Production Costs and Revenue
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Short Run
The time period where at least 1 of the factors of production is in fixed supply, in most cases these fixed factors are Land and Machinery.
Long Run
A time period where all of the factors of production are variable.
Law of Diminishing Returns
If one variable factor is increased but another is fixed (short term) then the resultant increase in output will be less for each unit of input added.
Marginal Returns of Labour
The change in quantity of total output due to the employment of 1 additional worker.
Increasing Marginal Returns of Labour
Likely to occur when a small Labour force expands, as all workers can now specialise, leading to greater maginal returns.
Dimishing Marginal Returns of Labour
After the point where Marginal Returns peaks, the additional units of labour will not have sufficient work to do and thus the marginal return decreases.
Returns to Scale
The responsiveness of a change in the output of a business to a change in the factor inputs.
Economies of Scale
The cost advantage of expansing scale of production in the long run (where average cost decreases as output increases).
Purshasing Economies of Scale
Where large firms can purchase materials in bulk, getting a lower rate per unit than other customers.
Selling Economies of Scale
All types of marketing have costs, normally fixed meaning the more untis the more that fixed quantity is divided by.
Managerial Economies of Scale
As firms grow managers can divide labour between workers, leading to specialisation and greater productivity.
Financial Economies of Scale
Firms with a greater reputation are seen as being less risky to loan money to, allowing them to get loans at lower interest rates.
Technical Economies of Scale
Larger businesses have access to advanced machinery, making them more productive.
Research Economies of Scale
Large firms can invest in R&D, allowing them to develop and improve their existing products.
Risk-Bearing Economies of Scale
Large Firms can produce a range of products across several markets, allowing them to continue operating even if one of these products fails.
Economies of Scope
Where it becomes cheaper to produce several different products instead of specialising in just a few.
Managerial Diseconomies of Scale
As companies expand across multiple time zones there become several time lags on communication, reducing company efficiency.
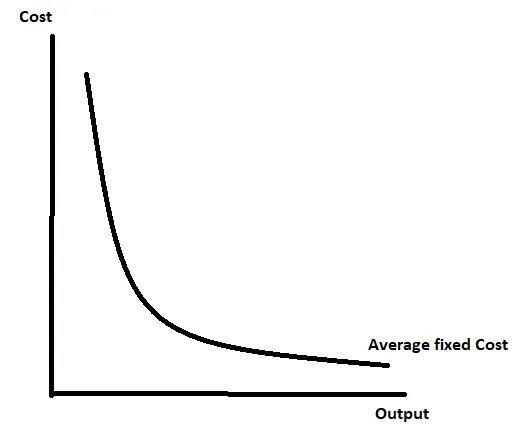
Average Fixed Cost Curve
A firm’s fixed cost divided by the output, they fall as output increases because they are spread across more output.
Average Variable Cost Curve
Overall variable costs divided by the unit output of a firm, they begin to until they reach a minimum point before rising again.
Average Total Cost Curve
A curve created by adding the fixed and variable cost curves, it is the total cost of production divided by the units output.
Marginal Cost
The cost to a firm of producing one additional unit of output, it cuts the ATC Curve at its lowest point.
Total Revenue
All the money a firm earns from selling the total output of a product.
Marginal Revenue
The additional revenue resulting form the sale of an additional unit of output.
Perfect Competition
Within this market structure MR and AR are equal as every firm is a price taker meaning the price remains constant within the market.
Monopoly
Within this market structure the Average Revenue is equivalent to the demand curve, they either set the price they sell a good at or the quantity of the good they sell.
Profit
Total revenue - Total cost, it’s the difference in money a company has before and after selling a produced good.
Profit Maximisation
Firms want to make the most money possible, and do this by producing at the point where MR=MC as beyond this point the cost of each additional unit is higher than the reveneue it produces.
Normal Profit
The minimum level of profit necessary for existing firms to survive, it is the revenue earned by a business - their explicit (direct) costs and their implicit (opportunity) costs.
Abnormal (supernormal) profit
Additional Profit earned beyond normal profit. In the long run and in the absence of entry barriers these profits attract new firms into the market in the long run.
Invention
The creation of something which previously did not exist.
Innovation
The improvent of something that has already been invented, making it into a marketable product.
Mechanisation
Where humans operate machines that are used in production.
Automation
Where machines operate machines, such as computer controlled robots.
Disruptive Innovation
Innovation that helps create a new market whilst disrupting an existing market over years or decades.
Sustaining Innovation
Innovation that helps to develop an existing market, enabling firms within a market to offer better value.