Week 4 - Skeletal Congenital, Hereditary and Degenerative
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering scoliosis basics, structural vs non-structural, congenital and neuromuscular scoliosis, imaging and bone-age related topics, NAI, and osteogenesis imperfecta.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
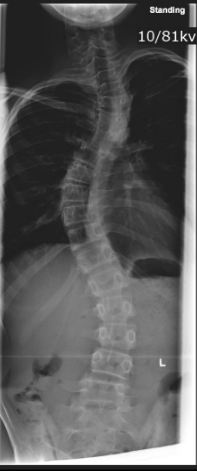
What is scoliosis?
Lateral spinal deviation >20°, often with rotation causing rib prominence.
What proportion of scoliosis is structural vs non-structural?
≈80% structural, 20% non-structural (functional).
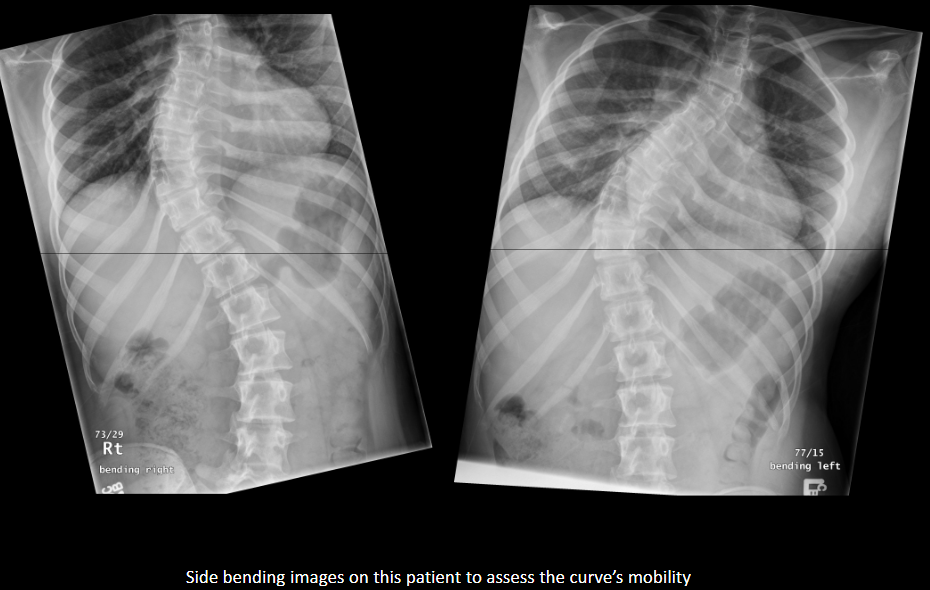
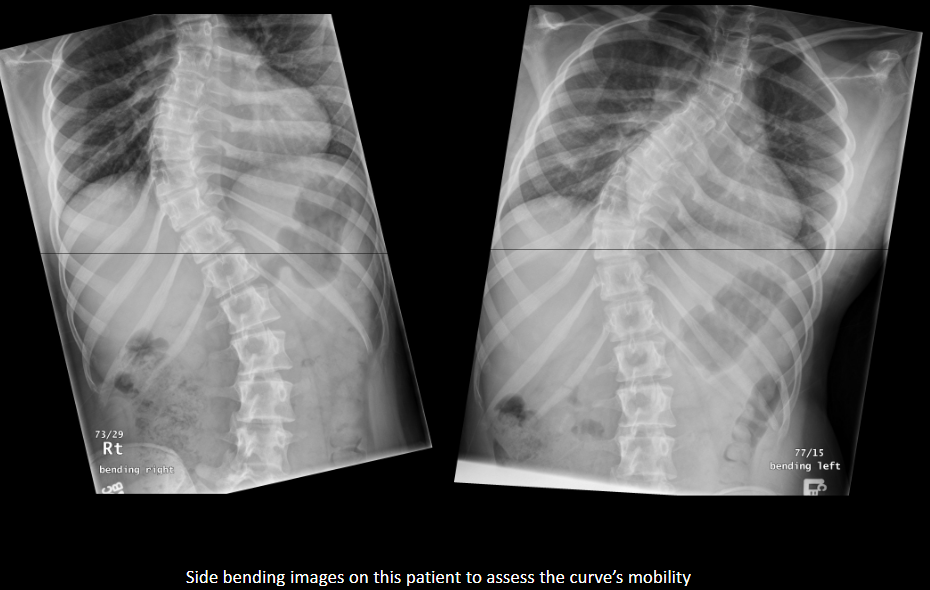
How can you distinguish structural from non-structural scoliosis on side-bending?
Structural scoliosis does not correct with side bending; non-structural scoliosis to a reasonable extent corrects.
List structural scoliosis subtypes.
Idiopathic, congenital, neuromuscular, radiation-induced, traumatic, degenerative, miscellaneous (tumors/surgery).
What is the most common structural scoliosis type?
Idiopathic.
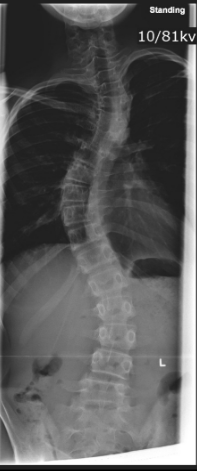
What is the key vertebral anomaly in congenital scoliosis?
Hemivertebra; may have fused or missing ribs.
Why can congenital scoliosis impair breathing?
Thoracic rib fusion → thoracic insufficiency limiting lung growth.
What conditions can cause neuromuscular scoliosis?
Cerebral palsy, spinal cord trauma, muscular dystrophy.
When does neuromuscular scoliosis often present?
11–16 years.
List two scoliosis complications.
Cardiopulmonary compromise; degenerative arthritis.
What assessment quantifies curve magnitude?
Cobb method.
Three approaches to assess skeletal maturity for scoliosis planning?
Left hand/wrist; vertebral ring epiphysis; iliac crest apophysis fusion.
Brace used and its indications for scoliosis?
Milwaukee brace; for flexible, skeletally immature patients with 20–40° progressive curves.
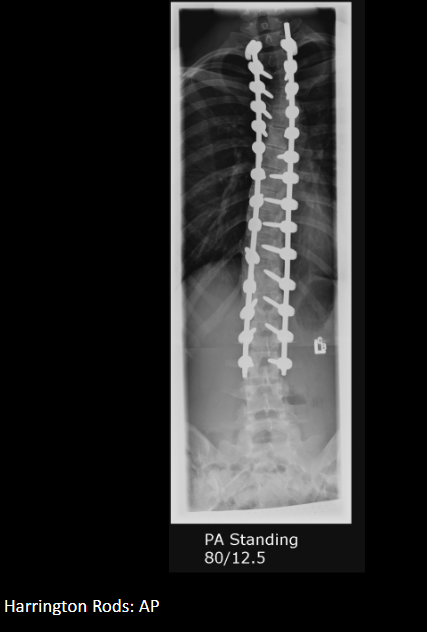
Surgical threshold for curve size?
Typically >40° or rapid progression.
Two common surgical implants for scoliosis.
Harrington rods; Dwyer screws/wires.
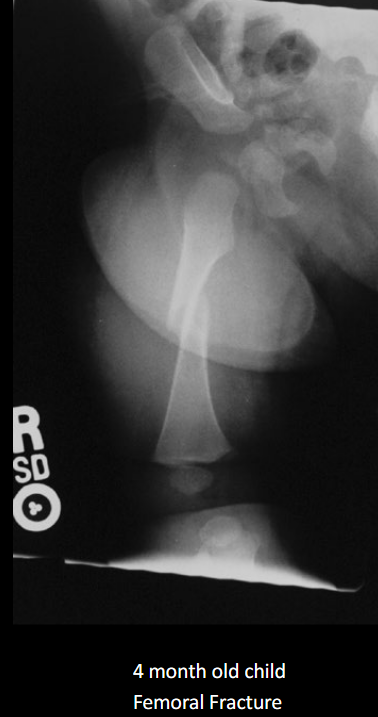
Define NAI.
Non-accidental injury/trauma; deliberate physical harm to a child.
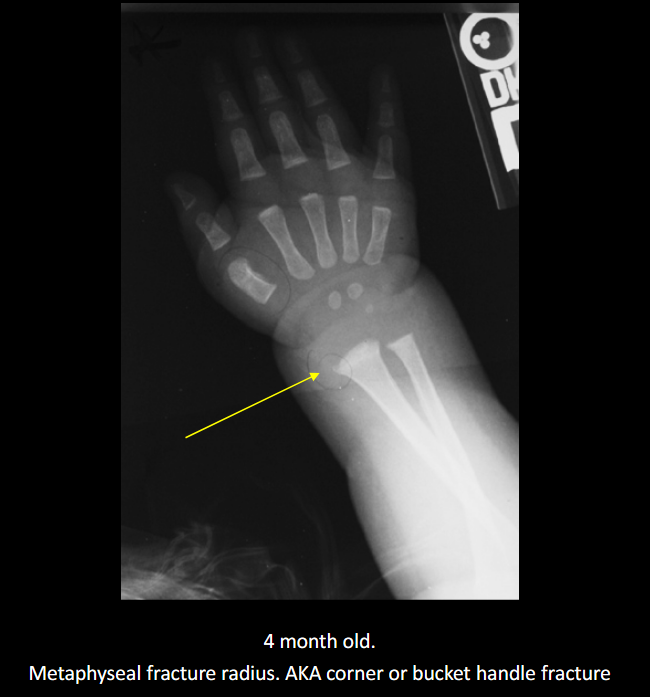
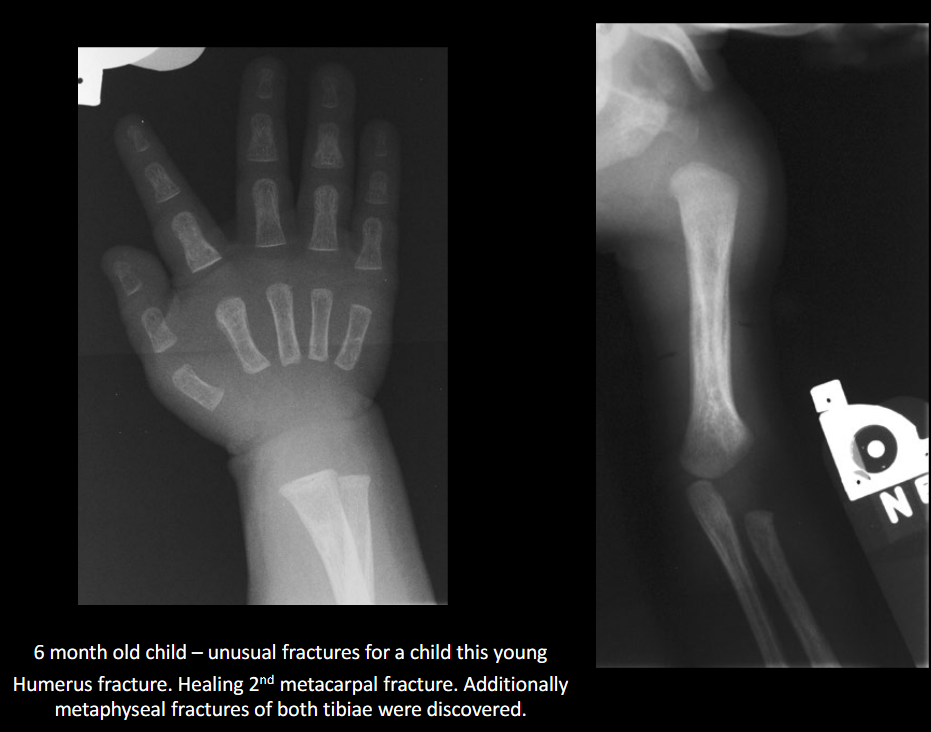
Classic metaphyseal injury in NAI?
Corner/bucket-handle fracture.
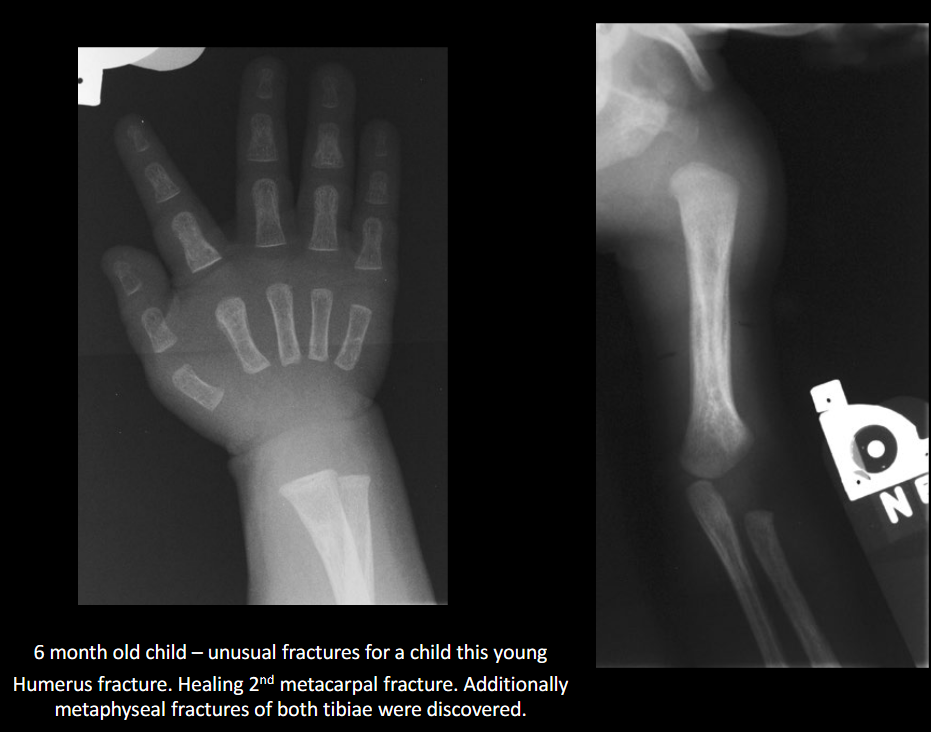
Why are posterior rib fractures suspicious for NAI?
From squeezing the thorax.
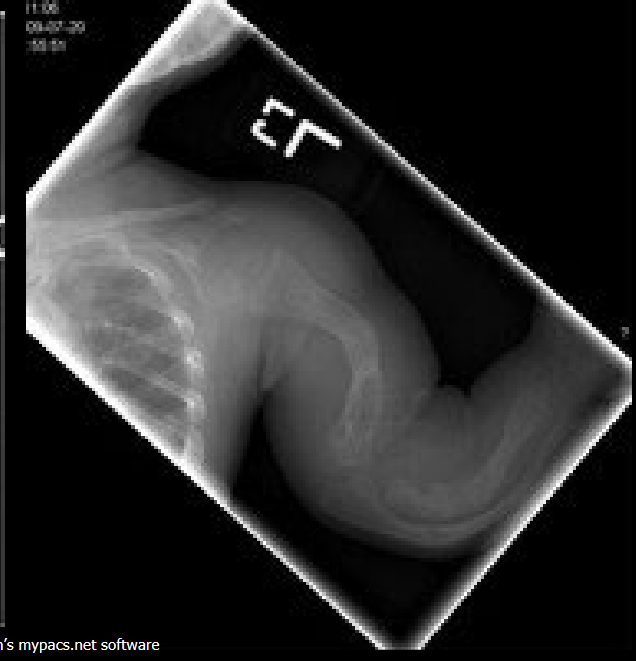
Preferred initial imaging in suspected NAI?
Skeletal survey (not a ‘babygram’).
Common intracranial finding in NAI on CT?
Subdural hematoma.
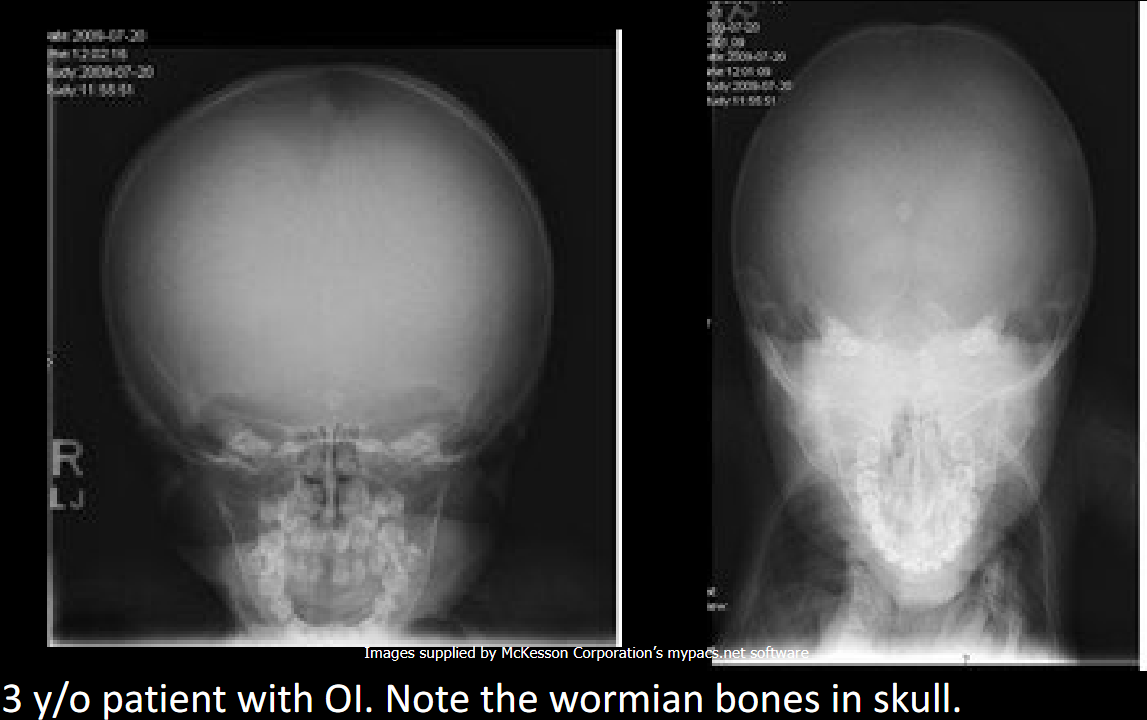
Define OI.(Osteogenesis Imperfecta)
Hereditary brittle bone disease due to collagen deficiency.
Two hallmark clinical signs of OI. (Osteogenesis Imperfecta)
Blue sclerae; joint laxity/muscle weakness.
Radiographic skull findings in OI.
Widened sutures and wormian bones.
Bone quality appearance in OI.
Marked osteoporosis with thin cortices.
Handling considerations in OI.
Gentle transfers, padding, lower kVp; beware confusion with NAI.
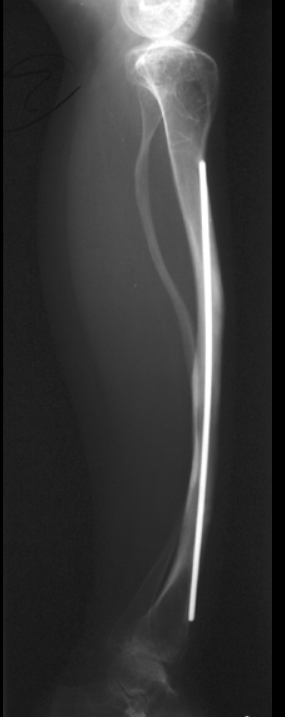
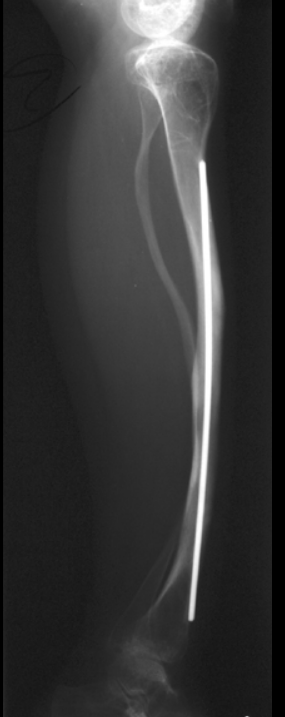
Long-bone stabilization device in OI.
Telescoping (extendable) rods.
Common cause of death in severe OI.
Respiratory failure (and susceptibility to pneumonia/asthma).
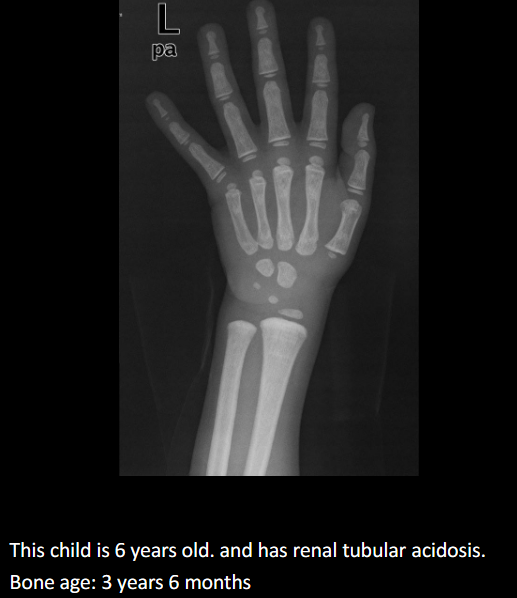
Purpose of bone age studies.
Assess growth/endocrine issues, stature, puberty timing, predict adult height.
Define advanced bone age.
2 years ahead of chronological age.
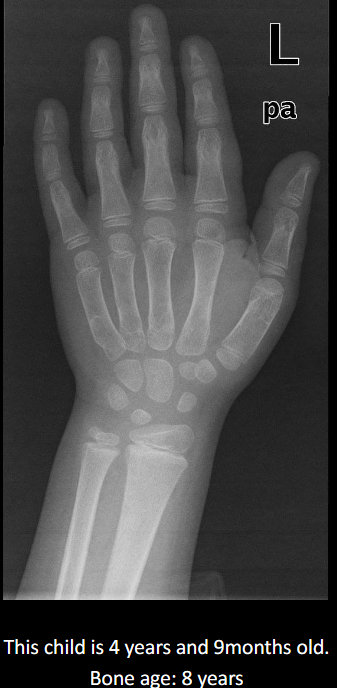
List causes of advanced bone age.
Increase sex steroids, precocious puberty, endocrine disorders, CAH, familial tall stature, obesity.
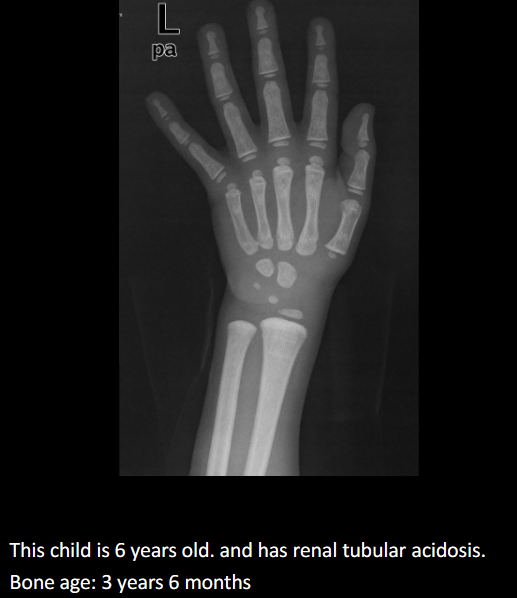
Define delayed bone age.
2 years behind chronological age; aka CDGP.
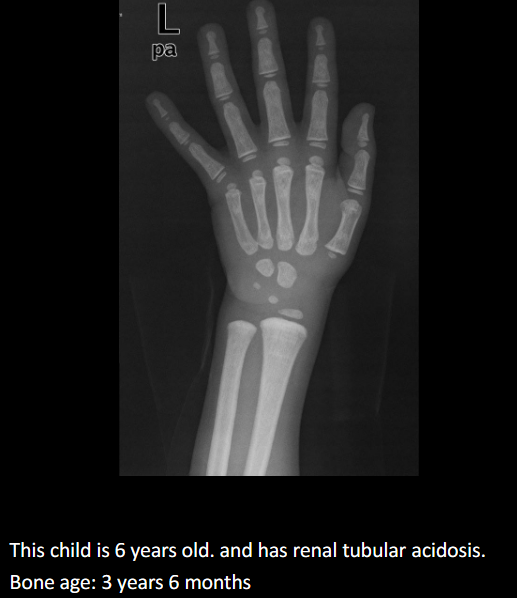
List causes of delayed bone age.
↓ hormones; systemic (heart/urinary/digestive), chromosomal, familial short stature, idiopathic.
Typical stature in advanced bone age.
Tall for age.
Typical stature in delayed bone age.
Short for age.
Standard imaging and method for bone age.
PA hand & wrist, Greulich & Pyle comparison.
Alternate projection under age 3.
AP knee (fun fact from PPT).
Earliest ossifying carpal bones (examples).
Capitate 1–3 months, Hamate 2–4 months.
Late ossifying carpal bone.
Pisiform 8–12 years.
Distal radius/ulna metaphyseal timing.
Radius ~1 year; Ulna 5–6 years.
Professional stance in NAI cases.
Remain neutral, non-judgmental; follow code of ethics.