Chapter 4: Analytical Psychology (Carl Jung)
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Psyche
Personality: Latin word for spirit or soul
Diffuse and General Life Energy
He used libido in two ways: Firstly, it posits that libido is everything that governs life
Narrower psychic energy that fuels the work of the personality
He used libido in two ways: Secondly, it is more focused on the psychological aspect of our lives. It posits that the activities that have a high psychic value are activities that use a great deal of psychic energy
Principle of Opposition
There is the existence of opposites or polarities in physical energy (i.e. introversion and extraversion). It suggests that the conflict between polarities is the primary motivator of behavior and generator of energy.
Principle of Equivalence
The physical energy that is expended in bringing about some condition is not lost but rather is shifted to another part of the personality
Principle of Entropy
Refers to the equalization of energy differences. It is the tendency towards balance or equilibrium within the personality
Personality
According to Jung, ____ is no divisible, rather its an integration of the unconcious and concious aspects forming our affect, behavior, and cognitions.
Self
The total sum of the integrated personality; including their qualities (apparent, empirical, observable) and potentials (pre-disposition and is not apparent but is part of the self)
Conscious Growth
Outward flow of libido
Inner Development
Inward flow of libido
Ego Inflation
Living in the conscious and ignoring the potentialities that lies in the unconscious. In other words, when we live based on the things we know about ourselves, we ignore the potential that we have
Psychic Inflation
Missing out on your qualities or the things that are present in you ie when we only deal with our unconscious self
Entropy
The goal of personality is to reach __
Individuation
The process of restoring wholeness to the psyche in adult development. The goal is to move the center of personality from the ego to some midpoint between the ego and the unconscious
Conscious/Ego
It is the center of the consciousness and an individual’s will; “Gatekeeper to consciousness”. It is one’s awareness of oneself and is responsible the carrying out all the normal everyday activities of working life
Ego Inflation
An inflated consciousness is always egocentric and conscious of nothing but its own existence.
Marital Setbacks
The things you know about yourself may not be true
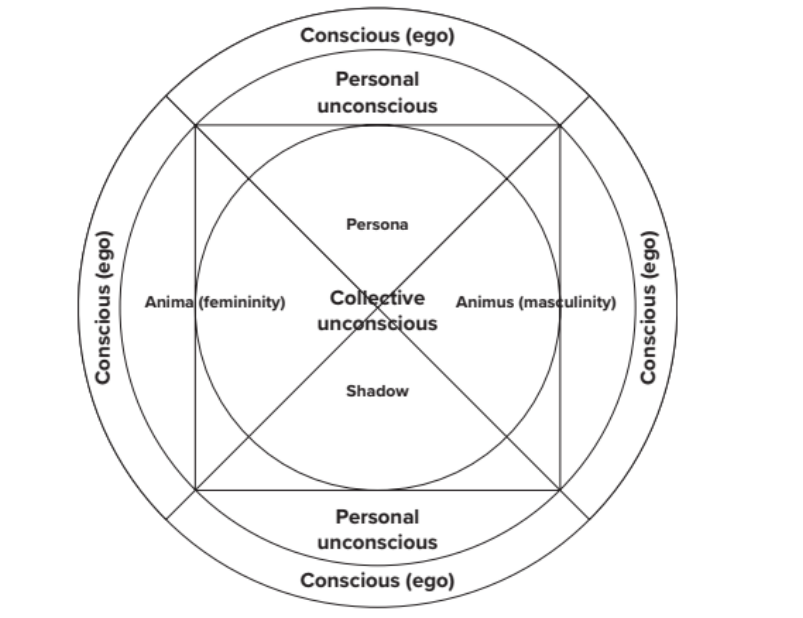
Personal Unconscious
It embraces all repressed, forgotten, or subliminally perceive experiences of the individual. It contains repressed infantile memories and impulses, forgotten events, and experiences originally perceived below the threshold of our consciousness.
Complex
Contents of the personal unconsious or the emotionally toned conglomeration of associated ideas. Largely personal, but may also be partly derived from humanity’s collection experience
Psychic Potentials
Our tendencies to behave
Collective Unconscious
Inherited, contained in human brain structure, and not dependent on personal experience to develop. Shaped by remote evolutionary experiences of the human species and transmitted to each individual through genetic inheritances.
Archetypes
Ancient or archaic images that derive from the collective unconscious. They are emotionally toned conglomeration of associated images but are generalized and derive from the contents of the collective unconscious.
Instinct
Our unconsious physical impulse toward action and the psychic counterpart of archetypes
Persona
It refers to masks worn by actors in the early theater. Reflect the roles that individuals play in the society.
Roles
Expected behavior for certain positions in the society that comes with certain expectations
Personal and Collective Unconscious
Location of our innate tendencies
Shadow`
The archetype of darkness and repression, represents those qualities we do not wish to acknowledge but attempt to hide from ourselves and others.Complete opposite of the ego and considered as the “Gatekeep to the unconsious”.
First Test of Courage
The continous strive to know one’s shadow is known as the ___. To come to grips with the darkness within ourselves is to achieve the “realization of the shadow”
Egocide
Compromising and sacrificing the things in your ego so that you can come to know about your shadows.
Anima
A man’s repressed or underdevelop feminine qualities (man’s inner woman). It is demonstrated as emotionality in males and is interpreted as eros, or the principle of relatedness
Animus
A women’s repressed or undeveloped masculine qualities (woman inner man). Demonstrated as dominance or power in females.
Paternal Logos
Sudden desire for power (e.g. control freak)
Falling in Love
What is the most common and potentially healthy instances of projection of the animus/anima?
Second Test of Courage
Integration happens when you come into terms with the repressed masculine or feminine side
Great Mother
It is a pre existing concept of a mother that is always associated with both positive and negative feelings. Derivative of the anima.
Fertility and Nourishment and Power and Destruction
The great mother represents two opposing forces
Wise Old Man
The archetype for wisdom and meaning. Further symbolizes humane preexisting knowledge of the mysteries of life.
Hero
The archetype that is represented in mythology and legends as a powerful person sometimes part god, who fights against great odds to conquer or vanquish evil in the form of dragons, monsters, serpents, or demons.
Self
It is inherited tendency to move toward growth, perfection, and completion. AKA the archetyoes of the archetypes.
Mandala
It symbolizes the symmetry and the amalgamation of the archetypes and the totality of personality.
Causality
A dynamic aspect of our personality that suggests present events stem from past experiences.
Teleology
A dynamic aspect of our personality that suggests how present events are motivated by goals and aspirations for the future that direct a person’s destiny.
Progression
A dynamic aspect of our personality characterized by how our adaptation to the outside world involves the forward flow of psychic energy. This inclines a person to react consistenly to a given set of environmental conditions.
Regression
A dynamic aspect of our personality characterized by how our adaptation to the inner world relies on backward flow of psychic energy. The necessary backward step in the sucessful attainment of a goal. Commonly exemplifies during mid-life crisis
Attitudes
An aspect of personality which constitutes our predisposition to think, act, or react in a characteristic direction
Tripartite theory of Attitudes
Cognitive, Behavioral, and Affective
Introverted
Psychic energy is always derived from inside. It is oriented towards the inside, becoming more subjective.
Extraverted
Psychic energy is always derived from outside. oriented towards the object, making it objective.
Psychological Functions
The different ways of perceiving both the external real world and the inner world
Rational
A psychological function that is guided by logic and reason (these perceptions will inform you in decision making)
Nonrational
A psychological function that is guided by sensing
Thinking
It is the production of a chain of ideas through logical intellectual activity. It is concerned with objective truth, judgement, and impersonal analysis. The highest form of judgement, but is not the goal.
Introverted Thinking
Subjective Thinking. Free of the opinions of others and internal reasoning that leads to detachment from reality.
Extraverted Thinking
A type of thinking characterized by reliance on concrete thoughts and strict accordance with societal rules: “Rigid and cold”
Introverted Thinking
The type of thinking wherein interpretation is controlled more by internal meaning than objective facts and is concerned with privacy (“stubborn, aloof, arrogant, and inconsiderate”)
Feeling
Evaluation of idea or event. Value judgement which helps you make decisions.
Introverted Feeling
This type of feeling uses subjective perceptions to make value judgements and is capable of deep emotions but avoid any outward expression of it; “withdrawn, cold, self-assured”
Extraverted Feeling
This type of feeling uses objective data to make evaluations and uses external values and widely accepted standards of judgements
Sensing
It is the reception of external stimulus and transmission of that stimuli to perceptual consciousness. It refers to a focus on direct sense experiment, perception of details, and concrete facts.
Extraverted Sensing
A type of sensing that is largely based on objective facts ie our 5 senses
Introverted Sensing
A type of sensing observations that are not real or though internal sights and sounds (e.g. pagiging delulu)
Intuiting
Involving perception beyond the workings of consciousness. comprehend in terms of possibilities, past experiences, future goals, and unconscious processes.
Extraverted Intuition
A type of intuition where we use objective facts by past experiences (e.g. magsuot daw ng red underwear during board exam)
Introverted Intuition
A type of intuitions where we derived based on internal experiences
Thinking
What is the highest form of psychological function?
Self
This is achieved when all of the polor opposites are not in conflict; when an individual reach the perfect balance
Anarchic
A phase in childhood characterized by chaotic and sporadic consciousness. Here lies the existence of the “islands of consciousness”.
Monarchic
A phase in childhood characterized by the development of the ego. This is where logical and verbal thinking begins. Meanwhile, the islands of consciousness become larger, more numerous, and inhabited by the primitive ego.
Dualistic
A phase in childhood characterized by the divition of the ego into objective and subjective
Identity Crisis
A phenomena wherein you have already chosen an identity but you don’t want to part ways with your past identity.
Youth
A period in life characterized by increased activity, maturing sexuality, growing consciousness. And recognition that the problem-free era of childhood is gone forever
Middle life
A phase of life marked by immense potential, yet also defined by self-questioning and facing the unconscious aspects of the self.
Self-Realization or Individuation
The psychological rebirth characterized by the process of becoming an individual or whole person