CDCA OSCE
1/428
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
429 Terms
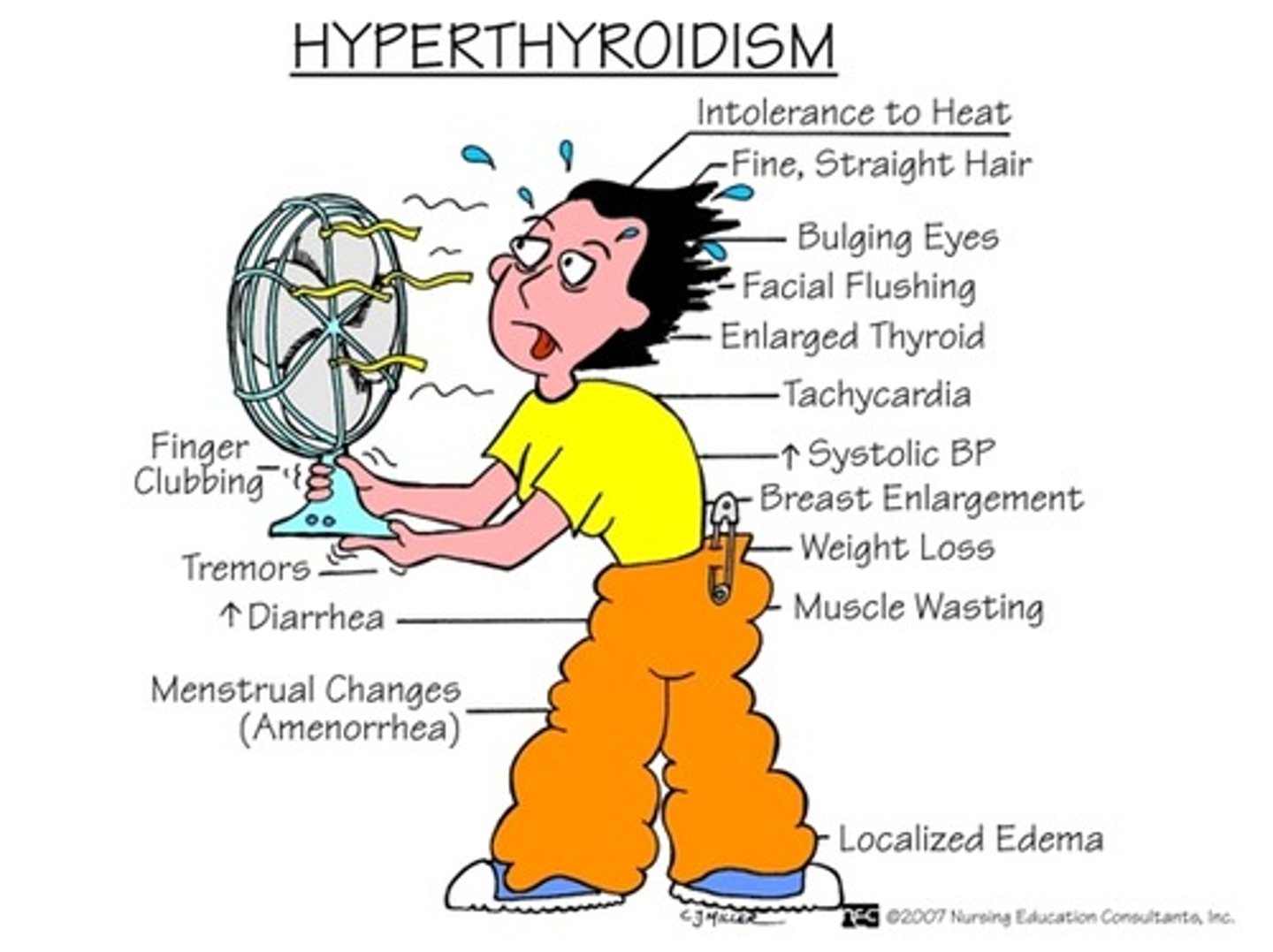
bulging eyes (exophthalmos), weight loss, and Graves disease are all due to _____
hyperthyroidism
signs/symtoms of skinny, weight loss
Graves disease
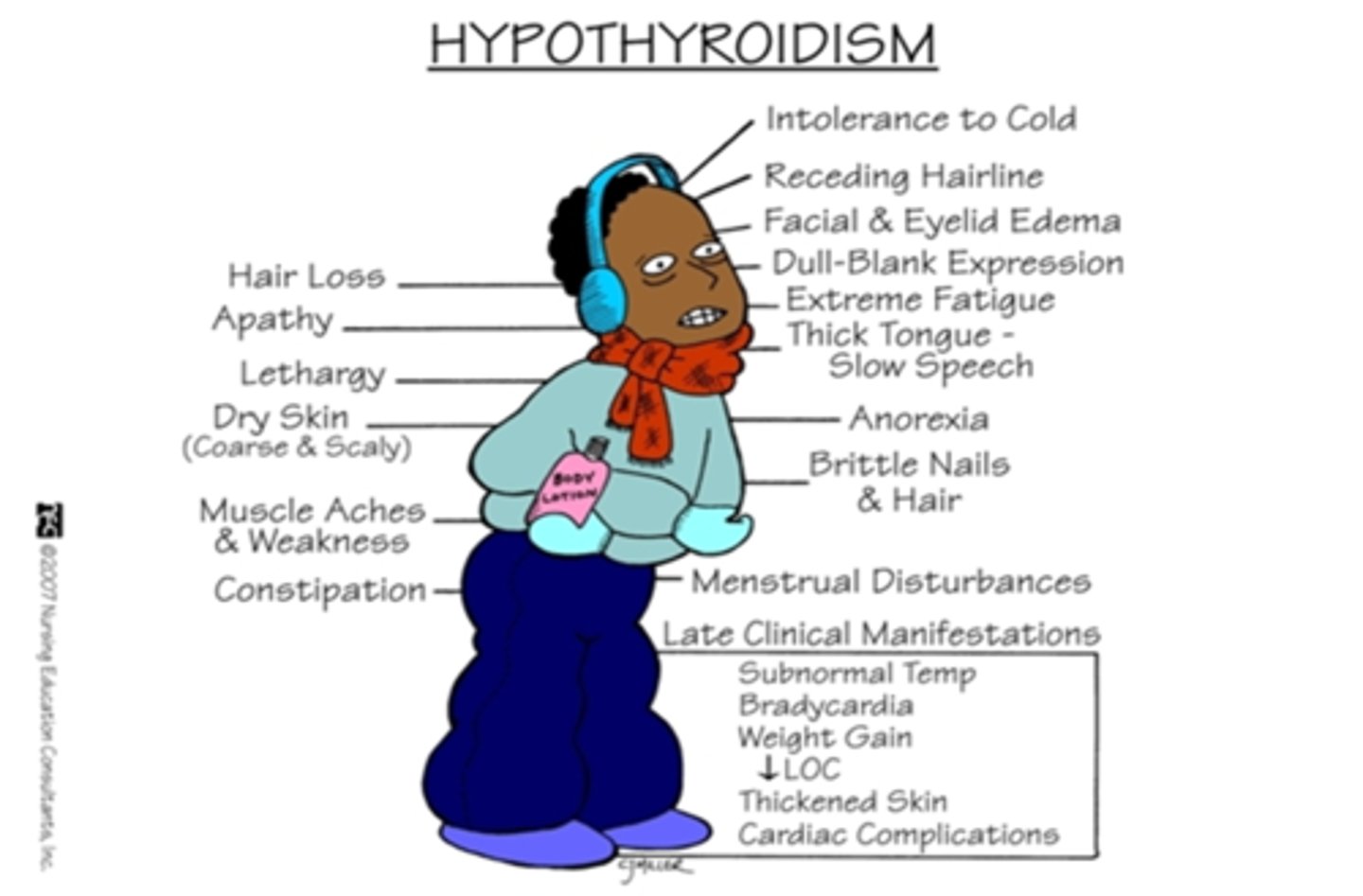
weight gain, dry hair, lower voice, feels cold
hypothyroidism
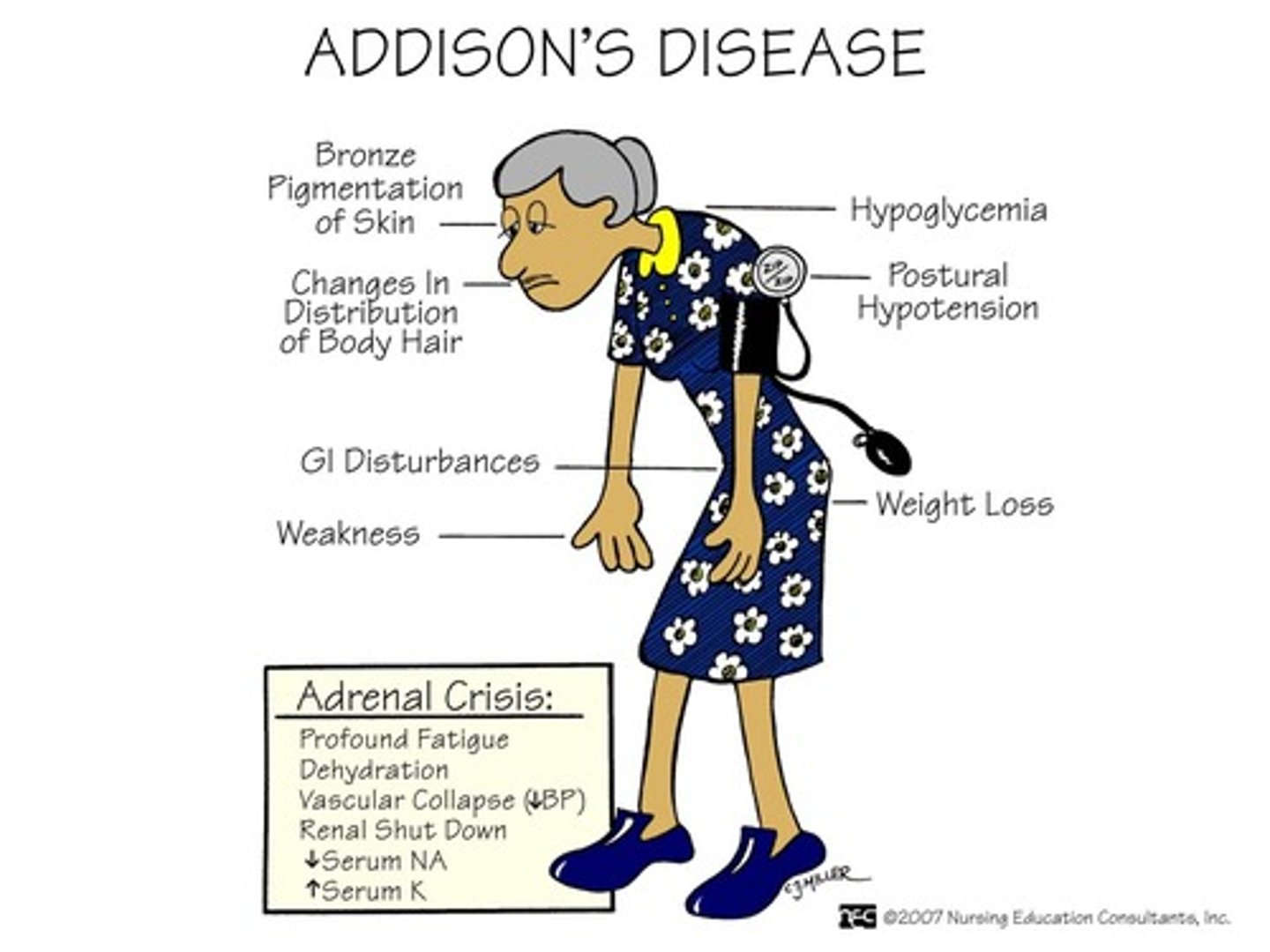
Acute adrenal insufficnecy is also known as ____disease. A patient on steroids might have an attack if not supplmeneted by ___ the steroid dose before dental treatment due to thier inability to produce extra ___ in response to stress
addisons disease
doubling the dose of steroids
cortisol in response to stress
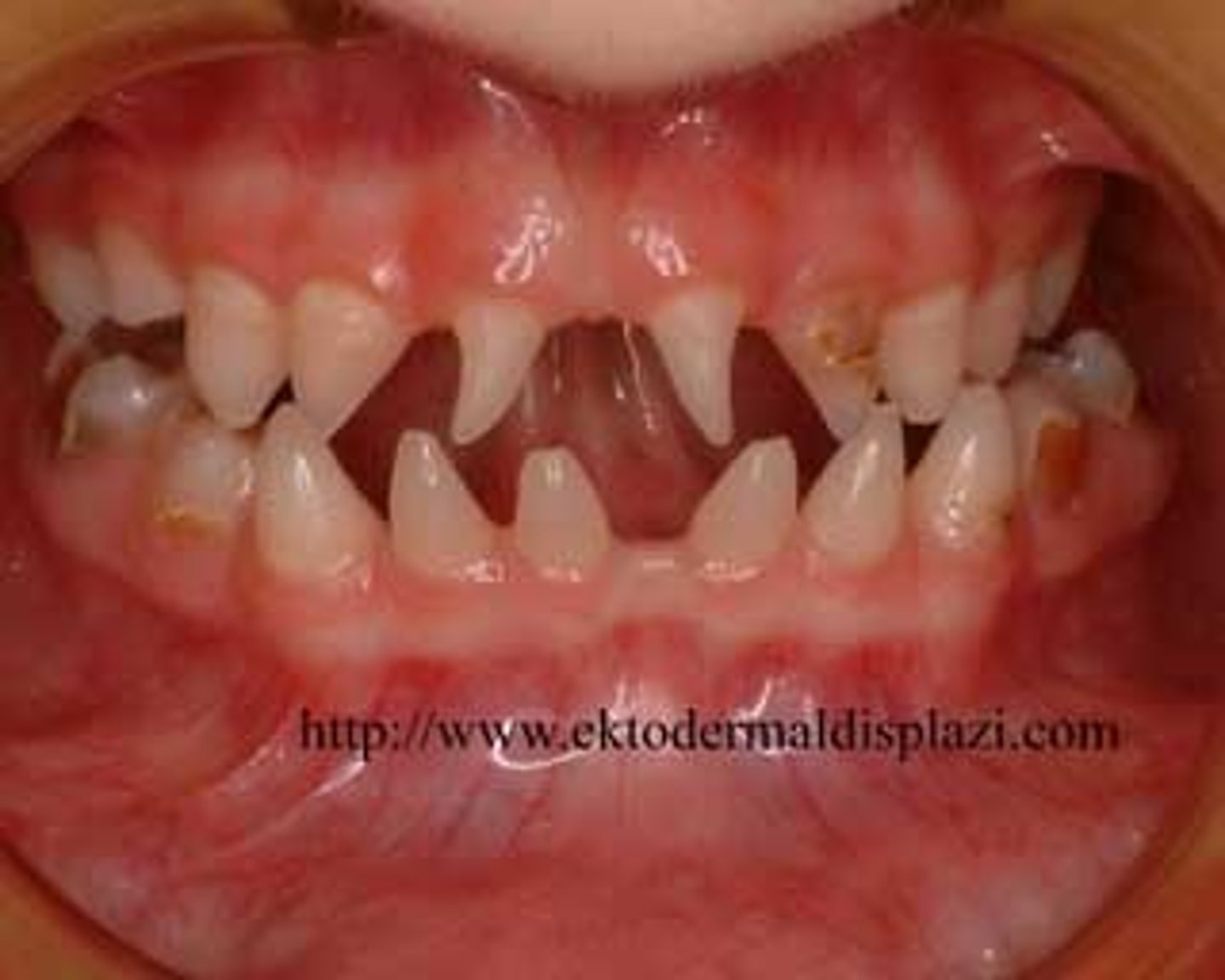
patient with reduced or missing teeth on a pan
ectodermal dysplasia
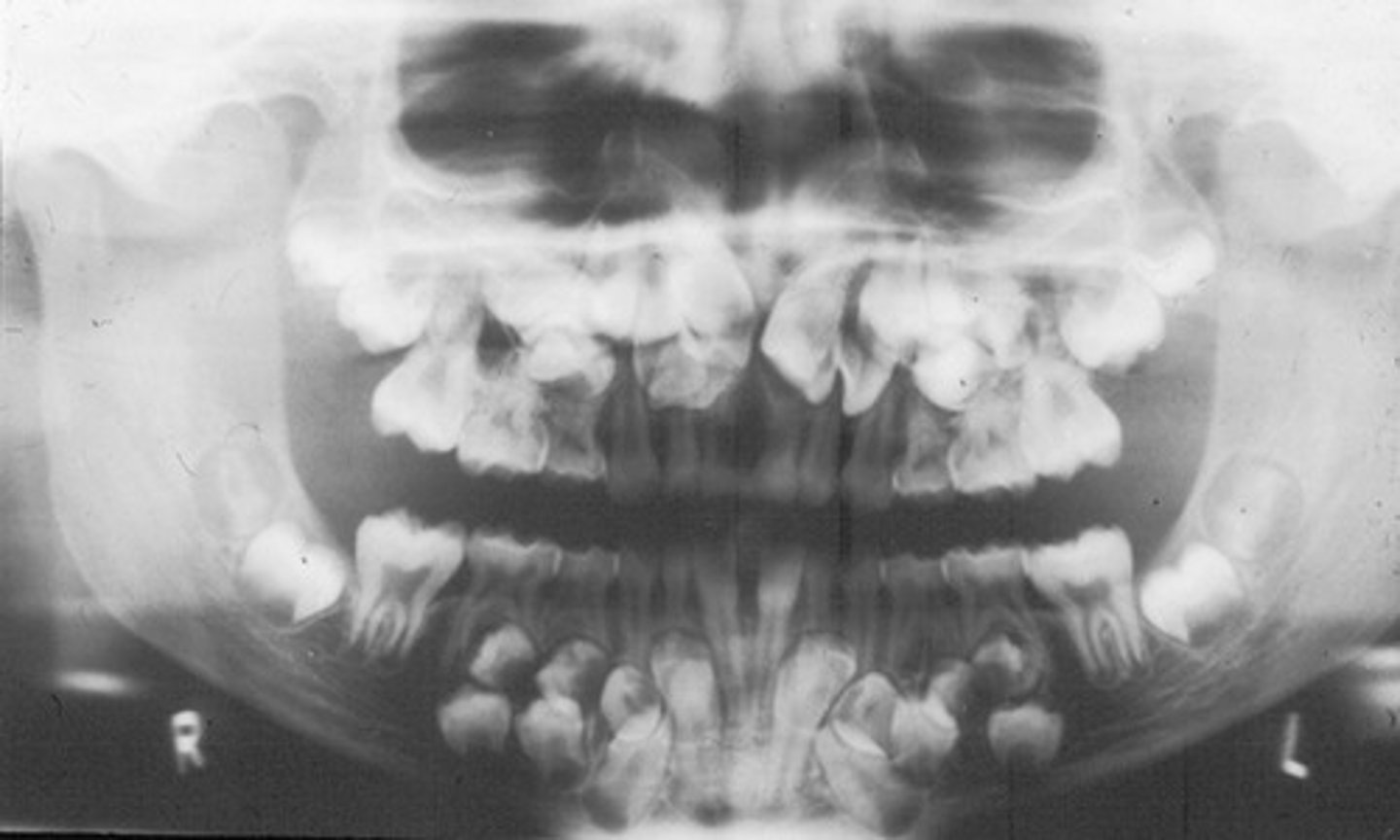
patient has supernumerary teeth (extra teeth) ... likely diagnosis?
cleiodcranial dysplasia
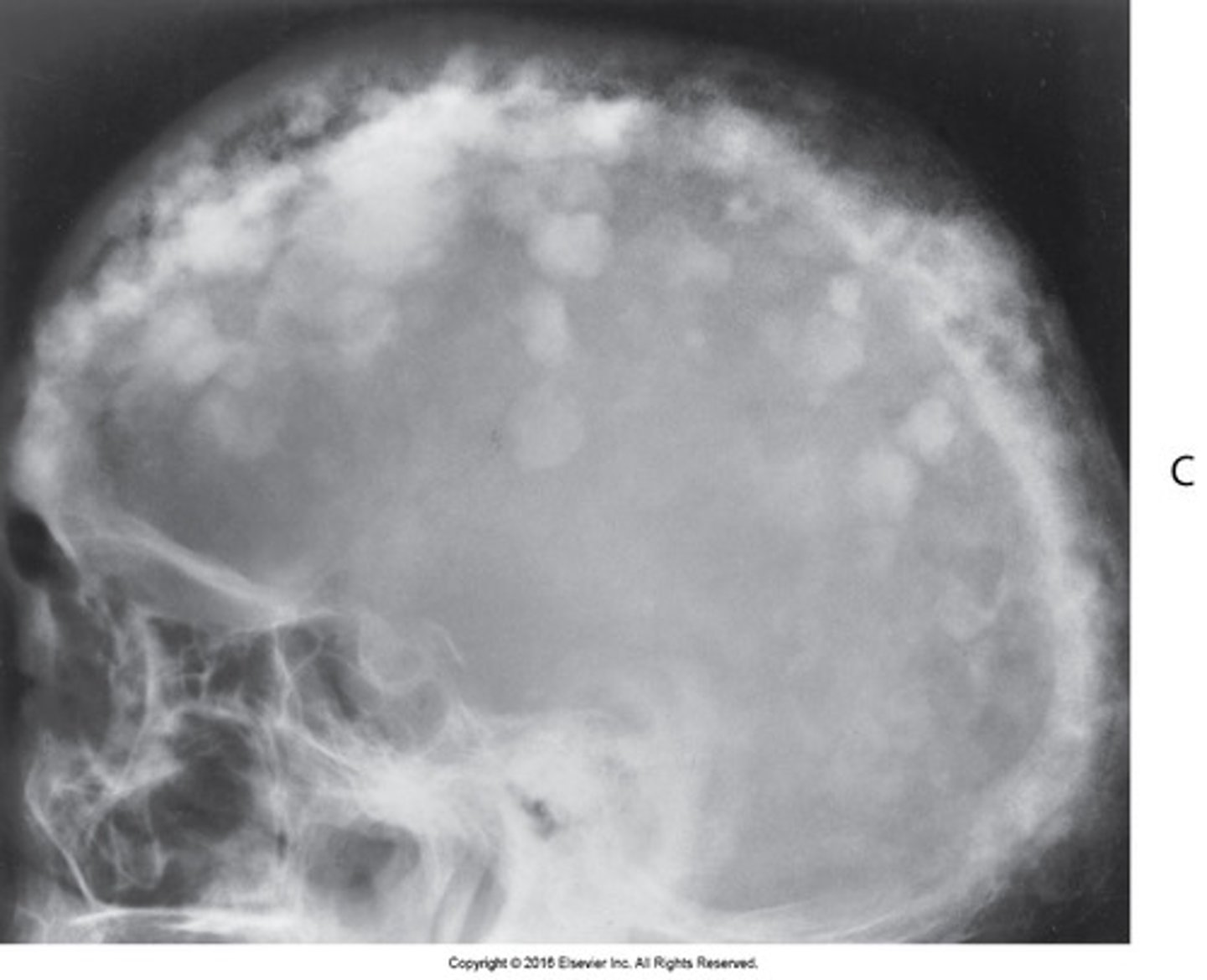
: can cause hypercementosis of the roots, generalized skull and jaw enlragment with COTTON WOOL appearance of bone
Pagets disease
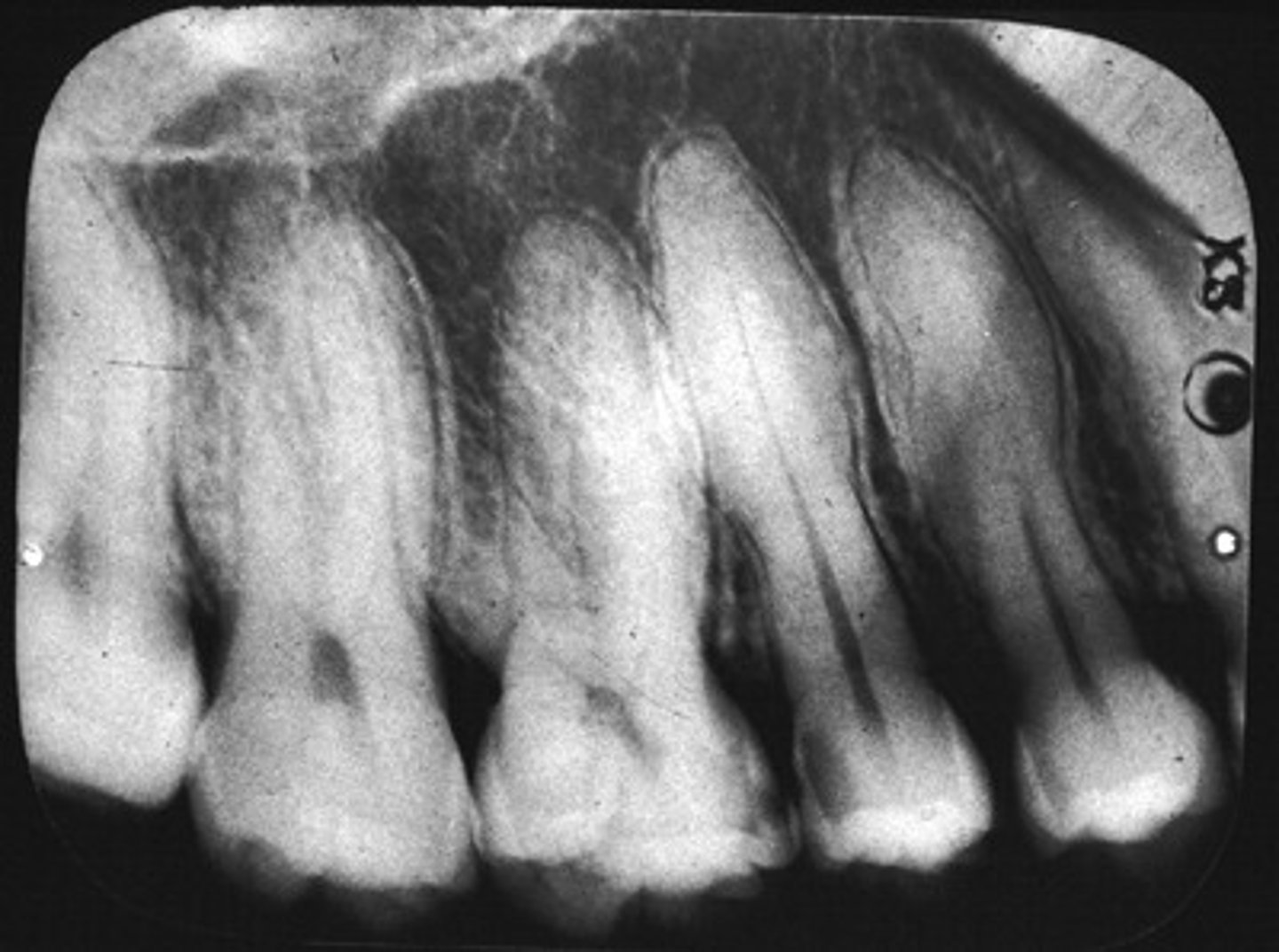
hypercementosis will follow the ____ on a PAX
PDL
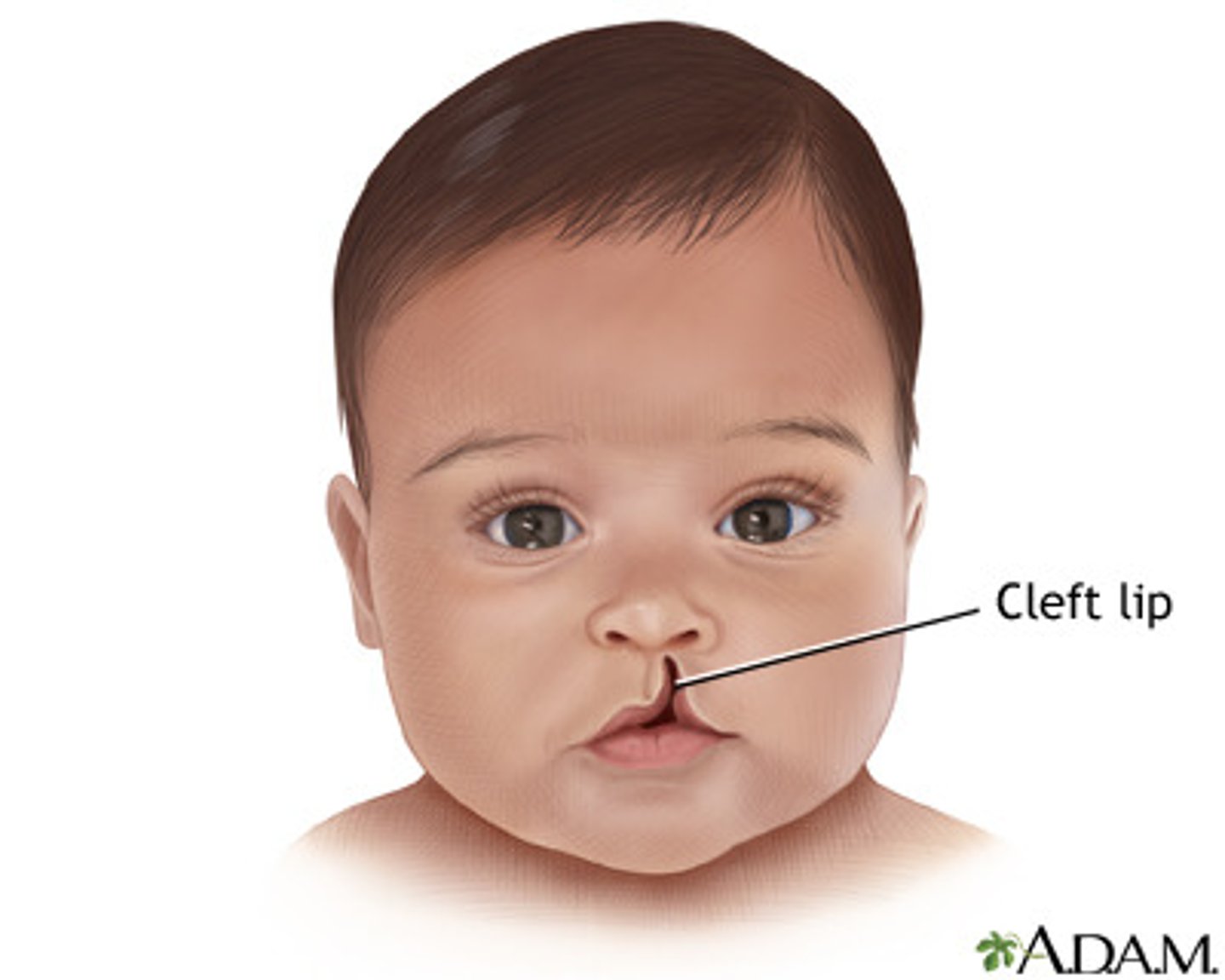
Cleft lip is defection fusion of the ____ and _____
medial nasal process
maxillary process
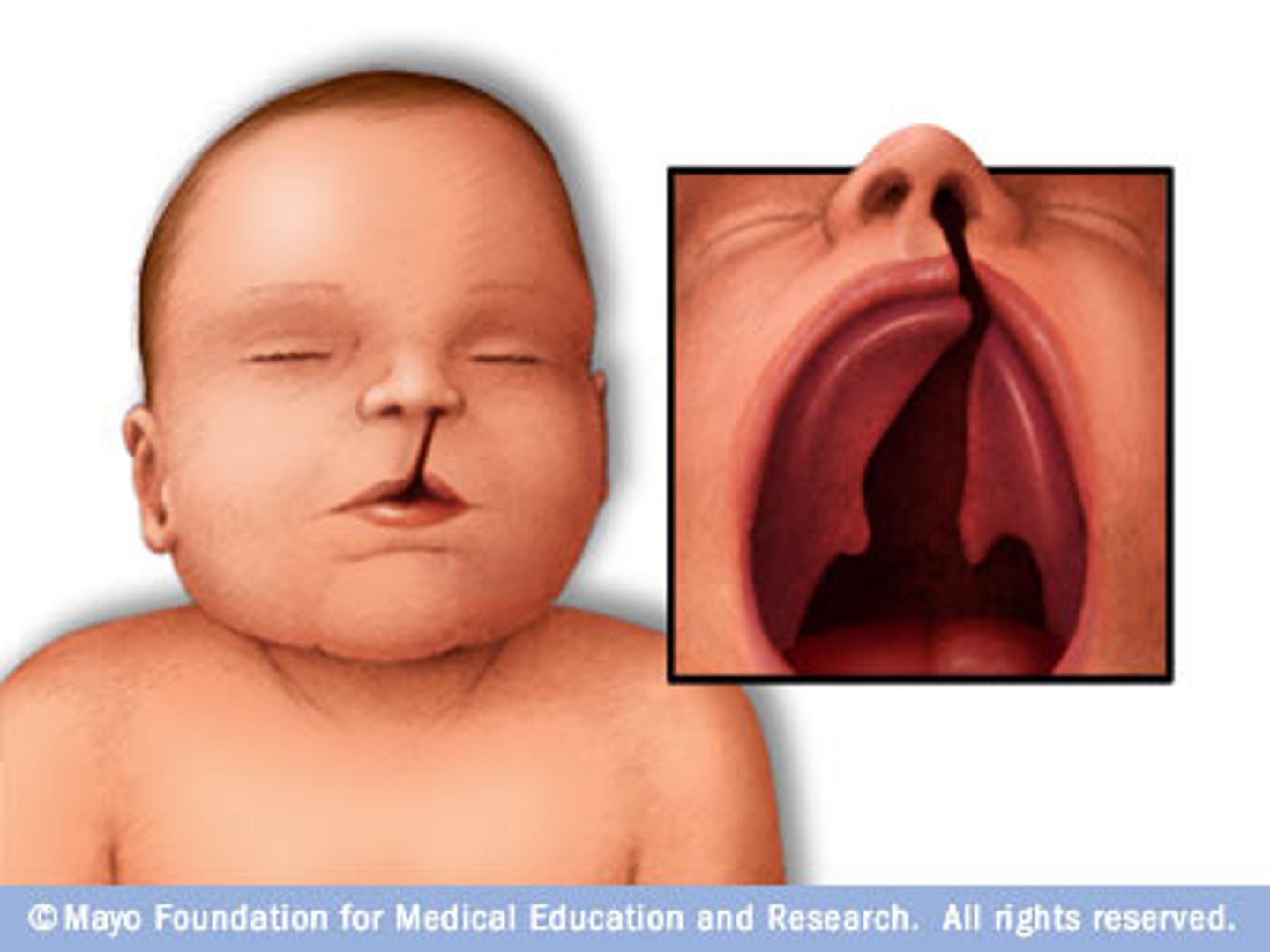
failure of the palatal shelves to fuse result in ____
BIFID UVULA
cleft palate, bifid uvula
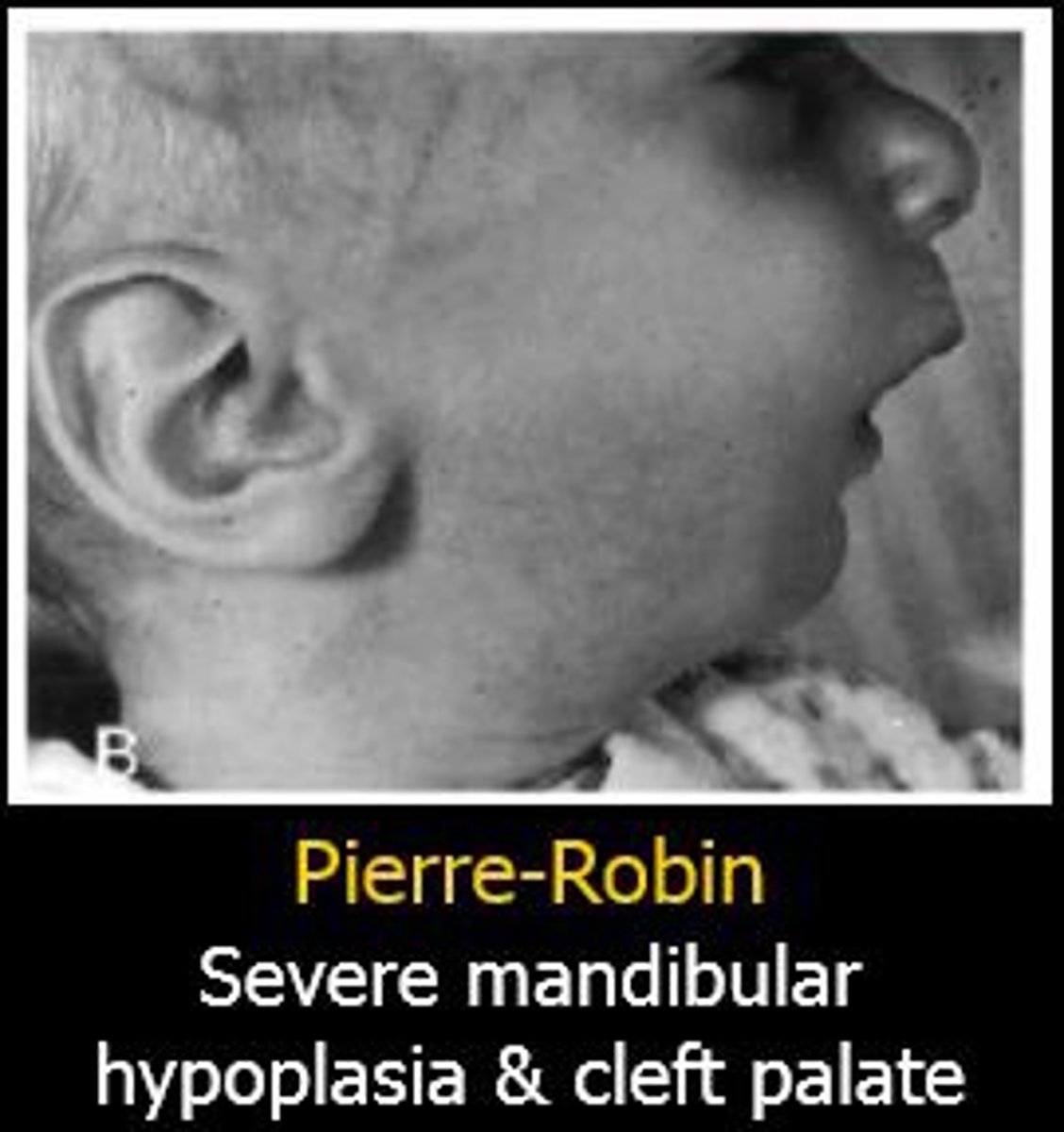
patient with cleft palate, mandibular micrognathia, glosspotopis (airway obstruction)
Pierre robin syndrome
looks like white and brown spots on the teeth
hypocalcified teeth
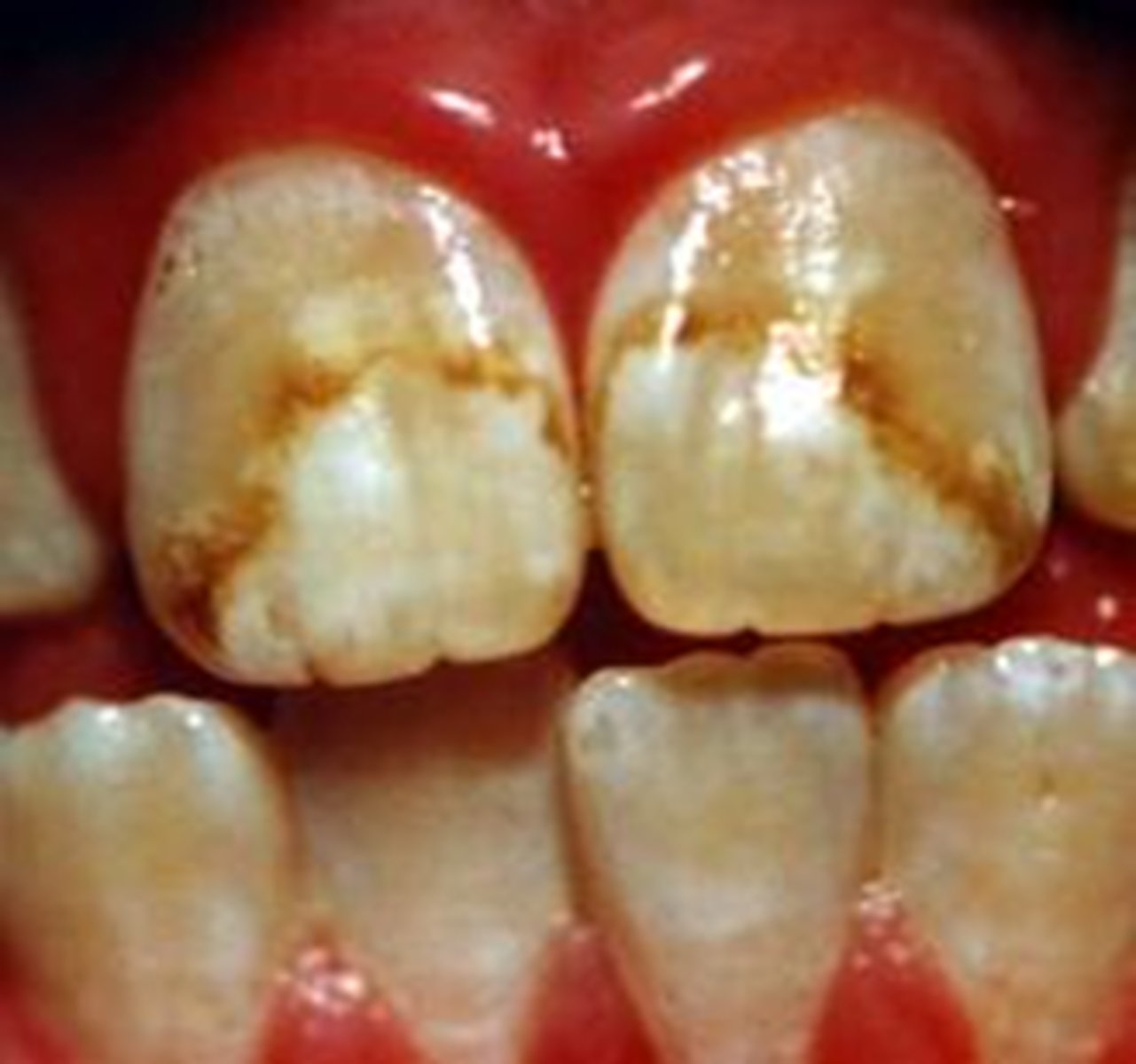
___ cannot be reversed
but microabrainsion and aching can improve aesthetics, but cannot reverse the condition
fluorosis
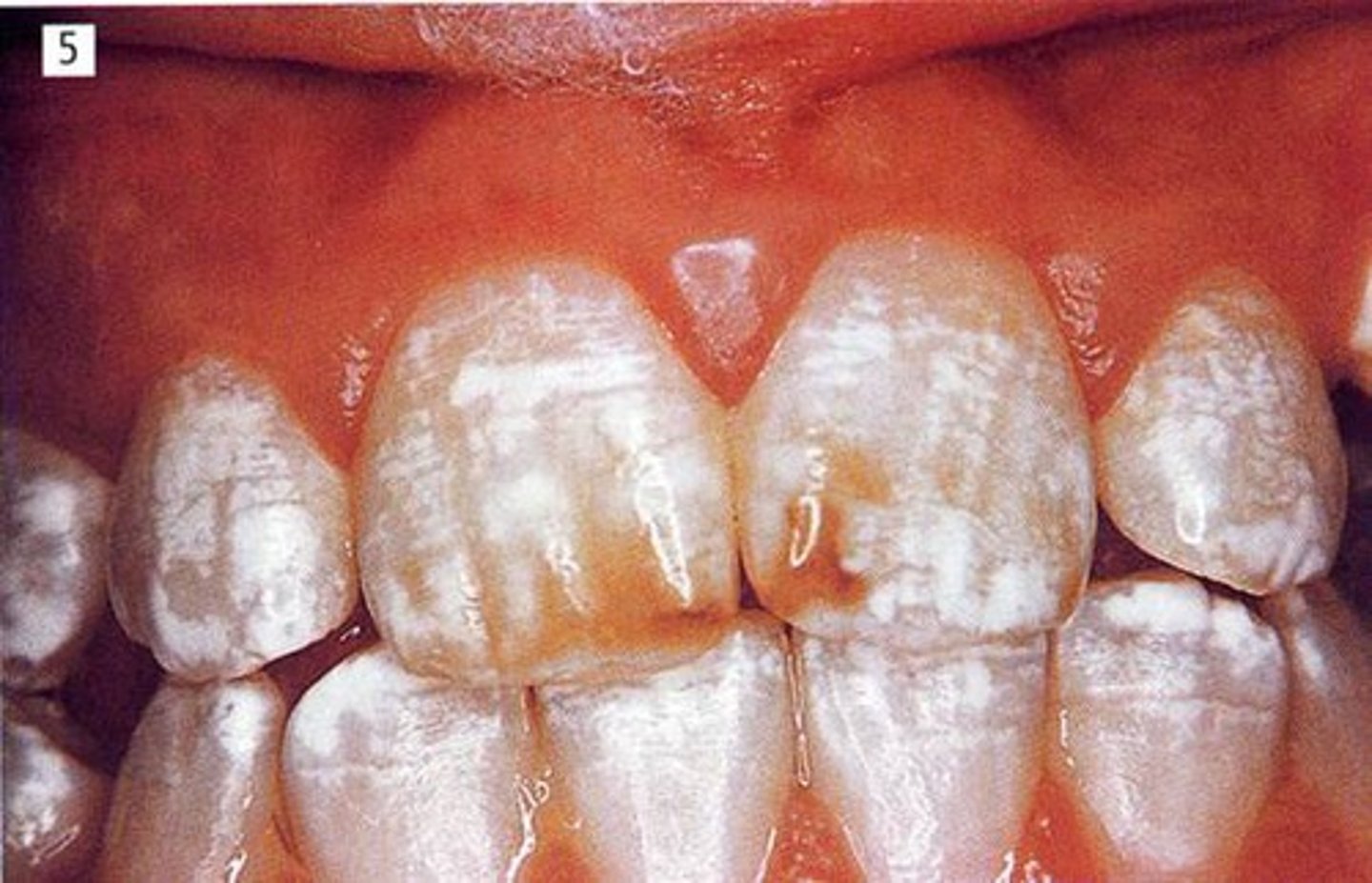
flurosis can be caued by a patient living in a region wher the fluoride content in the water is ____ppm. Normal is ____ppm
4ppm
normal is 0.7ppm
patient has no enamel on the teeth on bitewing or panx
amelognesis imperfecta
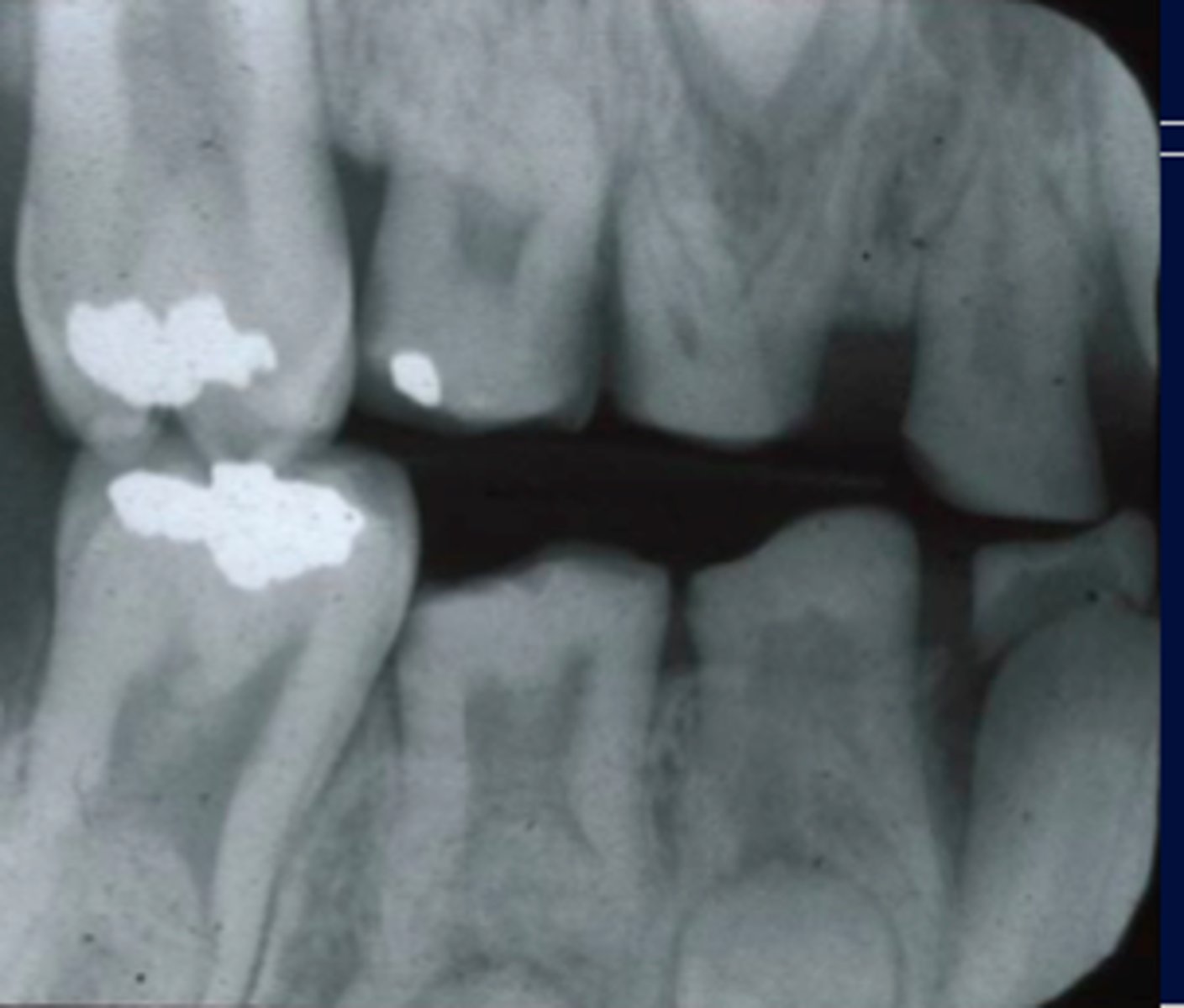
can see OBLITERATED pulp chambers on radiogrpahs and teeth have a TRANSLUCENT or opalescent hue (greyish or blue)
also known as osteogenisis imperfect
associated with collagenn maturation problem, non systemic
dentogenisis imperfecta
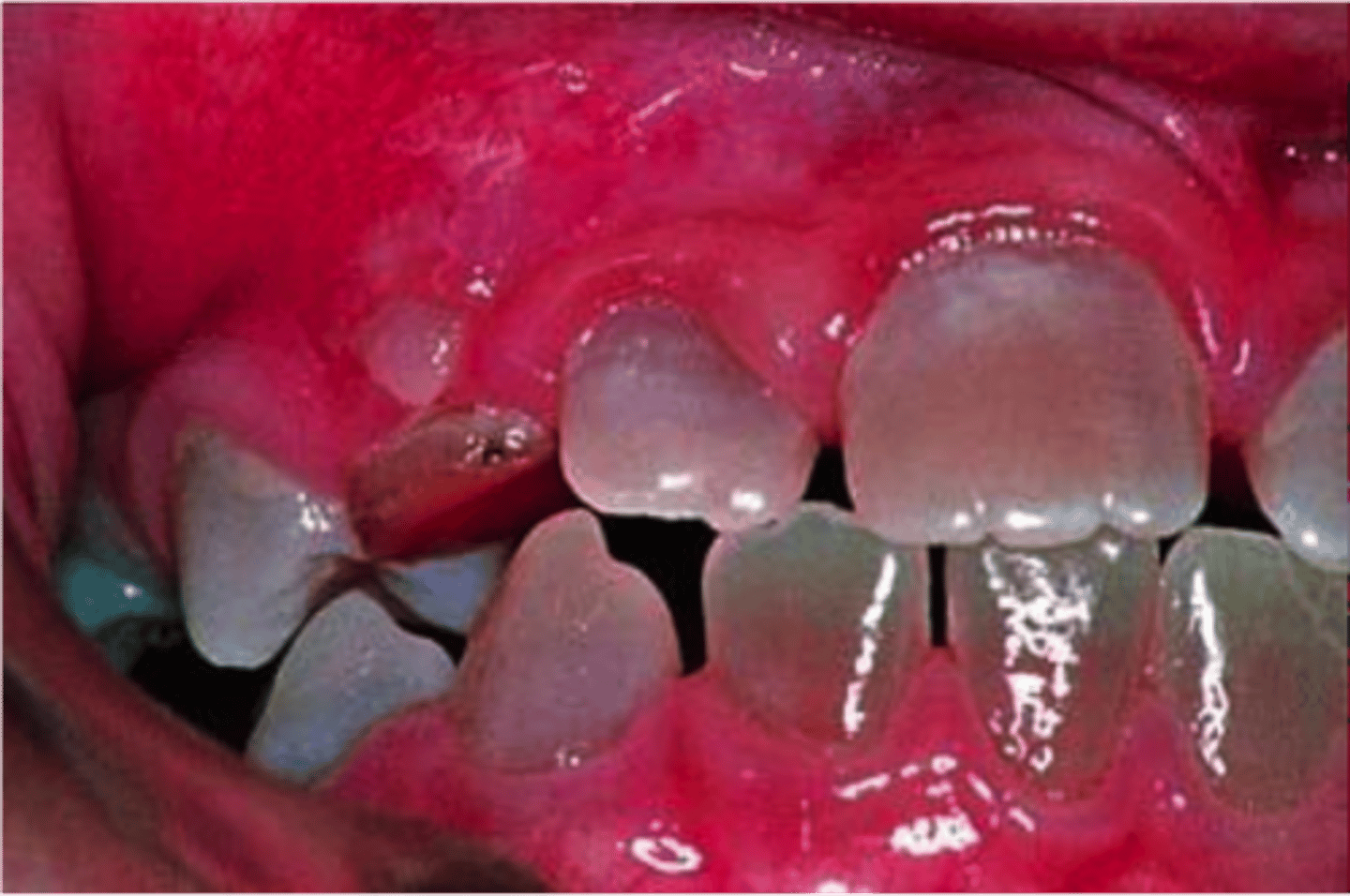
mulberry molars, screwdriver shaped incisors , maxillary anteriors with central depression
syphillis
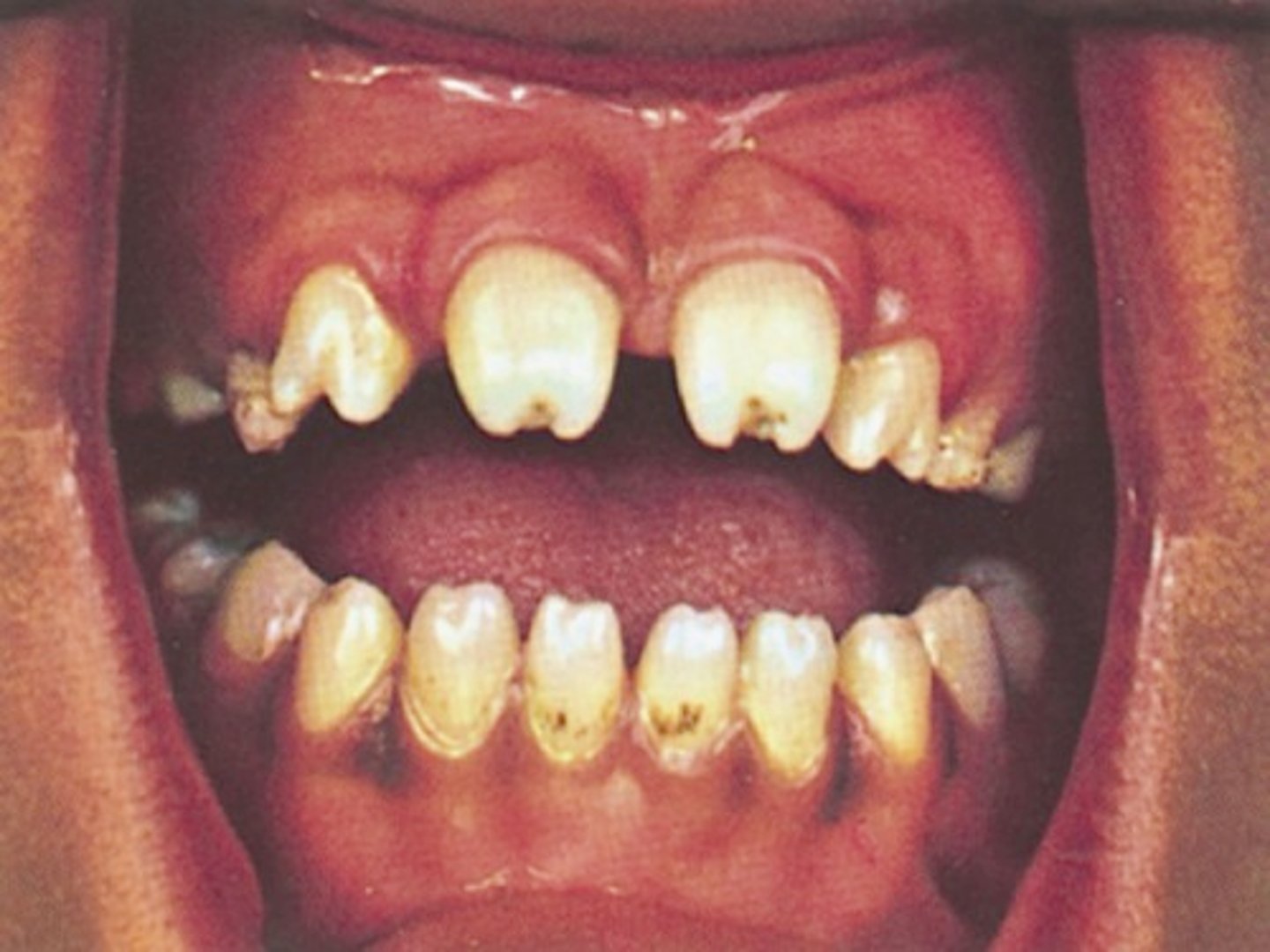
___ also known as twinning is due to incomplete formation of two teeth, common on incisors, seen in maxillary laterals
gemination
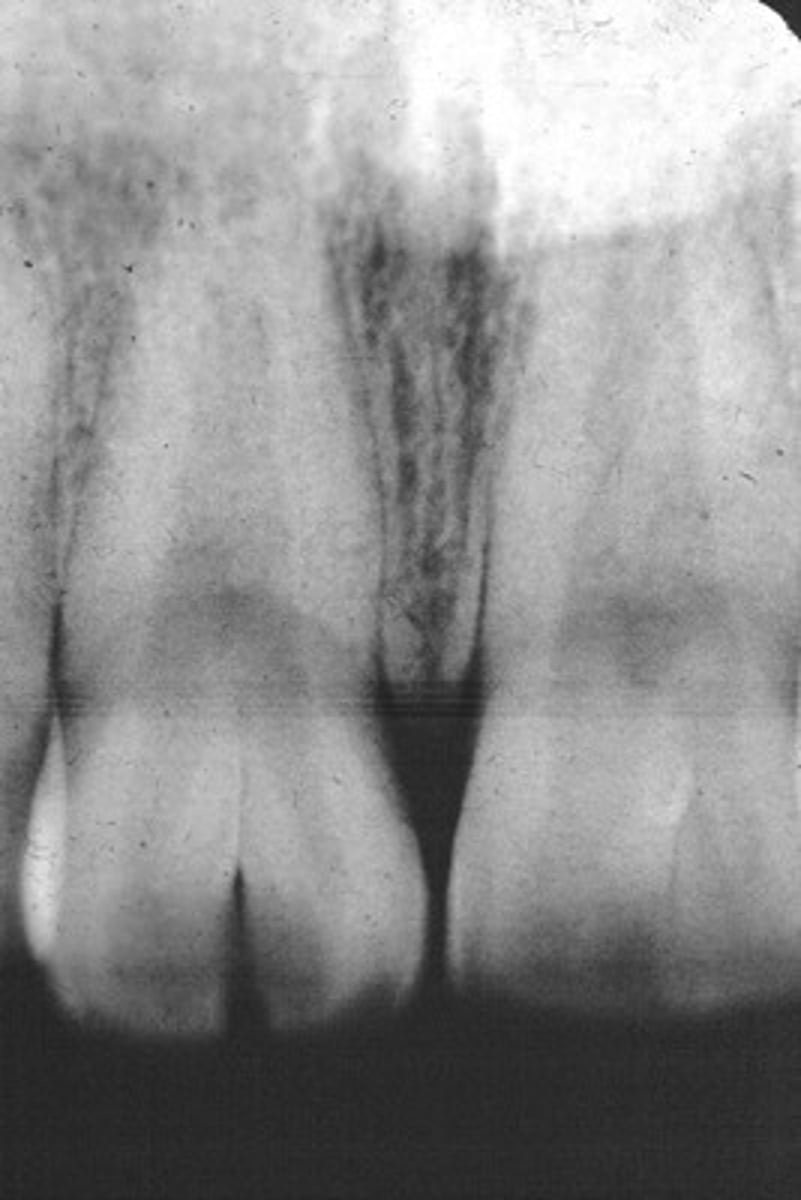
bull shaped crowns with shortened roots on PAN or fms
What can be a 2 contributing factors?
taurodontism
overweight, hypertension
Tzanck test is to diagnose ________ (small painful ulcers that recure every 5-6 months with fever) Treatment is ___ with ____ and analgesics
acute herpactic gingivostomatitis
pallative care with lidocaine rinses and analgesics
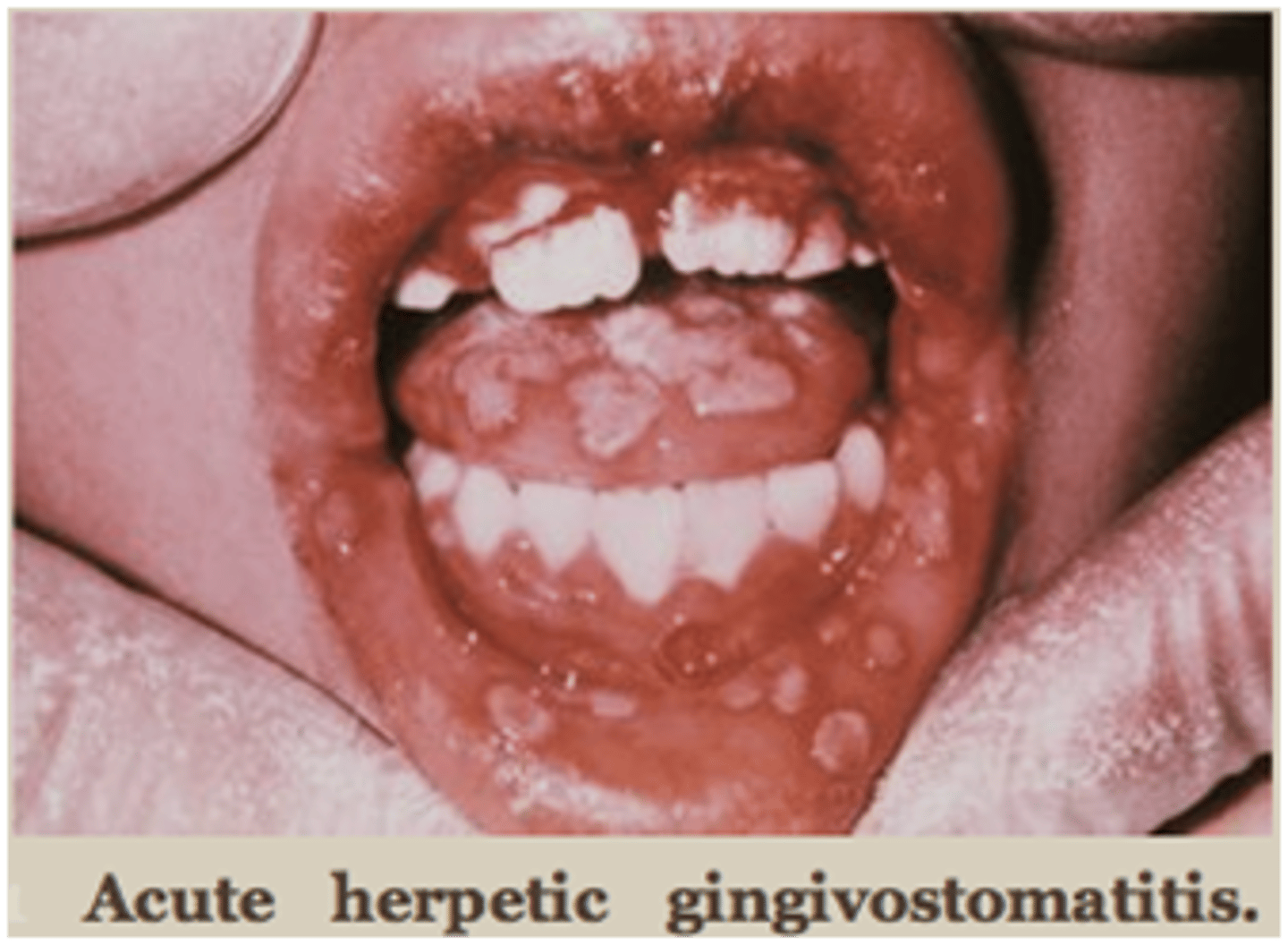
long standing and heal with a scar, can see on the lip and palate, pemphoid can also heal with a scar
major apthous ulcers
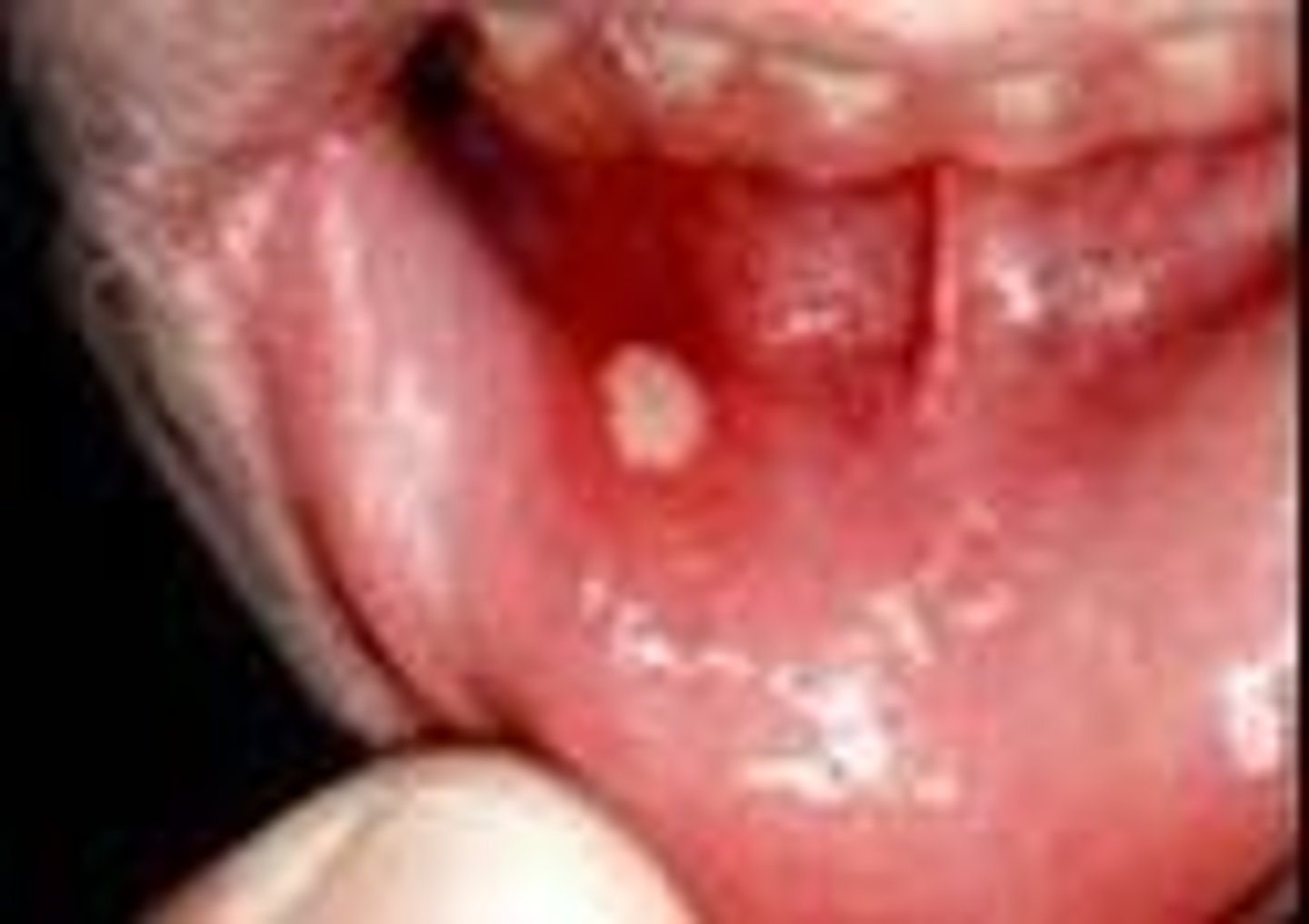
mucocele on the lower lip can be due to an ____ salivary gland, treat with _____. Inside the mucocel is ____ (mucus)
injured salivary gland
treat with excision
saliva,mucous
A standard cartridge as ___ml of 2% lidcaine at ___mg. the active ingredient , and 1:100,000 (____) of EPI vasoconstrictor
1.8ml
36mg
0.018mg of EP
t/f: according to cdc regulations, you are not required to wash hands before and after removing gloves ?
true
Sodium hypochlorite should be changed ___
daily
to test the autoclave to ensure that it is properly sterilizing by doing a ___ test using biological indicators ___
spore test
Tx for tetracycline staining?
best to leave alone
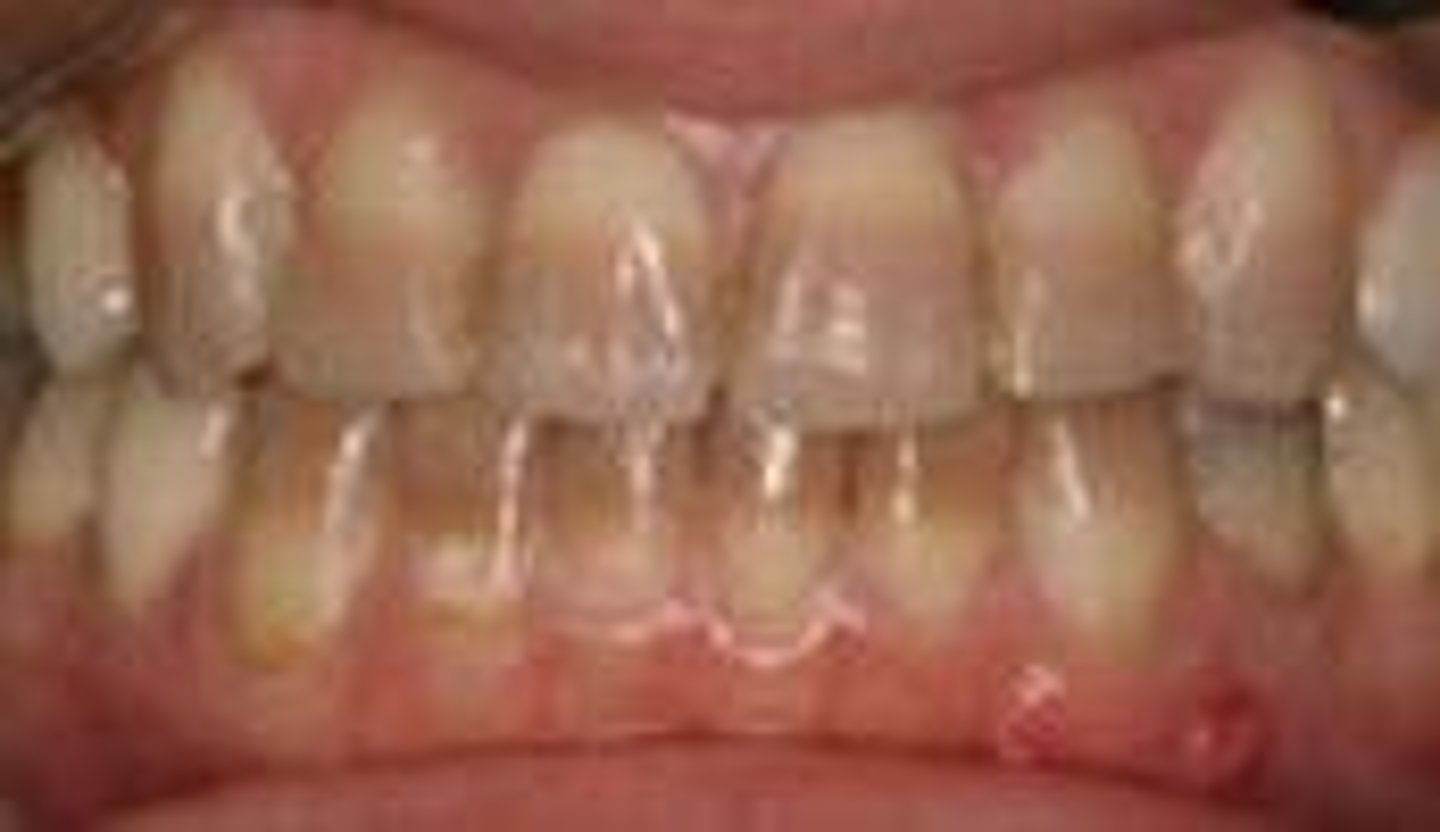
____ can cause rampant decay due to lack of saliva to buffer acidic PH
xerostomia
____: can cause rampant caries in todder/infant
baby bottle syndrome
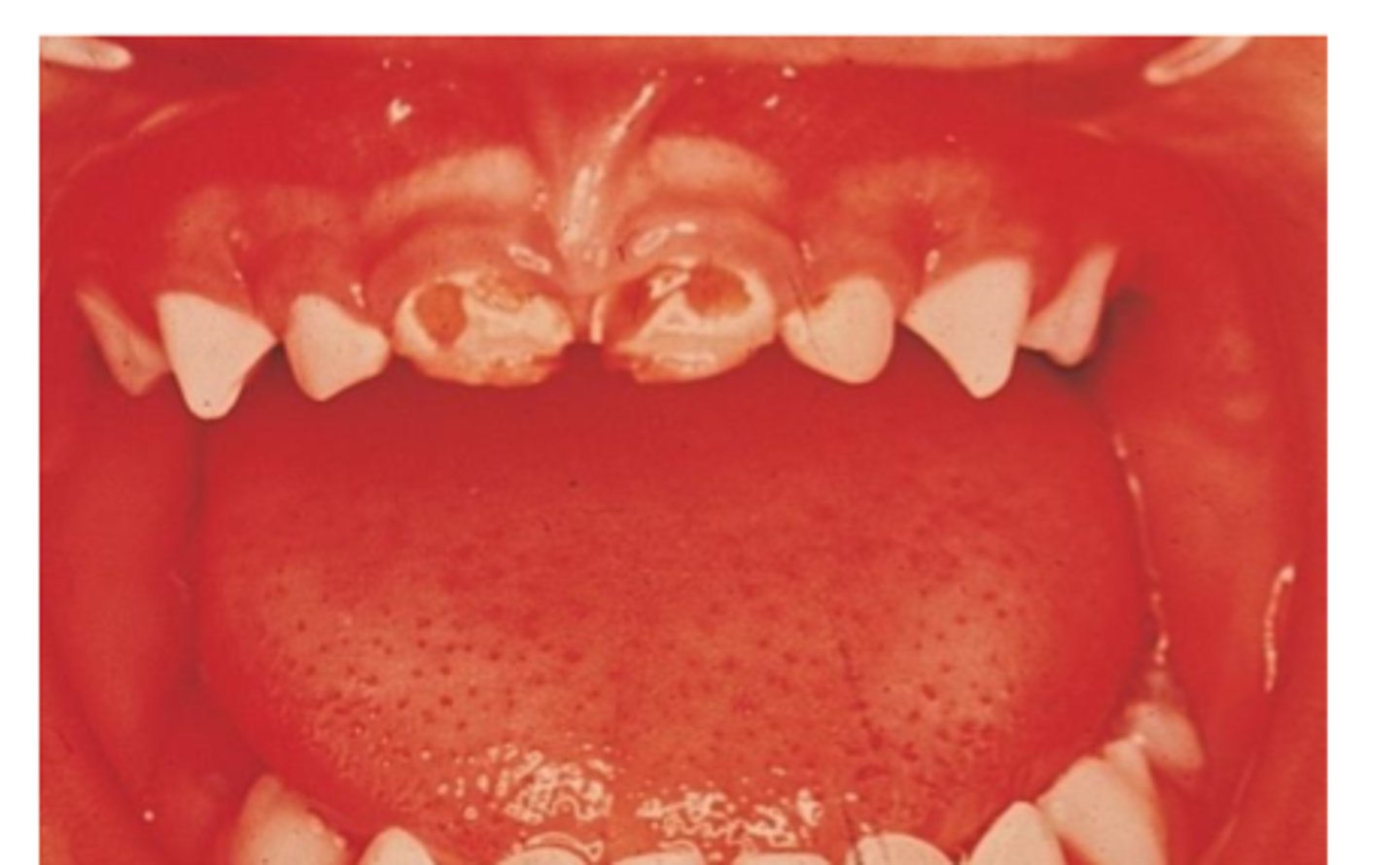
a patient on steriods will need ___
supplemenation
a MI can produce ___ symptoms while ___ does not
GI
syncope does not induce GI symptoms
T/F use retraction cord that contains epi for patient with recent MI
false
correct sympotms of MI. The other two are more likely ____
chest pain
upset stomach
pounding heart beat
left arm
jaw jerk
pain
indigestion
all except indigestion and upset stomach
angina
patienttakes nitroglycerine tablet with no effect in 5 min, you give a second and third tablet and still nothing happens. Patient is most likley have a ____
Myocaridal infarction
angina perctoris symptoms .Usually precipitated by exertion of _____. commonly with see __ _and ___ occur
chest discomfort(not pain) epigrastrium area, usually preciptated by stress and exertion
nasua and vomitting
if a patient is sitting in dental chair with hands on heart, first thing you do is give the patient _____
0.4mg of nitroglycerine tablet
if patient is having a myocradial infarction/chest pain, andminster anti anginal drugs such as _____.
when to not give this to the patient as can cause severe drop in blood pressure
0.4mg nitroglycerine/vasodilation
viagra or cialis
What does MONA stand for and when is it used?
morphine, oxygen, nitroglycerine, asprin
angina treatment
Norpace/disopyramide
Antiarrhythmic/antianginal agent
Valium (diazepam) has metabolies for long duration and binds to ___ receptors to cause inhibtory effects . will have ___ channel opening
It is a ___ used for anxiety, siezures ,and insomina
GABA
Cl
benzodiazapine
Pottasium-sparing diuretics for hypertension and edema (2)
WHEN IS IT NOT USED
TRAMETERNE AND SPIRONLACTONE
NOT USED FOR IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCtion
Stent has been placed for patient undergoing kidney dialysis . Does patient require medicaiton?
No, does not require medication
if a patient has kidney disease, what can you prescribe and NOT prescribe
Tylenol (acetaminophen)
NOT aspirin, advil or naproxen (nsaids are metabolzied in the kidney)
t/f: If a patient has a kidney transplant, the patient may require antibiotic(stress dose)
true- due to anti rejection medications
analgesic for mild to moderate pain: NOT USED IF PATIENT HAS KIDNEY FAULURE
PROPROXEPHINE
antihistmine to prevent motion sickness and as a sedative for insomina when benzodiapenines are contacindicated. Can be used to treat allergic reactions
common side effects are tardive dysinesia, xerostomia
promethazine
bronchiodilater inhaler that relaxes muscles. Used for asthma
albuterol
t/f: should administer nitrous oxide to an asthmatic
false
angioedema of the upper lip has been dianosed as an allergic reaction with no other signs of allergy. The most apporpriate treatment is ?
oral administration of antihistmine (benedryl)
a 60 year old female taking naproxene, one asprin dialy who is allergic to penicillin is most likely taking the naproxene for ___. Do not make a a precision attachment for her due to her lack of ___ as a result of the arthritis
arthritis
lack of dexterity
patient has malaise, lethargy, itching, may have an allergic reaction. Give ____
benedryl
the major difference between syncope and severe analphylatic shock is there can be ____ in anaphylatic shock
diffuculity in breathing
patient undergoing anaphylatic shock. TX includes (4)
place patient in supine position
administer oxygen manually
monitor vitals
give 0.3-0.5ml of EPI SC or IM
the first thing to do if a patient experiences syndrome (fainting or hypotension) in the dental chair is to place patient in _____ position
place patient in trendelenburg position (supine) with feet higher than head by 15-30 degrees to increase cerebral perfusion pressure
When is trendelenburg position contraindicated and instead would use just horizontal position?
hypovolumic shock (loss of blood volume)
medical history of patient taking penicillin and has an allegic reaction on the lower lip. Tx? (2)
apply topical steriods or swithc antibiotics
anaphylactic shock tx? (2)
Epi 1:1000, 0.5 ml SQ, repeat every 10-20 min PRN
or steroid
dentist has needlestick , have ht patient do an ____ test to detect _____
then do ___ to confirm ELISA
elisa test to convern HIV antibiodies
Western blot
AIDS patient treatment include ___ precautions, try to avoid invasive procedures and _____ treatment
univerisal precautions
try to avoid invasive procedures
no treatment
A patient taking Isonizid, Rifampin or Pyaziminade has ___
tuberculosis
if you patient is having a seizure , first acition is to protect ___ and __ _form injurying themselves ,clear the area and _____ against the dental chair
yourself and patient from injury
clear the are and hold hands against dental chair
____ or ____is the test to evaluate blood coagulation (clotting) time and to monitor response o oral anticoagualant therapy like COUMARIN and liver disease
Prothrobmin test (PT)
INR
Name this disease:
pale gums due to decrease RBC count. diagnose by complete blood count test. What is sign of anemia RBC?
Anemia
2 million RBC
normal RBC range ?
4.7-5million
name this disease :
patient have low platelet count (poor clotting).
Normal platelet count is ____-_____.
Below 50,000 per microliter is _____
thrmobocytopenia
150,000-450,000
thromboyctopenia
name this diseaes:
symtoms inlcude increased WBC above normal and ginival bleeding. Blood level example : RBC-2.2million, platelets-24,00, WBC-79,000
What is normal WBC count?
How to diagnose(2)
lekuemia
4000-10,000
complete blood count, bone marrow examination
Name this disease:
can be caused by calcium channel blockers even after a few months.
Treatment and last option?
gingival hyperplasia
reduce or switch their medication
gingivectomy
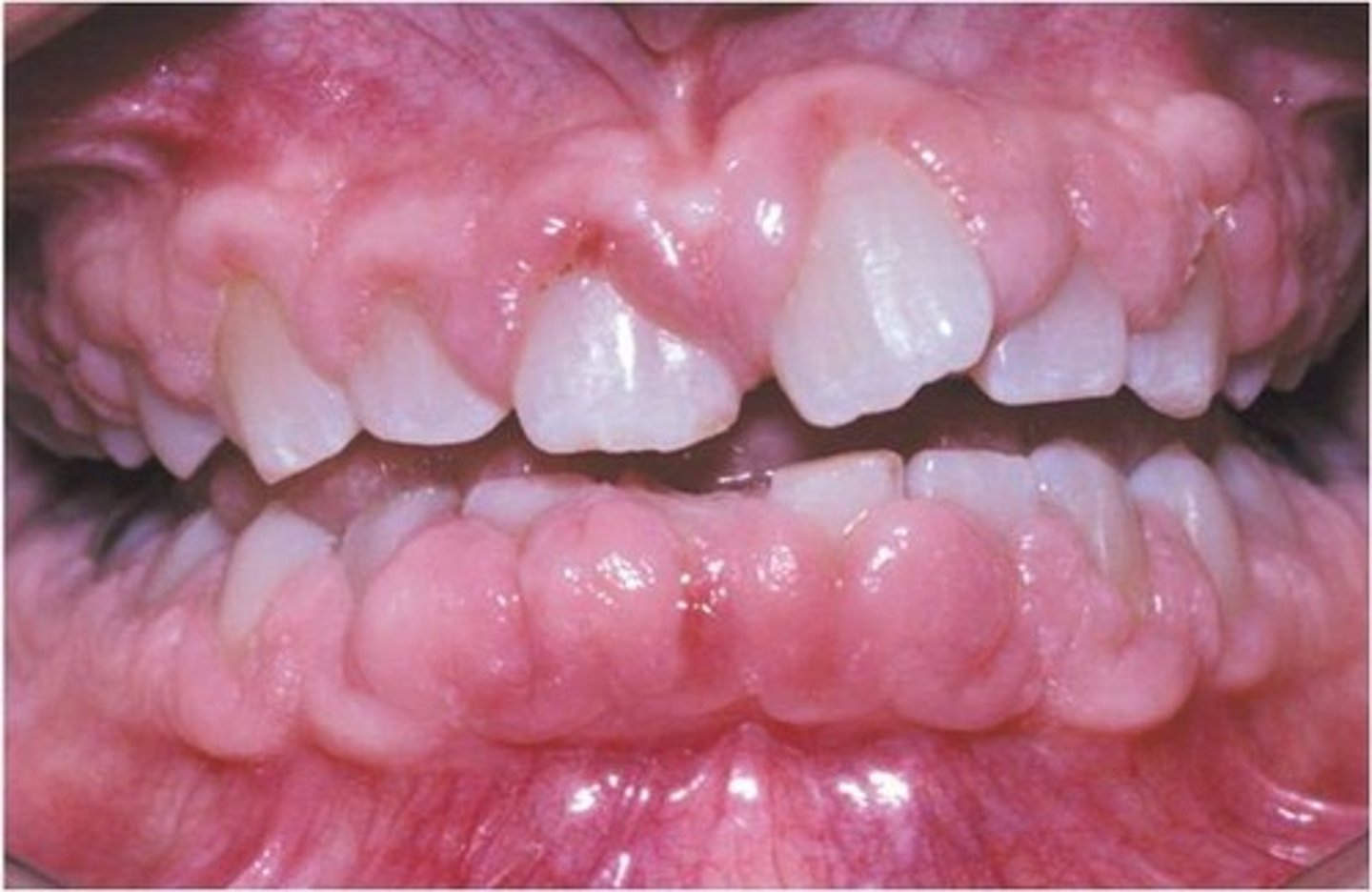
patient with acid reflux and had mild dental pian. What can you prescribe?
acetominophin, no NSAIDS
tetracycline and oral contraceptives _____ the antibiotics effectivness
WEAKEN
penicillin allergic patient pre medication: ___ or ____ with dosages for adults
clindamycin 600mg/20mg/kg
erythromycin 500mg/15mg/kg
non allergic penicillin patient premedication with dosage for adult and kid and time
amoxcillin 1 hour prior to treatment
adult: 2g
kid: 50mg
Hip joint replacent prohpylaix is only given the first ___ years after surgery only
2 years
t/f: No ab is need for patient with rheumatic heart disease
false
true/false: should give antibiotic prophylaxis for a patient wit ha history of bacterial endocardtitis?
true
true/false: antibiotic prophylaxis is premedication indicated for all dental procedures on indicated patients ?
false, only for those that will be invasive and cause gingival bleeding
Name of disease:
on a pan view looks like a bone under the angle of the mandible. It is elongation and clarification of the temporal ____ at the back of the throat that occurs after a tonsillectomy or trauma.
eagle syndome
temporal styloid process
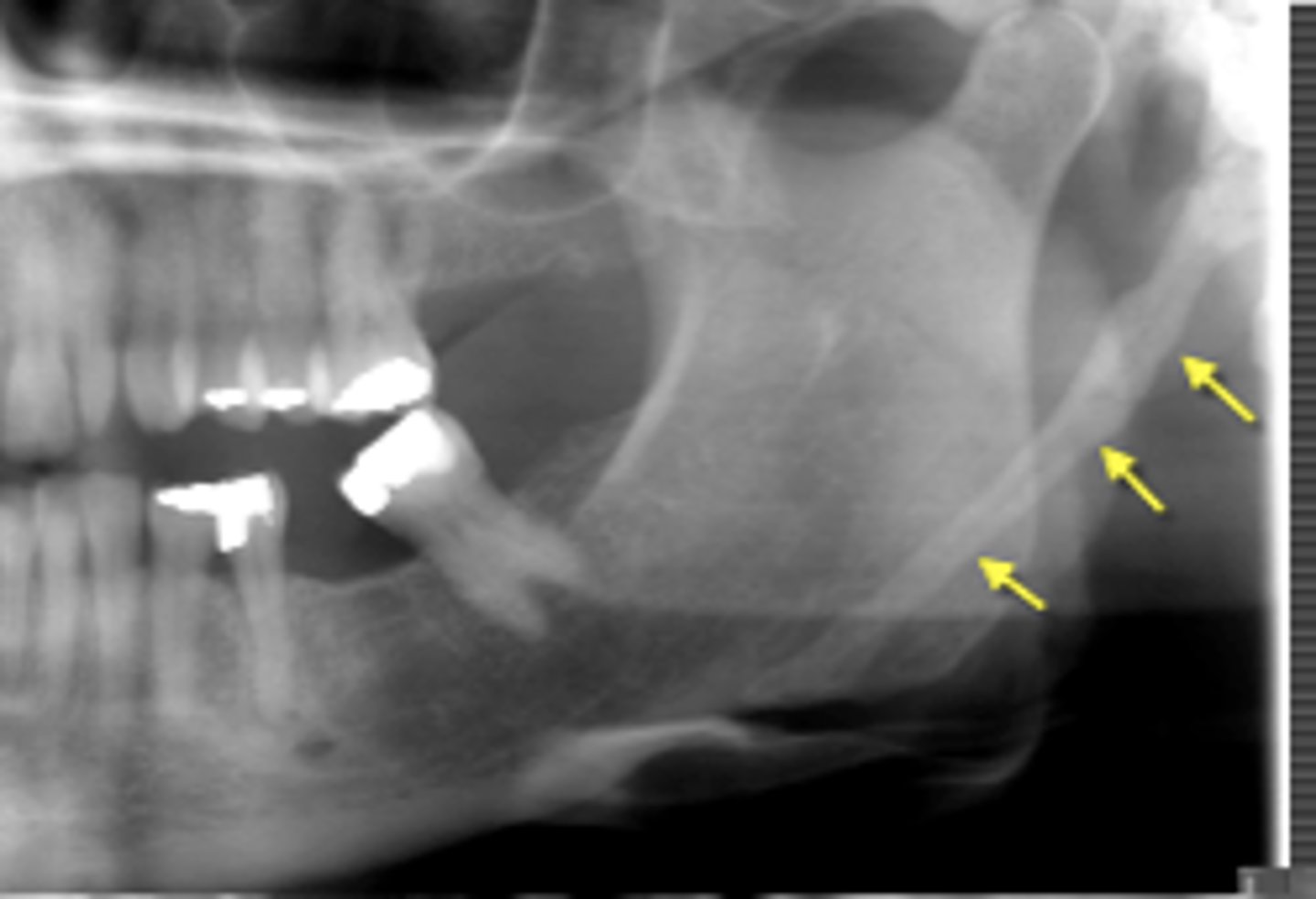
name of disease :
elongatoin and minerlaized of the styloid process that impinges on the carotid arteries and nerves. Patient ocmplains of aunilateral neck pain when turning thier head, possible sore throat, dysphagia.
Tx?
Mild cases:_____
severe cases:____
carotid artery syndrome
mild cases: none except reassurance or local corticosteroids to relieve pain
severe caess: surgical intraoral excision of the process
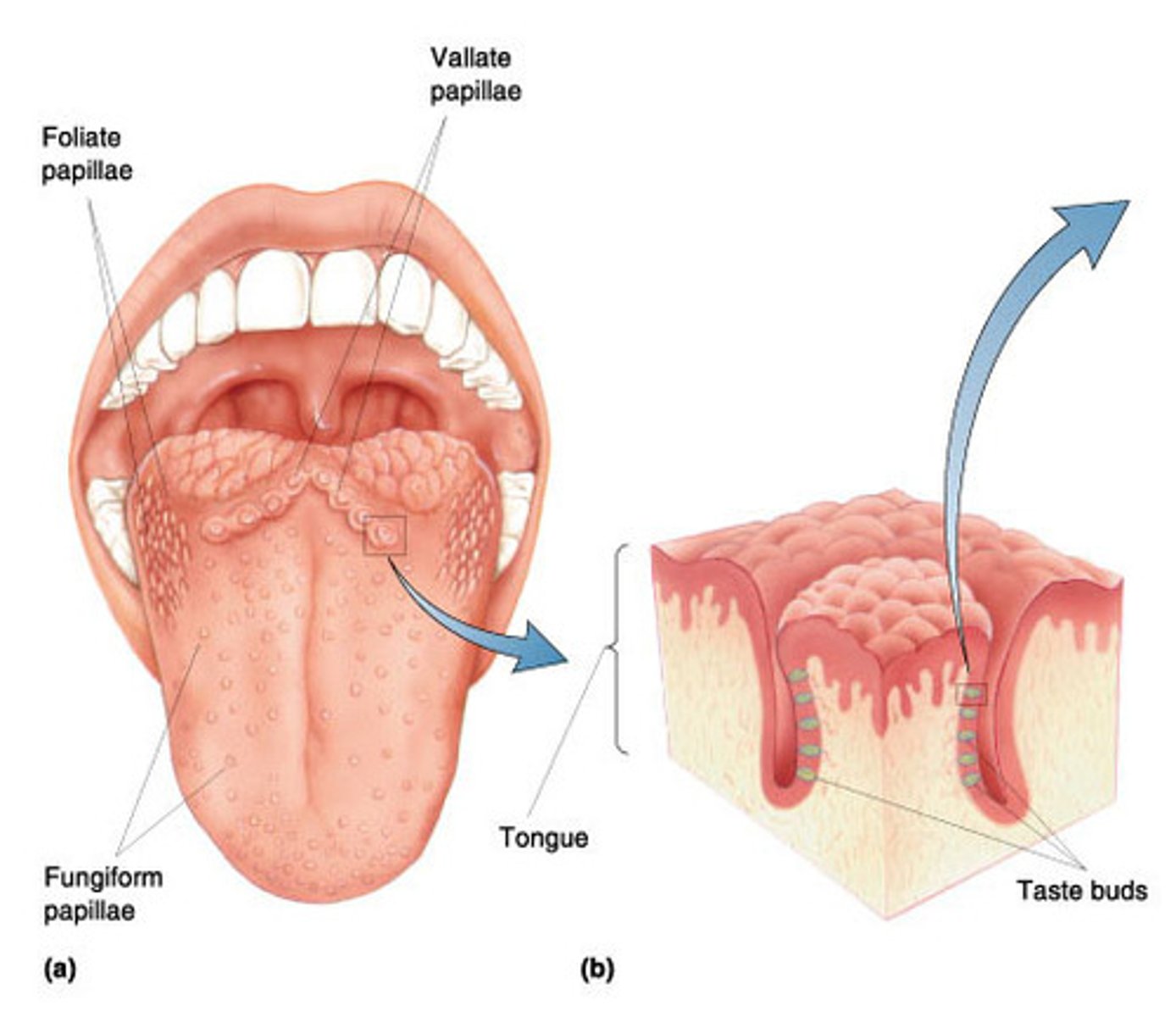
largest, least numerous arranged in inverted V shaped row at the back of the tongue?
does or does not have taste bud?
circumvillate papillae
does have taste buds
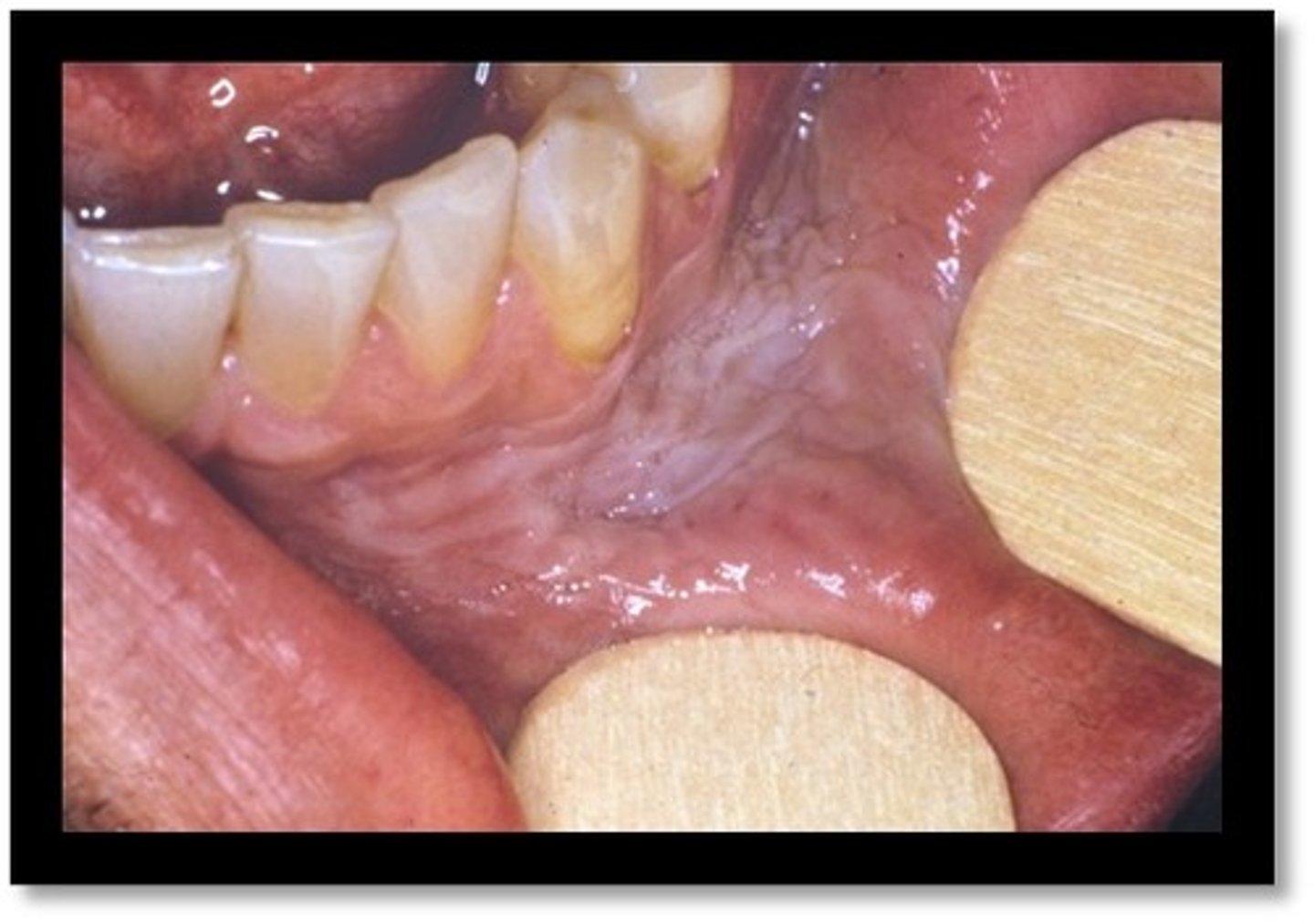
smokless tocacco pouch keratosis
is the development of a white mucosal lesion in the area of tobacco contact
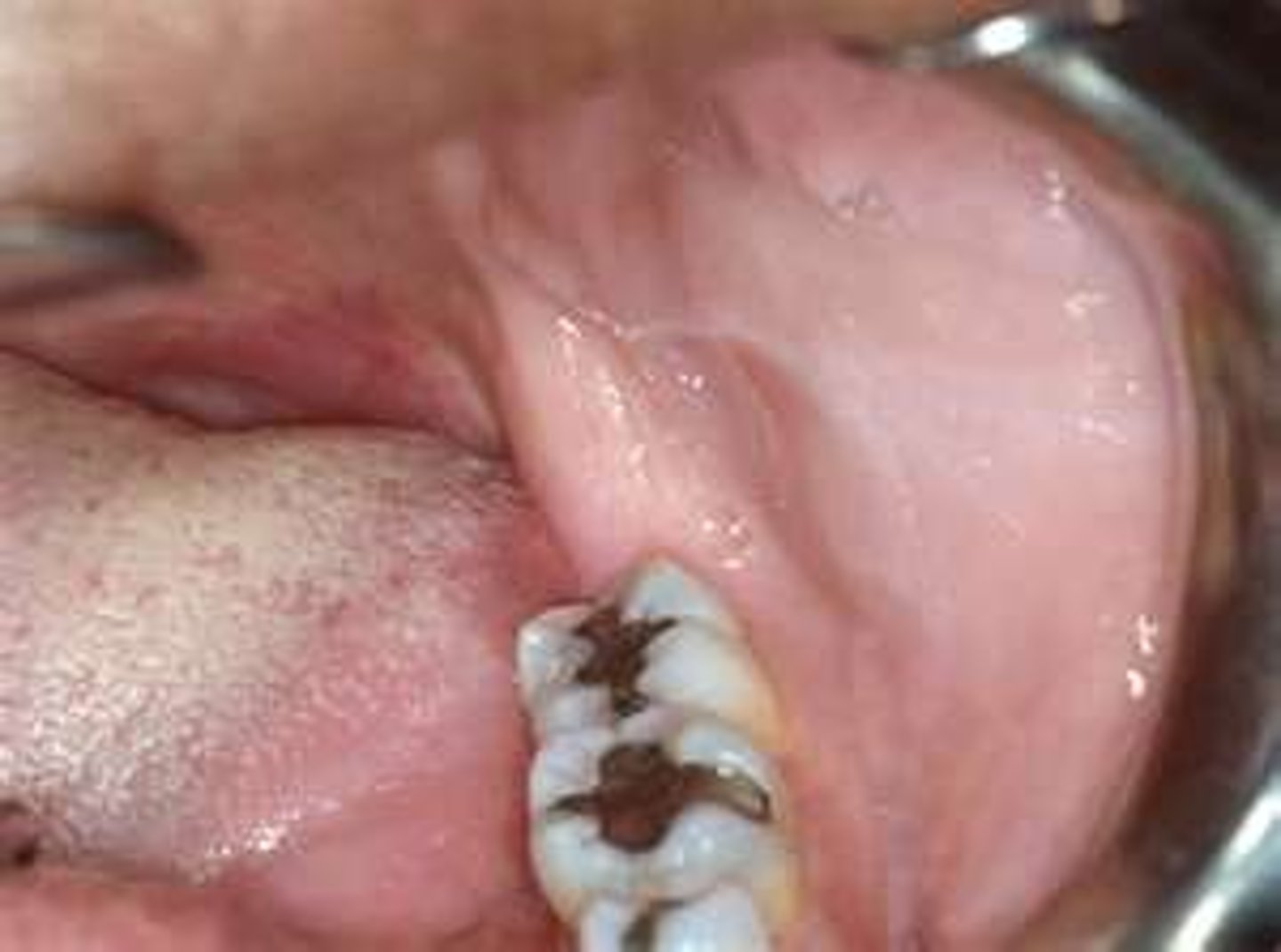
Name the pathology:
ca nbe caused by cheeck biting, dentures, orthodontic appliances, uneven teeth, and aggressive oral hygiene (benign hardening of the check mucosa due to excess kertain)
Tx:
linea alba
tx: remove the irritants is the proper treatment
Name the pathology: viral infection causing oral ulcers and inflammtion. Mainly affects the children
TX: (3)
herpetic stomatitis
tx: acyclovir, liquid diet and numbing medication , lidocaine rinse if pain severe
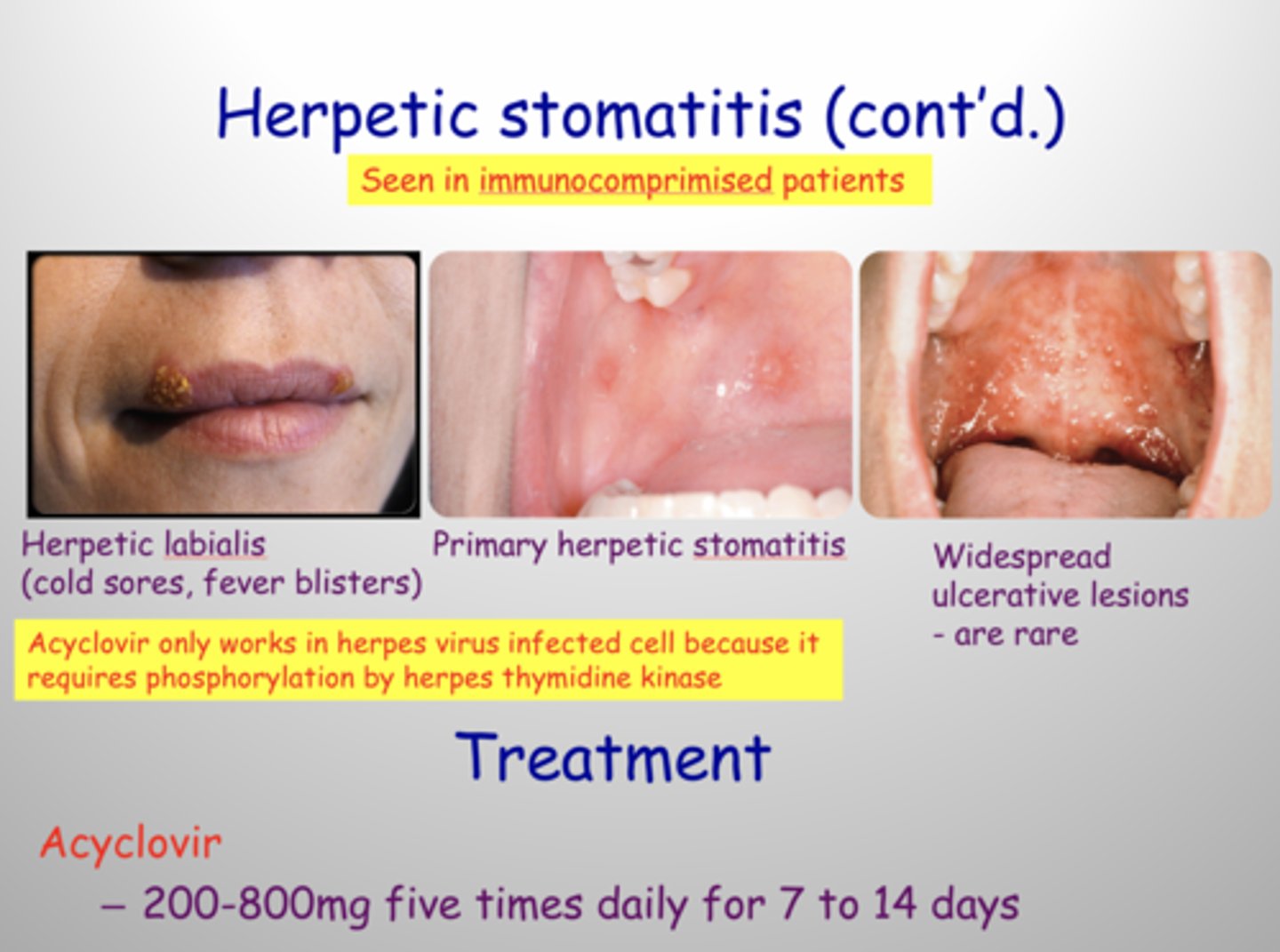
Name the pathology: PALATAL AND MUCCOBUCCAL FOLD LESIONS ARE OFTEN ASSOICATED WITH THIS
TOBACCO, SNUFF
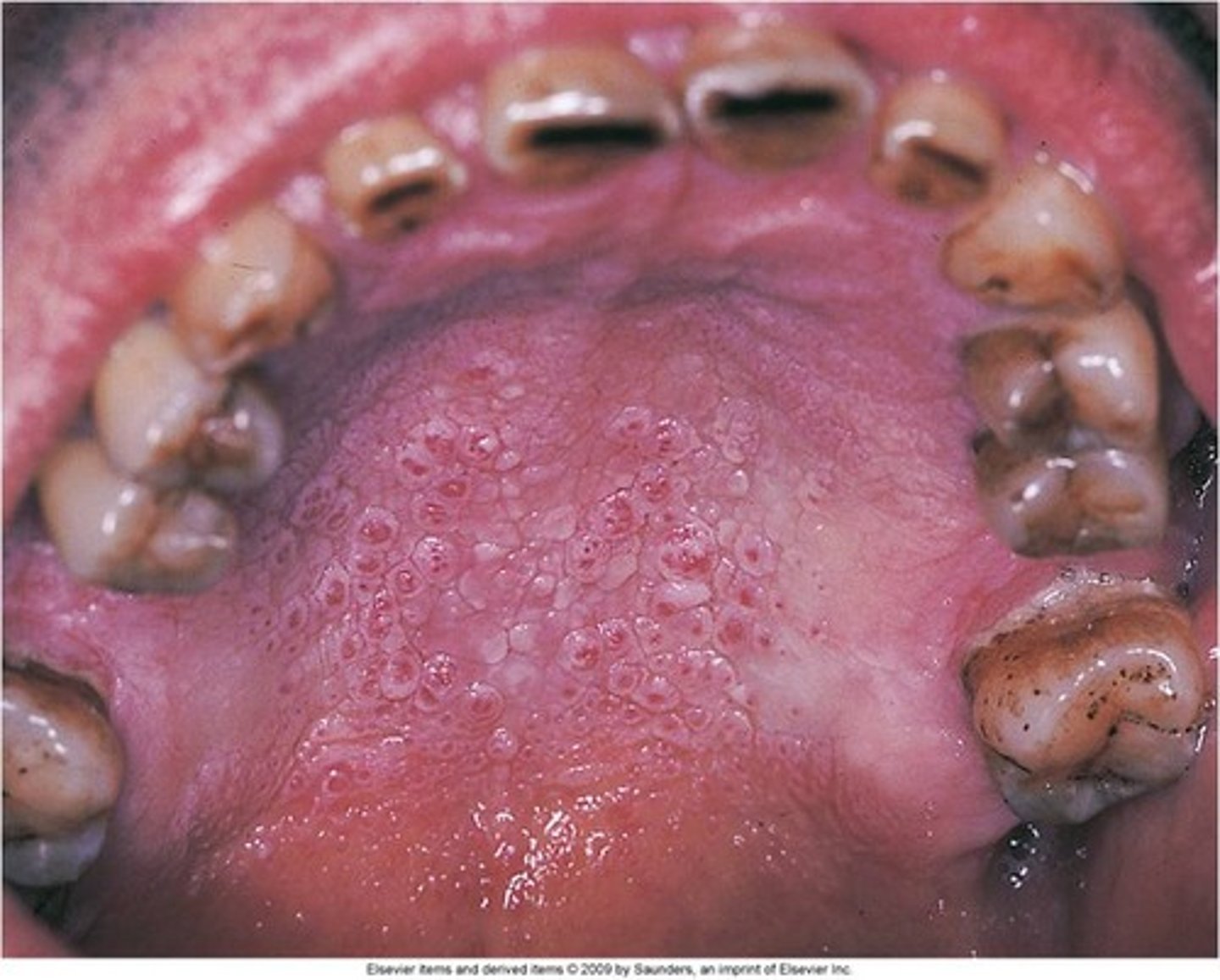
Name the pathology: picture of palate with numerous small raised areas with central red dots caused by pipe smoking
This is not premalignant and is caused by the ____ form the smoke. Not the chemicals
tx?
nicotonic stomatitis
heat from the smoke, not the chemicals
is reversible, need to stop smoking
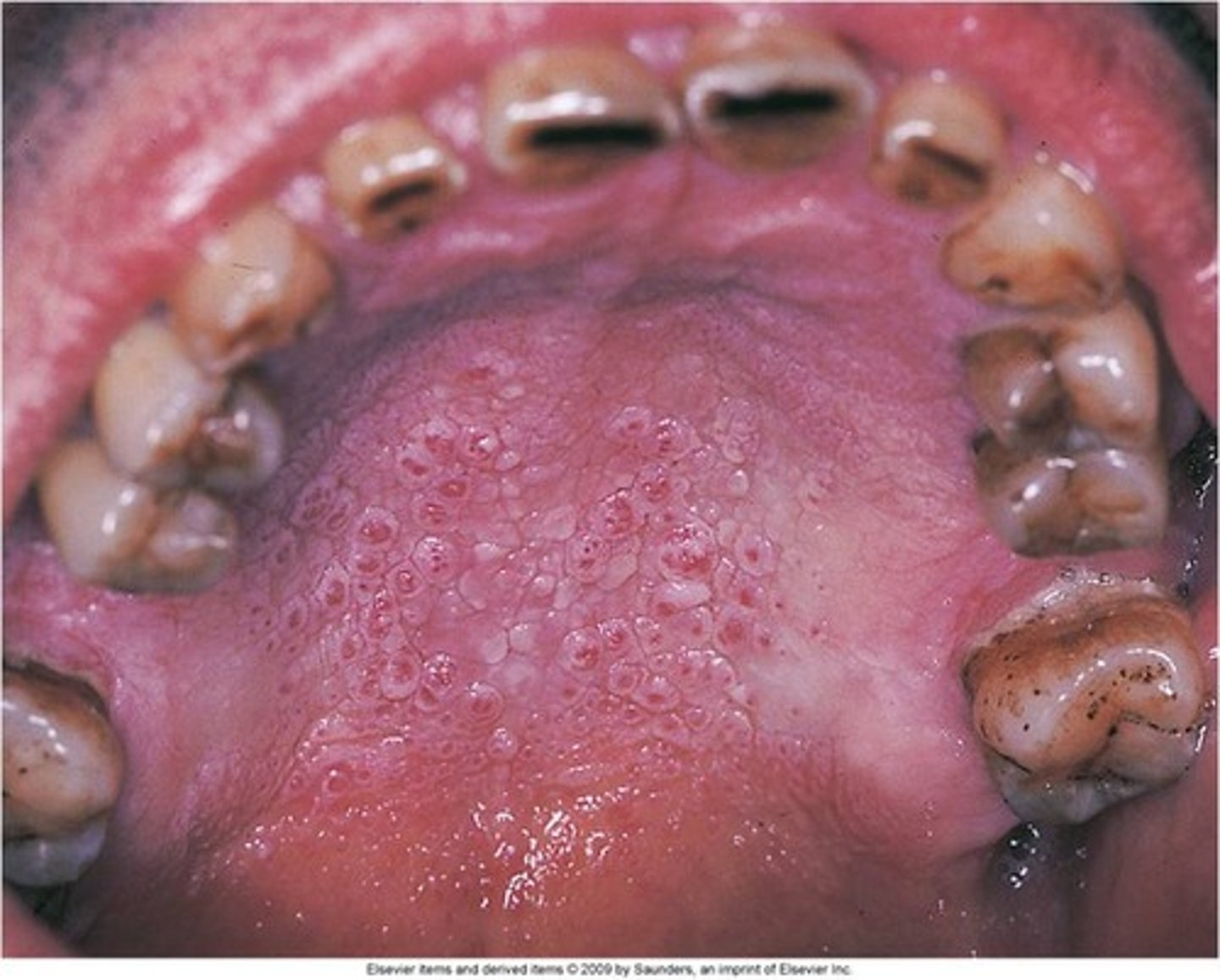
Name the pathology: can be seen on the palate in a pipe smoker
nicotonic stomatitis
Name the pathology:
Hepatitis that ca be caused by inoculation(serum, vaccination) iv drug use and blood transfusions
hepatitis C
Name the pathology: occurs on the lower lip an lateral tongue borders. may have a crusted or cauliflower appearance
Squamous cell carcinoma
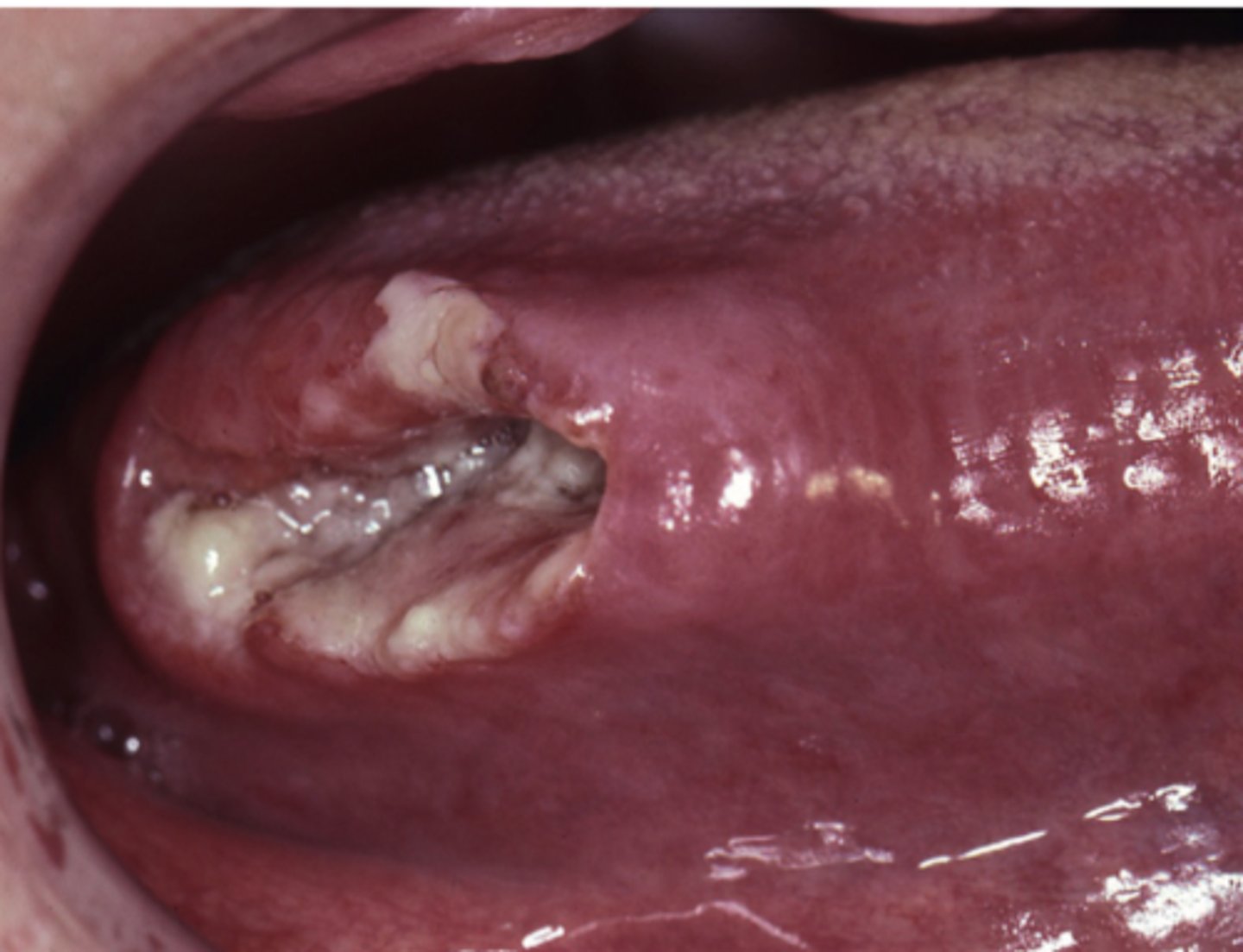
patient comes in with hard palate swelling hat has been there for about 2 years. The patient tells you they had a similiar lesion removed some years ago
tx?
surgical removal
You see a swelling under the tongue on the floor of the mouth (ranula). What do you do for treatment ?(2)
surgical removal or masupialize
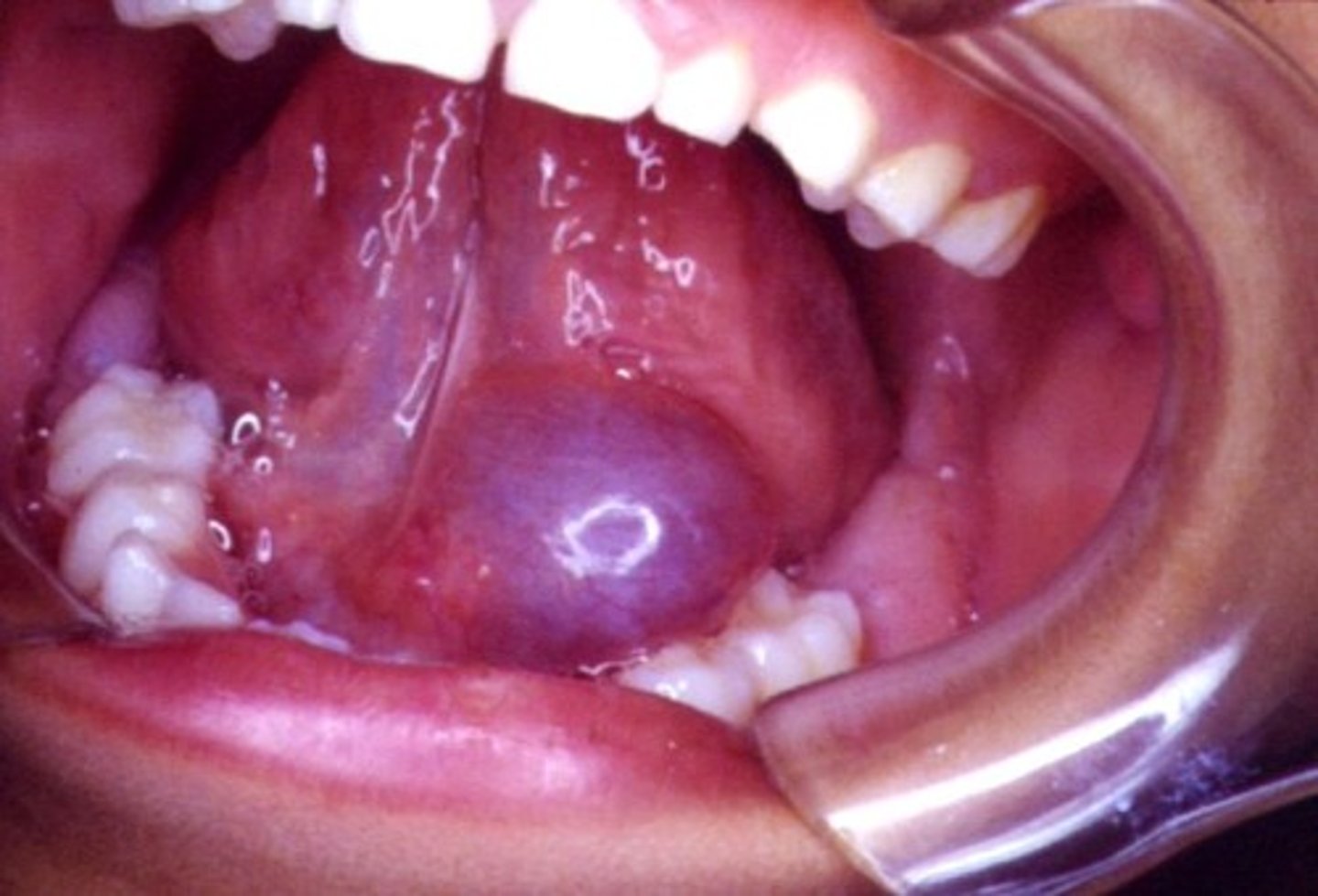
Dense, firm ulcer with indurated borders is of 4 months duration. It has been gradually increasing in size and severely restricts tongue movement. What do you do?
perform incisional biopsy
You see a hard palate with a midline swelling present for several years. Pt is concerned about this swelling because there is a family history of carcinoma. What do you do?
treatment: leave along and reassure the patient
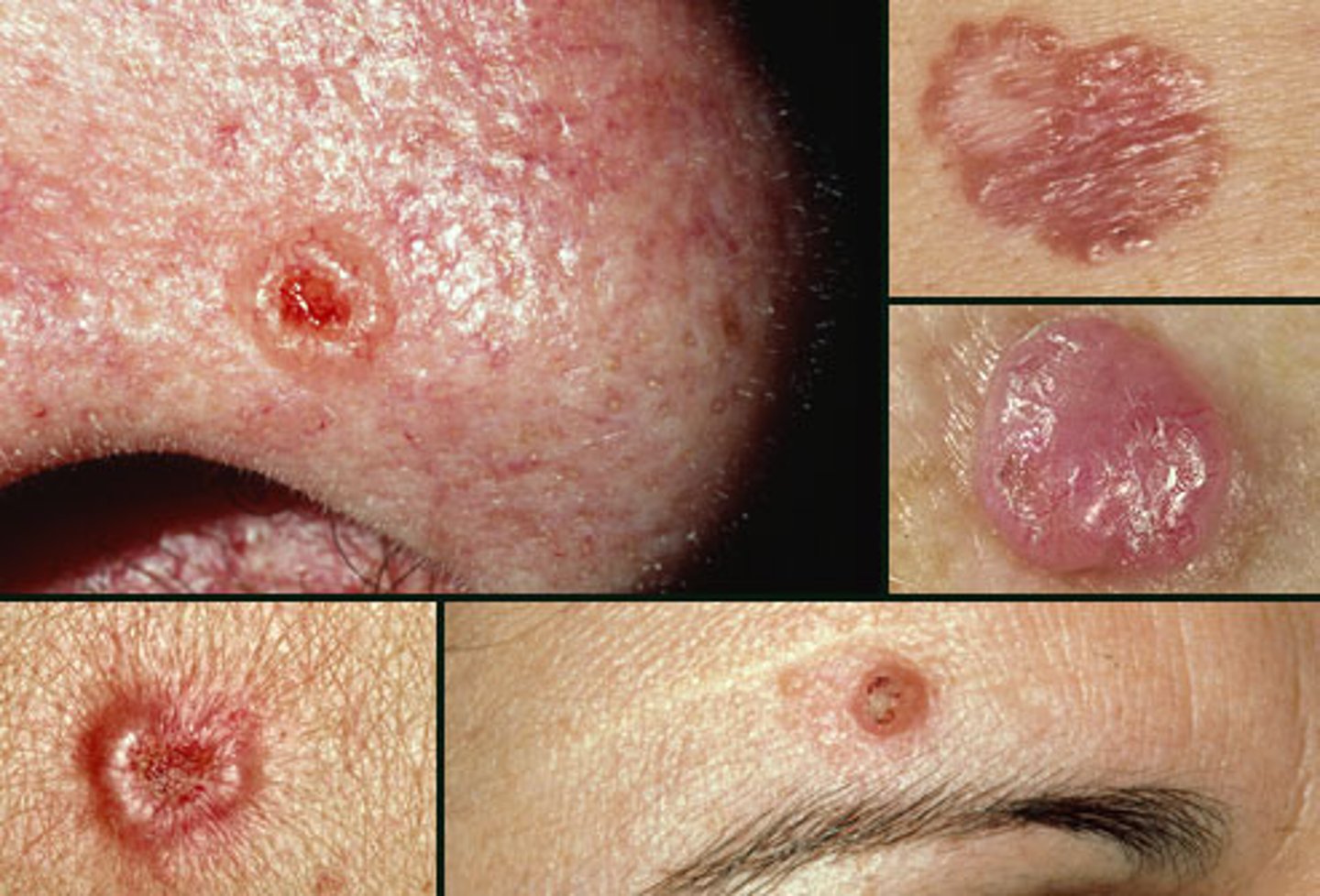
Name the pathology: occurs on the face (might see under eyes)
patient has RAISED lesion under the ye present for about 2 years.
TX?
basal cell carcinoma
biopsy and surgica lremoval
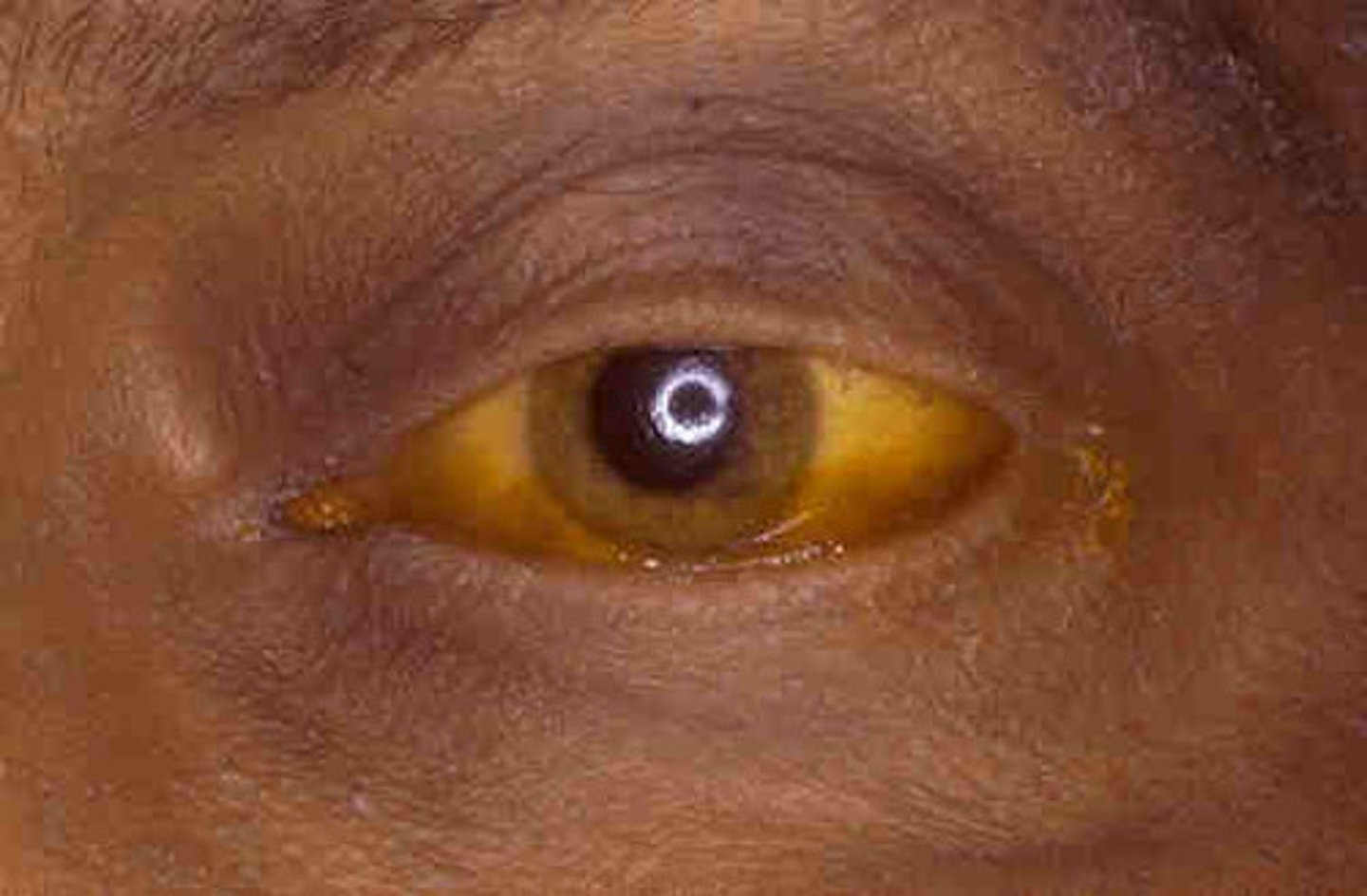
heptatis serum can be acute or chronic , prlonged incubaton 4-26 weeks?
hep b
hepatitis infectious required from raw steamed shellfish, contaiminated water or food
hep A
T/f: a patient who has Hepatitis A over a year ago is okay to treat?
When is Hepatitis A okay to treat: after _____ fro mthe onset of jaundice.
How is it transmitted?
true, it resolves within a couple of weeks usually on its own
after one 1
transmitted fecal oral route
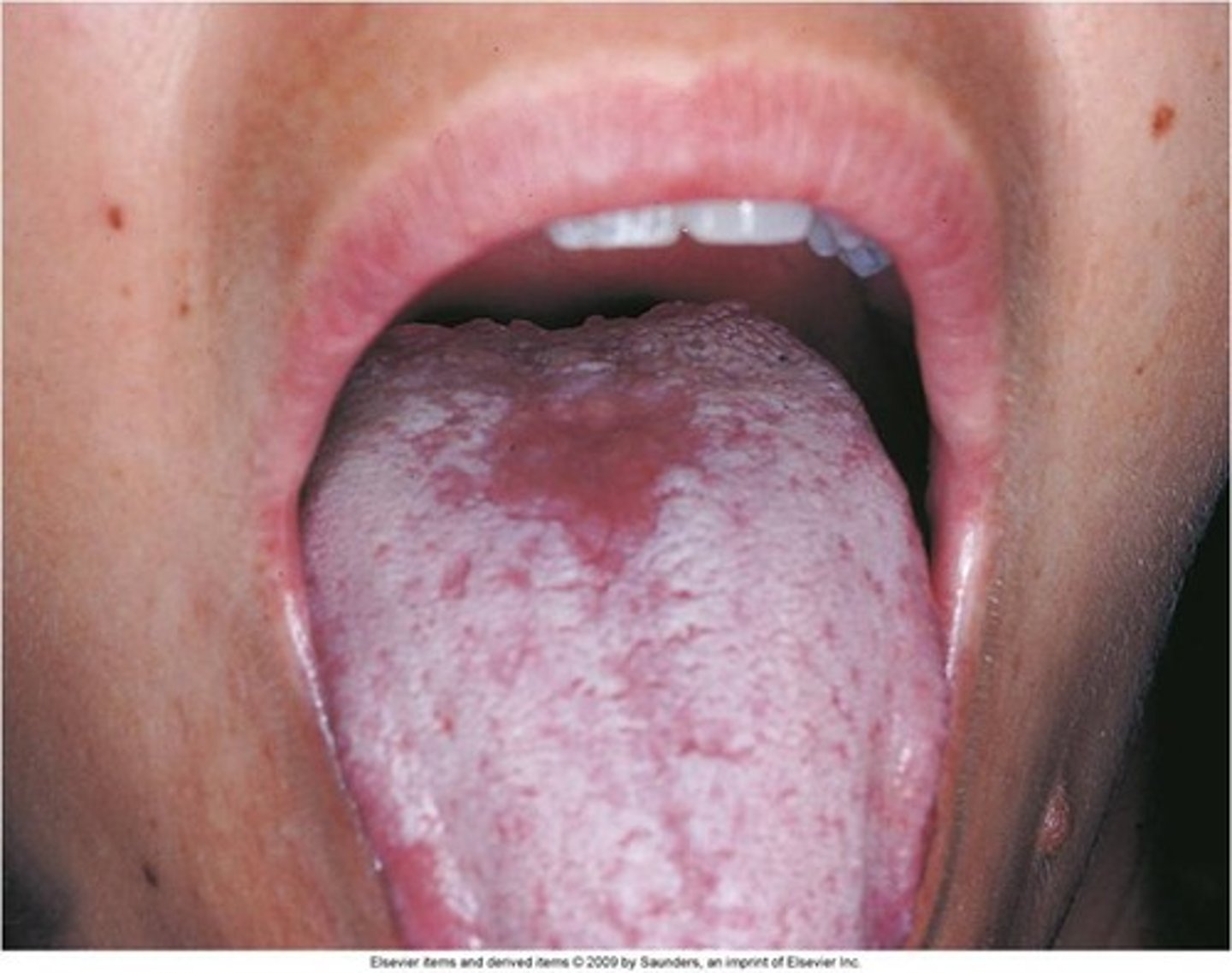
Name the pathology: looks like little dialted blood vessels (telangiectasis) on the tongue
multiple telangiestasias
Median Rhomboid Glossitis (Central Papillary Atrophy) is type of ___ infection.
Tx
candida
nystatin
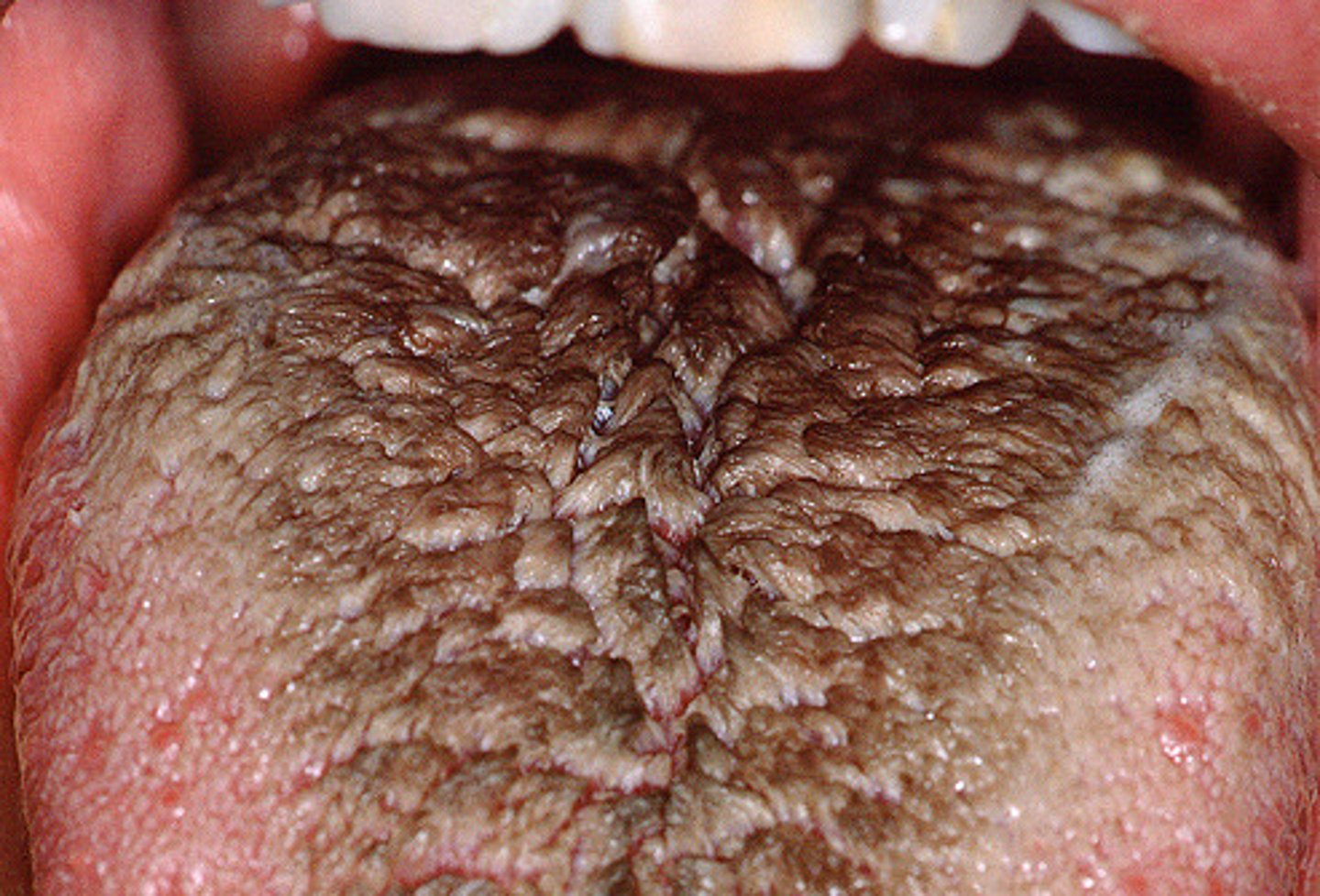
Hairy tongue : looks nasty. treat by taking the patient of thier medicaitons , use ___ and improve oral hygiene (brush tongue)
mouthrinses, medications , and improve OH
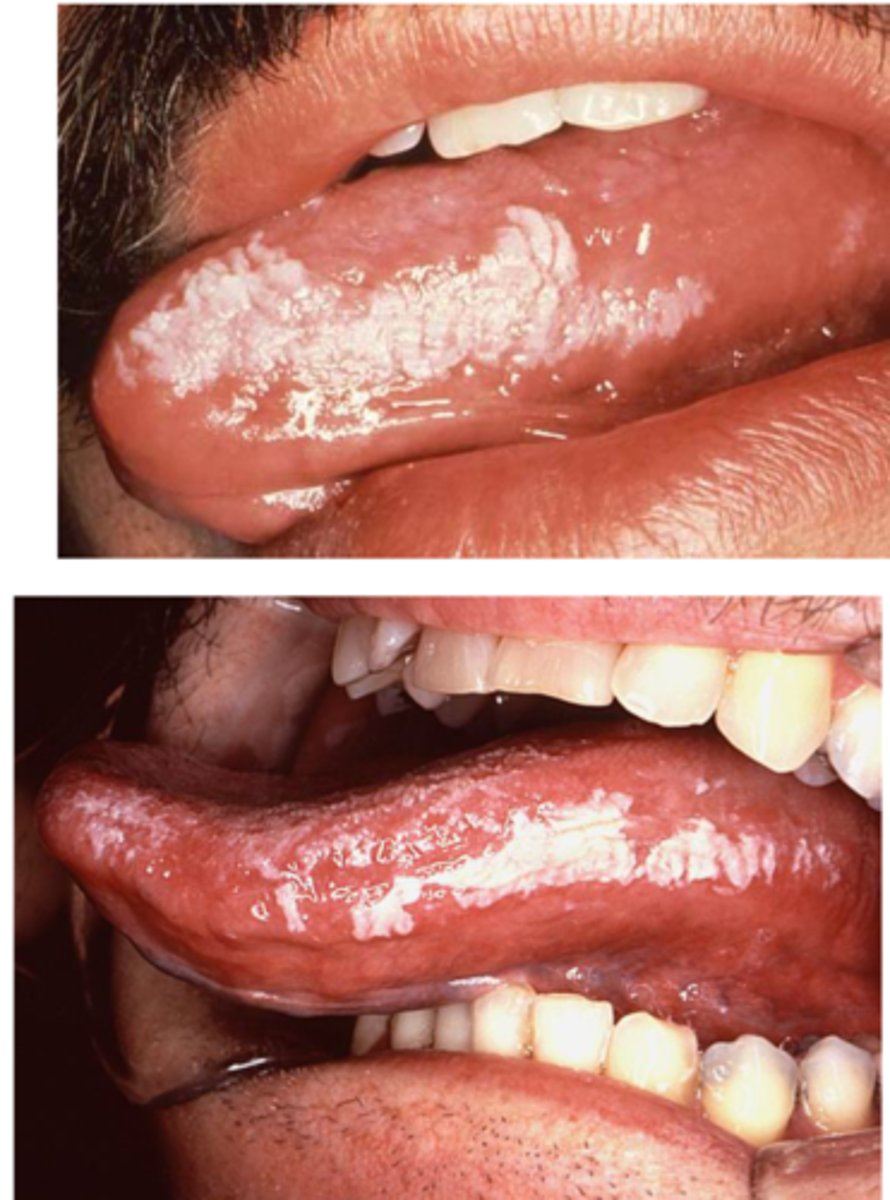
Oral hairy leukoplakia (AIDS)
presents as white plaque usually on the lateral border of the tongue that does not rub off. Associated with __ and ___
Presents as a white mucosal plaque that does not rub off, usually on the lateral border of the tongue; associated with EBV and AIDS
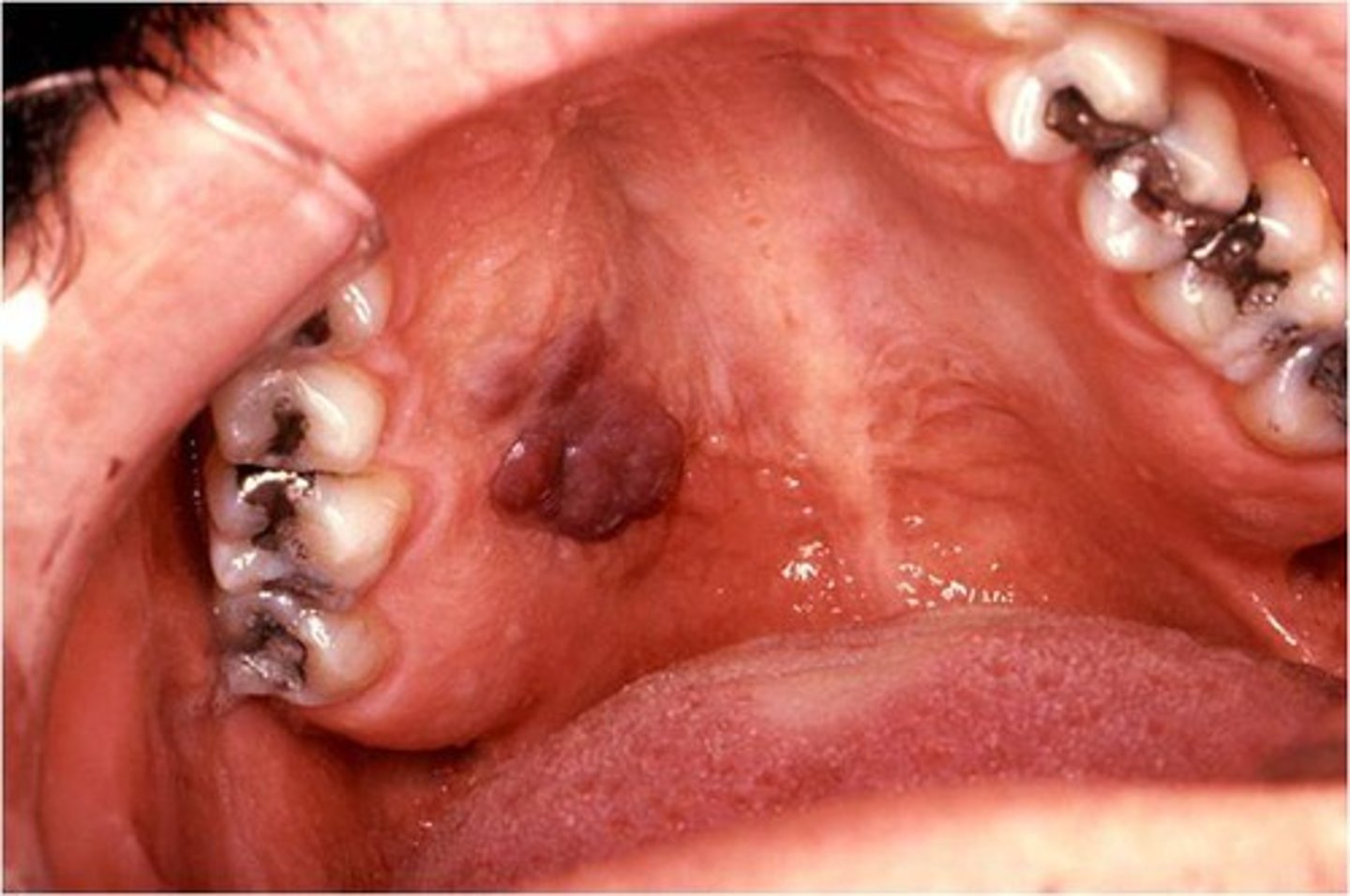
Name the pathology: oral manfestation in aids patients. a malginant cnacer of the lining of blood vesels on the ______. May present as purple lesionson the palte. TX: ?
kaposi sarcoma
hard palate
tx: provide normal dntal treatment but NO invasive treatment
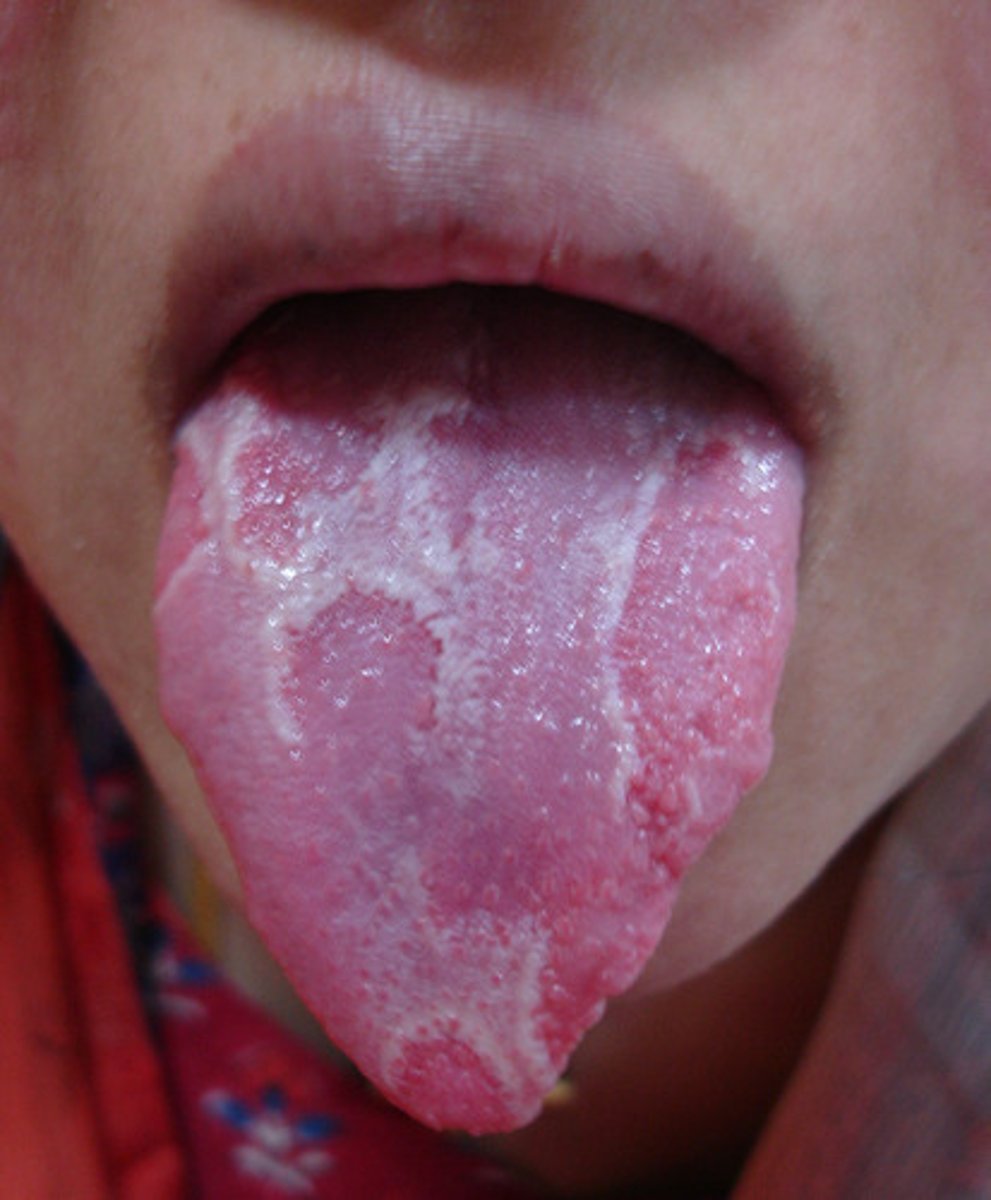
Geographic tongue (migratory glossitis) caused by atrophy of the ___ papillae on tongue
tx: ?
Pattern of normal coating interspersed with bright red, shiny, circular bald areas caused by atrophy of the filiform papillae, with raised pearly borders. Pattern resembles a map and changes with time. Not significant, and its cause is not known.
tx: ressure patient and leave alone