Chapter 11- Muscular System
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
The muscular system is comprised of....
voluntary controlled muscles of the body
What is the origin?
attachment of a muscle tendon to the stationary bone
What is the attachment of a muscle tendon to the stationary bone called?
origin
What is the attachment of the muscle tendon to the movable bone called?
insertion
What is insertion?
attachment of the muscle tendon to the movable bone
What is the fleshy portion of the muscle between the tendons called?
belly or body
The origin is usually the ______ attatchment.
proximal
The insertion is usually the _____ attatchment.
distal
Muscles are attached to _________.
the articulating bones that form
What is RMA?
reverse muscle action
The _____ is pulled toward the ______.
Insertion to origin
Bones act as _______
levers
Joints function as the _______ of the lever like bones.
fulcrums
What are the two different types of forces?
effort and load/resistance
What is effort?
the force exerted to achieve a movement
What is load/resistance?
the weight that opposes movement
Levers are classified into three types:
first-class
second-class
third-class
Leverage is the _____ or ______ gained by a lever.
mechanical advantage or mechanical disadvantage
Whats an example of a first-class lever?
muscles in back of neck
Whats an example of a second-class lever?
calf muscle
Which lever is the most uncommon in the human body?
second-class levers
What should you think of when you think of first-class levers?
scissors
Whats an example of a third-class lever?
the arm (elbow and biceps brachii)
Which lever is the most common?
third class lever
What should you think of when you think of second-class levers?
wheel-barrow
What should you think of when you think of third-class levers?
tweezers
What is the first-class lever?
the fulcrum between the effort and load (EFL)
What is the second-class lever?
the fulcrum ay one end, the effort at the opposite end, and the load between them (ELF)
What does E, L and F stand for?
Effort
Load
Fulcrum
What is the third-class lever?
the fulcrum at one end, the load at the opposite end, and the effort between the (FEL)
Skeletal muscle fibers within a muscle are arranged in bundles?
fascicles
What are all the arrangements of fascicles called?
parallel
fusiform
circular
triangular
pennate
What do the arrangements of fascicles affect?
the power of a muscle and its range of motion
What is an agonist?
a muscle that causes a desired action
Another word for agonist is?
prime mover
Most movements require ______ muscles
several
What is the muscle, whose effect is opposite to that of the prime mover, called?
antagonist
An _______ must relax in order to permit the _______ to cause the desired action.
antagonist, agonist
A _________ is a muscle that serves to prevent unwanted movements at intermediate joints to helps the prime mover function more efficiently
synergist
What does a fixator muscle do?
stabilizes the origin of a prime mover
T/F: A muscle can only be one of these: antagonist, synergist, fixator, or agonist
False, a muscle can be more than one of these
What is a muscle compartment?
a group of muscles that have a common function
How many skeletal muscles are there?
over 600
rectus
straight
transversus
crosswise
oblique
indirect; slanting
maximus
largest of group
minimus
smallest of group
medius
middle
brevis
short
major
more important, bigger or more serious than others of the same type
minor
small, unimportant than others of same type
delta
deltoid
trapezius
trapezoid shape
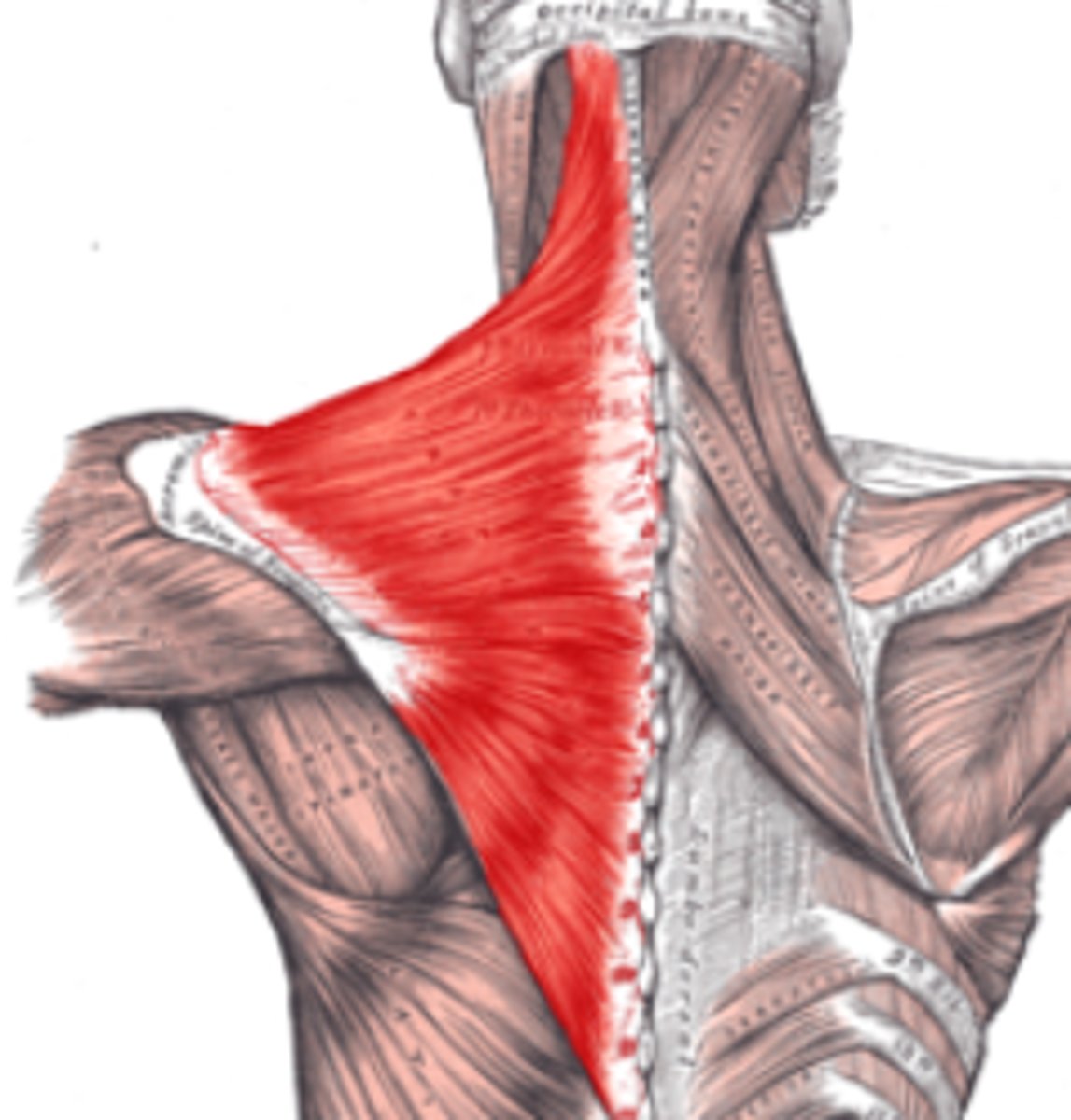
serrates
saw-toothed
rhomboid
shaped like rhombus
extensor
extends
abductor
away from the midline
adductor
muscle that moves a part toward the midline
levator
raises or elevates a body part
depressor
lowers or depresses a body part
supinator
supinates
tensor
makes a body part rigid
biceps
two heads
triceps
three heads
quadriceps
four heads
What is innervation?
nerve supply
______ is the movable or more movable bone.
insertion
_____ always moves toward the ______.
insertion, origin
Most facial muscles are very ______.
thin
Facial Expressions are innervated by:
Roman numeral 7/VII
How many bellies does the occipitofrontalis have?
2, frontal, occipital
Where is the orbicularis oculi?
around the eye
Whats the origin of orbicularis oculi?
muscle fibers around mouth
What's nicknamed the "kissing muscle"?
orbicularis oculi
Whats the insertion of orbicularis oculi?
into skin at corners/angles of mouth
Whats the action of orbicularis oculi?
close and protrude lips; as in kissing
Whats nicknamed the "smiling muscle"?
Zygomaticus Major/Minor
Whats the origin of the zygomaticus major?
zygomatic bone
Whats the insertion of the zygomaticus major?
skin at angles of mouth