16 Macroeconomic equilibrium
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
New classical
increase in AD
decrease in AD
if increase in AD, with SRAS and and LRAS, inflationary gap
level of output greater than level of output
only possible in short run, SRAS shifts back, above previous
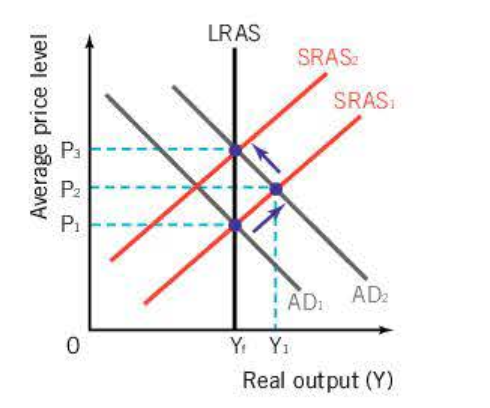
If decrease in AD, deflationary gap
price of FOP’s fell, firms COP fall, sras shifts outwards
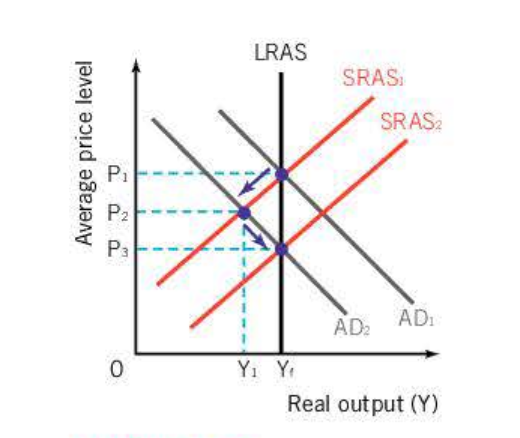
Keynesian perspective - inflationary/defaltionary
AS can be perfectly elastic - due to spare capacity
Deflationary gap whereby level of AD not sufficient to buy up potential output, that could be produced at full employment
Three categories of public gov spending
capital - spending that adds to capital stock of economy
current - tend to be ongoing, eg wages
transfer - benefits paid to people
How do government get income
tax and indirect taxes
social security payments
corporate taxes
tariffs
gov owned businesses
What is fiscal policy
defined as set of government’s policies relating to its expenditure and taxation rates
expansionary vs deflationary fiscal - AD
expansionary - increase ad
deflationary - decrease AD
Aims of fiscal policy
maintain low and stable rate of inflation
low unemployment rate
stable economic environment for growth
reduce fluctuations is business cycle
promote equitable income distribution
external balance between export revenue and import expenditure
What is expansionary fiscal policy? and effect
if want to encourage increase C, lower income tax
encourage investment, lower corporate taxes, more profit, increase investment
increase g spending
inflationary pressure, APL increase
trade off between lower unemployment and increase prices
How have fiscal policy helped before
in great depression, helped with deep recession
G expenditure can be used to target specific sectors of the economy
Constraints of fiscal policy
Time lags
Changing tax rates takes time
even after implemented, takes time for AD to change - people have to recognise and react
Political pressure
often influenced by political factors, rather than economic
Sustainable debt
may have to run budget deficits
accumulate into unsustainable debt
effect of net exports
expansionary, may lead to increase in IR
lead to increase in exchange rate (exports less attractive, imports more)
fall in (x-m)
Crowding out
if G spending increases, through increased borrowing, monopolise funds
firms don’t have access to funds, and this investment drops
less shift in AD
Increase in D for borrowing, IR increases thus contractionary monetary effects
Inability to achieve specific targets
large changes, effect may areas of economy
difficult to predict outcome
What is gov debt
It is the accumulation of all the budget deficits over the years and represents the total amount of money that the government owes to its creditors, both domestic and foreign.
How is gov debt expressed
normally expressed as a percentage of GDP
shows the percentage of annual national output that the government owes, both domestically and abroad
What does deficit spending by gov drive
Drives economic growth
Debt servicing costs
amount of money needed to make payments on the principal and interest on a loan in a given time period
Relationship between gov debt and servicing costs
As gov debt increases, so do servicing costs
Bad effects of gov debt.
Lead to crowding out of private investments
Interest payments increase as a % of G budget expenditure, damaging effect on other areas of spending, benefits and services from gov must be cut
require higher rates of taxation to fund expenditure
decrease ability of gov to respond to emergencies, gov has to borrow. If debt too big, fewer fiscal options available
What effect does G spending have to fix deflationary gap
Financial increase in AD be greater than amount of spending
What happens to injections in economy
multiplied by economy, people receive a share of the income and spend part of what they receive
What happens to the income
goes back to gov as form of tax
some saved
spent on foreign goods and services
spent on domestic goods/services
goes to income for others, happens in rounds
MPC
Marginal propensity to consume, income spent on domestic goods and services
What happens when all the money has been respent
final addition, gives value of the contribution that the injection had on national income
MPW is the value of MPS + MRT (Marginal rate of taxation) + MPI (MP import)
What can be used for value of multiplier
MPC or MPW (Marginal propensity to withdraw)
Formulas

Any change in withdrawls =
change multiplier
What must gov estimate to fill deflationary gap
estimate gap between equilibrium output and full employment
value of multiplier
What is monetary policy
official policies governing supply of money and level of interest rates in an economy
expansionary - increase AD
deflationary - decrease AD
What do commercial banks set
interest rates
What is the central bank
government bank
ultimate control of money supply in an economy
What is the central bank responsible for
mostly responsible for maintaining low and stable rate of inflation in economy
Goals of monetary policy
maintain low and stable rate of inflation
low unemployment rate
stable economic environment for growth
reduce fluctuations is business cycle
promote equitable income distribution
external balance between export revenue and import expenditure
What is expansionary monetary policy
increase AD
banks might lower base rate of interest
reduces cost of borrowing, increase C and I
Increase supply of money
lower its price, lower rate of interest, since IR is the price of money
increase I and C
Effect on economy of expansionary monetary policy
inflationary pressure
increase in real output, increase in national income, economic growth, decrease unemployment
Strength of monetary policy
Relatively quick
No political intervention
generally adjusted by central bank, no political processes to be approved
Absence of “crowding out“
Ability to make small changes
more precise than fiscal
Limitations of monetary
time lags
Can take months, by then economic factors may have changed, no longer applicable
Ineffectiveness when IR are low
cannot continuously lower interest rates. When approach zero no more cuts available
low consumer and business confidence
How do commercial banks create money
credit creation
occurs when lend money to consumers, more than they get, they lend out
money multiplier
Money multiplier related to min. reserve requirement
& calcularion
percentage of deposits than commercial banks are legally required to hold in reserve, to meet cash requirement of depositor
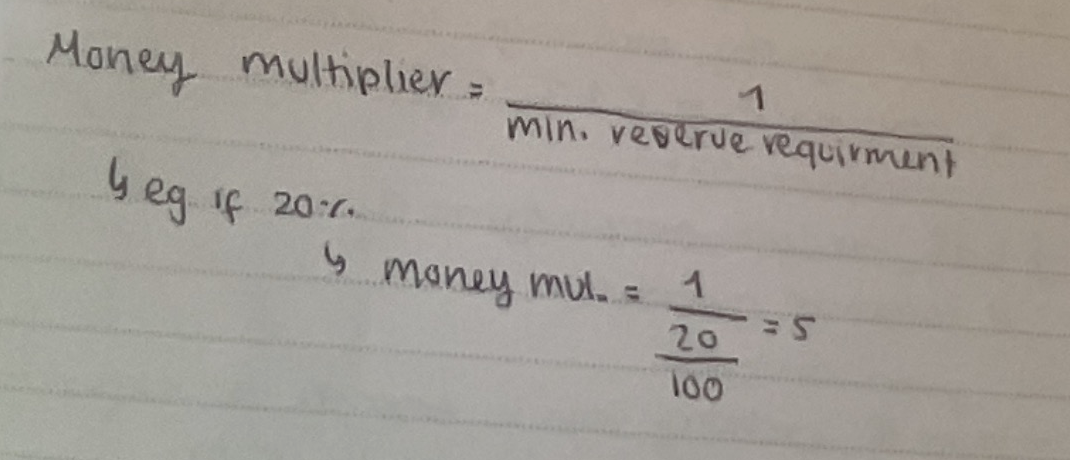
Tools available for G to control money supply
minimum reserve requirement
larger them MRR, smaller the multiplier
if gov wants to reduce money supply, increase MRR
reduce ability of banks to create credit, reduce money supply
increase IR, thus lower AD
If gov wants to increase MS, reduce MRR
ability of banks to create credit, increase money supply
lower interest rate and increase AD
open market operations
involve buying and selling gov, securities by central bank
gov security is a bond. offers interest on nominal value of bond. very low risk
changes in central bank min, lending rate
when they raise it: increases the cost of borrowing. reducing c and I
lower: encourage investment and C so increase AD
Quantitive easing
CB injects new money into economy by purchasing assets, mostly securities, from commercial banks and other financial institutions with newly created electronic cash
expansionary effects:
increase reserve of commercial banks as they sell securities. Increase liquidity, encourage to lend more to firms and households
IR reduces, reduces debt: increase confidence
Lower IR, exchange rates drop, exports less expensive. imports more expensive. Increase (X-M)
What is gov security
gov security is a bond. offers interest on nominal value of bond. very low risk
Min. lending rate
the rate of interest which the central bank charges on loans and advances to commercial banks.
What is interest rate
Opportunity costs of holsing/spending money
Nominal rate of interest
Rate of interest available in money market not allowing for inflation
real rate of interest
adjusted for inflationI
If nominal IR increase
Give up large return on their savings and investment, so hold/demand less money
If nominal IR decreases
opportunity cost of spending/holding money will be less, hold/demand more money
Graph money supply
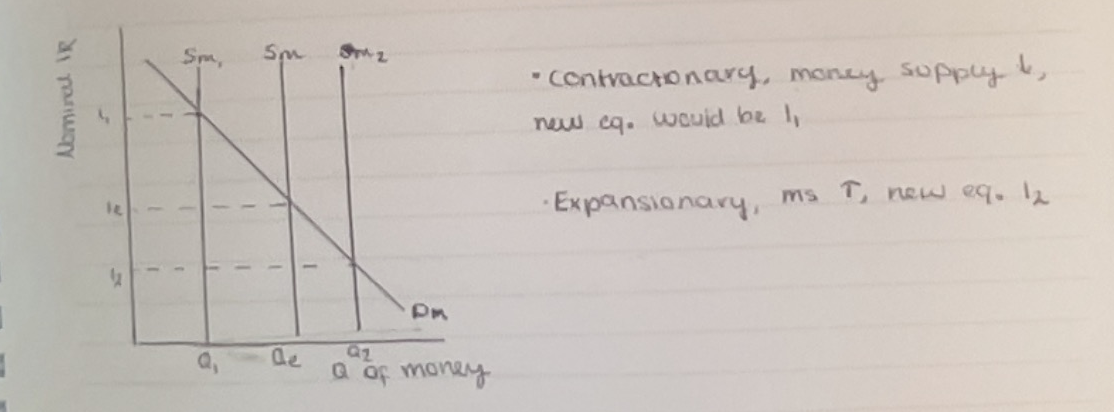
Real rate of interest equal to
and example
= nominal rate of interest - inflation rate
