Overview of Illicit Drugs and Forensic Toxicology
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Drug
a natural or synthetic substance that is designed to produce a specific set of psychological and/or physiological effects on the human body or animals
Illicit
forbidden by law, rules, or custom
Drug abuse
when a drug is consumed for purposes other than what intended for, usually psychoactive effects
1906: Pure Food and Drug Act
Did not allow states to transfer drugs across state lines that were mislabeled/adultured
1914: Harrison Act
Regulated the sale of opium and cocaine
1930: Bureau of Narcotics
Enforced taxes on imported drugs
1956: Narcotic Drug Control Act
Increased penalties on drugs
1970: Comprehensive Controlled Substance Act
Uniform Controlled Substances Act - state level control of illicit substances
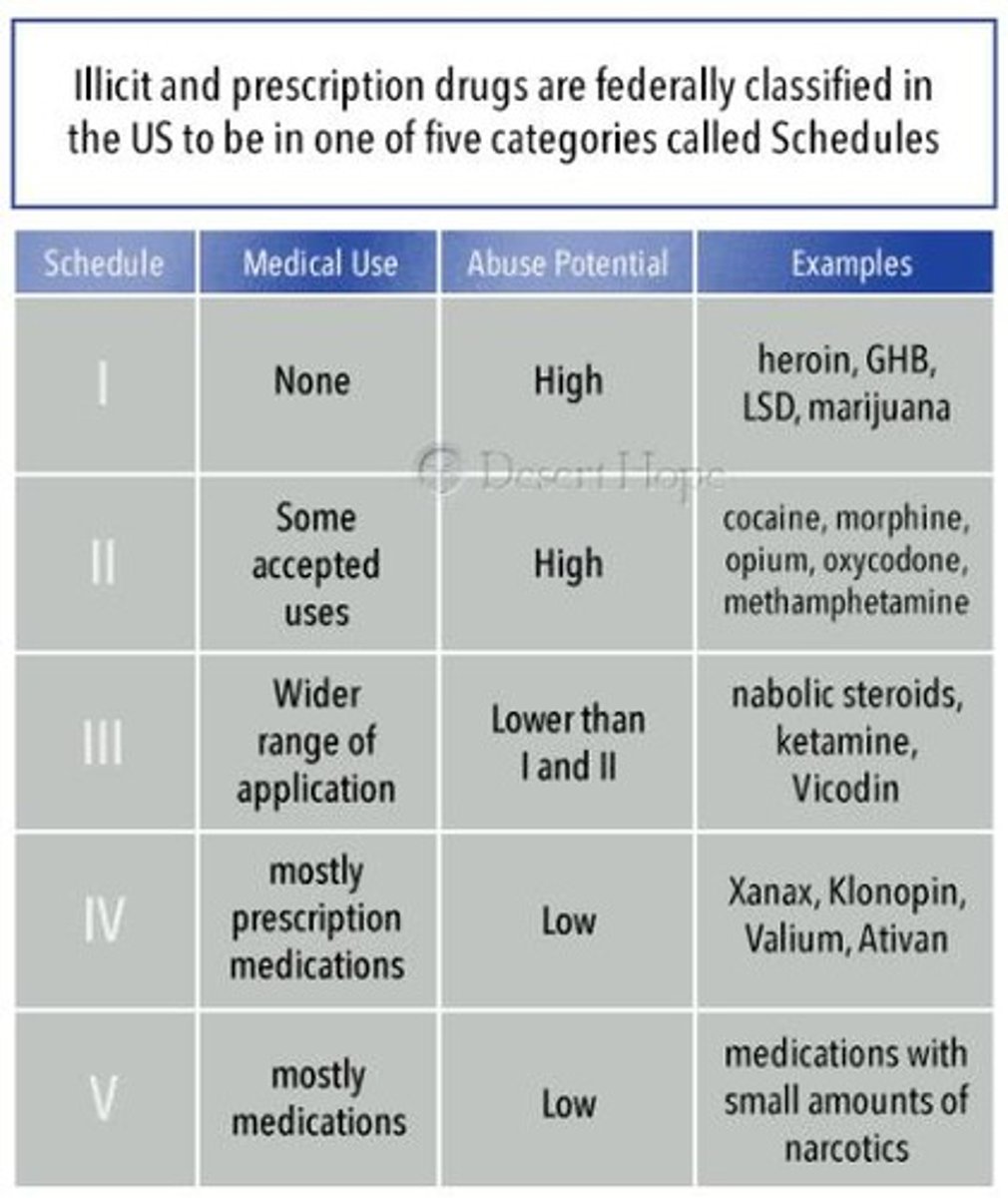
Drug Schedules
FDA uses factors to evaluate how to schedule/classify illicit drugs
Pharmacological effects
One of the factors FDA uses to evaluate drugs for scheduling/classification
Ability to produce psychological dependence and physical addiction
One of the factors FDA uses to evaluate drugs for scheduling/classification
A legitimate medical use for the substance
One of the factors FDA uses to evaluate drugs for scheduling/classification
Five Schedules
based on potential for abuse, pharmacology, and medical use
Naturally Occurring
found in nature in plants (marijuana, shrooms)
Plant Extracts
naturally occurring, but needs to be extracted (cocaine)
Semi-Synthetic
derived chemically from a natural substance (LSD)
Synthetic
totally man-made (ecstasy)
Stimulants
elevate one's mood
Depressants
de-elevate one's mood
Narcotic
relieves pain
Hallucinogen
alters mind
Forensic Toxicology
study of harmful effects of drugs
Postmortem Toxicology
analysis conducted after death to determine drug presence
Human Performance
evaluation of drug effects on athletes, etc.
Doping Control
monitoring athletes for illegal drug use
Workplace Drug Screening
testing employees for drug use
Chemical analysis of biological samples
to identify poisons and determine their amounts
Interpretation of results
how it affects the person's functioning/stability
Toxicology
study of harmful effects of drugs
Pharmacology
study of how drugs enter the body and how distributed and eliminated
Poison
substance that causes illness or death of a living organism (toxic effect)
Pharmacokinetics
what happens to the drug by the organism - how it moves in and out of the body
Pharmacodynamics
what happens to the organism when a drug is taken
Absorbance
how drugs are introduced to the body; passage of drugs through tissue into bloodstream
Alcohol (Oral)
into stomach and then absorbed mostly in the upper part of the small intestine
Distribution
anywhere there is blood, which is everywhere
Concentration of drug
is not the same; more blood = more drug; depends on chemical and physical properties
Metabolism
effect of the liver on the drug
Alcohol Metabolism Rate
90% of alcohol is metabolized at a rate of 0.015% per hour
Excretion/Elimination
Primarily through urine - water soluble metabolites; exhales, sweat, bile, breast milk
Addiction
psychological dependence of a drug
Dependence
physical need for the drug to function - failure to provide drug causes withdrawal
Synergism
total effect on the body of 2+ drugs taken together is greater than taken separately
Tolerance
body's organ systems adapt to a drug, need more of the drug for the same level of effect
Screening Test
Alcohol - field sobriety (walking line, saying alphabet backwards, etc.) & portable breath test
Confirmatory Test for Alcohol
Breath Test Instrument (BRAC); living person at the police station
Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC)
postmortem measurement using GCMS - headspace
Explosion
sudden violent escape of gases from a central point
Combustion Reaction
fuel (flammable objects/substances) and oxygen produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy
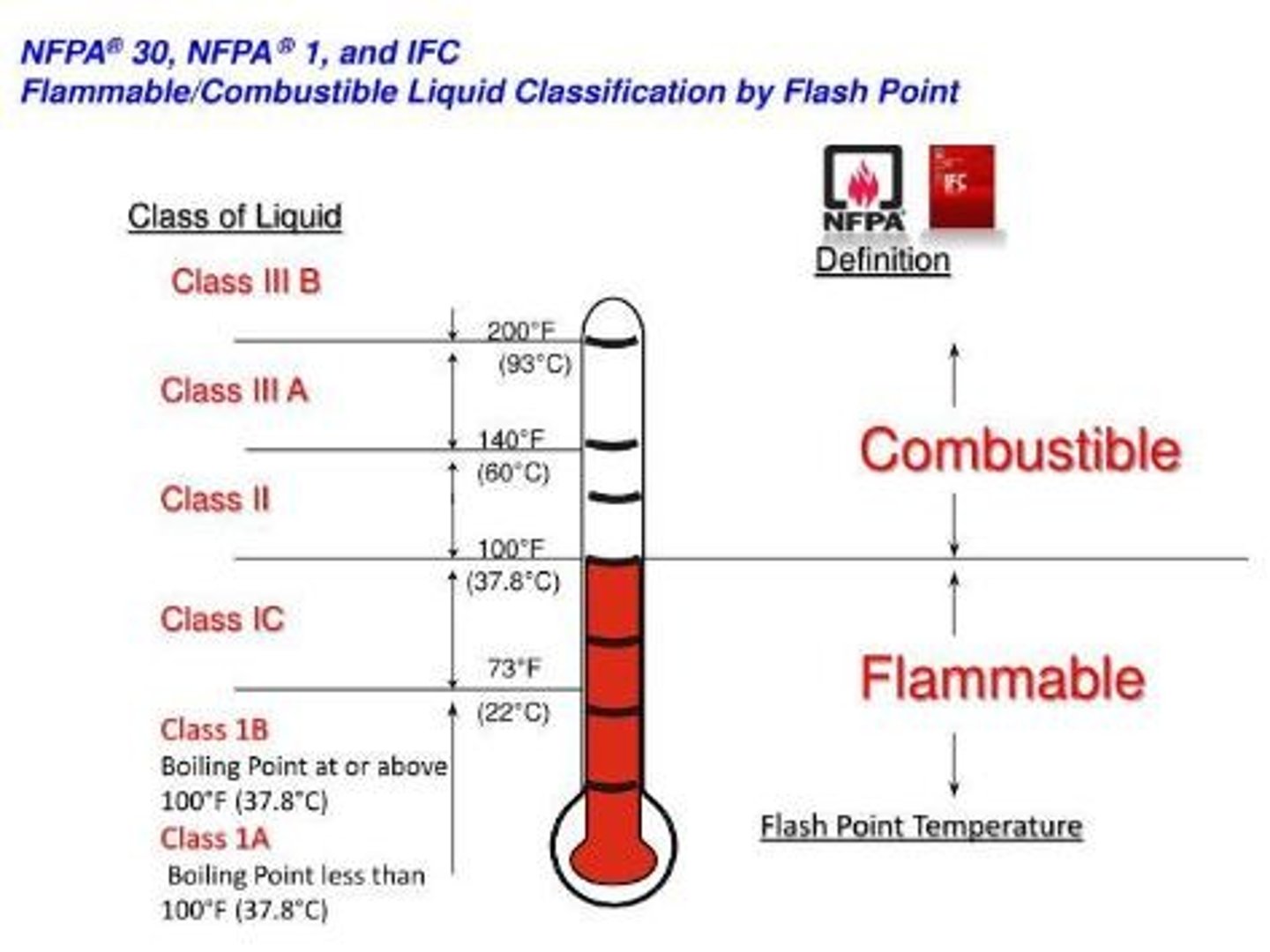
Flash Point
lowest temperature at which a liquid gives off enough vapors to form an ignitable mixture with air
Smoke
occurs when there is an incomplete combustion in a fire - 'fuel rich'
Flashover/Backdraft
occurs when the fire burns with a limited supply of oxygen and then is suddenly ventilated, resulting in an explosive fire
Types of Fires
Natural, Accidental, Deliberate/Incendiary
Ignition Types
Self-ignition, Direct ignition, Electrical, Weather-related, Mechanical
Arson
A deliberate/incendiary fire that was set with criminal intent
Analysis of Fire Debris
Collection and packaging of debris; isolating the possible accelerant from the fire debris
High Order Explosion
occurs at or near its maximum theoretical detonation velocity
Low Order Explosion
occurs with less than optimal efficiency
Classifications of Explosives
Low Explosives, High Explosives, Initiating/Primary, Non-initiating/Secondary