Lecture 13: Photosynthesis: Carbon Fixation & Cell Division
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10/1/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
How do weedkillers disrupt photosynthesis?
Weedkillers interfere with the chloroplasts or ETC, preventing the plant from producing sugars for energy and leading to cell damage or death. These inhibitors act by blocking the photosystem II complex.
Examples of weedkillers that block PSII
DCMU
Paraquat
What would cyanide do if it entered the mitochondrial ETC?
Cyanide would bind to complex 4 in the mitochondrial ETC, altering the shape of its active site. Consequently, electrons cannot be released to oxygen and the ETC would shut down. The result would be death (suffocation)
Where do the dark reactions (Calvin Cycle) take place?
The stroma of the chloroplasts
What are the Calvin Cycle inputs?
CO2
ATP
NADPH
What are the Calvin cycle outputs?
Sugars
ADP
NADP+
Why is the Calvin cycle a cycle?
Because what goes in comes out - a transformation - no net usage of plant material
Diagram the Calvin cycle showing the carbon inputs and outputs, where energy is used, and the fixation, reduction, and regeneration stages of the biochemistry.
Image
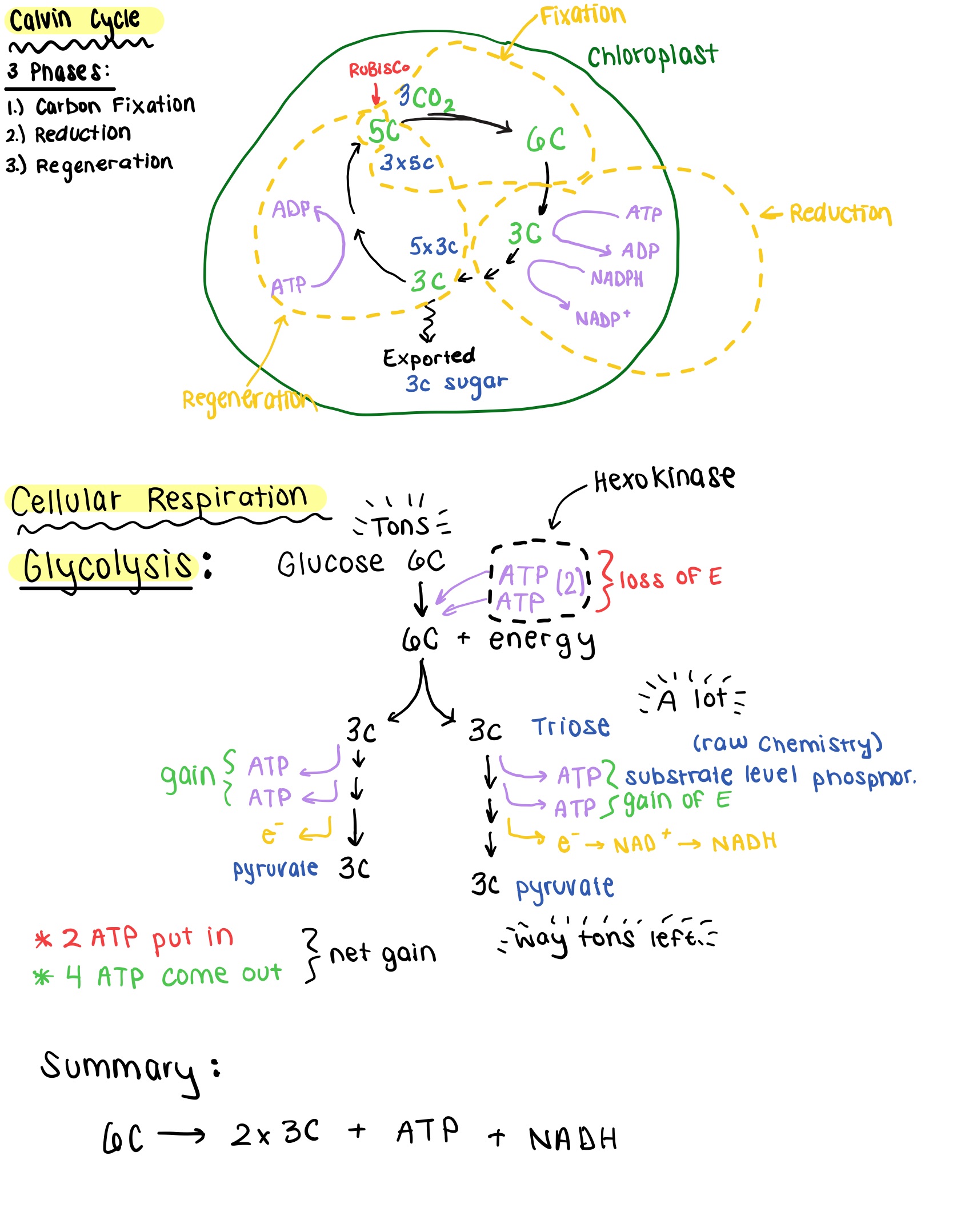
Explain why photosynthetic carbon fixation is called C3 photosynthesis, and how it can lead to the production of 6-carbon sugars.
Photosynthetic carbon fixation is called C3 photosynthesis because the first stable organic product formed from the enzyme RuBisCO fixing carbon dioxide is 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA), a three-carbon compound
Diagram the Cell Cycle
Image
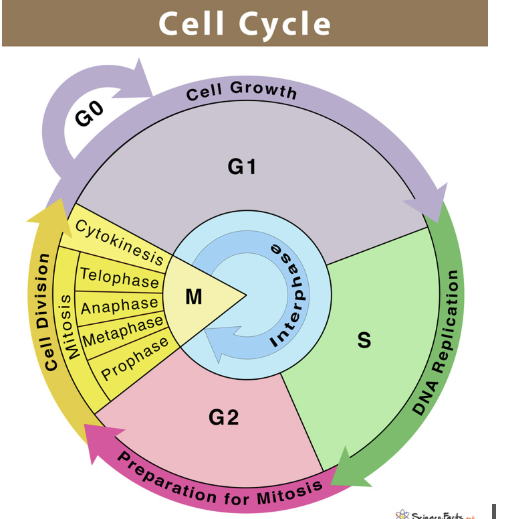
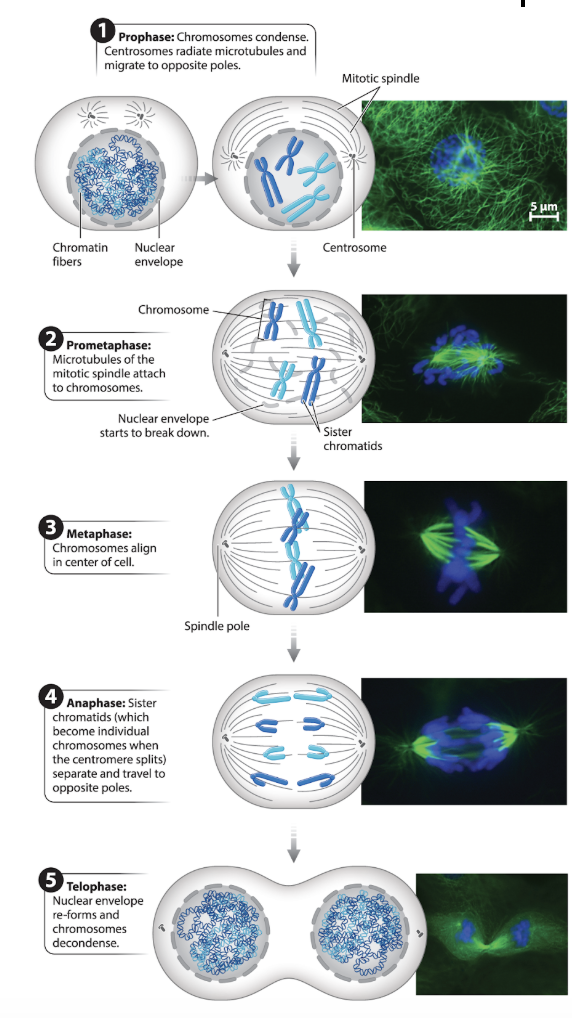
Diagram and explain the phases of Mitosis
Image
Define Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase
An enzyme that catalyzes the first step of the Calvin cycle, where CO2 is fixed by combining it with ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP)
The most abundant enzyme on Earth
Define RuBisCO
Short for Ribulose - 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, it’s the enzyme that initiates carbon fixation in the Calvin Cycle
Define Ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP)
A 5-carbon sugar that acts as the CO2 acceptor in the Calvin Cycle. It reacts with CO2 in a reaction catalyzed by RuBisCO
Define Calvin Cycle
The set of light-independent reactions in photosynthesis that take place in the stroma of chloroplasts. It uses ATP and NADPH to fix CO2 into glucose. It has three phases
Fixation
Reduction
Regernation
Define Fixation
The first phase of the Calvin Cycle, where CO2 is attached to RuBP, forming an unstable 6-carbon compound that splits into two 3-carbon molecules (3-PGA)
Define Reduction
The second phase of the Calvin cycle, where ATP and NADPH are used to convert 3-PGA into G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate), a sugar
Define regeneration
The third phase of the Calvin cycle, where some G3P is used to regenerate RuBP so the Calvin cycle can continue
Define cell cycle
The entire life cycle of a cell, including the stages of growth (interphase), a preparation for division, and cell division (mitosis and cytokinesis)
Define centriole
A cylindrical structure involved in forming the spindle fibers during mitosis in animal cells
Define chromatin
the uncondensed, thread-like form of DNA in the nucleus during interphase
Define chromosome
condensed form of chromatin, visible during cell division; contains genetic information
Define centromere
the region where two sister chromatids are joined together; attachment point for spindle fibers
Define kinetochore
a protein structure on the ceontromere where spindle fibers attach during mitosis
Define sister chromatid
one of two identical copies of a chromosome connected at the centromere
Define spindle
A structure made of microtubules that separates chromosomes during mitosis
Define Interphase
The longest part of the cell cycle, consisting of G1 (growth), S (DNA synthesis), and G2 (preparation for mitosis). The cell performs normal functions and duplicates its DNA
Define Prophase
The first phase of mitosis
Chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes
Nuclear envelope begins to break down
Spindle fibers start to form
Define Metaphase
The second phase of mitosis
Chromosomes align at the cell’s equator (metaphase plate)
Spindle fibers attach to centromeres via kinetochores
Define Anaphase
The third phase of mitosis
Sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle and move to opposite poles
Define Telephase
The fourth phase of mitosis
Where the separated chromosomes arrive at opposite ends of the cell
The nuclear envelop reforms around each set of chromosomes to create two new nuclei
The chromosomes decondense, and the mitotic spindle disassembles
Define Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplast, resulting in two separate daughter cells
In plant cells, a cell plate forms during this process
Define cell plate
a structure that forms in plant cells during cytokinesis. It eventually develops into a new cell wall separating the two daughter cells