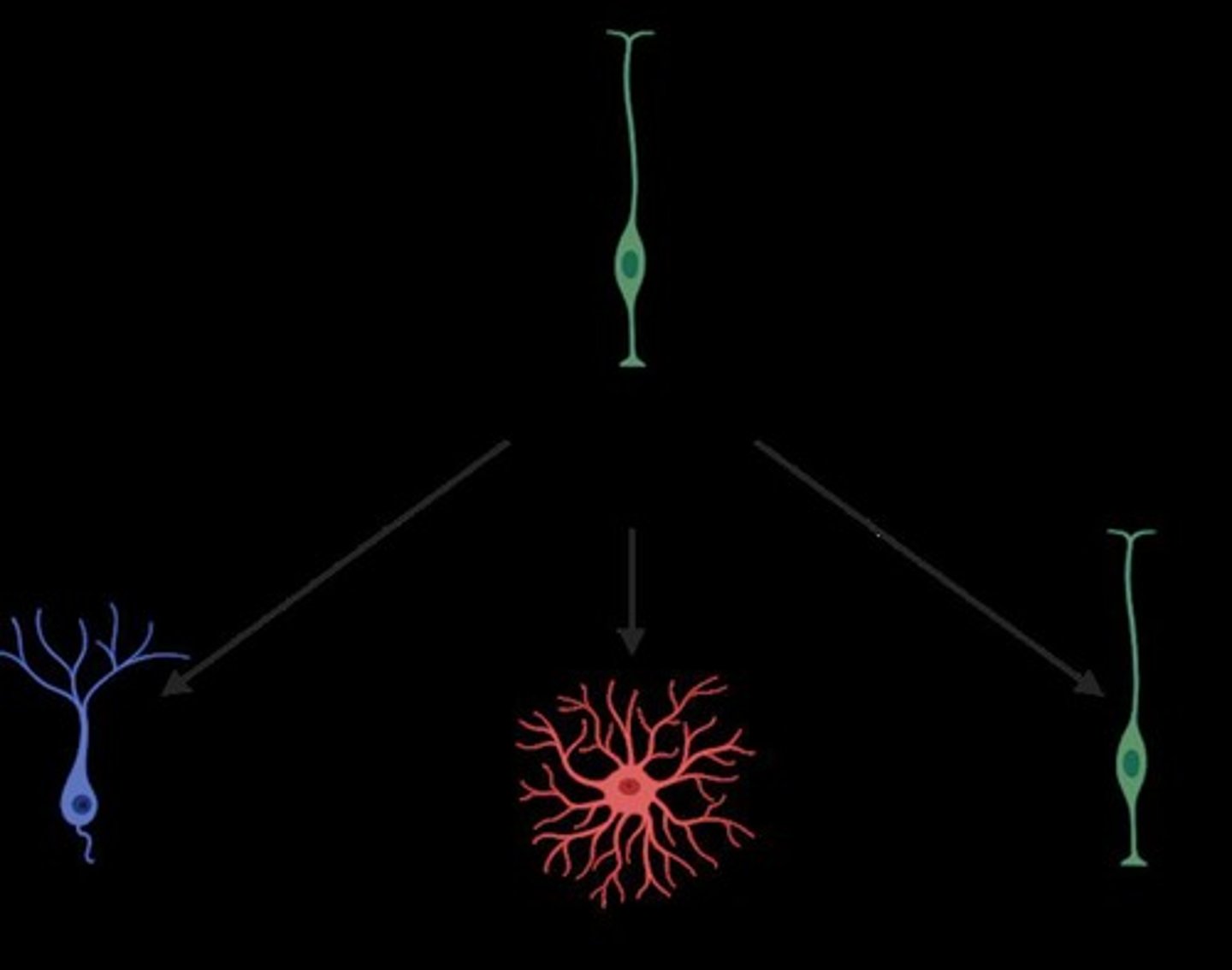
How are neurons and glia formed from neural stem cells?
Neural stem cells can undergo symmetrical division to create identical daughter cells or asymmetrical division to create neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes.
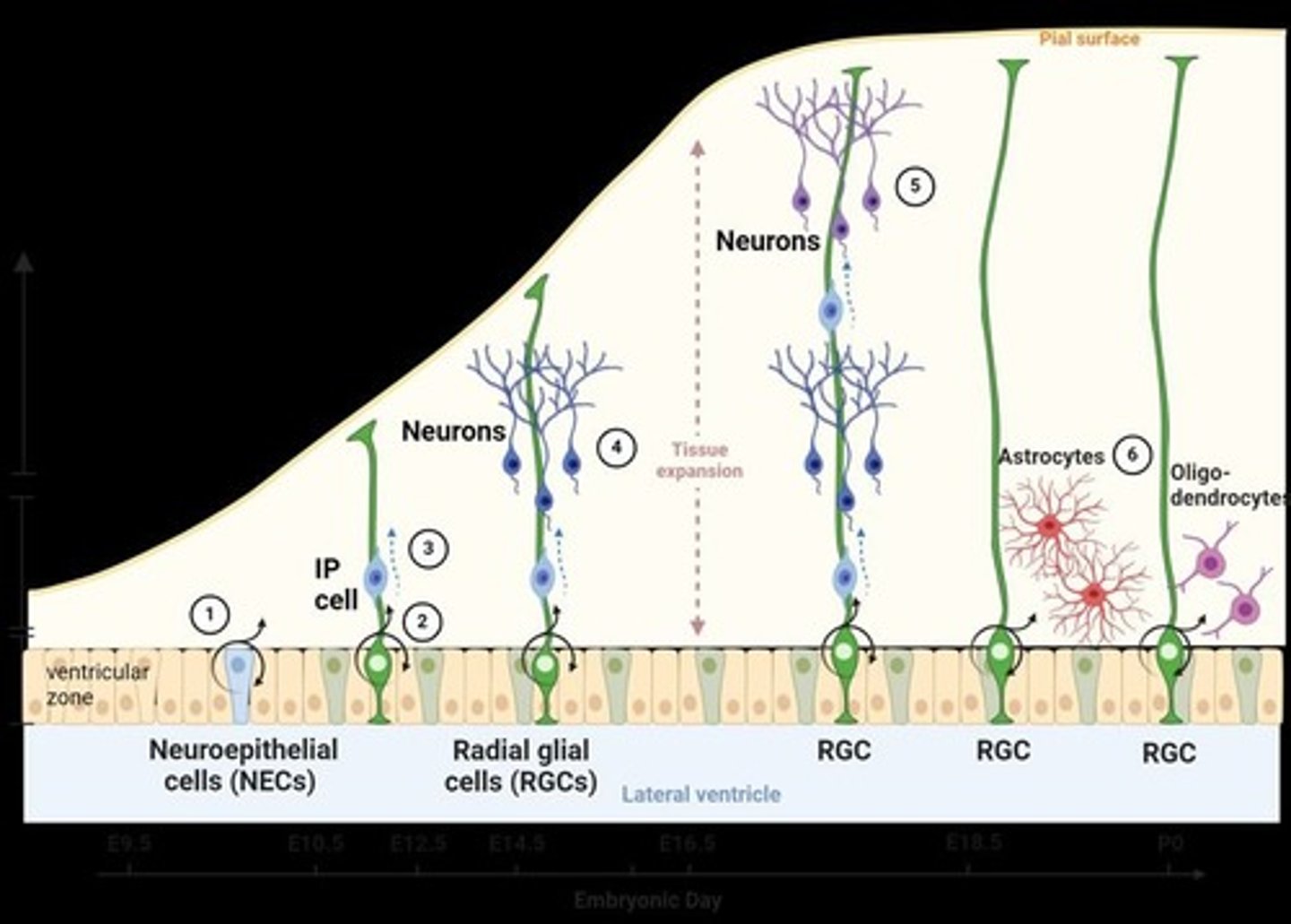
What are radial glial cells (RGCs)?
Cells that early stem cells divide to create, which guide the migration of neurons.
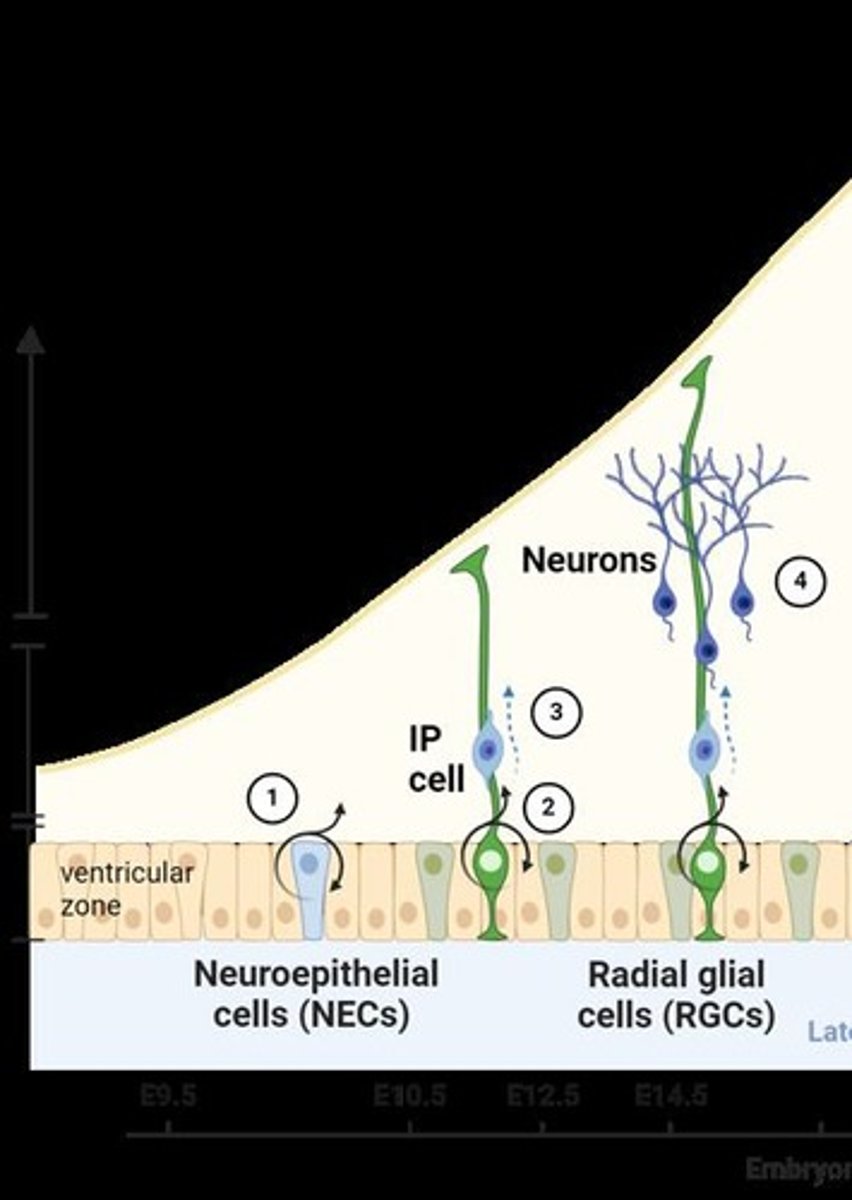
What is neurogenesis?
The birth, survival, migration, and differentiation of new neurons.
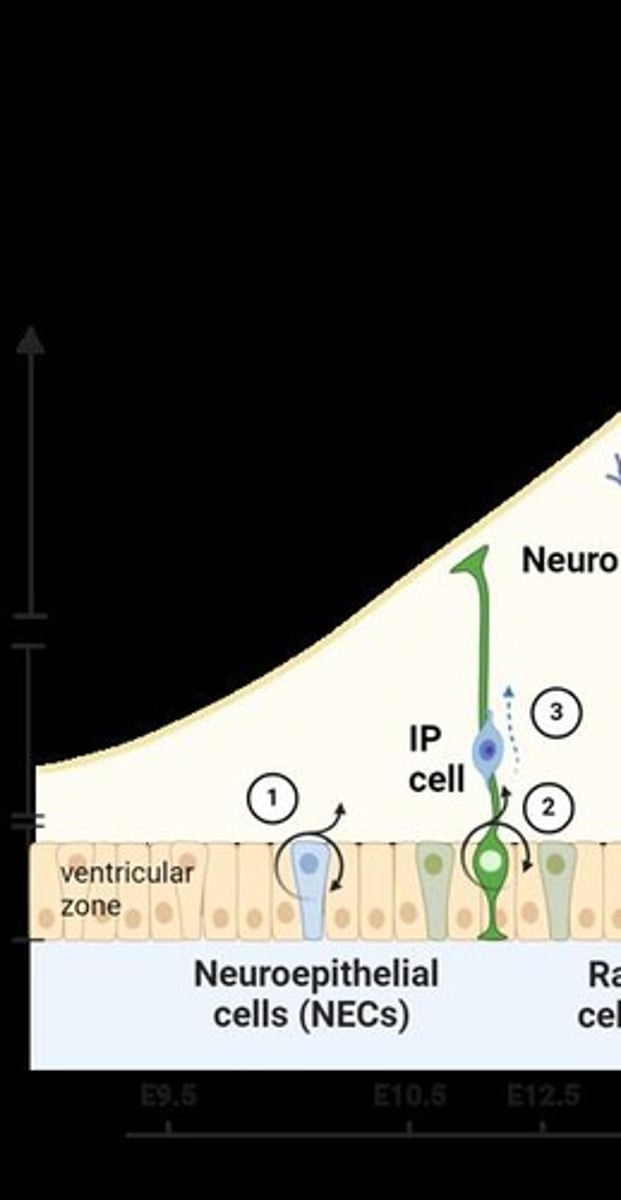
What is gliogenesis?
The birth, survival, migration, and differentiation of new glia.
What is the inside-out formation of cortical layers?
The process where inner layers of the cortex form first, followed by outer layers, with radial glial cells transforming into astrocytes after layer formation.
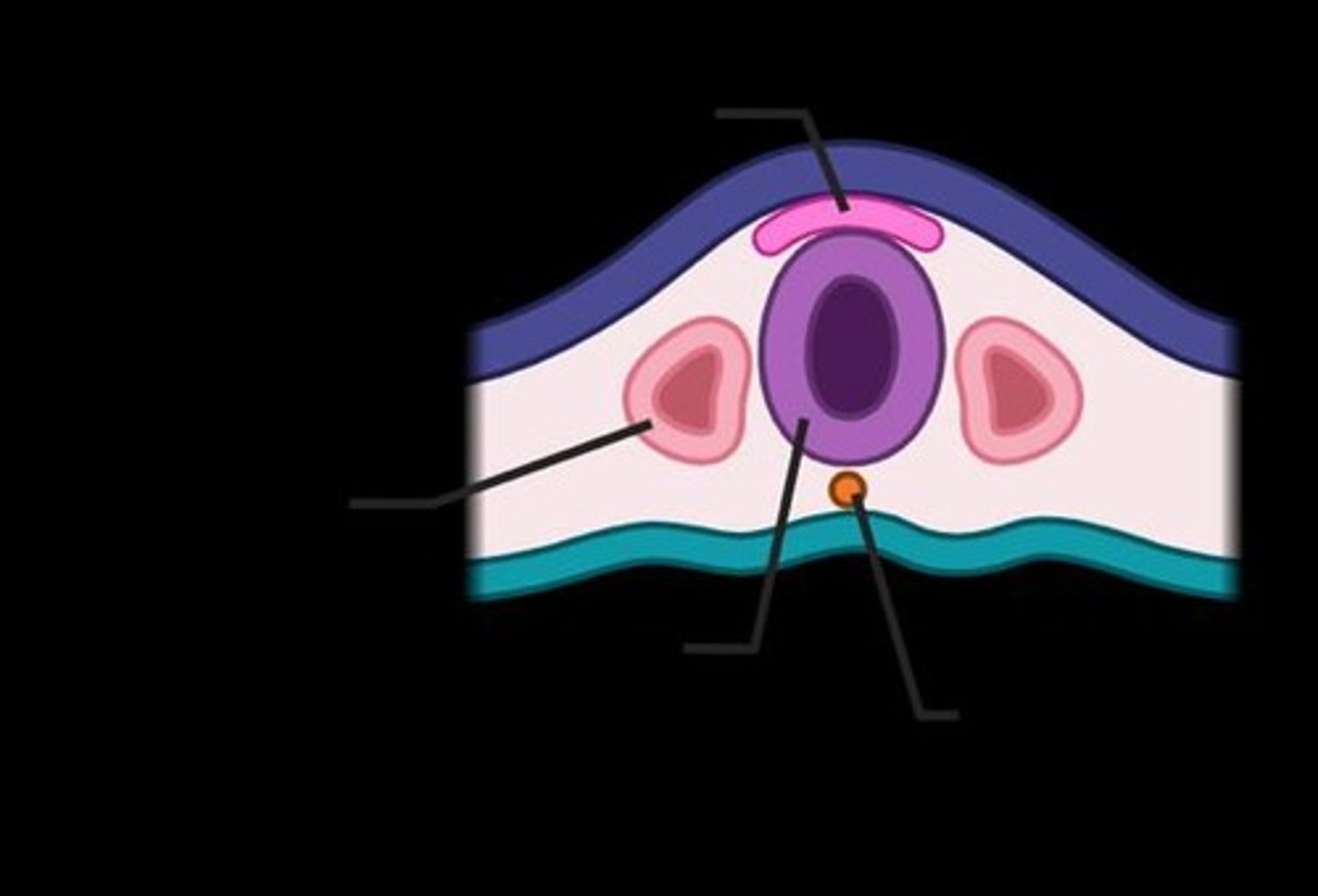
What is synaptogenesis?
The formation of synapses, where immature synapses initially have few vesicles and no post-synaptic density.
What is synaptic pruning?
The elimination of synapses through apoptosis, where unused synapses decay.
What is myelination and when does it occur?
The increase in myelin, which is substantial in the first year of life and is highly plastic.
What is neural plasticity?
The ability of the brain to adapt and reorganize in response to environmental stimuli.
What are critical periods in brain development?
Periods when environmental stimuli can lead to long-term positive or negative effects on development.
What is fetal alcohol spectrum disorder?
A range of changes caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy, leading to intellectual disability and various developmental issues.
What are some effects of fetal alcohol syndrome?
Altered facial development, low body weight, impaired brain development, poor coordination, vision and hearing problems, and changes in heart, kidney, and bone development.
What is the significance of the early childhood environment on CNS impairment?
A poor environment in early childhood can impair later cognition.
What is the role of oligodendrocytes in myelination?
Oligodendrocytes are sensitive to environmental stimuli and contribute to the formation of myelin.
How does the infant brain grow by adulthood?
The infant brain increases in size by a factor of up to 5, due to growth of synaptic connections and myelination.
What is the impact of adolescence on brain development?
Many brain regions are not yet mature, leading to increased sensitivity to stress and drugs, with long-lasting effects.