Constructing Half Equations
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is a half equation used for?
Half equations are used to show the separate oxidation and reduction reactions that occur in a redox reaction.
What must a half equation be in order to ensure that it is correct?
Half equations must be balanced in terms of the species present and the charges of the species on both sides of the equation.
State the rules needed when writing a half equation (reaction occurs in acidic conditions).
Balance all species apart from oxygen and hydrogen.
Balance any oxygen with water (H20). The water molecules should be added on the opposite side of the equation from the oxyanion.
Balance any hydrogen with H+ ions. The hydrogen ions should be added to the opposite side of the equation from the water molecules.
Balance charges with electrons (e-) by adding electrons to the side with the most positive overall charge (usually the same side as the hydrogen ions).
Example: Write a half equation showing the conversion of Cr2O72- to Cr3+.
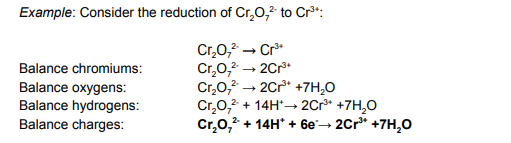
State the rules needed when writing a half equation (reaction occurs in alkaline conditions).
Balance all species apart from oxygen and hydrogen.
For every oxygen atom in the oxyanion present, add a water molecule to the same side of the equation as the oxyanion.
Balance any oxygen by adding hydroxide ions to the opposite side of the equation from the water molecules and the oxyanion.
Balance the overall charges on both sides of the equation by adding electrons to the side with most positive overall charge (usually the opposite side from the hydroxide ions).
Example: Write a half equation showing the conversion of SO42−(aq)→S(s).
SO42−(aq)→S(s)
SO42−(aq)+ 4H2O(l) →S(s)
SO42−(aq)+ 4H2O(l) →S(s) + 8OH−
SO42−(aq) + 4H2O(l) + 6e−→ S(s) + 8OH−
State the steps used in order to combine half equations.
Write the two redox equations with one beneath the other so that the arrows align.
Multiply one or both of the half-equations so that the number of electrons is the same in both half-equations.
Combine the half-equations into a single equation with all the reactants on the left hand side and the products on the right hand side. You do not need to include the electrons as they will cancel each other out.
Example of combining half equations to form a full equation.
Equation 1
2I−(aq)→ I2(s) + 2e−
Equation 2
SO42−(aq) + 8H++ 6e−→ S(s)+4H2O(l)
Equation 1
6I−(aq)→ 3I2(s) +6e− (this has been multiplied by 3).
Equation 2
SO42−(aq) + 8H++ 6e−→ S(s) + 4H2O(l)
Full equation: SO42−(aq)+ 8H+ + 6I−→S(s) + 4H2O(l)+3I2(s)